Obd2 Diagnostic Cables are essential tools that empower automotive technicians and enthusiasts to diagnose and troubleshoot vehicle issues effectively. This comprehensive guide from OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN delves into the intricacies of OBD2 diagnostic cables, exploring their functionality, applications, and the crucial role they play in modern automotive diagnostics.
Contents
- 1. Understanding the OBD2 Diagnostic System
- 2. What is an OBD2 Diagnostic Cable?
- 3. Key Features of an OBD2 Diagnostic Cable
- 4. Types of OBD2 Diagnostic Cables
- 5. How to Choose the Right OBD2 Diagnostic Cable
- 6. The OBD2 Connector: A Closer Look
- 7. OBD2 Protocols Explained
- 8. The Role of CAN Bus in OBD2
- 9. Common OBD2 Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
- 10. The Importance of Accurate OBD2 Data Interpretation
- 11. How to Use an OBD2 Diagnostic Cable and Scanner
- 12. Maintaining Your OBD2 Diagnostic Cable
- 13. Advanced OBD2 Diagnostics Techniques
- 14. The Future of OBD2 Technology
- 15. OBD2 and Electric Vehicles (EVs)
- 16. Safety Precautions When Using OBD2 Diagnostic Cables
- 17. OBD2 Diagnostic Cable Troubleshooting
- 18. OBD2 Data Logging for Performance Analysis
- 19. OBD2 and Vehicle Inspections
- 20. WWH-OBD and OBDonUDS
- 21. Benefits of Using Information and Services from OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN
- 22. Call to Action: Get Expert Advice from OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN
- 23. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) About OBD2 Diagnostic Cables
1. Understanding the OBD2 Diagnostic System
What is the OBD2 system and why is it important?
The On-Board Diagnostics II (OBD2) system is a standardized system implemented in virtually all cars and light trucks sold in the United States since 1996. According to the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), the OBD2 system monitors the performance of a vehicle’s major components, including those responsible for controlling emissions. The OBD2 system is designed to:
- Monitor vehicle emissions
- Diagnose malfunctions
- Provide access to vehicle data
The OBD2 system is a crucial tool for mechanics and car owners, enabling them to diagnose and repair issues quickly and efficiently. According to a study by the National Institute for Automotive Service Excellence (ASE), using OBD2 scanners can reduce diagnostic time by up to 50%.
2. What is an OBD2 Diagnostic Cable?
What exactly is an OBD2 diagnostic cable and what does it do?
An OBD2 diagnostic cable is a specialized cable that connects an OBD2 scanner or diagnostic tool to a vehicle’s OBD2 port. This connection enables the scanner to communicate with the vehicle’s computer system, retrieving diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs), sensor data, and other valuable information. According to SAE International, the standardization of the OBD2 port (SAE J1962) ensures compatibility across different vehicle makes and models.
The OBD2 diagnostic cable acts as a bridge, allowing technicians and car owners to:
- Access vehicle diagnostic data
- Identify the source of problems
- Monitor vehicle performance
3. Key Features of an OBD2 Diagnostic Cable
What are the essential features of a quality OBD2 diagnostic cable?
A reliable OBD2 diagnostic cable should possess several key features to ensure optimal performance and longevity.
- Durability: The cable should be constructed from high-quality materials that can withstand frequent use and exposure to automotive environments.
- Shielding: Proper shielding is essential to minimize interference and ensure accurate data transmission.
- Compatibility: The cable must be compatible with a wide range of OBD2 scanners and vehicle models.
- Length: An adequate cable length provides flexibility and ease of use during diagnostic procedures.
4. Types of OBD2 Diagnostic Cables
What are the different types of OBD2 cables available?
OBD2 diagnostic cables come in various forms to suit different needs and applications.
- Standard OBD2 Cable: This is the most common type, used for basic diagnostics and code reading.
- Extension Cable: Provides extra length for easier access to the OBD2 port, especially in tight spaces.
- Adapter Cable: Converts the OBD2 port to a different connector type, allowing compatibility with older vehicles or specialized equipment.
5. How to Choose the Right OBD2 Diagnostic Cable
How do I select the best OBD2 cable for my needs?
Choosing the right OBD2 diagnostic cable depends on several factors, including:
- Vehicle Compatibility: Ensure the cable is compatible with your vehicle’s make, model, and year.
- Scanner Compatibility: Verify that the cable is compatible with your OBD2 scanner or diagnostic tool.
- Intended Use: Consider the type of diagnostic tasks you’ll be performing and choose a cable that meets those requirements.
6. The OBD2 Connector: A Closer Look
What are the specifications of the OBD2 connector?
The OBD2 connector, also known as the Data Link Connector (DLC), is a standardized 16-pin connector that provides access to a vehicle’s diagnostic data. As specified in SAE J1962, the OBD2 connector pinout is as follows:
- Pin 2: SAE J1850 Bus+
- Pin 4: Chassis Ground
- Pin 5: Signal Ground
- Pin 6: CAN High (J-2284)
- Pin 7: ISO 9141-2 K Line
- Pin 10: SAE J1850 Bus-
- Pin 14: CAN Low (J-2284)
- Pin 15: ISO 9141-2 L Line
- Pin 16: Battery Power
7. OBD2 Protocols Explained
What are the different communication protocols used in OBD2?
OBD2 communication relies on several protocols to transmit data between the scanner and the vehicle’s computer.
- CAN (Controller Area Network): The most common protocol, used in most modern vehicles.
- ISO 9141-2: Used in older European and Asian vehicles.
- SAE J1850 VPW: Used in older GM vehicles.
- SAE J1850 PWM: Used in older Ford vehicles.
- KWP2000 (ISO 14230): Used in some European and Asian vehicles.
Understanding these protocols is crucial for ensuring compatibility between your OBD2 scanner and the vehicle you’re diagnosing.
8. The Role of CAN Bus in OBD2
Why is CAN bus so important in modern OBD2 systems?
The Controller Area Network (CAN) bus is a robust and efficient communication protocol that has become the standard for OBD2 systems in modern vehicles. As detailed in ISO 15765-4, CAN bus offers several advantages over older protocols, including:
- Higher Data Transfer Rates: CAN bus allows for faster communication between the scanner and the vehicle’s computer.
- Improved Reliability: CAN bus is less susceptible to interference and errors, ensuring more accurate data transmission.
- Enhanced Functionality: CAN bus supports advanced diagnostic features and capabilities.
According to a report by the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA), the adoption of CAN bus has significantly improved the accuracy and efficiency of vehicle diagnostics.
9. Common OBD2 Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
What are some typical OBD2 DTCs and what do they indicate?
OBD2 diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) are alphanumeric codes that indicate specific problems detected by the vehicle’s computer system. Some common DTCs include:
| Code | Description | Possible Causes |
|---|---|---|
| P0300 | Random/Multiple Cylinder Misfire Detected | Faulty spark plugs, ignition coils, fuel injectors, vacuum leaks, low compression |
| P0171 | System Too Lean (Bank 1) | Vacuum leaks, faulty oxygen sensor, low fuel pressure, MAF sensor malfunction |
| P0420 | Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold | Faulty catalytic converter, oxygen sensor issues, exhaust leaks |
| P0301 | Cylinder 1 Misfire Detected | Faulty spark plug, ignition coil, fuel injector, low compression in cylinder 1 |
| P0113 | Intake Air Temperature Sensor Circuit High Input | Faulty IAT sensor, wiring issues, poor connection |
| P0011 | “A” Camshaft Position – Timing Over-Advanced or System Performance (Bank 1) | Low oil level, faulty camshaft position sensor, faulty oil control valve, timing chain or belt worn |
These are just a few examples of the many DTCs that can be retrieved using an OBD2 scanner. Consulting a comprehensive OBD2 DTC database, such as the one provided by OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN, is essential for accurate diagnosis and repair.
10. The Importance of Accurate OBD2 Data Interpretation
Why is it important to understand the data provided by an OBD2 scanner?
Interpreting OBD2 data accurately is crucial for effective vehicle diagnostics. A misinterpretation of DTCs or sensor readings can lead to incorrect repairs and wasted time and resources. According to a study by the Automotive Research Association of India (ARAI), technicians who receive proper training in OBD2 data interpretation are significantly more likely to diagnose and repair vehicles correctly.
11. How to Use an OBD2 Diagnostic Cable and Scanner
What are the steps to use an OBD2 scanner to diagnose a vehicle?
Using an OBD2 diagnostic cable and scanner is a straightforward process.
- Locate the OBD2 Port: The OBD2 port is typically located under the dashboard, near the steering column.
- Connect the Scanner: Plug the OBD2 diagnostic cable into the vehicle’s OBD2 port and connect the other end to the scanner.
- Turn on the Ignition: Turn the vehicle’s ignition to the “on” position, but do not start the engine.
- Power on the Scanner: Turn on the OBD2 scanner and follow the on-screen instructions.
- Read Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs): Use the scanner to retrieve any stored DTCs.
- Interpret the DTCs: Consult an OBD2 DTC database to understand the meaning of the codes.
- Clear the DTCs (Optional): After addressing the underlying issue, you can use the scanner to clear the DTCs.
- Monitor Sensor Data (Optional): Use the scanner to monitor real-time sensor data for further analysis.
12. Maintaining Your OBD2 Diagnostic Cable
How can I properly care for my OBD2 cable to ensure its longevity?
Proper maintenance can extend the life of your OBD2 diagnostic cable.
- Store the Cable Properly: When not in use, store the cable in a clean, dry place, away from extreme temperatures and direct sunlight.
- Avoid Sharp Bends: Avoid bending the cable sharply, as this can damage the internal wires.
- Clean the Connectors: Keep the connectors clean and free from dirt and debris.
- Inspect Regularly: Regularly inspect the cable for any signs of damage, such as cracks, fraying, or exposed wires.
13. Advanced OBD2 Diagnostics Techniques
What are some advanced diagnostic techniques that use OBD2 data?
Beyond basic code reading, OBD2 data can be used for advanced diagnostic techniques.
- Freeze Frame Data Analysis: Analyzing freeze frame data, which captures sensor readings at the moment a DTC was triggered, can provide valuable insights into the conditions that led to the problem.
- Live Data Streaming: Monitoring live sensor data can help identify intermittent problems and diagnose performance issues.
- Mode 6 Data Analysis: Accessing Mode 6 data, which provides detailed test results from the vehicle’s self-diagnostic routines, can help pinpoint specific component failures.
14. The Future of OBD2 Technology
How is OBD2 technology evolving?
OBD2 technology continues to evolve, driven by advancements in automotive technology and increasing regulatory requirements. Some key trends include:
- Wireless OBD2 Scanners: Wireless OBD2 scanners that connect to smartphones or tablets via Bluetooth or Wi-Fi are becoming increasingly popular.
- Cloud-Based Diagnostics: Cloud-based diagnostic platforms that provide access to vast databases of diagnostic information and repair procedures are emerging.
- Enhanced Security Features: Security features to protect vehicle data and prevent unauthorized access are being integrated into OBD2 systems.
According to a report by MarketsandMarkets, the global automotive diagnostics market is expected to reach $45.9 billion by 2027, driven by the increasing complexity of vehicle systems and the growing demand for advanced diagnostic solutions.
15. OBD2 and Electric Vehicles (EVs)
Does OBD2 apply to electric vehicles?
While OBD2 was initially designed for internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles to monitor emissions, its relevance to electric vehicles (EVs) is evolving. While legislated OBD2 has originally been designed for the purpose of emissions control/testing, electric vehicles are not required to support OBD2 in any shape or form. This can be seen in practice from the fact that almost none of the modern EVs support any of the standard OBD2 requests. Instead, most of them utilize OEM-specific UDS communication. Generally, this makes it impossible to decode data from these electric vehicles, except for cases where the decoding rules have been reverse engineered – see e.g. our case studies for electric cars incl. Tesla, Hyundai/Kia, Nissan and VW/Skoda EVs.
OBD2 is today implemented in a variety of ways and has limitations in regards to e.g. data richness and lower-layer protocols. In response to this, modern alternatives have been developed including WWH-OBD (World Wide Harmonized OBD) and OBDonUDS (OBD on UDS). Both seek to streamline and enhance OBD communication by leveraging the UDS protocol as basis. To learn more about these protocols, see our intro to UDS.
16. Safety Precautions When Using OBD2 Diagnostic Cables
What safety measures should I take when working with OBD2 systems?
When working with OBD2 diagnostic cables and scanners, it’s essential to take appropriate safety precautions.
- Read the Manual: Always read and follow the manufacturer’s instructions for the scanner and cable.
- Wear Safety Glasses: Wear safety glasses to protect your eyes from potential hazards.
- Disconnect the Battery (Optional): In some cases, it may be necessary to disconnect the vehicle’s battery to prevent electrical shock.
- Work in a Well-Ventilated Area: When working on the vehicle, ensure that the area is well-ventilated to avoid inhaling harmful fumes.
17. OBD2 Diagnostic Cable Troubleshooting
What should I do if my OBD2 cable isn’t working properly?
If you encounter problems with your OBD2 diagnostic cable, try these troubleshooting steps.
- Check the Connections: Ensure that the cable is securely connected to both the vehicle’s OBD2 port and the scanner.
- Inspect the Cable: Inspect the cable for any signs of damage.
- Test with a Different Vehicle: If possible, test the cable with a different vehicle to rule out a problem with the vehicle’s OBD2 system.
- Consult the Manual: Refer to the scanner’s manual for troubleshooting tips.
18. OBD2 Data Logging for Performance Analysis
How can OBD2 data be used to analyze vehicle performance?
OBD2 data can be a valuable resource for analyzing vehicle performance. By logging and analyzing sensor data, you can:
- Monitor Engine Performance: Track parameters such as RPM, speed, and fuel consumption.
- Identify Performance Issues: Detect problems such as misfires, lean conditions, and other performance-related issues.
- Optimize Tuning: Fine-tune engine parameters for optimal performance and fuel efficiency.
Several tools and software platforms are available for logging and analyzing OBD2 data, including those offered by OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN. The CANedge lets you easily record OBD2 data to an 8-32 GB SD card. Simply connect it to e.g. a car/truck to start logging – and decode the data via free software/APIs and our OBD2 DBC.
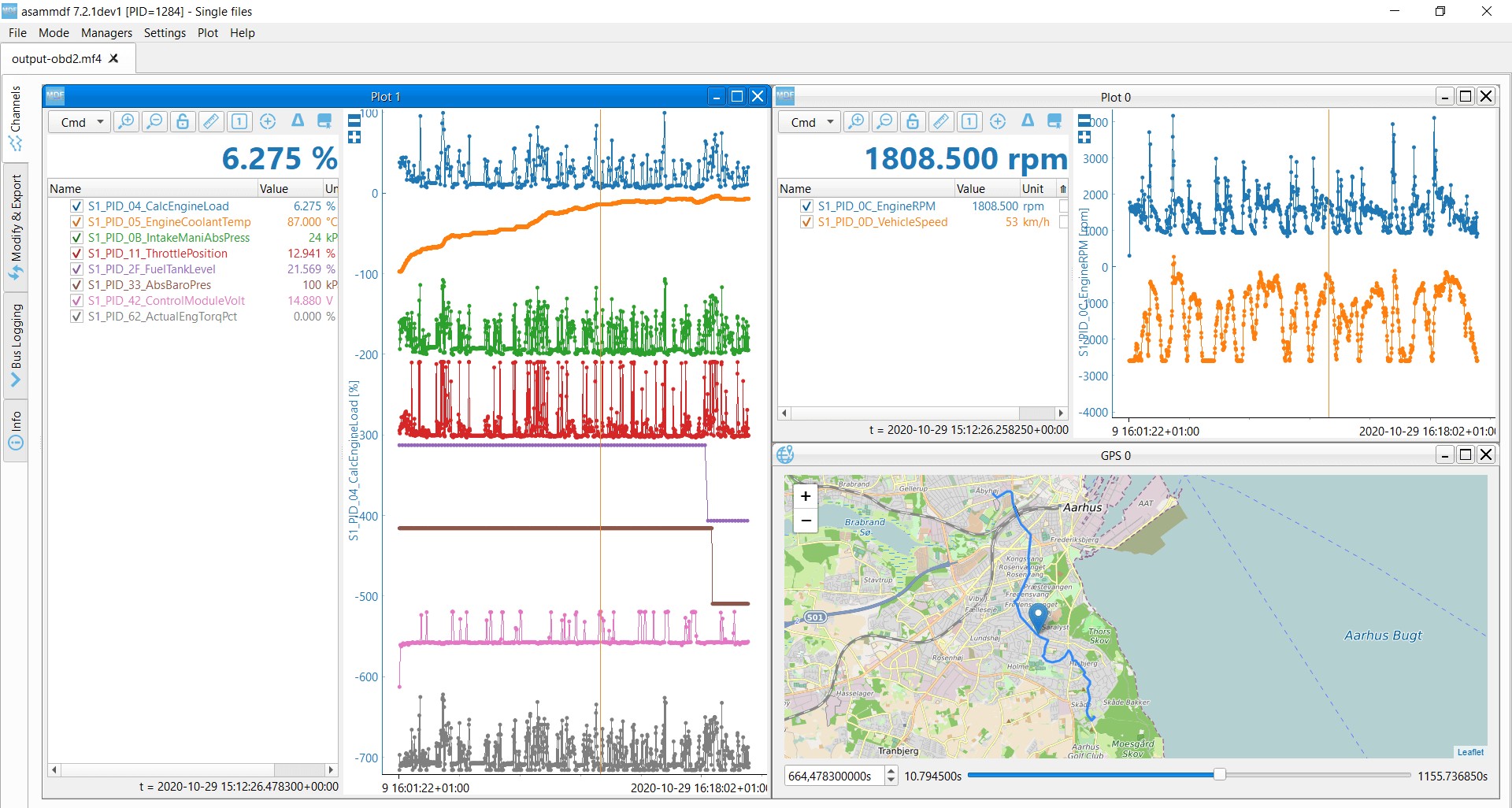 OBD2 data decoded visual plot asammdf CAN bus DBC file
OBD2 data decoded visual plot asammdf CAN bus DBC file
19. OBD2 and Vehicle Inspections
How is OBD2 used in vehicle safety and emissions inspections?
OBD2 plays a crucial role in vehicle safety and emissions inspections. During these inspections, technicians use OBD2 scanners to:
- Check for DTCs: Identify any stored DTCs that indicate potential problems.
- Verify System Readiness: Ensure that all OBD2 systems are functioning correctly and ready to monitor emissions.
- Assess Emissions Performance: Evaluate the vehicle’s emissions performance and compliance with regulatory standards.
20. WWH-OBD and OBDonUDS
What are WWH-OBD and OBDonUDS?
OBD2 is today implemented in a variety of ways and has limitations in regards to e.g. data richness and lower-layer protocols. In response to this, modern alternatives have been developed including WWH-OBD (World Wide Harmonized OBD) and OBDonUDS (OBD on UDS). Both seek to streamline and enhance OBD communication by leveraging the UDS protocol as basis. To learn more about these protocols, see our intro to UDS.
21. Benefits of Using Information and Services from OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN
How can OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN help me with my automotive diagnostic needs?
OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN offers a wealth of resources and services to help you with your automotive diagnostic needs.
- Comprehensive OBD2 DTC Database: Access a comprehensive database of OBD2 DTCs, with detailed explanations and troubleshooting tips.
- Expert Technical Support: Receive expert technical support from experienced automotive technicians.
- Training Resources: Access training resources, including articles, tutorials, and videos, to enhance your diagnostic skills.
- OBD2 Scanner Reviews: Read reviews of the latest OBD2 scanners and diagnostic tools.
- OBD2 Diagnostic Cable Recommendations: Get personalized recommendations for OBD2 diagnostic cables based on your specific needs.
22. Call to Action: Get Expert Advice from OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN
Are you facing challenges in diagnosing your vehicle’s problems? Do you want to improve your automotive diagnostic skills? Contact OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN today for expert advice and support. Our team of experienced automotive technicians can help you:
- Understand how to use an OBD2 scanner effectively.
- Identify the root cause of your vehicle’s problems.
- Find efficient and cost-effective repair solutions.
- Enhance your knowledge and skills in automotive diagnostics and repair.
Don’t let vehicle problems slow you down. Reach out to OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN for personalized assistance and unlock the power of OBD2 diagnostics.
Contact Information:
- Address: 123 Main Street, Los Angeles, CA 90001, United States
- WhatsApp: +1 (641) 206-8880
- Website: OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN
23. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) About OBD2 Diagnostic Cables
Here are some frequently asked questions about OBD2 diagnostic cables:
-
What is an OBD2 scanner?
An OBD2 scanner is a device used to read diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) from a vehicle’s computer system.
-
How do I read OBD2 codes?
Connect an OBD2 scanner to the vehicle’s OBD2 port and follow the scanner’s instructions to retrieve the DTCs.
-
What are common car problems and how can they be fixed?
Common car problems include misfires, lean conditions, and catalytic converter failures. These problems can be fixed by addressing the underlying causes, such as faulty spark plugs, vacuum leaks, or oxygen sensor issues.
-
How do I choose the right OBD2 cable?
Choose an OBD2 cable that is compatible with your vehicle’s make, model, and year, as well as your OBD2 scanner or diagnostic tool.
-
What is the difference between OBD1 and OBD2?
OBD1 is an older, non-standardized diagnostic system, while OBD2 is a standardized system used in virtually all cars and light trucks sold in the United States since 1996.
-
Can I use an OBD2 scanner on any car?
You can use an OBD2 scanner on any car that is OBD2-compliant, which includes most cars and light trucks sold in the United States since 1996.
-
How do I clear OBD2 codes?
After addressing the underlying issue, you can use an OBD2 scanner to clear the DTCs.
-
What does the check engine light mean?
The check engine light indicates that the vehicle’s computer system has detected a problem.
-
Is it safe to drive with the check engine light on?
It depends on the nature of the problem. If the check engine light is flashing, it indicates a serious problem that requires immediate attention. If the light is on but not flashing, you can usually drive the vehicle to a repair shop, but it’s best to get it checked as soon as possible.
-
Where can I find more information about OBD2 diagnostics?
You can find more information about OBD2 diagnostics on websites like OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN, which offers a wealth of resources and services to help you with your automotive diagnostic needs.
By leveraging the power of OBD2 diagnostic cables and scanners, and by taking advantage of the resources and expertise available at OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN, you can ensure that your vehicle remains in top condition and avoid costly repairs. Remember, accurate diagnostics are the first step toward effective and efficient automotive maintenance.