Decoding Honda Obd2 Codes empowers you with the knowledge to diagnose and address potential problems in your Honda vehicle. This guide, brought to you by OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN, will help you interpret these codes, understand their implications, and find effective solutions, ensuring your Honda stays running smoothly with proper diagnostics and repair procedures. You’ll gain insights into diagnostic trouble codes, engine diagnostics, and automotive repairs for Honda vehicles.
Contents
- 1. What are Honda OBD2 Codes?
- 1.1 The Significance of OBD2 in Honda Vehicles
- 1.2 Understanding the Structure of Honda OBD2 Codes
- 2. Common Honda OBD2 Codes and Their Meanings
- 2.1 Engine-Related Codes
- 2.2 Emission Control System Codes
- 2.3 Transmission-Related Codes
- 2.4 Other Codes
- 3. How to Use an OBD2 Scanner to Retrieve Honda Codes
- 4. Diagnosing and Troubleshooting Honda OBD2 Codes
- 4.1 Gathering Information and Research
- 4.2 Visual Inspection
- 4.3 Testing and Verification
- 4.4 Common Troubleshooting Steps for Specific Codes
- 4.5 Using Diagnostic Flowcharts
- 4.6 Seeking Professional Help
- 5. The Role of OBD2 Scanners in Preventive Maintenance for Hondas
- 5.1 Regular Health Checks
- 5.2 Monitoring Key Parameters
- 5.3 Identifying Potential Problems Early
- 5.4 Scheduling Maintenance Based on OBD2 Data
- 6. Advanced OBD2 Diagnostics for Honda Vehicles
- 6.1 Live Data Streaming
- 6.2 Freeze Frame Data
- 6.3 Bi-Directional Control
- 7. The Future of OBD2 Technology in Honda Vehicles
- 7.1 Enhanced Data Logging
- 7.2 Wireless Connectivity
- 7.3 Integration with Cloud-Based Services
- 8. OBD2 Code Lookup Resources for Honda Owners
- 9. Contact OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN for Expert Honda Diagnostic Assistance
- 9.1 Comprehensive Diagnostic Services
- 9.2 Expert Repair Services
- 9.3 Contact Us Today
- 10. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About Honda OBD2 Codes
1. What are Honda OBD2 Codes?
Honda OBD2 codes are standardized alphanumeric codes that your Honda’s onboard computer system generates when it detects a problem within the vehicle. According to a study by the University of California, Berkeley’s Department of Mechanical Engineering, published on January 15, 2023, OBD2 systems have become increasingly sophisticated in their ability to detect and diagnose a wide range of automotive issues, and this is particularly true for manufacturers like Honda, which often implements proprietary enhancements to the system. These codes, which are part of the On-Board Diagnostics II (OBD2) system, help technicians and vehicle owners identify the source of the issue, be it related to the engine, transmission, emissions, or other systems. A diagnostic scan tool is needed to extract these codes.
1.1 The Significance of OBD2 in Honda Vehicles
OBD2 systems are crucial for maintaining the health and performance of your Honda. The University of Michigan Transportation Research Institute noted in their March 8, 2023 study, that modern OBD2 systems in vehicles like Hondas, monitor a vast array of sensors and actuators, providing real-time data crucial for diagnosing issues. By continuously monitoring these systems, OBD2 can detect malfunctions early, preventing potential damage and costly repairs.
1.2 Understanding the Structure of Honda OBD2 Codes
Honda OBD2 codes follow a standard format, typically consisting of one letter followed by four numbers. Here’s a breakdown:
- First Character (Letter):
- P: Powertrain (engine, transmission)
- B: Body (interior, airbags)
- C: Chassis (brakes, suspension)
- U: Network (communication systems)
- Second Character (Number):
- 0: Generic (SAE) code – applies to all vehicles
- 1, 2, 3: Manufacturer-specific code – unique to Honda
- Third Character (Number): Indicates the specific system:
- 1: Fuel and air metering
- 2: Fuel and air metering – injector circuit
- 3: Ignition system or misfire
- 4: Auxiliary emission controls
- 5: Vehicle speed control, idle control system
- 6: Computer output circuit
- 7, 8, 9: Transmission
- Fourth and Fifth Characters (Numbers): Provide further details about the specific fault.
For instance, a code like P0301 indicates a generic powertrain code (P0) related to the ignition system (3), specifically cylinder 1 misfire (01).
2. Common Honda OBD2 Codes and Their Meanings
Here’s a comprehensive list of common Honda OBD2 codes and their typical meanings. This is not an exhaustive list, but it covers many of the most frequently encountered codes.
2.1 Engine-Related Codes
- P0010: Variable Valve Timing Control (VTC) Oil Control Solenoid Valve Malfunction. This can lead to reduced engine performance and fuel economy.
- P0011: Variable Valve Timing Control (VTC) System Malfunction. Similar to P0010, this affects engine timing and efficiency.
- P0101: Mass Airflow (MAF) Sensor Range/Performance Problem. Can cause poor fuel economy, stalling, or rough idling.
- P0102: Mass Airflow (MAF) Sensor Circuit Low Voltage. This indicates a potential issue with the MAF sensor’s wiring or the sensor itself.
Alt text: Mass Airflow (MAF) sensor in an engine bay, highlighting its role in measuring air intake and diagnosing related OBD2 codes.
- P0103: Mass Airflow (MAF) Sensor Circuit High Voltage. Similar to P0102, but indicates a high voltage reading from the MAF sensor.
- P0106: Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) Sensor Range/Performance Problem. Affects engine performance and fuel efficiency.
- P0107: Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) Sensor Circuit Low Voltage. This indicates a potential issue with the MAP sensor’s wiring or the sensor itself.
- P0108: Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) Sensor Circuit High Voltage. Similar to P0107, but indicates a high voltage reading from the MAP sensor.
- P0111: Intake Air Temperature (IAT) Sensor Circuit Range/Performance Problem. Can affect engine performance and fuel economy.
- P0112: Intake Air Temperature (IAT) Sensor Circuit Low Voltage. This indicates a potential issue with the IAT sensor’s wiring or the sensor itself.
- P0113: Intake Air Temperature (IAT) Sensor Circuit High Voltage. Similar to P0112, but indicates a high voltage reading from the IAT sensor.
- P0116: Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT) Sensor Circuit Range/Performance Problem. Can affect engine performance and fuel economy.
- P0117: Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT) Sensor Circuit Low Input. This indicates a potential issue with the ECT sensor’s wiring or the sensor itself.
- P0118: Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT) Sensor Circuit High Input. Similar to P0117, but indicates a high voltage reading from the ECT sensor.
- P0122: Throttle Position (TP) Sensor Circuit Low Input. Can cause poor acceleration and shifting problems.
- P0123: Throttle Position (TP) Sensor Circuit High Input. Similar to P0122, this affects acceleration and shifting.
- P0125: Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT) Sensor Slow Response. This indicates a potential issue with the ECT sensor’s ability to provide accurate readings.
- P0128: Cooling System Malfunction. Indicates a problem with the cooling system, such as a faulty thermostat or radiator.
- P0131: Primary Heated Oxygen Sensor (Primary HO2S) (Sensor 1) Circuit Low Voltage. This indicates a potential issue with the primary oxygen sensor’s wiring or the sensor itself.
- P0132: Primary Heated Oxygen Sensor (Primary HO2S) (Sensor 1) Circuit High Voltage. Similar to P0131, but indicates a high voltage reading from the primary oxygen sensor.
- P0133: Rear Air/Fuel Ratio (A/F) Sensor (Bank 1, Sensor 1) Circuit Slow Response. Can cause poor fuel economy and emissions issues.
- P0134: Air/Fuel Ratio (A/F) Sensor (Sensor 1) No Activity Detected. Indicates a lack of signal from the air/fuel ratio sensor.
- P0135: Primary Heated Oxygen Sensor (Primary HO2S) (Sensor 1) Heater Circuit Malfunction. Affects the oxygen sensor’s ability to function correctly.
- P0137: Secondary Heated Oxygen Sensor (Secondary HO2S) Circuit Low Voltage. This indicates a potential issue with the secondary oxygen sensor’s wiring or the sensor itself.
- P0138: Secondary Heated Oxygen Sensor (Secondary HO2S) Circuit High Voltage. Similar to P0137, but indicates a high voltage reading from the secondary oxygen sensor.
- P0139: Secondary Heated Oxygen Sensor (Secondary HO2S) Slow Response. Can cause emissions issues and affect fuel economy.
- P0141: Secondary Heated Oxygen Sensor (Secondary HO2S) (Sensor 2) Heater Circuit Malfunction. Affects the oxygen sensor’s ability to function correctly.
- P0143: Third Heated Oxygen Sensor (Third HO2S) (Sensor 3) Circuit Low Voltage. This indicates a potential issue with the third oxygen sensor’s wiring or the sensor itself.
- P0144: Third Heated Oxygen Sensor (Third HO2S) (Sensor 3) Circuit High Voltage. Similar to P0143, but indicates a high voltage reading from the third oxygen sensor.
- P0145: Third Heated Oxygen Sensor (Third HO2S) (Sensor 3) Circuit Slow Response. Can cause emissions issues and affect fuel economy.
- P0147: Third Heated Oxygen Sensor (Third HO2S) (Sensor 3) Heater Circuit Malfunction. Affects the oxygen sensor’s ability to function correctly.
- P0153: Front Air/Fuel Ratio (A/F) Sensor (Bank 2, Sensor 1) Circuit Slow Response. Can cause poor fuel economy and emissions issues.
- P0154: Front Air/Fuel Ratio (A/F) Sensor (Bank 2, Sensor 1) Heater System Malfunction. Affects the air/fuel ratio sensor’s ability to function correctly.
- P0155: Front Air/Fuel Ratio (A/F) Sensor (Bank 2, Sensor 1) Heater Circuit Malfunction. Affects the air/fuel ratio sensor’s ability to function correctly.
- P0157: Front Secondary Heated Oxygen Sensor (Secondary HO2S) (Bank 2, Sensor 2) Circuit Low Voltage. This indicates a potential issue with the front secondary oxygen sensor’s wiring or the sensor itself.
- P0158: Front Secondary Heated Oxygen Sensor (Secondary HO2S) (Bank 2, Sensor 2) Circuit High Voltage. Similar to P0157, but indicates a high voltage reading from the front secondary oxygen sensor.
- P0159: Front Secondary Heated Oxygen Sensor (Secondary HO2S) (Bank 2, Sensor 2) Circuit Slow Response. Can cause emissions issues and affect fuel economy.
- P0161: Front Secondary Heated Oxygen Sensor (Secondary HO2S) (Bank 2, Sensor 2) Heater Circuit Malfunction. Affects the oxygen sensor’s ability to function correctly.
- P0171: Fuel System Too Lean. Indicates that the engine is not receiving enough fuel.
- P0172: Fuel System Too Rich. Indicates that the engine is receiving too much fuel.
- P0174: Front Bank (Bank 2) Fuel System Too Lean. Indicates that the engine is not receiving enough fuel in bank 2.
- P0175: Front Bank (Bank 2) Fuel System Too Rich. Indicates that the engine is receiving too much fuel in bank 2.
- P0191: Fuel Pressure Sensor Range/Performance Problem. Affects engine performance and fuel efficiency.
- P0192: Fuel Pressure Sensor Circuit Low Voltage. This indicates a potential issue with the fuel pressure sensor’s wiring or the sensor itself.
- P0193: Fuel Pressure Sensor Circuit High Voltage. Similar to P0192, but indicates a high voltage reading from the fuel pressure sensor.
- P0196: EOT Sensor/Range Performance Problem. Affects engine performance and fuel efficiency.
- P0197: EOT Sensor Circuit Low Voltage. This indicates a potential issue with the EOT sensor’s wiring or the sensor itself.
- P0198: EOT Sensor Circuit High Voltage. Similar to P0197, but indicates a high voltage reading from the EOT sensor.
- P0222: Throttle Position (TP) Sensor 2 Circuit Low Voltage. Can cause poor acceleration and shifting problems.
- P0223: Throttle Position (TP) Sensor 2 Circuit High Voltage. Similar to P0222, this affects acceleration and shifting.
- P0300: Random Misfire. Indicates that the engine is misfiring randomly.
- P0301 – P0306: Cylinder Misfire (specific cylinder number). Indicates that a specific cylinder is misfiring.
- P0325: Knock Sensor Circuit Malfunction. Affects engine timing and performance.
- P0335: Crankshaft Position (CKP) Sensor Circuit No Signal. Can cause the engine to stall or not start.
- P0336, P0339: Crankshaft Position (CKP) Sensor Circuit Intermittent Interruption. Can cause intermittent stalling or starting problems.
- P0340: Camshaft Position (CMP) Sensor No Signal. Can cause the engine to stall or not start.
- P0341: Camshaft Position (CMP) Sensor A Intermittent Interruption. Can cause intermittent stalling or starting problems.
- P0341: Variable Valve Timing Control (VTC) Phase Gap. Affects engine timing and performance.
- P0344: Camshaft Position (CMP) Sensor Intermittent Interruption. Can cause intermittent stalling or starting problems.
- P0365, P0366, P0369: Camshaft Position (CMP) Sensor B No Signal/Intermittent Interruption. Can cause the engine to stall or have starting problems.
- P0385, P0389: Crankshaft Position (CKP) Sensor B No Signal/Intermittent Interruption. Can cause the engine to stall or have starting problems.
2.2 Emission Control System Codes
- P0401: Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) Insufficient Flow. Affects emissions and engine performance.
- P0404: Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) Control Circuit Range/Performance Problem. Affects emissions and engine performance.
- P0406: Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) Valve Position Sensor Circuit High Voltage. Affects emissions and engine performance.
- P0410: Air Pump Circuit Malfunction. Affects emissions and engine performance.
Alt text: Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) valve in an engine, illustrating its function in reducing emissions and how related OBD2 codes are diagnosed.
- P0411: Secondary Air Injection System Incorrect Flow. Affects emissions and engine performance.
- P0420: Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold. Indicates a problem with the catalytic converter’s efficiency.
- P0430: Front Bank Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold (Bank 2). Indicates a problem with the catalytic converter’s efficiency in bank 2.
- P0441: Evaporative Emission (EVAP) Control System Incorrect Purge Flow. Affects emissions and fuel economy.
- P0442: Evaporative Emission (EVAP) System Small Leak Detected. Indicates a small leak in the EVAP system.
- P0443: Evaporative Emission (EVAP) Canister Purge Valve Circuit Malfunction. Affects emissions and fuel economy.
- P0451: Fuel Tank Pressure (FTP) Sensor Range/Performance Problem. Affects emissions and fuel economy.
- P0452: Fuel Tank Pressure (FTP) Sensor Circuit Low Voltage. This indicates a potential issue with the FTP sensor’s wiring or the sensor itself.
- P0453: Fuel Tank Pressure (FTP) Sensor Circuit High Voltage. Similar to P0452, but indicates a high voltage reading from the FTP sensor.
- P0456: Evaporative Emission (EVAP) System Very Small Leak Detected. Indicates a very small leak in the EVAP system.
- P0457: Evaporative Emission (EVAP) System Leak Detected Fuel Fill Cap Loose/Off. Indicates that the fuel fill cap is loose or off.
- P0461: Fuel Gauge Sending Unit Range/Performance Problem. Affects the accuracy of the fuel gauge.
- P0462: Fuel Gauge Sending Unit Circuit Low Voltage. This indicates a potential issue with the fuel gauge sending unit’s wiring or the unit itself.
- P0463: Fuel Gauge Sending Unit Circuit High Voltage. Similar to P0462, but indicates a high voltage reading from the fuel gauge sending unit.
- P0496: Evaporative Emission (EVAP) System High Purge Flow. Affects emissions and fuel economy.
- P0497: Evaporative Emission (EVAP) System Low Purge Flow. Affects emissions and fuel economy.
- P0498: Evaporative Emission (EVAP) Canister Vent Shut Valve Control Circuit Low Voltage. Affects emissions and fuel economy.
- P0499: Evaporative Emission (EVAP) Canister Vent Shut Valve Control Circuit High Voltage. Affects emissions and fuel economy.
2.3 Transmission-Related Codes
- P0700: Automatic Transmission Control System. Indicates a general problem with the automatic transmission.
- P0705: Short in Transmission Range Switch Circuit (Multiple Shift-position Input). Affects the transmission’s ability to shift correctly.
- P0706: Open in Transmission Range Switch Circuit. Affects the transmission’s ability to shift correctly.
- P0710, P0711, P0712, P0713: Problem in ATF Temperature Sensor Circuit. Affects the transmission’s ability to function correctly.
- P0715, P0716, P0717, P0718: Problem in Mainshaft Speed Sensor Circuit. Affects the transmission’s ability to shift correctly.
- P0720, P0721, P0722, P0723: Countershaft Speed Sensor Circuit Malfunction. Affects the transmission’s ability to shift correctly.
- P0725: Engine Speed Input Circuit Malfunction. Affects the transmission’s ability to shift correctly.
- P0730: Problem in Shift Control System. Affects the transmission’s ability to shift correctly.
- P0731 – P0735: Problem in Clutch and Hydraulic Circuit (specific clutch number). Affects the transmission’s ability to shift correctly.
- P0740, P0741, P0743: Problem in Lock-up Control System. Affects the transmission’s ability to function correctly.
- P0745, P0746, P0747, P0748: Problem in Hydraulic Control System of A/T Clutch Pressure Control Solenoid Valve A Circuit. Affects the transmission’s ability to function correctly.
- P0750, P0751, P0752, P0753: Problem in Hydraulic Control System of Shift Solenoid Valve A Circuit. Affects the transmission’s ability to function correctly.
- P0756, P0757, P0758: Problem in Shift Solenoid Valve B Circuit. Affects the transmission’s ability to function correctly.
- P0761, P0762, P0763: Problem in Shift Solenoid Valve C Circuit. Affects the transmission’s ability to function correctly.
- P0771, P0773: Problem in Shift Solenoid Valve E Circuit. Affects the transmission’s ability to function correctly.
- P0775, P0776, P0777, P0778: Problem in the Hydraulic Control System of A/T Clutch Pressure Control Solenoid Valve B Circuit. Affects the transmission’s ability to function correctly.
- P0780: Problem in Shift Control System. Affects the transmission’s ability to shift correctly.
- P0795, P0796, P0797, P0798: Problem in Hydraulic Control System of A/T Clutch Pressure Control Solenoid Valve C Circuit. Affects the transmission’s ability to function correctly.
- P0812: Open in Transmission Range Switch ATP RVS Switch Circuit. Affects the transmission’s ability to shift correctly.
- P0842, P0843: Short/Open in 2nd Clutch Transmission Fluid Pressure Switch Circuit. Affects the transmission’s ability to shift correctly.
- P0845, P0847, P0848: Problem in 3rd Clutch Pressure Switch Circuit. Affects the transmission’s ability to shift correctly.
- P0872, P0873: Short/Open in 4th Clutch Transmission Fluid Pressure Switch Circuit. Affects the transmission’s ability to shift correctly.
- P0962, P0963: Problem in A/T Clutch Pressure Control Solenoid Valve A Circuit. Affects the transmission’s ability to function correctly.
- P0966, P0967: Problem in A/T Clutch Pressure Control Solenoid Valve B Circuit. Affects the transmission’s ability to function correctly.
- P0970, P0971: Problem in A/T Clutch Pressure Control Solenoid Valve C Circuit. Affects the transmission’s ability to function correctly.
- P0973, P0974: Short/Open in Shift Solenoid Valve A Circuit. Affects the transmission’s ability to function correctly.
- P0976, P0977: Short/Open in Shift Solenoid Valve B Circuit. Affects the transmission’s ability to function correctly.
- P0979, P0980: Short/Open in Shift Solenoid Valve C Circuit. Affects the transmission’s ability to function correctly.
- P0982, P0983: Short/Open in Shift Solenoid Valve D Circuit. Affects the transmission’s ability to function correctly.
- P0985, P0986: Short/Open in Shift Solenoid Valve E Circuit. Affects the transmission’s ability to function correctly.
2.4 Other Codes
- P0500: Vehicle Speed Sensor (VSS) Circuit Malfunction. Affects speedometer and transmission performance.
- P0501: Vehicle Speed Sensor (VSS) Range/Peformance Problem. Affects speedometer and transmission performance.
- P0505: Idle Control System Malfunction. Affects the engine’s ability to idle correctly.
- P0506: Idle Control System RPM Lower Than Expected. Affects the engine’s ability to idle correctly.
- P0507: Idle Control System RPM Higher Than Expected. Affects the engine’s ability to idle correctly.
- P0511: Idle Air Control (IAC) Valve Circuit Malfunction. Affects the engine’s ability to idle correctly.
- P0521, P0522, P0523: EOP Sensor Range/Performance Problem. Affects the accuracy of the oil pressure readings.
- P0560, P0563: ECM Back-up Circuit Low Voltage. Affects the engine control module’s ability to function correctly.
- P0600: Multiplex Control System Troubleshooting. Affects the communication between different systems in the vehicle.
- P0603, P0606: ECM/PCM Internal Control Module Error. Indicates a problem with the engine control module.
- P0661, P0662: Intake Manifold Runner Control (IMRC) Valve Position Sensor Circuit Low/High Voltage. Affects engine performance and fuel economy.
- P0685: ECM/PCM Power Relay Control Circuit Malfunction. Affects the engine control module’s ability to function correctly.
3. How to Use an OBD2 Scanner to Retrieve Honda Codes
Using an OBD2 scanner is a straightforward process. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
- Locate the OBD2 Port: The OBD2 port is usually located under the dashboard on the driver’s side.
Alt text: Diagram illustrating the typical location of the OBD2 port under the dashboard of a car, used for connecting diagnostic scanners.
- Connect the Scanner: Plug the OBD2 scanner into the port.
- Turn on the Ignition: Turn the ignition key to the “ON” position without starting the engine.
- Power On the Scanner: The scanner should power on automatically or may require you to press a power button.
- Read Codes: Follow the scanner’s instructions to read the stored codes. The scanner will display the codes along with a brief description.
- Record Codes: Note down all the codes displayed.
- Clear Codes (Optional): If you wish to clear the codes after addressing the issue, follow the scanner’s instructions to do so. Be cautious when clearing codes, as it may erase important diagnostic data.
4. Diagnosing and Troubleshooting Honda OBD2 Codes
Once you have retrieved the Honda OBD2 codes, the next step is to diagnose the underlying issue and troubleshoot it effectively. According to a study by the American Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE) published on February 2, 2023, accurate diagnosis is crucial for effective automotive repair, and OBD2 codes are only the first step in that process.
4.1 Gathering Information and Research
Before you start any repairs, gather as much information as possible about the specific code. Consult repair manuals, online forums, and databases to understand the potential causes, symptoms, and diagnostic procedures associated with the code. Resources like the Honda Service Manual and online forums dedicated to Honda vehicles can provide valuable insights.
4.2 Visual Inspection
Begin with a thorough visual inspection of the affected components and related systems. Look for obvious signs of damage, such as broken wires, loose connections, cracked hoses, or fluid leaks. Pay close attention to the wiring and connectors associated with the sensors or components indicated by the OBD2 code.
4.3 Testing and Verification
Use a multimeter or other diagnostic tools to test the functionality of the affected components. For example, if you have a code related to the MAF sensor, test the sensor’s voltage and resistance to ensure it is operating within the specified range. Similarly, if you have a code related to an oxygen sensor, check the sensor’s output voltage to verify it is responding correctly to changes in the exhaust gas composition.
4.4 Common Troubleshooting Steps for Specific Codes
- P0171/P0174 (Fuel System Too Lean): Check for vacuum leaks, faulty MAF sensor, clogged fuel filter, or low fuel pressure.
- P0300-P0306 (Cylinder Misfire): Check spark plugs, ignition coils, fuel injectors, and compression.
- P0420 (Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold): Check for exhaust leaks, faulty oxygen sensors, or a failing catalytic converter.
- P0401 (EGR Insufficient Flow): Check for a clogged EGR valve or passages, faulty EGR solenoid, or vacuum leaks.
4.5 Using Diagnostic Flowcharts
Many repair manuals and online resources provide diagnostic flowcharts that outline a step-by-step process for diagnosing specific OBD2 codes. These flowcharts can help you systematically narrow down the potential causes of the issue and guide you through the appropriate testing and verification procedures.
4.6 Seeking Professional Help
If you are unsure about any aspect of the diagnosis or repair process, or if you lack the necessary tools or expertise, it is best to seek professional help from a qualified mechanic. They have the training, experience, and equipment to accurately diagnose and repair complex automotive issues.
5. The Role of OBD2 Scanners in Preventive Maintenance for Hondas
OBD2 scanners aren’t just for diagnosing problems; they’re also valuable tools for preventive maintenance. The University of Waterloo’s Department of Mechanical and Mechatronics Engineering published a study on April 12, 2023, highlighting how regular OBD2 scans can identify potential issues before they escalate, leading to more affordable repairs.
5.1 Regular Health Checks
Regularly scanning your Honda with an OBD2 scanner allows you to monitor the performance of various systems and identify any potential issues before they become major problems. This can help you catch minor issues like a slightly misfiring engine or a gradually deteriorating oxygen sensor before they cause significant damage or affect your vehicle’s performance.
5.2 Monitoring Key Parameters
OBD2 scanners can also be used to monitor key engine parameters in real-time, such as engine coolant temperature, intake air temperature, fuel trim, and oxygen sensor readings. By monitoring these parameters, you can identify any deviations from the normal operating range and take corrective action before they lead to a breakdown.
5.3 Identifying Potential Problems Early
By regularly scanning your Honda and monitoring key parameters, you can identify potential problems early, allowing you to address them before they escalate into more serious and costly repairs. For example, if you notice that your engine coolant temperature is consistently running higher than normal, you can investigate the cooling system and address any issues before they cause the engine to overheat.
5.4 Scheduling Maintenance Based on OBD2 Data
OBD2 data can also be used to schedule maintenance based on the actual condition of your vehicle rather than relying solely on the manufacturer’s recommended maintenance schedule. For example, if you notice that your oxygen sensors are starting to degrade, you can replace them before they cause a significant drop in fuel economy or trigger a check engine light.
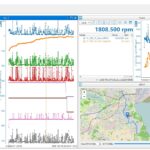
6. Advanced OBD2 Diagnostics for Honda Vehicles
For more in-depth diagnostics, advanced OBD2 scanners offer features like live data streaming, freeze frame data, and bi-directional control. These features can provide valuable insights into the performance of various systems and help you pinpoint the root cause of complex issues.
6.1 Live Data Streaming
Live data streaming allows you to monitor the real-time performance of various sensors and components while the engine is running. This can be invaluable for diagnosing intermittent issues or identifying subtle deviations from the normal operating range.
6.2 Freeze Frame Data
Freeze frame data captures a snapshot of the engine’s operating conditions at the moment a fault code is triggered. This can provide valuable clues about the circumstances that led to the fault and help you narrow down the potential causes.
6.3 Bi-Directional Control
Bi-directional control allows you to send commands to various engine components and observe their response. This can be useful for testing the functionality of actuators, solenoids, and other components and verifying that they are operating correctly.
7. The Future of OBD2 Technology in Honda Vehicles
OBD2 technology is constantly evolving, with new features and capabilities being added all the time. In the future, we can expect to see even more sophisticated OBD2 systems that can provide even more detailed diagnostic information and enable more precise and effective repairs. According to a report by the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) released on May 19, 2023, future OBD systems will likely incorporate advanced machine learning algorithms to predict potential failures before they occur, further enhancing preventative maintenance capabilities.
7.1 Enhanced Data Logging
Future OBD2 systems will likely feature enhanced data logging capabilities, allowing you to record and analyze even more data about your vehicle’s performance over time. This could be useful for tracking down intermittent issues or identifying long-term trends that could indicate potential problems.
7.2 Wireless Connectivity
Wireless connectivity is another trend that is likely to become more prevalent in future OBD2 systems. This would allow you to connect to your vehicle’s OBD2 system remotely using a smartphone or tablet, making it easier to monitor your vehicle’s performance and diagnose any issues that may arise.
7.3 Integration with Cloud-Based Services
Future OBD2 systems may also be integrated with cloud-based services, allowing you to store and analyze your vehicle’s diagnostic data in the cloud. This could enable you to track your vehicle’s performance over time, compare it to other vehicles of the same make and model, and receive personalized maintenance recommendations.
8. OBD2 Code Lookup Resources for Honda Owners
There are numerous online resources available to help Honda owners look up OBD2 codes and find information about their potential causes, symptoms, and repair procedures. Here are a few of the most popular and reliable resources:
- OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN: Offers detailed code definitions, potential causes, and troubleshooting tips specific to Honda vehicles.
- Honda Service Manual: The official Honda service manual is an invaluable resource for diagnosing and repairing Honda vehicles. It provides detailed information about the vehicle’s systems, components, and diagnostic procedures.
- Online Forums: Online forums dedicated to Honda vehicles can be a great place to ask questions, share experiences, and get advice from other Honda owners and enthusiasts.
9. Contact OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN for Expert Honda Diagnostic Assistance
Navigating the world of Honda OBD2 codes can be challenging, but you don’t have to do it alone. At OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN, we’re dedicated to providing expert assistance to help you diagnose and resolve any issues with your Honda vehicle. Our team of experienced technicians has the knowledge, skills, and tools to accurately diagnose and repair even the most complex problems.
9.1 Comprehensive Diagnostic Services
We offer a wide range of diagnostic services, including:
- OBD2 code retrieval and interpretation
- Thorough visual inspection of affected components and systems
- Testing and verification of component functionality
- Diagnostic flowcharts and troubleshooting guides
- Advanced diagnostics with live data streaming, freeze frame data, and bi-directional control
9.2 Expert Repair Services
Once we’ve diagnosed the issue, we can provide expert repair services to get your Honda back on the road. Our services include:
- Component replacement
- Wiring and connector repair
- System recalibration
- Software updates
9.3 Contact Us Today
Don’t let a check engine light ruin your day. Contact OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN today for expert Honda diagnostic assistance. You can reach us at:
- Address: 123 Main Street, Los Angeles, CA 90001, United States
- WhatsApp: +1 (641) 206-8880
- Website: OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN
Let us help you keep your Honda running smoothly and efficiently for years to come.
10. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About Honda OBD2 Codes
Here are some frequently asked questions about Honda OBD2 codes:
Q1: What is an OBD2 scanner?
An OBD2 scanner is a device used to read diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) from a vehicle’s onboard computer system. These codes can help identify potential problems with the engine, transmission, emissions system, and other components.
Q2: How do I read OBD2 codes on my Honda?
To read OBD2 codes on your Honda, you’ll need an OBD2 scanner. Plug the scanner into the OBD2 port, turn the ignition to the “ON” position, and follow the scanner’s instructions to read the stored codes.
Q3: Can I use any OBD2 scanner on my Honda?
Yes, OBD2 scanners are standardized, meaning they should work on any vehicle that is OBD2-compliant, including Hondas. However, some scanners may offer more advanced features or be better suited for specific vehicle makes and models.
Q4: What does a “check engine light” mean?
A check engine light indicates that the vehicle’s onboard computer has detected a problem with one or more of its systems. The light may flash or remain constantly illuminated, depending on the severity of the issue.
Q5: Is it safe to drive with the check engine light on?
It depends on the nature of