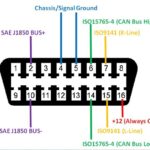
The Dodge Obd2 P0133 code indicates a slow response from the oxygen sensor in Bank 1, Sensor 1, which can affect your vehicle’s fuel efficiency and emissions. At OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN, we provide comprehensive information and services to help you diagnose and resolve this issue, ensuring your Dodge runs smoothly and efficiently. Understanding the root causes, symptoms, and diagnostic procedures can save you time and money while keeping your vehicle environmentally friendly; let’s explore air fuel ratio sensor malfunctions, exhaust system leaks, and PCM software updates.
Contents
- 1. Understanding the Dodge OBD2 P0133 Code
- 1.1. What Does Bank 1 Sensor 1 Mean?
- 1.2. Role of the Oxygen Sensor
- 1.3. How the PCM Detects the P0133 Code
- 2. Common Symptoms of the Dodge P0133 Code
- 3. Potential Causes of the Dodge P0133 Code
- 4. Diagnosing the Dodge P0133 Code: A Step-by-Step Guide
- 4.1. Step 1: Read and Record the Freeze Frame Data
- 4.2. Step 2: Inspect the Oxygen Sensor
- 4.3. Step 3: Test the Oxygen Sensor Heater Circuit
- 4.4. Step 4: Check for Exhaust Leaks
- 4.5. Step 5: Check for Intake Air Leaks
- 4.6. Step 6: Monitor Oxygen Sensor Data
- 4.7. Step 7: Perform a “Wiggle Test”
- 5. Repairing the Dodge P0133 Code: Solutions and Procedures
- 5.1. Replacing the Oxygen Sensor
- 5.2. Repairing Exhaust Leaks
- 5.3. Repairing Intake Air Leaks
- 5.4. Repairing Wiring Issues
- 5.5. Addressing Low Fuel Pressure
- 5.6. Replacing the Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor
- 5.7. Updating the PCM Software
- 6. Using OBD2 Scanner for Dodge P0133 Diagnosis
- 7. Tips to Prevent the Dodge P0133 Code
- 8. Understanding Air Fuel Ratio Sensor
- 8.1. How Air Fuel Ratio Sensors Work
- 8.2. Differences Between Oxygen Sensors and Air Fuel Ratio Sensors
- 8.3. Diagnosing P0133 Code with Air Fuel Ratio Sensors
- 9. The Importance of Regular Vehicle Maintenance
- 9.1. Key Maintenance Tasks
- 9.2. Benefits of Regular Maintenance
- 10. Common Mistakes to Avoid When Diagnosing and Repairing P0133 Code
- 11. Advanced Diagnostic Techniques for P0133 Code
- 11.1. Using a Lab Scope
- 11.2. Performing a Fuel Trim Analysis
- 11.3. Testing the Catalytic Converter
- 12. Dodge Specific Information for P0133 Code
- 12.1. Common Dodge Models Affected
- 12.2. Known Issues Specific to Dodge
- 12.3. Where to Find Dodge Specific Diagnostic Information
- 13. Understanding the Role of Aftermarket Parts
- 13.1. Quality Considerations for Aftermarket Oxygen Sensors
- 13.2. Potential Issues with Aftermarket Parts
- 13.3. OEM vs Aftermarket: Making the Right Choice
- 14. How to Choose the Right OBD2 Scanner for Your Needs
- 15. Benefits of Professional Diagnostic Services
- 15.1. Expertise and Experience
- 15.2. Specialized Equipment
- 15.3. Warranty Protection
- 15.4. Saving Time and Money
- 16. Conclusion: Taking Action on the Dodge P0133 Code
- 17. FAQs About Dodge OBD2 P0133 Code
- 17.1. What does the P0133 code mean on a Dodge?
- 17.2. Can I drive my Dodge with a P0133 code?
- 17.3. How do I fix the P0133 code on my Dodge?
- 17.4. How much does it cost to fix a P0133 code?
- 17.5. What is Bank 1 Sensor 1 on a Dodge?
- 17.6. How often should I replace my oxygen sensors on my Dodge?
- 17.7. Can a bad catalytic converter cause a P0133 code?
- 17.8. What tools do I need to diagnose a P0133 code?
- 17.9. Is it safe to use aftermarket oxygen sensors on my Dodge?
- 17.10. Can I clear the P0133 code myself after making repairs?
1. Understanding the Dodge OBD2 P0133 Code
The Dodge OBD2 P0133 code, specifically related to “Oxygen Sensor Circuit Slow Response (Bank 1, Sensor 1),” signifies that the powertrain control module (PCM) has detected a delayed response from the oxygen sensor. According to a study by the University of California, Berkeley’s Department of Mechanical Engineering, oxygen sensors must rapidly switch between detecting rich and lean conditions to ensure optimal engine performance and emissions control. When this switching time exceeds a specified threshold, the P0133 code is triggered. This delay can lead to increased fuel consumption and higher emissions, impacting both your wallet and the environment.
1.1. What Does Bank 1 Sensor 1 Mean?
Bank 1 refers to the side of the engine containing cylinder number one. Sensor 1 is the oxygen sensor located upstream of the catalytic converter. This sensor plays a crucial role in measuring the oxygen content of the exhaust gases before they enter the catalytic converter. This data is then used by the PCM to adjust the air-fuel mixture for optimal combustion.
1.2. Role of the Oxygen Sensor
The oxygen sensor’s primary function is to measure the amount of oxygen in the exhaust gases. This information is vital for the PCM to maintain an efficient air-fuel ratio. A properly functioning oxygen sensor ensures the engine produces the best possible power while minimizing harmful emissions. According to the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), a faulty oxygen sensor can increase fuel consumption by as much as 40% and significantly raise emissions levels.
1.3. How the PCM Detects the P0133 Code
The PCM monitors the voltage signal from the oxygen sensor. When the sensor fails to switch between lean (low voltage) and rich (high voltage) conditions within a specified time frame, the PCM interprets this as a slow response. The specific voltage thresholds and response times vary depending on the vehicle make and model, but generally, the sensor needs to switch in less than 100 milliseconds.
2. Common Symptoms of the Dodge P0133 Code
Recognizing the symptoms associated with the Dodge P0133 code can help you identify the problem early and prevent further damage. Here are some common symptoms:
- Check Engine Light Illumination: This is the most obvious symptom. The check engine light will turn on to alert you to a problem.
- Rough Idle: The engine may idle roughly or stall, especially when the vehicle is cold.
- Decreased Fuel Economy: You may notice a significant drop in your vehicle’s fuel efficiency.
- Engine Hesitation: The engine may hesitate or lack power during acceleration.
- Black Smoke from Exhaust: In some cases, you may see black smoke coming from the exhaust, indicating a rich fuel mixture.
- Failed Emissions Test: A faulty oxygen sensor can cause your vehicle to fail an emissions test.
3. Potential Causes of the Dodge P0133 Code
Several factors can trigger the Dodge P0133 code. Identifying the root cause is essential for effective repair. Here are some potential causes:
- Defective Oxygen Sensor: The oxygen sensor itself may be faulty due to age, contamination, or physical damage. According to a study by the Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE), oxygen sensors typically have a lifespan of 60,000 to 100,000 miles.
- Exhaust Leaks: Exhaust leaks upstream of the oxygen sensor can dilute the exhaust gases, causing the sensor to read incorrectly.
- Intake Air Leaks: Intake air leaks can also affect the air-fuel mixture, leading to a slow response from the oxygen sensor.
- Wiring Issues: Damaged, corroded, or loose wiring connections to the oxygen sensor can disrupt the signal to the PCM.
- Low Fuel Pressure: Insufficient fuel pressure can cause a lean fuel mixture, affecting the oxygen sensor’s performance.
- Defective Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor: A faulty coolant temperature sensor can provide incorrect information to the PCM, influencing the air-fuel mixture.
- PCM Software Issues: In rare cases, the PCM software may need to be updated to properly interpret the oxygen sensor’s signals.
4. Diagnosing the Dodge P0133 Code: A Step-by-Step Guide
Diagnosing the Dodge P0133 code requires a systematic approach. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you identify the problem:
4.1. Step 1: Read and Record the Freeze Frame Data
Use an OBD2 scanner to read the diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) and record the freeze frame data. The freeze frame data provides a snapshot of the engine conditions when the code was triggered, including engine speed, load, and coolant temperature. This information can be valuable in duplicating the problem during testing.
4.2. Step 2: Inspect the Oxygen Sensor
Visually inspect the oxygen sensor for any signs of damage, such as cracks, corrosion, or contamination. Check the wiring and connectors for loose connections or damage.
4.3. Step 3: Test the Oxygen Sensor Heater Circuit
The oxygen sensor heater circuit helps the sensor reach its operating temperature quickly. Use a multimeter to test the heater circuit for proper voltage and resistance. Refer to your vehicle’s service manual for the correct specifications.
4.4. Step 4: Check for Exhaust Leaks
Inspect the exhaust system for any leaks, especially upstream of the oxygen sensor. You can use a smoke machine to help locate leaks. Exhaust leaks can dilute the exhaust gases and cause the oxygen sensor to read incorrectly.
4.5. Step 5: Check for Intake Air Leaks
Inspect the intake air system for leaks, especially around the intake manifold and vacuum lines. You can use a carburetor cleaner to spray around these areas while the engine is running. If the engine speed changes, it indicates a vacuum leak.
4.6. Step 6: Monitor Oxygen Sensor Data
Use an OBD2 scanner to monitor the oxygen sensor’s voltage signal while the engine is running. The sensor should switch between lean and rich conditions within a specified time frame. A slow or erratic signal indicates a problem with the sensor.
4.7. Step 7: Perform a “Wiggle Test”
While monitoring the oxygen sensor data, perform a “wiggle test” by gently moving the wiring and connectors. If the signal changes, it indicates a wiring or connection problem.
5. Repairing the Dodge P0133 Code: Solutions and Procedures
Once you have diagnosed the cause of the Dodge P0133 code, you can proceed with the necessary repairs. Here are some common solutions:
5.1. Replacing the Oxygen Sensor
If the oxygen sensor is faulty, replacing it is the most common solution. Follow these steps:
- Disconnect the Negative Battery Cable: Disconnecting the negative battery cable prevents electrical shorts during the replacement process.
- Locate the Oxygen Sensor: The oxygen sensor is typically located in the exhaust manifold or exhaust pipe, upstream of the catalytic converter.
- Disconnect the Electrical Connector: Disconnect the electrical connector from the oxygen sensor.
- Remove the Oxygen Sensor: Use an oxygen sensor socket to remove the sensor from the exhaust system.
- Install the New Oxygen Sensor: Apply anti-seize compound to the threads of the new oxygen sensor and install it into the exhaust system.
- Connect the Electrical Connector: Connect the electrical connector to the new oxygen sensor.
- Reconnect the Negative Battery Cable: Reconnect the negative battery cable.
- Clear the DTCs: Use an OBD2 scanner to clear the DTCs and verify that the P0133 code is no longer present.
5.2. Repairing Exhaust Leaks
If you find an exhaust leak, repair it as soon as possible. Small leaks can often be repaired with exhaust sealant or patching material. Larger leaks may require welding or replacing the damaged exhaust components.
5.3. Repairing Intake Air Leaks
Repair any intake air leaks by replacing damaged vacuum lines or gaskets. Ensure that all connections are tight and secure.
5.4. Repairing Wiring Issues
Repair any damaged or corroded wiring connections to the oxygen sensor. Use electrical tape or heat shrink tubing to protect the repaired wires.
5.5. Addressing Low Fuel Pressure
If low fuel pressure is the cause, you may need to replace the fuel filter, fuel pump, or fuel pressure regulator. Consult a qualified mechanic for assistance.
5.6. Replacing the Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor
If the engine coolant temperature sensor is faulty, replace it with a new one. Refer to your vehicle’s service manual for the correct replacement procedure.
5.7. Updating the PCM Software
In rare cases, the PCM software may need to be updated to properly interpret the oxygen sensor’s signals. This can typically be done by a qualified mechanic using specialized diagnostic equipment.
6. Using OBD2 Scanner for Dodge P0133 Diagnosis
An OBD2 scanner is an indispensable tool for diagnosing and resolving the Dodge P0133 code. Here are some ways you can use an OBD2 scanner effectively:
- Reading DTCs: The primary function of an OBD2 scanner is to read diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs). This allows you to identify the specific problem triggering the check engine light.
- Clearing DTCs: After making repairs, you can use the OBD2 scanner to clear the DTCs and reset the check engine light.
- Monitoring Live Data: OBD2 scanners can monitor live data from various sensors, including the oxygen sensor. This allows you to observe the sensor’s performance in real-time and identify any anomalies.
- Performing Component Tests: Some advanced OBD2 scanners can perform component tests, such as testing the oxygen sensor heater circuit.
- Accessing Freeze Frame Data: As mentioned earlier, the freeze frame data provides valuable information about the engine conditions when the code was triggered.
7. Tips to Prevent the Dodge P0133 Code
While some causes of the Dodge P0133 code are unavoidable, there are steps you can take to prevent the code from occurring:
- Regular Maintenance: Follow your vehicle’s recommended maintenance schedule, including replacing the oxygen sensor at the recommended intervals.
- Use Quality Fuel: Using high-quality fuel can help prevent contamination of the oxygen sensor.
- Address Exhaust Leaks Promptly: Repair any exhaust leaks as soon as possible to prevent them from affecting the oxygen sensor’s performance.
- Avoid Short Trips: Short trips can prevent the engine from reaching its optimal operating temperature, which can affect the oxygen sensor’s performance.
- Regularly Inspect Wiring: Regularly inspect the wiring and connectors to the oxygen sensor for any signs of damage or corrosion.
8. Understanding Air Fuel Ratio Sensor
In modern vehicles, the air fuel ratio (AFR) sensor has replaced the traditional oxygen sensor in many applications. According to a study by Bosch, AFR sensors provide more precise and rapid measurements of the air-fuel mixture, resulting in improved engine performance and reduced emissions.
8.1. How Air Fuel Ratio Sensors Work
AFR sensors use a more sophisticated technology to measure the air-fuel mixture. They can detect a wider range of air-fuel ratios and respond more quickly to changes in engine conditions. This allows the PCM to make more precise adjustments to the fuel delivery, resulting in improved fuel efficiency and reduced emissions.
8.2. Differences Between Oxygen Sensors and Air Fuel Ratio Sensors
While both oxygen sensors and AFR sensors measure the oxygen content in the exhaust gases, there are some key differences:
- Measurement Range: AFR sensors can measure a wider range of air-fuel ratios than traditional oxygen sensors.
- Response Time: AFR sensors respond more quickly to changes in engine conditions.
- Complexity: AFR sensors are more complex than traditional oxygen sensors and require more sophisticated diagnostic equipment.
8.3. Diagnosing P0133 Code with Air Fuel Ratio Sensors
When diagnosing the P0133 code on a vehicle equipped with an AFR sensor, it’s essential to use a scan tool that is capable of reading and interpreting the AFR sensor data. The diagnostic procedures are similar to those used for traditional oxygen sensors, but the specific voltage and current values may be different.
9. The Importance of Regular Vehicle Maintenance
Regular vehicle maintenance is crucial for preventing a wide range of problems, including the Dodge P0133 code. By following your vehicle’s recommended maintenance schedule, you can ensure that all components are functioning properly and prevent minor issues from turning into major problems.
9.1. Key Maintenance Tasks
Here are some key maintenance tasks that can help prevent the Dodge P0133 code:
- Replacing the Oxygen Sensor: Replace the oxygen sensor at the recommended intervals to ensure optimal performance.
- Checking for Exhaust Leaks: Regularly check the exhaust system for leaks and repair them promptly.
- Inspecting Wiring: Inspect the wiring and connectors to the oxygen sensor for any signs of damage or corrosion.
- Using Quality Fuel: Use high-quality fuel to prevent contamination of the oxygen sensor.
- Maintaining Proper Fuel Pressure: Ensure that the fuel system is functioning properly and maintaining proper fuel pressure.
9.2. Benefits of Regular Maintenance
Regular vehicle maintenance offers numerous benefits, including:
- Improved Fuel Economy: Properly maintained vehicles typically achieve better fuel economy.
- Reduced Emissions: Regular maintenance can help reduce harmful emissions.
- Increased Reliability: Well-maintained vehicles are more reliable and less likely to break down.
- Extended Lifespan: Regular maintenance can extend the lifespan of your vehicle.
- Higher Resale Value: Vehicles with a good maintenance history typically have a higher resale value.
10. Common Mistakes to Avoid When Diagnosing and Repairing P0133 Code
Diagnosing and repairing the Dodge P0133 code can be challenging, and it’s easy to make mistakes. Here are some common mistakes to avoid:
- Assuming the Oxygen Sensor is Always the Problem: While a faulty oxygen sensor is a common cause of the P0133 code, it’s essential to perform a thorough diagnosis to identify the root cause.
- Not Checking for Exhaust Leaks: Exhaust leaks can significantly affect the oxygen sensor’s performance, so it’s crucial to check for leaks before replacing the sensor.
- Ignoring Wiring Issues: Damaged or corroded wiring can disrupt the signal to the PCM, so it’s essential to inspect the wiring and connectors.
- Using Incorrect Diagnostic Procedures: Using the wrong diagnostic procedures can lead to inaccurate results and wasted time.
- Failing to Clear the DTCs: After making repairs, it’s essential to clear the DTCs and verify that the P0133 code is no longer present.
11. Advanced Diagnostic Techniques for P0133 Code
For complex cases of the P0133 code, advanced diagnostic techniques may be necessary. These techniques require specialized equipment and expertise.
11.1. Using a Lab Scope
A lab scope can be used to analyze the oxygen sensor’s voltage signal in detail. This can help identify subtle issues that may not be apparent with a standard OBD2 scanner.
11.2. Performing a Fuel Trim Analysis
Fuel trim analysis involves monitoring the short-term and long-term fuel trim values to identify any issues with the air-fuel mixture. This can help pinpoint problems such as vacuum leaks, fuel injector issues, or a faulty mass airflow sensor.
11.3. Testing the Catalytic Converter
In some cases, a faulty catalytic converter can cause the P0133 code. Testing the catalytic converter involves measuring the temperature and pressure before and after the converter to determine if it is functioning properly.
12. Dodge Specific Information for P0133 Code
While the general diagnostic and repair procedures for the P0133 code apply to most vehicles, there may be some Dodge-specific considerations.
12.1. Common Dodge Models Affected
The P0133 code is commonly seen in various Dodge models, including:
- Dodge Charger
- Dodge Challenger
- Dodge Grand Caravan
- Dodge Durango
- Dodge Ram
12.2. Known Issues Specific to Dodge
Some Dodge models have known issues that can contribute to the P0133 code, such as:
- Faulty oxygen sensor connectors
- Exhaust manifold leaks
- PCM software issues
12.3. Where to Find Dodge Specific Diagnostic Information
Dodge-specific diagnostic information can be found in the vehicle’s service manual, online forums, and technical service bulletins (TSBs).
13. Understanding the Role of Aftermarket Parts
When repairing the P0133 code, it’s essential to consider the role of aftermarket parts. While aftermarket parts can be a cost-effective alternative to OEM parts, they may not always meet the same quality standards.
13.1. Quality Considerations for Aftermarket Oxygen Sensors
When replacing the oxygen sensor, it’s essential to choose a high-quality aftermarket part from a reputable manufacturer. Lower-quality aftermarket oxygen sensors may not provide accurate readings or last as long as OEM parts.
13.2. Potential Issues with Aftermarket Parts
Potential issues with aftermarket parts include:
- Inaccurate readings
- Premature failure
- Compatibility issues
13.3. OEM vs Aftermarket: Making the Right Choice
When choosing between OEM and aftermarket parts, it’s essential to weigh the cost savings against the potential risks. In some cases, it may be worth paying extra for an OEM part to ensure quality and reliability.
14. How to Choose the Right OBD2 Scanner for Your Needs
Choosing the right OBD2 scanner can make diagnosing and repairing the P0133 code much easier. Here are some factors to consider when choosing an OBD2 scanner:
- Compatibility: Make sure the scanner is compatible with your vehicle’s make and model.
- Features: Consider the features you need, such as live data monitoring, component testing, and freeze frame data access.
- Ease of Use: Choose a scanner that is easy to use and has a clear and intuitive interface.
- Price: OBD2 scanners range in price from affordable to high-end. Choose a scanner that fits your budget and meets your needs.
- Reviews: Read reviews from other users to get an idea of the scanner’s performance and reliability.
15. Benefits of Professional Diagnostic Services
While it’s possible to diagnose and repair the P0133 code yourself, there are many benefits to using professional diagnostic services.
15.1. Expertise and Experience
Professional technicians have the expertise and experience to accurately diagnose and repair complex issues like the P0133 code.
15.2. Specialized Equipment
Professional repair shops have access to specialized equipment, such as lab scopes and smoke machines, which can help them diagnose problems more accurately.
15.3. Warranty Protection
Many professional repair shops offer warranty protection on their work, which can provide peace of mind.
15.4. Saving Time and Money
While it may seem more expensive to use professional diagnostic services, it can actually save you time and money in the long run by ensuring that the problem is diagnosed and repaired correctly the first time.
16. Conclusion: Taking Action on the Dodge P0133 Code
The Dodge P0133 code indicates a slow response from the oxygen sensor in Bank 1, Sensor 1, which can affect your vehicle’s fuel efficiency and emissions. By understanding the causes, symptoms, diagnostic procedures, and repair options, you can take action to resolve the issue and keep your Dodge running smoothly and efficiently. Remember to consider the role of aftermarket parts, choose the right OBD2 scanner, and weigh the benefits of professional diagnostic services.
At OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN, we are committed to providing you with the information and resources you need to diagnose and repair your vehicle. If you have any questions or need assistance, please don’t hesitate to contact us.
Experiencing the frustration of a P0133 code on your Dodge? Don’t let a slow-responding oxygen sensor compromise your vehicle’s performance and fuel efficiency. Contact OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN today for expert guidance and reliable solutions. Our team of experienced technicians can help you diagnose the root cause of the problem and recommend the most effective repair options. Reach out to us via Whatsapp at +1 (641) 206-8880 or visit our website at OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN for more information. Let us help you get your Dodge back on the road with optimal performance and reduced emissions. Our address is 123 Main Street, Los Angeles, CA 90001, United States.
17. FAQs About Dodge OBD2 P0133 Code
17.1. What does the P0133 code mean on a Dodge?
The P0133 code on a Dodge indicates that the oxygen sensor in Bank 1, Sensor 1 is responding slowly to changes in the exhaust gas composition. This can affect fuel efficiency and emissions.
17.2. Can I drive my Dodge with a P0133 code?
While you can technically drive with a P0133 code, it’s not recommended. The code can cause reduced fuel efficiency, poor engine performance, and potential damage to the catalytic converter.
17.3. How do I fix the P0133 code on my Dodge?
To fix the P0133 code, you’ll need to diagnose the root cause of the problem. Common solutions include replacing the oxygen sensor, repairing exhaust leaks, and addressing wiring issues.
17.4. How much does it cost to fix a P0133 code?
The cost to fix a P0133 code can vary depending on the cause of the problem and the repair shop you choose. Replacing the oxygen sensor typically costs between $150 and $300, while more complex repairs can cost more.
17.5. What is Bank 1 Sensor 1 on a Dodge?
Bank 1 refers to the side of the engine containing cylinder number one. Sensor 1 is the oxygen sensor located upstream of the catalytic converter on that side of the engine.
17.6. How often should I replace my oxygen sensors on my Dodge?
Oxygen sensors typically have a lifespan of 60,000 to 100,000 miles. Refer to your vehicle’s service manual for the recommended replacement interval.
17.7. Can a bad catalytic converter cause a P0133 code?
Yes, a bad catalytic converter can sometimes cause a P0133 code. If the catalytic converter is not functioning properly, it can affect the oxygen sensor’s readings.
17.8. What tools do I need to diagnose a P0133 code?
To diagnose a P0133 code, you’ll need an OBD2 scanner, a multimeter, and potentially a smoke machine or lab scope.
17.9. Is it safe to use aftermarket oxygen sensors on my Dodge?
While aftermarket oxygen sensors can be a cost-effective alternative to OEM parts, it’s essential to choose a high-quality part from a reputable manufacturer to ensure proper performance and reliability.
17.10. Can I clear the P0133 code myself after making repairs?
Yes, you can use an OBD2 scanner to clear the P0133 code after making repairs. However, it’s essential to verify that the code does not return, as this indicates that the underlying problem has not been resolved.