Can Obd2 Be Used On Obd1 Cars? No, an OBD2 scanner cannot be directly used on OBD1 cars because they utilize different communication protocols and connector types; however, adapters and specialized scan tools can bridge this gap. OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN helps you understand the intricacies of automotive diagnostics and ensures you get the right tools for the job. Discover effective solutions for seamless vehicle diagnostics and learn about OBD system compatibility and diagnostic tool functionality.
Contents
- 1. Understanding OBD1 and OBD2 Systems
- 1.1. What is OBD1?
- 1.2. What is OBD2?
- 1.3. Key Differences Between OBD1 and OBD2
- 2. Why OBD2 Scanners Don’t Work Directly on OBD1 Cars
- 2.1. Protocol Incompatibility
- 2.2. Connector Differences
- 2.3. Software and Firmware Limitations
- 3. Bridging the Gap: Using Adapters and Specialized Tools
- 3.1. OBD1 Adapters
- 3.2. OBD1 Scan Tools
- 3.3. Combination OBD1/OBD2 Scan Tools
- 4. Choosing the Right Tool for Your OBD1 Car
- 4.1. Factors to Consider
- 4.2. Recommended OBD1 Scan Tools
- 4.3. Where to Buy OBD1 Scan Tools
- 5. How to Use an OBD1 Scan Tool
- 5.1. Locating the OBD1 Port
- 5.2. Connecting the Scan Tool
- 5.3. Diagnosing the Vehicle
- 6. Common OBD1 Problems and Their Solutions
- 6.1. Difficulty in Finding the Correct Adapter
- 6.2. Interpreting Manufacturer-Specific DTCs
- 6.3. Limited Data Availability
- 6.4. Intermittent Communication Issues
- 7. The Future of Automotive Diagnostics
- 7.1. OBD3 and Beyond
- 7.2. The Rise of Telematics
- 7.3. The Impact of Electric Vehicles (EVs)
- 8. Ensuring Your Scan Tool is Up-To-Date
- 9. The Importance of Professional Advice
- 9.1. When to Seek Professional Help
- 9.2. Benefits of Consulting Professionals
- 10. How OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN Can Help
- 10.1. Expert Advice and Support
- 10.2. Wide Selection of Scan Tools and Adapters
- 10.3. Diagnostic and Repair Information
- 10.4. Training and Education
- FAQ: Can OBD2 Be Used on OBD1 Cars?
- Q1: What is the main difference between OBD1 and OBD2?
- Q2: Can I use an OBD2 scanner on my OBD1 car with an adapter?
- Q3: What type of scan tool do I need for an OBD1 car?
- Q4: Where can I find the OBD1 port in my car?
- Q5: Are OBD1 scan tools more expensive than OBD2 scan tools?
- Q6: Can I update the software on my OBD1 scan tool?
- Q7: What are some common problems when diagnosing OBD1 cars?
- Q8: What is OBD3?
- Q9: How can OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN help me with OBD1 diagnostics?
- Q10: Where can I buy OBD1 adapters?
1. Understanding OBD1 and OBD2 Systems
The world of automotive diagnostics involves decoding the language spoken by your car’s computer. On-Board Diagnostics (OBD) systems are the key to this communication. The evolution from OBD1 to OBD2 marked a significant leap in standardization and the amount of data accessible. However, this also means they aren’t directly compatible.
1.1. What is OBD1?
OBD1, the predecessor to OBD2, was implemented in vehicles before 1996. These early systems lacked standardization, meaning each manufacturer had its own unique diagnostic connector, communication protocol, and set of diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs). This made diagnosing vehicle issues a complex task, often requiring specialized tools and knowledge specific to each make and model. According to a 1993 Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE) paper, the lack of uniformity in OBD1 systems presented significant challenges for technicians.
1.2. What is OBD2?
In 1996, OBD2 became the standard for all cars sold in the United States, mandated by the Clean Air Act Amendments of 1990. Unlike OBD1, OBD2 introduced a standardized 16-pin diagnostic connector (SAE J1962), a universal set of diagnostic trouble codes (SAE J2012), and standardized communication protocols (SAE J1850, ISO 9141, CAN). This standardization allowed a single scan tool to communicate with any OBD2-compliant vehicle, simplifying diagnostics and making it more accessible to both professional technicians and DIY enthusiasts. A study by the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) in 1995 highlighted the benefits of OBD2 in improving emissions monitoring and diagnostics.
1.3. Key Differences Between OBD1 and OBD2
Here’s a table summarizing the key differences between OBD1 and OBD2:
| Feature | OBD1 | OBD2 |
|---|---|---|
| Standardization | Non-standardized, manufacturer-specific | Standardized connector, protocols, and DTCs |
| Connector Type | Varies by manufacturer | Standard 16-pin (SAE J1962) |
| Diagnostic Trouble Codes | Manufacturer-specific | Standardized (SAE J2012) |
| Communication Protocols | Manufacturer-specific | Standardized (SAE J1850, ISO 9141, CAN) |
| Data Access | Limited and manufacturer-dependent | More comprehensive and standardized |
| Implementation | Pre-1996 vehicles | 1996 and newer vehicles |
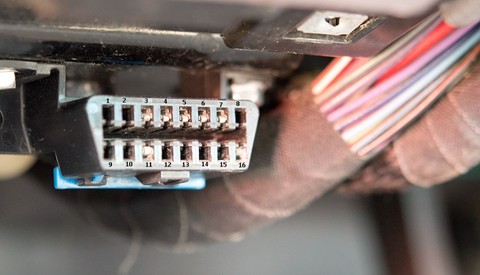 OBD1 and OBD2 ports comparison
OBD1 and OBD2 ports comparison
This image shows a standard OBD2 port, characterized by its 16-pin configuration, which is a key feature that distinguishes it from the various non-standardized OBD1 ports.
2. Why OBD2 Scanners Don’t Work Directly on OBD1 Cars
The fundamental differences in communication protocols and connector types are why OBD2 scanners cannot directly interface with OBD1 vehicles.
2.1. Protocol Incompatibility
OBD2 scanners are designed to communicate using specific standardized protocols. OBD1 systems, on the other hand, use a variety of manufacturer-specific protocols. This means an OBD2 scanner simply won’t be able to understand the data coming from an OBD1 car’s computer. As stated in a technical paper from Bosch, a leading automotive supplier, the communication barrier is a primary obstacle.
2.2. Connector Differences
The physical connectors are also different. OBD2 uses a standardized 16-pin connector, while OBD1 connectors vary in shape and number of pins depending on the manufacturer and model. This physical incompatibility prevents an OBD2 scanner from even being plugged into an OBD1 port without an adapter.
2.3. Software and Firmware Limitations
OBD2 scanners are programmed with software and firmware that is designed to interpret standardized OBD2 data. They lack the necessary programming to understand the unique data formats and codes used by OBD1 systems.
3. Bridging the Gap: Using Adapters and Specialized Tools
While an OBD2 scanner cannot directly read OBD1 data, there are ways to access the diagnostic information from these older vehicles.
3.1. OBD1 Adapters
Adapters can physically connect an OBD2 scanner to an OBD1 port. These adapters simply change the connector shape and pinout, but they do not translate the communication protocols. Therefore, using an adapter alone will not allow an OBD2 scanner to read OBD1 data.
3.2. OBD1 Scan Tools
The most reliable way to diagnose OBD1 vehicles is to use a scan tool specifically designed for OBD1 systems. These tools come equipped with the necessary software and adapters to communicate with a wide range of OBD1 vehicles. They can read manufacturer-specific diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs), access live data, and perform other diagnostic functions.
3.3. Combination OBD1/OBD2 Scan Tools
Some scan tools are designed to work with both OBD1 and OBD2 vehicles. These tools typically include a variety of adapters and software that allows them to switch between OBD1 and OBD2 modes. These combination tools offer a versatile solution for technicians working on a wide range of vehicles.
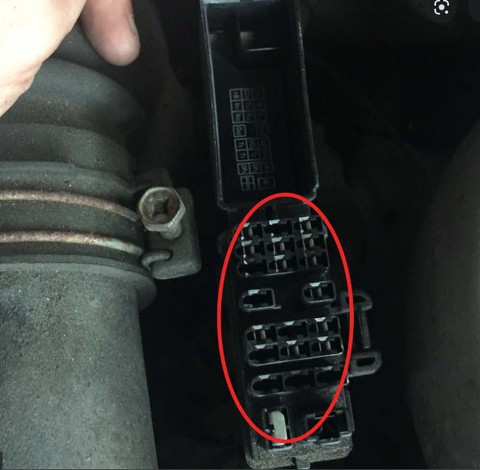 Toyota 22-pin OBD1 adapter
Toyota 22-pin OBD1 adapter
The image shows a Toyota 22-pin OBD1 adapter, essential for connecting diagnostic tools to older Toyota vehicles that predate the standardized OBD2 port.
4. Choosing the Right Tool for Your OBD1 Car
Selecting the appropriate diagnostic tool for your OBD1 vehicle depends on several factors, including your budget, technical expertise, and the specific vehicles you need to diagnose.
4.1. Factors to Consider
- Vehicle Coverage: Ensure the scan tool supports the specific make, model, and year of your OBD1 vehicle.
- Functionality: Determine the level of functionality you need. Do you only need to read DTCs, or do you also need to access live data, perform actuation tests, and reset systems?
- Ease of Use: Choose a tool with a user-friendly interface and clear instructions.
- Budget: OBD1 scan tools can range in price from a few hundred dollars to several thousand. Set a budget and find a tool that meets your needs within that range.
- Updates: Check if the tool is updateable. Updated software ensures compatibility with a wider range of vehicles and access to the latest diagnostic information.
4.2. Recommended OBD1 Scan Tools
- Actron CP9145: This is a basic OBD1 scan tool that can read and clear DTCs on many older vehicles. It is a good option for DIYers on a budget.
- Innova 3145: This scan tool offers broader coverage and functionality than the Actron CP9145. It can read live data and perform some actuation tests.
- Snap-on MT2500 Red Brick: This is a professional-grade scan tool that offers comprehensive coverage and functionality for OBD1 and early OBD2 vehicles. It is a popular choice among professional technicians.
- OTC 4000E Scan Tool: Another professional-grade tool with extensive OBD1 coverage and advanced diagnostic capabilities.
4.3. Where to Buy OBD1 Scan Tools
OBD1 scan tools can be purchased from a variety of sources, including:
- Online Retailers: Amazon, eBay, and other online retailers offer a wide selection of OBD1 scan tools.
- Automotive Parts Stores: Many auto parts stores, such as AutoZone and Advance Auto Parts, sell OBD1 scan tools.
- Tool Suppliers: Companies like Snap-on and Mac Tools sell professional-grade OBD1 scan tools directly to technicians.
5. How to Use an OBD1 Scan Tool
Using an OBD1 scan tool typically involves the following steps:
5.1. Locating the OBD1 Port
OBD1 ports are typically located under the dashboard on the driver’s side, but their exact location can vary depending on the vehicle. Some OBD1 ports may also be located in the engine compartment. Consult your vehicle’s repair manual to find the exact location of the OBD1 port.
5.2. Connecting the Scan Tool
- Turn off the vehicle’s ignition.
- Connect the appropriate adapter to the scan tool.
- Plug the adapter into the OBD1 port.
- Turn on the scan tool.
5.3. Diagnosing the Vehicle
- Follow the scan tool’s instructions to select the correct vehicle make, model, and year.
- Choose the diagnostic function you want to perform, such as reading DTCs or accessing live data.
- Follow the scan tool’s instructions to interpret the data and diagnose the vehicle’s issues.
6. Common OBD1 Problems and Their Solutions
Diagnosing OBD1 vehicles can be challenging due to the lack of standardization. However, understanding common OBD1 problems and their solutions can help streamline the process.
6.1. Difficulty in Finding the Correct Adapter
With so many different OBD1 connector types, finding the correct adapter can be difficult. Consult your vehicle’s repair manual or an online adapter guide to identify the correct adapter for your vehicle. You can also use the OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN website to check our car list for a confirmation.
6.2. Interpreting Manufacturer-Specific DTCs
OBD1 DTCs are manufacturer-specific, meaning they vary from one make and model to another. You will need a repair manual or a database of OBD1 DTCs to interpret the codes.
6.3. Limited Data Availability
OBD1 systems typically provide less data than OBD2 systems. This can make it more difficult to diagnose certain issues. You may need to rely on other diagnostic techniques, such as visual inspection and component testing, to supplement the data from the scan tool.
6.4. Intermittent Communication Issues
Communication issues can occur due to faulty wiring, corroded connectors, or a malfunctioning vehicle computer. Inspect the wiring and connectors for damage or corrosion. You may also need to test the vehicle’s computer to ensure it is functioning properly.
7. The Future of Automotive Diagnostics
While OBD2 is the current standard, the automotive industry is constantly evolving. New diagnostic technologies and protocols are being developed to meet the demands of increasingly complex vehicles.
7.1. OBD3 and Beyond
The EPA has proposed OBD3, which would require vehicles to report emissions-related faults directly to regulatory agencies via wireless communication. This would allow for real-time monitoring of vehicle emissions and faster identification of polluting vehicles. The implementation of OBD3 is still under discussion.
7.2. The Rise of Telematics
Telematics systems, which combine telecommunications and informatics, are becoming increasingly common in modern vehicles. These systems can collect and transmit a wide range of vehicle data, including diagnostic information, location data, and driving behavior. Telematics data can be used for a variety of purposes, such as remote diagnostics, predictive maintenance, and usage-based insurance.
7.3. The Impact of Electric Vehicles (EVs)
Electric vehicles (EVs) present new challenges and opportunities for automotive diagnostics. EVs have different diagnostic needs than gasoline-powered vehicles, requiring specialized tools and knowledge. As EVs become more prevalent, the diagnostic industry will need to adapt to meet the unique demands of these vehicles.
8. Ensuring Your Scan Tool is Up-To-Date
To ensure your scan tool can correctly interpret diagnostic information and work seamlessly with a wide array of vehicles, keeping it updated is crucial. Scan tool manufacturers frequently release updates to their software to include new vehicle models, updated diagnostic trouble codes, and enhanced features. These updates can usually be downloaded from the manufacturer’s website. Here are the typical steps to update your scan tool:
- Visit the Manufacturer’s Website: Navigate to the official website of your scan tool’s manufacturer.
- Download the Update Software: Find the support or downloads section and look for the software update for your specific scan tool model.
- Install the Software: Download and install the update software on your computer.
- Connect Your Scan Tool: Use a USB cable to connect your scan tool to your computer.
- Run the Update: Launch the update software and follow the on-screen prompts to update your scan tool’s firmware and software.
Regularly updating your scan tool not only ensures compatibility with the latest vehicles but also enhances its functionality and accuracy, making your diagnostic tasks more efficient and reliable.
9. The Importance of Professional Advice
Navigating the complexities of OBD1 and OBD2 systems, along with selecting the correct diagnostic tools, can be intimidating. Expert guidance can make a substantial difference, especially when dealing with older vehicles or interpreting complex diagnostic data. Consulting with experienced mechanics or automotive diagnostic specialists can provide invaluable insights and prevent costly errors.
9.1. When to Seek Professional Help
- Uncertainty About the Correct Tool: If you’re unsure which scan tool or adapter is appropriate for your vehicle, seeking advice from a professional can save time and money.
- Difficulty Interpreting Codes: Diagnostic trouble codes can be ambiguous. A professional can provide a precise interpretation and suggest appropriate repairs.
- Complex Diagnostic Issues: For complex or intermittent problems, professional diagnostic equipment and expertise may be necessary to pinpoint the root cause.
9.2. Benefits of Consulting Professionals
- Accurate Diagnosis: Professionals have the knowledge and tools to accurately diagnose a wide range of automotive issues.
- Cost-Effective Solutions: By identifying the problem correctly the first time, professionals can help avoid unnecessary repairs and expenses.
- Access to Advanced Equipment: Professional mechanics have access to advanced diagnostic tools that are not typically available to DIY enthusiasts.
- Peace of Mind: Knowing that your vehicle is being diagnosed by a qualified professional can provide peace of mind and assurance that the job is being done correctly.
10. How OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN Can Help
At OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN, we understand the complexities of automotive diagnostics and offer a range of resources to help you diagnose and repair your vehicle.
10.1. Expert Advice and Support
Our team of experienced technicians can provide expert advice and support to help you choose the right scan tool, interpret diagnostic codes, and troubleshoot vehicle issues.
10.2. Wide Selection of Scan Tools and Adapters
We offer a wide selection of OBD1 and OBD2 scan tools, as well as adapters for a variety of vehicles. We can help you find the right tool for your needs and budget.
10.3. Diagnostic and Repair Information
Our website features a wealth of diagnostic and repair information, including:
- OBD1 and OBD2 Code Definitions: We provide detailed descriptions of OBD1 and OBD2 diagnostic trouble codes.
- Troubleshooting Guides: We offer step-by-step troubleshooting guides for common vehicle problems.
- Repair Manuals: We provide access to repair manuals for a wide range of vehicles.
10.4. Training and Education
We offer training and education resources to help you improve your diagnostic skills. Our resources include:
- Online Courses: We offer online courses on a variety of diagnostic topics.
- Workshops: We host workshops and seminars on automotive diagnostics.
- Certification Programs: We offer certification programs for automotive technicians.
Don’t let the complexities of automotive diagnostics keep you off the road. Contact OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN today at 123 Main Street, Los Angeles, CA 90001, United States, or call us at +1 (641) 206-8880. Visit our website at OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN for more information. Let us help you diagnose and repair your vehicle quickly and efficiently.
FAQ: Can OBD2 Be Used on OBD1 Cars?
Here are some frequently asked questions about using OBD2 scanners on OBD1 cars:
Q1: What is the main difference between OBD1 and OBD2?
The main difference is standardization. OBD1 was manufacturer-specific with varying connectors and protocols, while OBD2 introduced a standard 16-pin connector, universal diagnostic trouble codes, and standardized communication protocols.
Q2: Can I use an OBD2 scanner on my OBD1 car with an adapter?
No, an adapter can physically connect the OBD2 scanner to the OBD1 port, but it does not translate the communication protocols. The OBD2 scanner will not be able to read the OBD1 data.
Q3: What type of scan tool do I need for an OBD1 car?
You need a scan tool specifically designed for OBD1 systems or a combination OBD1/OBD2 scan tool that includes the necessary software and adapters to communicate with OBD1 vehicles.
Q4: Where can I find the OBD1 port in my car?
OBD1 ports are typically located under the dashboard on the driver’s side, but their exact location can vary. Consult your vehicle’s repair manual for the specific location.
Q5: Are OBD1 scan tools more expensive than OBD2 scan tools?
OBD1 scan tools can vary in price depending on their functionality and coverage. Some professional-grade OBD1 scan tools can be more expensive than basic OBD2 scanners.
Q6: Can I update the software on my OBD1 scan tool?
Yes, many OBD1 scan tools can be updated with the latest software to ensure compatibility with a wider range of vehicles and access to the latest diagnostic information. Check the manufacturer’s website for updates.
Q7: What are some common problems when diagnosing OBD1 cars?
Common problems include difficulty finding the correct adapter, interpreting manufacturer-specific diagnostic trouble codes, and limited data availability.
Q8: What is OBD3?
OBD3 is a proposed standard that would require vehicles to report emissions-related faults directly to regulatory agencies via wireless communication.
Q9: How can OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN help me with OBD1 diagnostics?
OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN offers expert advice and support, a wide selection of scan tools and adapters, diagnostic and repair information, and training and education resources to help you diagnose and repair your OBD1 vehicle.
Q10: Where can I buy OBD1 adapters?
OBD1 adapters can be purchased from online retailers like Amazon and eBay, as well as from automotive parts stores and tool suppliers.
We at OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN are here to assist you with all your diagnostic needs. Contact us today to learn more.
