Does an OBD2 scanner detect ABS (Anti-lock Braking System) issues? Yes, a capable OBD2 scanner can detect ABS problems by reading diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) related to the ABS. At OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN, we empower you with the knowledge and tools to understand and address these issues effectively, ensuring your vehicle’s safety systems are functioning optimally. This comprehensive guide will explore how OBD2 scanners work with ABS, common issues, and how to use this technology to keep your vehicle in top condition, all while highlighting the advantages of using OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN for your diagnostic and repair needs.
Contents
- 1. Understanding the OBD2 System and ABS
- 1.1 What is the OBD2 System?
- 1.2 What is the Anti-lock Braking System (ABS)?
- 1.3 How OBD2 Scanners Interact with ABS
- 2. Can an OBD2 Scanner Detect ABS Problems?
- 2.1 Types of OBD2 Scanners and ABS Compatibility
- 2.2 Identifying ABS Codes
- 2.3 Case Study: Research on ABS Diagnostics
- 3. Common ABS Problems Detectable by OBD2 Scanners
- 3.1 Wheel Speed Sensor Issues
- 3.2 ABS Module Failure
- 3.3 Hydraulic Issues
- 3.4 Brake Booster Problems
- 3.5 Practical Example of Using an OBD2 Scanner for ABS
- 4. Step-by-Step Guide: Using an OBD2 Scanner to Diagnose ABS Issues
- 4.1 Step 1: Prepare for the Scan
- 4.2 Step 2: Connect the OBD2 Scanner
- 4.3 Step 3: Read ABS Codes
- 4.4 Step 4: Interpret the Codes
- 4.5 Step 5: Perform Further Diagnostics
- 4.6 Step 6: Repair the Issue
- 5. Benefits of Using OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN for ABS Diagnostics
- 5.1 Comprehensive Code Database
- 5.2 Expert Guides and Tutorials
- 5.3 Product Recommendations
- 5.4 Community Support
- 5.5 RepairSolutions2 App Integration
- 6. Advanced Diagnostic Techniques for ABS
- 6.1 Using a Digital Multimeter
- 6.2 Oscilloscope Analysis
- 6.3 Hydraulic Pressure Testing
- 6.4 Data Logging and Analysis
- 7. Maintaining Your ABS for Optimal Performance
- 7.1 Regular Brake Inspections
- 7.2 Brake Fluid Maintenance
- 7.3 Wheel Speed Sensor Cleaning
- 7.4 ABS Module Protection
- 8. Troubleshooting Common ABS Light Issues
- 8.1 ABS Light On After Brake Replacement
- 8.2 ABS Light On After Battery Replacement
- 8.3 ABS Light On Intermittently
- 8.4 Expert Tip: Addressing Common ABS Light Issues
- 9. The Future of ABS Diagnostics
- 9.1 Artificial Intelligence (AI) in Diagnostics
- 9.2 Remote Diagnostics
- 9.3 Enhanced Sensor Technology
- 9.4 OBD3 and Beyond
- 10. Why Choose OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN?
- 10.1 Unmatched Expertise
- 10.2 Comprehensive Resources
- 10.3 Community Support
- 10.4 Cutting-Edge Technology
- 10.5 Dedication to Customer Satisfaction
- FAQ: Does OBD2 Scanner Detect ABS Problems?
- 1. What is an OBD2 scanner?
- 2. Can all OBD2 scanners detect ABS problems?
- 3. How do I know if my OBD2 scanner can read ABS codes?
- 4. What is an ABS code?
- 5. What are some common ABS codes?
- 6. Can I fix ABS problems myself using an OBD2 scanner?
- 7. What should I do if my OBD2 scanner shows an ABS code?
- 8. How often should I scan my car for ABS problems?
- 9. Are there any risks to using an OBD2 scanner for ABS diagnostics?
- 10. Where can I find more information about ABS diagnostics and OBD2 scanners?
- Take Action Now
1. Understanding the OBD2 System and ABS
The On-Board Diagnostics II (OBD2) system is a standardized system used in vehicles to monitor and control various functions, including the engine, transmission, and emissions systems. The ABS is a critical safety system designed to prevent the wheels from locking up during braking, allowing the driver to maintain steering control. Understanding how these two systems interact is crucial for effective vehicle maintenance.
1.1 What is the OBD2 System?
The OBD2 system was mandated in the United States for all cars manufactured after 1996. Its primary functions include:
- Monitoring Vehicle Performance: Continuously checks the performance of the engine and other systems.
- Detecting Malfunctions: Identifies issues that could affect performance or emissions.
- Storing Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs): Records specific codes that indicate the nature of the problem.
1.2 What is the Anti-lock Braking System (ABS)?
The ABS is designed to prevent wheel lockup during braking, which can cause skidding and loss of control. ABS achieves this by:
- Monitoring Wheel Speed: Sensors at each wheel monitor its rotational speed.
- Modulating Brake Pressure: If a wheel is about to lock up, the system reduces brake pressure to that wheel.
- Maintaining Steering Control: By preventing lockup, the driver can steer during braking.
According to the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA), vehicles equipped with ABS have a 35% lower risk of being involved in a crash.
1.3 How OBD2 Scanners Interact with ABS
OBD2 scanners can communicate with the ABS module to retrieve diagnostic information. This interaction involves:
- Reading ABS Codes: The scanner retrieves DTCs stored in the ABS module.
- Live Data Streaming: Some advanced scanners can display real-time data from the ABS sensors.
- Actuation Tests: Certain scanners can perform tests on ABS components to verify their functionality.
2. Can an OBD2 Scanner Detect ABS Problems?
Yes, an OBD2 scanner can detect ABS problems, but the extent of its capabilities depends on the scanner’s features. Not all OBD2 scanners are created equal; some basic models only read engine-related codes, while more advanced scanners can access other modules like ABS, SRS (airbag system), and transmission.
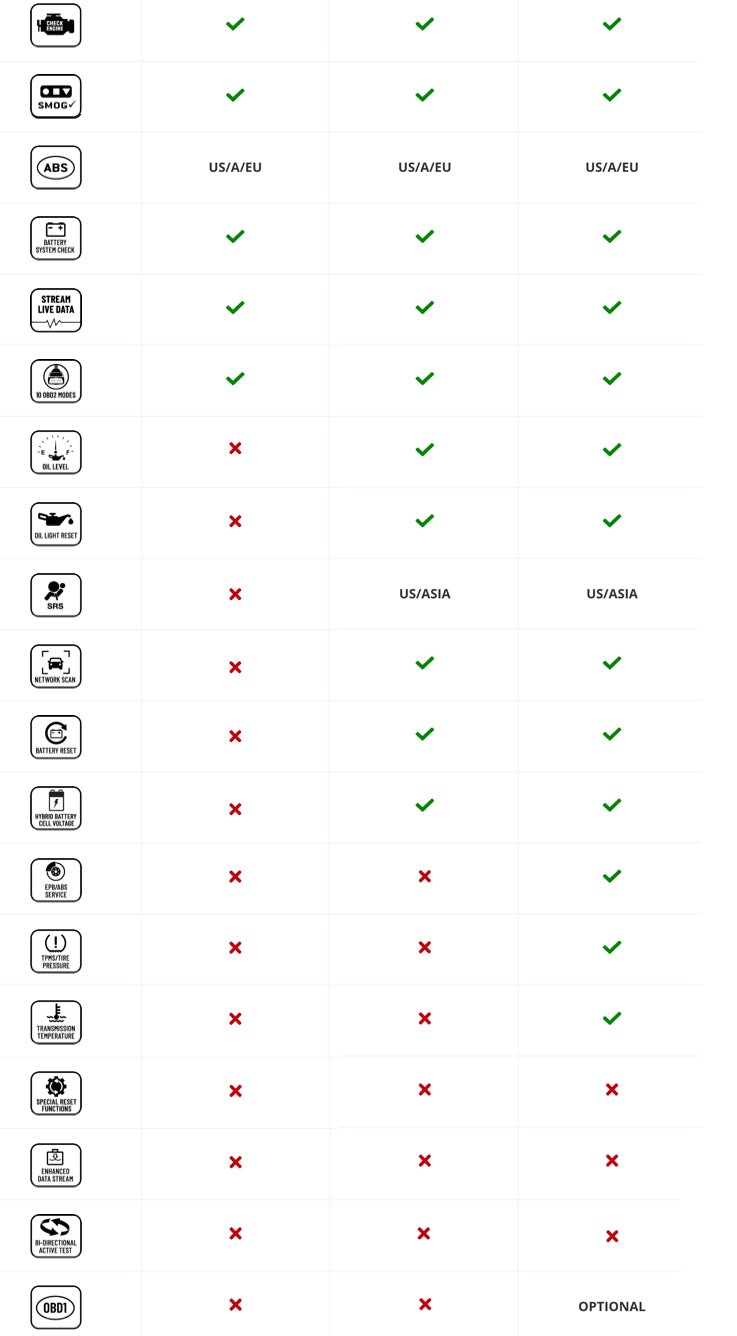
2.1 Types of OBD2 Scanners and ABS Compatibility
- Basic OBD2 Scanners: These typically only read engine codes (P-codes) and are not capable of accessing the ABS module.
- Enhanced OBD2 Scanners: These can read ABS codes (C-codes) and may offer additional features like live data and actuation tests.
- Professional-Grade Scanners: These offer the most comprehensive coverage, including ABS, SRS, transmission, and other systems, with advanced diagnostic capabilities.
2.2 Identifying ABS Codes
ABS codes, also known as C-codes (Chassis codes), indicate problems within the ABS. These codes are crucial for diagnosing and repairing ABS issues. Common ABS codes include:
| Code | Description | Possible Causes |
|---|---|---|
| C0031 | Right Front Wheel Speed Sensor Circuit Malfunction | Faulty wheel speed sensor, wiring issues, ABS module failure |
| C0034 | Right Rear Wheel Speed Sensor Circuit Malfunction | Faulty wheel speed sensor, wiring issues, ABS module failure |
| C0110 | ABS Pump Motor Control Circuit Malfunction | Faulty ABS pump motor, wiring issues, ABS module failure |
| C0265 | ABS Control Motor Relay Circuit Open or Shorted | Faulty relay, wiring issues, ABS module failure |
| C1210 | ABS Control Active | Normal operation during ABS activation |
| C1214 | System Relay Contact Circuit Open or Shorted | Faulty relay, wiring issues, ABS module failure |
| C1235 | Rear Wheel Speed Difference Excessive | Mismatched tire sizes, faulty wheel speed sensors, ABS module failure |
| C1241 | Low or High Battery Voltage | Weak battery, alternator issues, wiring problems |
| C1286 | Steering Sensor Signal Fault | Faulty steering angle sensor, wiring issues, ABS module failure |
| C1287 | Steering Assist Solenoid Valve Fault | Faulty solenoid valve, wiring issues, ABS module failure |
2.3 Case Study: Research on ABS Diagnostics
According to a study by the Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE), effective ABS diagnostics require scanners that can access and interpret ABS-specific DTCs. The study emphasized that using generic OBD2 scanners for ABS issues often leads to misdiagnosis and unnecessary repairs.
3. Common ABS Problems Detectable by OBD2 Scanners
Several common ABS problems can be detected using an OBD2 scanner capable of reading ABS codes. These issues can range from sensor malfunctions to hydraulic problems within the ABS unit.
3.1 Wheel Speed Sensor Issues
Wheel speed sensors are critical for the ABS to function correctly. These sensors monitor the speed of each wheel and send this information to the ABS module. Problems with these sensors include:
- Faulty Sensors: Sensors can fail due to physical damage or wear.
- Wiring Problems: Damaged or corroded wiring can disrupt the signal.
- Contamination: Debris or dirt can interfere with the sensor’s operation.
3.2 ABS Module Failure
The ABS module is the computer that controls the ABS. It can fail due to:
- Electrical Problems: Surges or shorts can damage the module.
- Internal Component Failure: Components within the module can wear out or fail.
- Corrosion: Moisture can cause corrosion and damage the module.
3.3 Hydraulic Issues
The ABS relies on hydraulic components to modulate brake pressure. Common problems include:
- Faulty Pump Motor: The pump motor can fail, preventing the system from building pressure.
- Stuck Valves: Valves can become stuck, preventing proper pressure modulation.
- Leaks: Leaks in the hydraulic lines can reduce system pressure.
3.4 Brake Booster Problems
The brake booster provides assistance to the driver when applying the brakes. Issues can include:
- Vacuum Leaks: Leaks in the vacuum lines can reduce booster effectiveness.
- Diaphragm Failure: The diaphragm inside the booster can fail, reducing or eliminating boost.
3.5 Practical Example of Using an OBD2 Scanner for ABS
Consider a scenario where the ABS light comes on in a vehicle. Using an enhanced OBD2 scanner, a technician retrieves the code C0031, indicating a problem with the right front wheel speed sensor. Further inspection reveals a damaged sensor and corroded wiring. Replacing the sensor and repairing the wiring resolves the issue, and the ABS light turns off.
4. Step-by-Step Guide: Using an OBD2 Scanner to Diagnose ABS Issues
Diagnosing ABS issues with an OBD2 scanner involves a systematic approach to identify the problem accurately. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
4.1 Step 1: Prepare for the Scan
- Gather Information: Collect information about the vehicle, including make, model, and year.
- Locate the OBD2 Port: Typically found under the dashboard on the driver’s side.
- Turn Off the Ignition: Ensure the ignition is off before connecting the scanner.
4.2 Step 2: Connect the OBD2 Scanner
- Plug in the Scanner: Connect the scanner to the OBD2 port.
- Turn on the Ignition: Turn the ignition to the “ON” position without starting the engine.
- Power On the Scanner: The scanner should power on automatically or require you to press a power button.
4.3 Step 3: Read ABS Codes
- Navigate to ABS Section: Use the scanner’s menu to navigate to the ABS or Brake section.
- Read Codes: Select the option to read codes. The scanner will display any stored DTCs related to the ABS.
- Record Codes: Write down the codes and their descriptions.
4.4 Step 4: Interpret the Codes
- Consult a Code Database: Use a reliable code database to understand the meaning of each code. OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN offers a comprehensive code database for this purpose.
- Identify Potential Causes: Based on the code descriptions, identify potential causes of the problem.
4.5 Step 5: Perform Further Diagnostics
- Visual Inspection: Check the affected components for physical damage, such as damaged sensors or wiring.
- Live Data Analysis: If your scanner supports it, use live data to monitor sensor readings and identify anomalies.
- Actuation Tests: Perform actuation tests to verify the functionality of ABS components, such as the pump motor and valves.
4.6 Step 6: Repair the Issue
- Replace Faulty Components: Replace any components identified as faulty during the diagnostic process.
- Repair Wiring: Repair any damaged wiring or connectors.
- Test the System: After making repairs, clear the codes and test the system to ensure the problem is resolved.
5. Benefits of Using OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN for ABS Diagnostics
OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN offers numerous benefits for diagnosing and repairing ABS issues, providing valuable resources and support for both novice and experienced technicians.
5.1 Comprehensive Code Database
Our website features an extensive code database that covers a wide range of ABS codes, providing detailed descriptions and potential causes for each code. This resource helps you quickly and accurately interpret DTCs.
5.2 Expert Guides and Tutorials
OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN offers expert guides and tutorials on using OBD2 scanners for ABS diagnostics. These resources provide step-by-step instructions and practical tips for identifying and resolving ABS issues.
5.3 Product Recommendations
We provide recommendations for the best OBD2 scanners for ABS diagnostics, based on your needs and budget. Our product reviews are unbiased and based on thorough testing and analysis.
5.4 Community Support
Our community forum allows you to connect with other technicians and DIY enthusiasts, share your experiences, and ask questions about ABS diagnostics. This collaborative environment fosters learning and problem-solving.
5.5 RepairSolutions2 App Integration
OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN integrates with the RepairSolutions2 app, providing access to repair information, diagrams, and procedures. This integration streamlines the diagnostic and repair process, saving you time and money.
6. Advanced Diagnostic Techniques for ABS
For complex ABS issues, advanced diagnostic techniques may be necessary to pinpoint the root cause. These techniques include:
6.1 Using a Digital Multimeter
A digital multimeter (DMM) can be used to test the electrical components of the ABS, such as wheel speed sensors and wiring.
- Testing Wheel Speed Sensors: Measure the resistance and voltage of the sensors to check for proper operation.
- Checking Wiring Continuity: Use the DMM to check for continuity in the wiring, ensuring there are no breaks or shorts.
6.2 Oscilloscope Analysis
An oscilloscope can be used to analyze the waveforms of the wheel speed sensors, providing a more detailed view of their operation.
- Identifying Signal Irregularities: The oscilloscope can reveal irregularities in the sensor signal that may not be apparent with a DMM.
- Diagnosing Intermittent Problems: The oscilloscope can capture intermittent problems that occur only under certain conditions.
6.3 Hydraulic Pressure Testing
Hydraulic pressure testing involves measuring the pressure in the ABS hydraulic lines to check for proper operation.
- Using a Pressure Gauge: Connect a pressure gauge to the hydraulic lines and measure the pressure under various conditions.
- Identifying Leaks and Blockages: Pressure testing can help identify leaks and blockages in the hydraulic system.
6.4 Data Logging and Analysis
Data logging involves recording the data from the ABS sensors and components over a period of time. This data can then be analyzed to identify patterns and anomalies.
- Using a Data Logger: Connect a data logger to the OBD2 port and record the data while driving.
- Analyzing the Data: Use software to analyze the data and identify any issues.
7. Maintaining Your ABS for Optimal Performance
Proper maintenance is essential for ensuring the ABS functions correctly and prolonging its lifespan. Key maintenance tasks include:
7.1 Regular Brake Inspections
Regularly inspect the brake system, including the brake pads, rotors, and hydraulic lines.
- Checking Brake Pad Thickness: Measure the thickness of the brake pads and replace them if they are worn.
- Inspecting Rotors: Check the rotors for cracks, warpage, and excessive wear.
- Checking Hydraulic Lines: Inspect the hydraulic lines for leaks and damage.
7.2 Brake Fluid Maintenance
Brake fluid absorbs moisture over time, which can reduce its effectiveness and damage the ABS components.
- Flushing the Brake Fluid: Flush the brake fluid every two to three years to remove moisture and contaminants.
- Using the Correct Fluid: Use the brake fluid recommended by the vehicle manufacturer.
7.3 Wheel Speed Sensor Cleaning
Clean the wheel speed sensors regularly to remove debris and dirt that can interfere with their operation.
- Removing the Sensors: Carefully remove the wheel speed sensors from the wheel hubs.
- Cleaning the Sensors: Clean the sensors with a soft brush and mild cleaner.
- Reinstalling the Sensors: Reinstall the sensors, ensuring they are properly seated.
7.4 ABS Module Protection
Protect the ABS module from moisture and physical damage.
- Checking the Module Enclosure: Ensure the module enclosure is intact and free from cracks.
- Applying Protective Coating: Apply a protective coating to the module to prevent corrosion.
8. Troubleshooting Common ABS Light Issues
The ABS light can illuminate for various reasons, ranging from simple issues to complex problems. Here are some common issues and how to troubleshoot them:
8.1 ABS Light On After Brake Replacement
If the ABS light comes on after replacing the brakes, it may be due to:
- Incorrect Installation: Ensure the brake pads and rotors are installed correctly.
- Wheel Speed Sensor Damage: Check the wheel speed sensors for damage during the brake replacement.
- Air in the Brake Lines: Bleed the brake lines to remove any air.
8.2 ABS Light On After Battery Replacement
If the ABS light comes on after replacing the battery, it may be due to:
- Voltage Spike: A voltage spike during the battery replacement can trigger the ABS light.
- Clearing the Codes: Use an OBD2 scanner to clear any stored ABS codes.
- Driving the Vehicle: Drive the vehicle for a short distance to allow the ABS system to recalibrate.
8.3 ABS Light On Intermittently
If the ABS light comes on intermittently, it may be due to:
- Loose Connections: Check the wiring and connections to the ABS components for looseness.
- Faulty Sensors: The sensors may be failing intermittently.
- ABS Module Issues: The ABS module may be experiencing internal problems.
8.4 Expert Tip: Addressing Common ABS Light Issues
According to automotive expert John Daly, “Addressing ABS light issues promptly is crucial for maintaining vehicle safety. Start with a thorough inspection of the wheel speed sensors and wiring, and then use an OBD2 scanner to identify any stored codes. Don’t hesitate to seek professional help if you’re unsure about the diagnosis or repair.”
9. The Future of ABS Diagnostics
The future of ABS diagnostics is evolving rapidly, with advancements in technology and diagnostic tools.
9.1 Artificial Intelligence (AI) in Diagnostics
AI is being integrated into diagnostic tools to improve accuracy and efficiency.
- AI-Powered Code Interpretation: AI can analyze DTCs and provide more accurate diagnoses.
- Predictive Maintenance: AI can predict potential ABS problems based on sensor data.
9.2 Remote Diagnostics
Remote diagnostics allow technicians to diagnose ABS issues remotely.
- Telematics Systems: Telematics systems can transmit vehicle data to a remote diagnostic center.
- Remote Access Tools: Technicians can remotely access the vehicle’s diagnostic system to perform tests and diagnose problems.
9.3 Enhanced Sensor Technology
Enhanced sensor technology is improving the accuracy and reliability of ABS sensors.
- High-Resolution Sensors: High-resolution sensors provide more detailed data about wheel speed and brake pressure.
- Wireless Sensors: Wireless sensors eliminate the need for wiring, reducing the risk of wiring problems.
9.4 OBD3 and Beyond
The next generation of OBD systems, such as OBD3, will offer even more advanced diagnostic capabilities.
- Real-Time Monitoring: OBD3 will provide real-time monitoring of vehicle systems.
- Automatic Reporting: OBD3 will automatically report any detected problems to the vehicle owner and service provider.
10. Why Choose OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN?
Choosing OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN for your ABS diagnostic needs ensures you receive the best possible support and resources.
10.1 Unmatched Expertise
Our team of automotive experts has years of experience in ABS diagnostics and repair. We provide accurate and reliable information to help you diagnose and resolve ABS issues effectively.
10.2 Comprehensive Resources
We offer a wide range of resources, including code databases, expert guides, tutorials, and product recommendations. Our resources are designed to empower you with the knowledge and tools you need to maintain your ABS system.
10.3 Community Support
Our community forum provides a collaborative environment where you can connect with other technicians and DIY enthusiasts, share your experiences, and ask questions about ABS diagnostics.
10.4 Cutting-Edge Technology
We stay up-to-date with the latest advancements in ABS diagnostics and technology. We offer product recommendations for the best OBD2 scanners and diagnostic tools on the market.
10.5 Dedication to Customer Satisfaction
We are committed to providing exceptional customer service. Our goal is to ensure you have a positive experience and find the solutions you need to maintain your ABS system.
FAQ: Does OBD2 Scanner Detect ABS Problems?
1. What is an OBD2 scanner?
An OBD2 scanner is a diagnostic tool used to read diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) from a vehicle’s onboard computer system, helping identify potential issues.
2. Can all OBD2 scanners detect ABS problems?
No, not all OBD2 scanners can detect ABS problems. You need an enhanced OBD2 scanner that specifically supports ABS code reading.
3. How do I know if my OBD2 scanner can read ABS codes?
Check the scanner’s specifications or user manual. It should explicitly state whether it supports ABS diagnostics.
4. What is an ABS code?
An ABS code, also known as a C-code, is a diagnostic trouble code that indicates a problem within the Anti-lock Braking System (ABS).
5. What are some common ABS codes?
Common ABS codes include C0031 (Right Front Wheel Speed Sensor Circuit Malfunction) and C0034 (Right Rear Wheel Speed Sensor Circuit Malfunction).
6. Can I fix ABS problems myself using an OBD2 scanner?
Yes, you can diagnose and sometimes fix ABS problems yourself using an OBD2 scanner, but it depends on the complexity of the issue. Some repairs may require professional assistance.
7. What should I do if my OBD2 scanner shows an ABS code?
Research the code to understand the potential causes, inspect the affected components, and consider seeking professional help if you’re not comfortable performing the repair yourself.
8. How often should I scan my car for ABS problems?
You should scan your car for ABS problems whenever the ABS light comes on or if you notice any issues with your braking system.
9. Are there any risks to using an OBD2 scanner for ABS diagnostics?
Using an OBD2 scanner is generally safe, but incorrect interpretations or repairs can lead to further issues. Always follow the manufacturer’s instructions and seek professional help if needed.
10. Where can I find more information about ABS diagnostics and OBD2 scanners?
You can find more information at OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN, which offers comprehensive guides, tutorials, and product recommendations for ABS diagnostics and OBD2 scanners.
Take Action Now
Ready to take control of your vehicle’s ABS diagnostics? Contact OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN today for expert guidance and support.
- Visit our website: OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN
- Call us: +1 (641) 206-8880
- Visit our location: 123 Main Street, Los Angeles, CA 90001, United States
- Connect via WhatsApp: +1 (641) 206-8880
At OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN, we are dedicated to helping you understand and resolve your vehicle’s ABS issues efficiently and effectively. Contact us today and experience the difference!
 OBD2 Scanner Port Location
OBD2 Scanner Port Location
Alt text: Image showing the typical location of an OBD2 port under the dashboard for easy access during vehicle diagnostics.
Alt text: The Innova 5410 OBD2 Scanner is displayed, an enhanced tool for reading ABS and other diagnostic codes in vehicles.
 OBD2 ABS Tutorial Screen
OBD2 ABS Tutorial Screen
Alt text: A screen capture from an OBD2 scanner demonstrates the ABS diagnostic section, detailing how to read and interpret ABS-related data and codes.
 ABS Scan Tool Tutorial Interface
ABS Scan Tool Tutorial Interface
Alt text: A tutorial interface on an ABS scan tool shows the process of accessing and interpreting ABS diagnostic information for vehicle maintenance.
 RepairSolutions2 App Interface
RepairSolutions2 App Interface
Alt text: Interface of the Innova RepairSolutions2 app presenting detailed ABS repair solutions and estimated costs, aiding in informed vehicle maintenance decisions.
 RepairSolutions2 App Detailed Repair Costs
RepairSolutions2 App Detailed Repair Costs
Alt text: A display from Innova RepairSolutions2 shows detailed repair costs and necessary parts for ABS system issues, supporting accurate budgeting and planning for vehicle repairs.
 Innova App Tutorial Elements
Innova App Tutorial Elements
Alt text: Innova App tutorial elements are showcased, guiding users through the steps to diagnose and address vehicle issues using the app’s features.
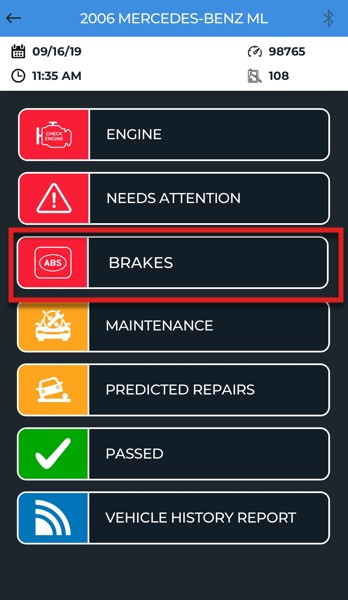
 Needs Attention Report Element
Needs Attention Report Element
Alt text: A view of the ‘Needs Attention’ report element in the Innova app, indicating issues requiring further investigation and research by Innova technicians.
