Connecting an OBD2 scanner to your PC allows you to diagnose car problems effectively and efficiently, and OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN provides you with all the necessary resources. This guide outlines the steps, benefits, and best practices for establishing a reliable connection, ensuring smooth data transfer and accurate vehicle diagnostics, and offering solutions for enhanced vehicle maintenance and diagnostics. Leverage the power of OBD2 technology for smarter car care.
Contents
- 1. Understanding the Basics of OBD2 Scanners and PCs
- 2. Preparing for the Connection
- 2.1. Ensuring Compatibility
- 2.2. Gathering Necessary Software and Drivers
- 3. Step-by-Step Guide to Connecting an OBD2 Scanner to a PC
- 3.1. Connecting via USB
- 3.2. Connecting via Bluetooth
- 3.3. Connecting via Wi-Fi
- 4. Troubleshooting Connection Issues
- 4.1. Common Problems and Solutions
- 4.2. Advanced Troubleshooting Tips
- 5. Using Diagnostic Software on Your PC
- 5.1. Reading and Interpreting Trouble Codes
- 5.2. Monitoring Live Data
- 6. Advanced Functions and Capabilities
- 6.1. Data Logging and Analysis
- 6.2. Performing Advanced Diagnostic Tests
- 7. Benefits of Using a PC with Your OBD2 Scanner
- 7.1. Enhanced Data Analysis
- 7.2. Comprehensive Reporting
- 8. Maintaining Your OBD2 Scanner and PC Connection
- 8.1. Software and Driver Updates
- 8.2. Physical Maintenance
- 9. Choosing the Right OBD2 Scanner for PC Connectivity
- 9.1. Top Recommended OBD2 Scanners for PC Use
- 9.2. Budget Considerations
- 10. Real-World Applications and Case Studies
- 10.1. Case Study: Diagnosing a Misfire
- 10.2. Case Study: Improving Fuel Efficiency
- 11. Legal and Ethical Considerations
- 11.1. Privacy Concerns
- 11.2. Data Security Measures
- 12. Future Trends in OBD2 Technology
- 12.1. Wireless Advancements
- 12.2. AI and Machine Learning Integration
- FAQ: Connecting OBD2 Scanner to PC
1. Understanding the Basics of OBD2 Scanners and PCs
What is an OBD2 scanner, and how does it work with a PC?
An OBD2 (On-Board Diagnostics II) scanner is a tool used to access a vehicle’s computer and diagnose problems. It retrieves diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) and other data that can help identify issues. Connecting it to a PC allows for in-depth analysis, data logging, and access to advanced software. According to the Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE), the OBD2 standard has been mandatory for all cars sold in the US since 1996, ensuring a uniform diagnostic interface.
- Functionality of OBD2 Scanners: An OBD2 scanner reads data from a vehicle’s ECU (Engine Control Unit), providing insights into various systems like engine performance, emissions, and more.
- PC Integration: Connecting an OBD2 scanner to a PC expands its capabilities, enabling more detailed data analysis, software updates, and access to comprehensive diagnostic reports.
- Benefits of PC Connection: Enhanced data analysis, software updates, detailed reporting.
2. Preparing for the Connection
What do you need to connect an OBD2 scanner to a PC?
To connect an OBD2 scanner to a PC, you will need a compatible scanner, a PC running Windows (or other supported operating system), the appropriate connection cable (USB, Bluetooth, or Wi-Fi), and the necessary software or drivers. Ensure all components are compatible to avoid connection issues.
- Required Hardware: OBD2 scanner, PC (Windows, macOS, Linux), USB cable (or Bluetooth/Wi-Fi adapter).
- Software Needs: Diagnostic software (e.g., OBDwiz), device drivers.
- Compatibility Checks: Verify scanner and software compatibility.
2.1. Ensuring Compatibility
How do you ensure the OBD2 scanner and PC are compatible?
Check the specifications of both the OBD2 scanner and the PC. Ensure that the scanner supports the operating system of the PC (Windows, macOS, Linux). Verify the connection type (USB, Bluetooth, Wi-Fi) is supported and that you have the necessary drivers or software. According to a study by the University of Michigan Transportation Research Institute, using incompatible devices can lead to data corruption and inaccurate diagnostics.
- Operating System Support: Verify compatibility with Windows, macOS, or Linux.
- Connection Type: Ensure USB, Bluetooth, or Wi-Fi compatibility.
- Driver and Software Verification: Confirm the availability of necessary drivers and software.
2.2. Gathering Necessary Software and Drivers
Where can you find the software and drivers required for the OBD2 scanner?
Typically, the software and drivers for your OBD2 scanner can be found on the manufacturer’s website or included with the scanner. Download and install these before connecting the scanner to ensure proper functionality. Reputable sources like Bosch and Snap-on provide comprehensive software suites for their scanners.
- Manufacturer’s Website: Download from official sources to avoid malware.
- Included Software: Check for CDs or download links provided with the scanner.
- Driver Installation: Install drivers before connecting the scanner.
3. Step-by-Step Guide to Connecting an OBD2 Scanner to a PC
How do you connect an OBD2 scanner to a PC using different connection methods?
The connection process varies depending on whether you are using a USB, Bluetooth, or Wi-Fi connection. Below are detailed steps for each method.
3.1. Connecting via USB
How do you connect an OBD2 scanner to a PC using a USB cable?
- Install Drivers: Install the necessary drivers from the manufacturer’s website before connecting the scanner.
- Connect the Scanner: Plug the OBD2 scanner into the OBD2 port in your vehicle and connect the USB cable from the scanner to your PC.
- Turn on the Vehicle: Turn the ignition to the “ON” position without starting the engine.
- Launch Software: Open the diagnostic software on your PC.
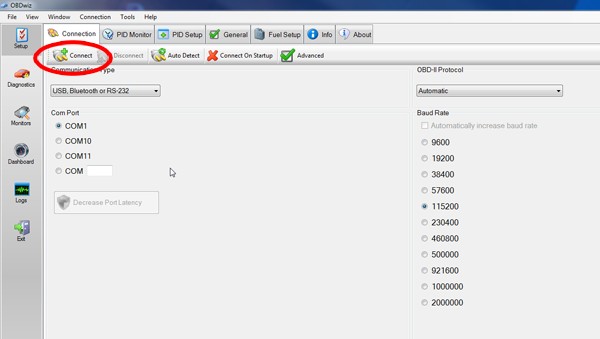
- Configure Connection: Select the appropriate COM port in the software settings.
- Establish Connection: Click “Connect” in the software to establish a connection with the scanner.
 OBD2 Scanner USB Connection
OBD2 Scanner USB Connection
- Driver Installation: Essential for proper communication.
- COM Port Selection: Correct COM port is crucial for establishing a connection.
- Software Configuration: Set up the software to recognize the scanner.
3.2. Connecting via Bluetooth
What are the steps for connecting an OBD2 scanner to a PC via Bluetooth?
- Enable Bluetooth: Ensure Bluetooth is enabled on your PC.
- Pair the Scanner: Put the OBD2 scanner in pairing mode by pressing the connect button on the device.
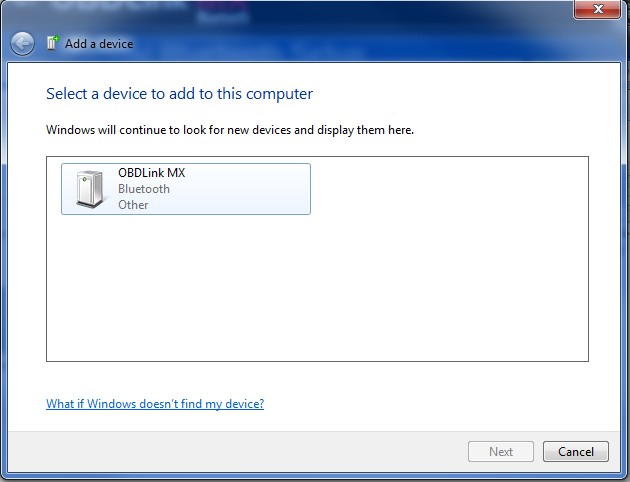
- Search for Devices: On your PC, search for available Bluetooth devices.
- Select the Scanner: Select your OBD2 scanner from the list of devices and pair it. You may need to enter a PIN (often “1234” or “0000”).
- Launch Software: Open the diagnostic software on your PC.
- Configure Connection: Select the Bluetooth COM port in the software settings.
- Establish Connection: Click “Connect” in the software to establish a connection with the scanner.
 Windows Bluetooth Devices
Windows Bluetooth Devices
- Bluetooth Pairing Mode: Activate pairing mode on the scanner.
- COM Port Configuration: Bluetooth uses a virtual COM port.
- PIN Code: Common PINs are “1234” or “0000”.
3.3. Connecting via Wi-Fi
How do you connect an OBD2 scanner to a PC using Wi-Fi?
- Scanner Setup: Configure the OBD2 scanner to connect to your Wi-Fi network.
- PC Connection: Ensure your PC is connected to the same Wi-Fi network.
- IP Address: Note the IP address of the OBD2 scanner. This is usually found in the scanner’s settings.
- Launch Software: Open the diagnostic software on your PC.
- Configure Connection: Enter the scanner’s IP address in the software settings.
- Establish Connection: Click “Connect” in the software to establish a connection with the scanner.
- Network Compatibility: Both devices must be on the same network.
- IP Address Configuration: Accurate IP address entry is crucial.
- Software Settings: Configure the software to recognize the Wi-Fi connection.
4. Troubleshooting Connection Issues
What should you do if the OBD2 scanner fails to connect to the PC?
If you encounter connection problems, check the following:
- Driver Issues: Ensure the drivers are correctly installed.
- COM Port Conflicts: Verify the correct COM port is selected.
- Bluetooth Pairing Problems: Re-pair the devices if necessary.
- Wi-Fi Connectivity: Ensure both devices are on the same network and the IP address is correct.
4.1. Common Problems and Solutions
What are some common problems when connecting an OBD2 scanner to a PC, and how can you fix them?
Common problems include driver conflicts, incorrect COM port selection, Bluetooth pairing failures, and Wi-Fi connectivity issues. Solutions include reinstalling drivers, selecting the correct COM port, re-pairing Bluetooth devices, and verifying Wi-Fi settings. According to a survey by the National Institute for Automotive Service Excellence (ASE), incorrect driver installation is a leading cause of OBD2 scanner connection problems.
- Driver Conflicts: Reinstall or update drivers.
- Incorrect COM Port: Select the correct COM port in the software settings.
- Bluetooth Pairing Failures: Re-pair devices, ensuring correct PIN entry.
- Wi-Fi Connectivity Issues: Verify network connection and IP address.
4.2. Advanced Troubleshooting Tips
What advanced steps can you take to troubleshoot OBD2 scanner connections?
If basic troubleshooting doesn’t work, try the following:
-
Firewall Settings: Ensure your firewall isn’t blocking the connection.
-
Software Updates: Update your diagnostic software to the latest version.
-
Hardware Issues: Test the OBD2 scanner and USB cable on another vehicle or PC.
-
Contact Support: Reach out to the scanner manufacturer for technical support.
-
Firewall Configuration: Allow the diagnostic software through the firewall.
-
Software Updates: Ensure you have the latest version.
-
Hardware Testing: Rule out faulty hardware.
-
Technical Support: Contact the manufacturer for expert assistance.
5. Using Diagnostic Software on Your PC
How do you use diagnostic software to read and interpret data from the OBD2 scanner?
Once the OBD2 scanner is connected to your PC, you can use diagnostic software to read and interpret data. Here’s how:
- Launch Software: Open the diagnostic software on your PC.
- Connect to Vehicle: Select the appropriate connection settings and connect to your vehicle.
- Read Trouble Codes: Use the software to read diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs).
- Interpret Data: Use the software’s database to interpret the meaning of the DTCs.
- Live Data: Monitor real-time data from your vehicle’s sensors.
5.1. Reading and Interpreting Trouble Codes
How do you read and understand diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs)?
Diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) are standardized codes that indicate specific problems in a vehicle. Use the diagnostic software to read these codes and then consult a DTC database to understand their meaning. Websites like OBD-Codes.com offer extensive DTC information.
- DTC Structure: Understand the code format (e.g., P0300 indicates a misfire).
- DTC Databases: Use online resources or software databases to look up codes.
- Example: P0301 means cylinder 1 misfire.
5.2. Monitoring Live Data
How do you monitor live data from your vehicle’s sensors using the diagnostic software?
Monitoring live data allows you to see real-time information from your vehicle’s sensors, such as engine temperature, RPM, and O2 sensor readings. This can help diagnose intermittent problems or assess overall performance.
- Sensor Readings: Monitor parameters like engine temperature, RPM, and O2 sensor voltage.
- Graphing: Use the software to graph live data for easier analysis.
- Data Logging: Record live data for later review.
6. Advanced Functions and Capabilities
What advanced functions can you perform when connecting an OBD2 scanner to a PC?
Connecting an OBD2 scanner to a PC unlocks advanced functions such as:
- Data Logging: Record and analyze vehicle data over time.
- Custom Diagnostics: Perform specialized diagnostic tests.
- Software Updates: Update the scanner’s firmware.
- Advanced Reporting: Generate detailed diagnostic reports.
6.1. Data Logging and Analysis
How can you use data logging to diagnose intermittent problems?
Data logging involves recording vehicle data over a period of time, which can be invaluable for diagnosing intermittent issues that don’t trigger a DTC. Analyze the logged data to identify patterns or anomalies.
- Recording Data: Set up the software to log specific parameters.
- Analyzing Data: Look for patterns or anomalies in the logged data.
- Intermittent Issues: Useful for diagnosing problems that don’t trigger DTCs.
6.2. Performing Advanced Diagnostic Tests
What kind of advanced diagnostic tests can you perform with a PC-connected OBD2 scanner?
Advanced diagnostic tests include:
-
O2 Sensor Tests: Evaluate O2 sensor performance.
-
EGR System Tests: Check the functionality of the EGR (Exhaust Gas Recirculation) system.
-
Injector Balance Tests: Assess injector performance.
-
Compression Tests: Measure cylinder compression.
-
O2 Sensor Tests: Verify sensor response and accuracy.
-
EGR System Tests: Ensure proper EGR valve operation.
-
Injector Balance Tests: Identify malfunctioning injectors.
-
Compression Tests: Measure cylinder compression for engine health assessment.
7. Benefits of Using a PC with Your OBD2 Scanner
What are the advantages of connecting an OBD2 scanner to a PC?
Connecting an OBD2 scanner to a PC offers numerous benefits:
- Larger Display: Easier to view and analyze data on a larger screen.
- Advanced Software: Access to more powerful diagnostic software.
- Data Logging: Ability to record and analyze data over time.
- Software Updates: Keep the scanner’s software up to date.
- Detailed Reporting: Generate comprehensive diagnostic reports.
7.1. Enhanced Data Analysis
How does connecting to a PC improve data analysis capabilities?
A PC provides a larger screen, more processing power, and advanced software, making it easier to analyze complex data sets and identify subtle issues that might be missed on a handheld scanner.
- Larger Screen: Easier to view and analyze data.
- Processing Power: Faster data processing and analysis.
- Advanced Software: Access to powerful diagnostic tools.
7.2. Comprehensive Reporting
What type of reports can you generate when using a PC with an OBD2 scanner?
You can generate detailed diagnostic reports that include DTCs, live data readings, freeze frame data, and test results. These reports can be saved, printed, and shared with mechanics or other professionals.
- DTC Reports: List of diagnostic trouble codes and their descriptions.
- Live Data Reports: Real-time sensor readings.
- Freeze Frame Data: Snapshot of data when a DTC was triggered.
- Test Results: Results of advanced diagnostic tests.
8. Maintaining Your OBD2 Scanner and PC Connection
How should you maintain your OBD2 scanner and PC connection for optimal performance?
To ensure optimal performance, regularly update the software and drivers, keep the connections clean and secure, and store the devices properly.
8.1. Software and Driver Updates
How often should you update the software and drivers for your OBD2 scanner?
Check for software and driver updates at least every three months, or whenever the manufacturer releases a new version. Keeping your software up to date ensures you have the latest features, bug fixes, and compatibility improvements.
- Regular Checks: Check for updates every three months.
- Manufacturer Notifications: Subscribe to manufacturer newsletters for update alerts.
- Compatibility: Ensure updates are compatible with your scanner and PC.
8.2. Physical Maintenance
What physical maintenance should you perform on your OBD2 scanner and PC connection?
Keep the OBD2 scanner and USB cable clean and free of debris. Ensure the connections are secure and undamaged. Store the devices in a dry, safe place when not in use.
- Clean Connections: Keep connections free of dirt and debris.
- Secure Connections: Ensure cables are securely connected.
- Proper Storage: Store devices in a dry, safe place.
9. Choosing the Right OBD2 Scanner for PC Connectivity
How do you select the best OBD2 scanner for connecting to a PC?
Consider the following factors when choosing an OBD2 scanner for PC connectivity:
- Compatibility: Ensure the scanner is compatible with your PC’s operating system.
- Connection Type: Choose a scanner with the connection type you prefer (USB, Bluetooth, Wi-Fi).
- Software Support: Verify the scanner comes with user-friendly and feature-rich software.
- Advanced Functions: Look for advanced functions like data logging and custom diagnostics.
9.1. Top Recommended OBD2 Scanners for PC Use
What are some of the best OBD2 scanners for connecting to a PC?
Some top-rated OBD2 scanners for PC use include:
-
OBDLink MX+: Known for its fast performance and compatibility with various software platforms.
-
ScanTool 427201 OBDLink LX: Offers excellent Bluetooth connectivity and comprehensive diagnostic capabilities.
-
BlueDriver Bluetooth Professional OBDII Scan Tool: Provides a user-friendly app and detailed diagnostic reports.
According to a review by Car and Driver, the OBDLink MX+ is praised for its reliability and advanced features. -
OBDLink MX+: Fast, reliable, and compatible with various software.
-
ScanTool 427201 OBDLink LX: Excellent Bluetooth connectivity.
-
BlueDriver Bluetooth Professional OBDII Scan Tool: User-friendly app and detailed reports.
9.2. Budget Considerations
How much should you expect to spend on an OBD2 scanner for PC connectivity?
Prices for OBD2 scanners with PC connectivity range from $50 to $500 or more. Entry-level scanners with basic functionality can be found for under $100, while advanced scanners with comprehensive features can cost several hundred dollars.
- Entry-Level Scanners: $50 – $100 (basic functionality).
- Mid-Range Scanners: $100 – $300 (good balance of features and price).
- High-End Scanners: $300+ (advanced features and comprehensive diagnostics).
10. Real-World Applications and Case Studies
How is connecting an OBD2 scanner to a PC used in real-world automotive diagnostics?
Connecting an OBD2 scanner to a PC is widely used in automotive repair shops and by car enthusiasts for:
- Diagnosing Check Engine Lights: Quickly identify the cause of the check engine light.
- Monitoring Vehicle Performance: Track real-time data to assess vehicle health.
- Performing Maintenance: Reset maintenance reminders and perform routine diagnostics.
- Troubleshooting Intermittent Issues: Log data over time to diagnose elusive problems.
10.1. Case Study: Diagnosing a Misfire
How can connecting an OBD2 scanner to a PC help diagnose a misfire issue?
A common use case is diagnosing a misfire. By connecting an OBD2 scanner to a PC, you can:
- Read DTCs: Identify the specific cylinder causing the misfire (e.g., P0301 for cylinder 1).
- Monitor Live Data: Check the performance of the ignition coil and fuel injector for that cylinder.
- Perform Compression Test: Use the software to perform a compression test and identify mechanical issues.
- Analyze Data: Review logged data to see when the misfire occurs and under what conditions.
- Read DTCs: Identify the misfiring cylinder.
- Monitor Live Data: Check ignition coil and fuel injector performance.
- Perform Compression Test: Identify mechanical issues.
- Analyze Data: Determine the conditions under which the misfire occurs.
10.2. Case Study: Improving Fuel Efficiency
How can an OBD2 scanner connected to a PC help improve fuel efficiency?
By connecting an OBD2 scanner to a PC, you can:
- Monitor O2 Sensor Readings: Ensure the O2 sensors are functioning correctly.
- Check Fuel Trims: Identify if the engine is running too rich or too lean.
- Evaluate MAF Sensor Performance: Check the mass airflow (MAF) sensor for accuracy.
- Adjust Parameters: Use the software to adjust engine parameters for optimal fuel efficiency.
- Monitor O2 Sensor Readings: Ensure proper sensor function.
- Check Fuel Trims: Identify rich or lean conditions.
- Evaluate MAF Sensor Performance: Verify MAF sensor accuracy.
- Adjust Parameters: Optimize engine settings for fuel efficiency.
11. Legal and Ethical Considerations
What are the legal and ethical considerations when using an OBD2 scanner connected to a PC?
When using an OBD2 scanner connected to a PC, it’s important to:
- Respect Privacy: Only access data from vehicles you own or have permission to diagnose.
- Comply with Laws: Follow all applicable laws regarding vehicle diagnostics and repair.
- Use Data Responsibly: Do not use the data for illegal or unethical purposes.
- Protect Data Security: Secure your diagnostic data to prevent unauthorized access.
11.1. Privacy Concerns
What privacy concerns should you be aware of when using an OBD2 scanner?
Be aware that OBD2 scanners can access sensitive vehicle data, so it’s crucial to respect privacy and only access data with proper authorization.
- Data Access: Only access data with permission.
- Data Security: Protect diagnostic data from unauthorized access.
- Legal Compliance: Follow all applicable laws and regulations.
11.2. Data Security Measures
What steps can you take to ensure the security of your diagnostic data?
Protect your diagnostic data by:
-
Using Strong Passwords: Secure your PC and diagnostic software with strong, unique passwords.
-
Encrypting Data: Encrypt sensitive data to prevent unauthorized access.
-
Regularly Backing Up Data: Back up your data to prevent loss in case of hardware failure or security breach.
-
Keeping Software Updated: Keep your diagnostic software and operating system up to date with the latest security patches.
-
Strong Passwords: Use unique and complex passwords.
-
Data Encryption: Encrypt sensitive data.
-
Regular Backups: Back up data to prevent loss.
-
Software Updates: Keep software updated with security patches.
12. Future Trends in OBD2 Technology
What future trends can we expect in OBD2 technology and PC connectivity?
Future trends include:
- Enhanced Wireless Connectivity: More advanced Bluetooth and Wi-Fi capabilities.
- Cloud-Based Diagnostics: Integration with cloud platforms for data storage and analysis.
- AI-Powered Diagnostics: Use of artificial intelligence to improve diagnostic accuracy.
- Integration with Mobile Devices: Seamless integration with smartphones and tablets.
12.1. Wireless Advancements
How will advancements in wireless technology impact OBD2 scanner connectivity?
Advancements in wireless technology will lead to faster, more reliable connections, greater range, and improved security. This will make it easier to connect OBD2 scanners to PCs and other devices.
- Faster Connections: Improved data transfer rates.
- Greater Range: Increased connectivity range.
- Enhanced Security: More secure wireless connections.
12.2. AI and Machine Learning Integration
How will AI and machine learning be used to improve OBD2 diagnostics?
AI and machine learning can be used to analyze vast amounts of vehicle data, identify patterns, and predict potential problems. This will improve diagnostic accuracy and help mechanics make more informed repair decisions.
- Data Analysis: AI can analyze large datasets to identify patterns.
- Predictive Diagnostics: AI can predict potential problems based on historical data.
- Improved Accuracy: AI can improve the accuracy of diagnostic results.
FAQ: Connecting OBD2 Scanner to PC
Q1: What is an OBD2 scanner?
An OBD2 (On-Board Diagnostics II) scanner is a tool used to access a vehicle’s computer system for diagnostics, providing insights into various systems like engine performance and emissions.
Q2: Why should I connect an OBD2 scanner to a PC?
Connecting to a PC allows for enhanced data analysis, software updates, detailed reporting, and access to advanced diagnostic software.
Q3: What do I need to connect an OBD2 scanner to a PC?
You need a compatible OBD2 scanner, a PC, a connection cable (USB, Bluetooth, or Wi-Fi), and the necessary software or drivers.
Q4: How do I ensure my OBD2 scanner is compatible with my PC?
Check the scanner’s specifications for compatibility with your PC’s operating system (Windows, macOS, Linux) and the connection type (USB, Bluetooth, Wi-Fi).
Q5: Where can I find the software and drivers for my OBD2 scanner?
Software and drivers are typically available on the manufacturer’s website or included with the scanner.
Q6: What are the steps for connecting an OBD2 scanner to a PC via USB?
Install drivers, connect the scanner, turn on the vehicle, launch software, configure the connection, and establish the connection in the software.
Q7: How do I connect an OBD2 scanner to a PC via Bluetooth?
Enable Bluetooth on your PC, put the scanner in pairing mode, search for devices, select the scanner, and connect via the diagnostic software.
Q8: What should I do if my OBD2 scanner fails to connect to my PC?
Check driver issues, COM port conflicts, Bluetooth pairing problems, or Wi-Fi connectivity.
Q9: How often should I update the software and drivers for my OBD2 scanner?
Check for updates at least every three months or when the manufacturer releases a new version.
Q10: What are some of the best OBD2 scanners for connecting to a PC?
Top-rated scanners include OBDLink MX+, ScanTool 427201 OBDLink LX, and BlueDriver Bluetooth Professional OBDII Scan Tool.
Connecting your OBD2 scanner to a PC is a powerful way to enhance your vehicle diagnostics capabilities. By following the steps and tips outlined in this guide, you can ensure a smooth and effective connection, enabling you to diagnose and resolve vehicle issues with greater precision.
Ready to take your car diagnostics to the next level? Contact OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN for expert advice and support on using OBD2 scanners and our comprehensive repair services. Call us at +1 (641) 206-8880, visit our website at OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN, or stop by our location at 123 Main Street, Los Angeles, CA 90001, United States. Let us help you unlock the full potential of your vehicle’s diagnostic system and keep your car running smoothly.
