The D16Y8 OBD2 crankshaft positioning sensor is a critical component for engine timing and performance. This guide, brought to you by OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN, will cover everything you need to know about the D16Y8 crank sensor, including its function, symptoms of failure, and how to diagnose and replace it. You’ll also discover how OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN can help you troubleshoot and resolve your automotive issues efficiently.
Contents
- 1. What is a D16Y8 OBD2 Crankshaft Positioning Sensor?
- 1.1. Role of the Crankshaft Positioning Sensor
- 1.2. Types of Crankshaft Positioning Sensors
- 1.3. D16Y8 Engine and OBD2 System
- 2. Common Symptoms of a Failing D16Y8 Crankshaft Positioning Sensor
- 2.1. Diagnosing Sensor Failure
- 2.2. Common OBD2 Error Codes Related to the Crankshaft Positioning Sensor
- 3. Step-by-Step Guide to Replacing the D16Y8 Crankshaft Positioning Sensor
- 3.1. Tools and Materials Needed
- 3.2. Safety Precautions
- 3.3. Step-by-Step Replacement Process
- 3.4. Post-Replacement Checks
- 4. The Importance of Using an OBD2 Scanner
- 4.1. Accurate Diagnostics
- 4.2. Real-Time Data Monitoring
- 4.3. Cost Savings
- 4.4. User-Friendly Interface
- 4.5. Wide Compatibility
- 4.6. Enhanced Vehicle Maintenance
- 5. Maintaining Your D16Y8 Engine
- 5.1. Regular Oil Changes
- 5.2. Air Filter Replacement
- 5.3. Spark Plug Replacement
- 5.4. Timing Belt Replacement
- 5.5. Coolant Flush
- 5.6. Fluid Checks
- 5.7. Visual Inspections
- 5.8. OBD2 Scanning
- 6. Troubleshooting Other Common D16Y8 Issues
- 6.1. Misfires
- 6.2. Idle Air Control (IAC) Valve Problems
- 6.3. Oxygen Sensor Issues
- 6.4. Catalytic Converter Failure
- 6.5. Fuel Pump Problems
- 7. Benefits of Choosing OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN
- 7.1. Wide Range of OBD2 Scanners
- 7.2. Expert Advice and Support
- 7.3. High-Quality Products
- 7.4. Competitive Pricing
- 7.5. Comprehensive Automotive Solutions
- 7.6. Commitment to Customer Satisfaction
- 8. FAQ About D16Y8 OBD2 and Crankshaft Positioning Sensors
- 9. Call to Action
1. What is a D16Y8 OBD2 Crankshaft Positioning Sensor?
A D16Y8 OBD2 crankshaft positioning sensor is an electronic device used in Honda Civic models with the D16Y8 engine to monitor the position and rotational speed of the crankshaft. This information is crucial for the engine control unit (ECU) to manage ignition timing and fuel injection accurately, optimizing engine performance and efficiency.
The crankshaft position sensor (CKP sensor) is a vital part of your car’s engine management system. Its primary function is to provide the engine control unit (ECU) with information about the crankshaft’s position and speed. This data allows the ECU to precisely control ignition timing and fuel injection, ensuring optimal engine performance. In OBD2 systems, the CKP sensor’s role is further enhanced with diagnostic capabilities, enabling early detection of engine issues.
1.1. Role of the Crankshaft Positioning Sensor
The crankshaft position sensor plays a vital role in several key engine functions:
- Ignition Timing: The ECU uses the CKP sensor’s data to determine when to fire the spark plugs. Accurate timing is essential for efficient combustion and power delivery.
- Fuel Injection: By knowing the crankshaft’s position, the ECU can precisely time fuel injection, ensuring the correct amount of fuel is delivered at the right moment.
- Engine Speed (RPM): The CKP sensor provides real-time data on the engine’s rotational speed, which is crucial for various control functions, including idle control and rev limiting.
- Diagnostic Functions: The OBD2 system monitors the CKP sensor’s performance. If the sensor fails or provides inaccurate data, it triggers a diagnostic trouble code (DTC), alerting the driver to a potential problem.
1.2. Types of Crankshaft Positioning Sensors
There are two main types of crankshaft positioning sensors:
- Magnetic Induction (Variable Reluctance): These sensors generate an AC voltage signal as a toothed wheel on the crankshaft passes by the sensor. The ECU interprets this signal to determine the crankshaft’s position and speed.
- Hall Effect: Hall effect sensors use a magnetic field and a semiconductor to produce a digital signal. They are generally more accurate and reliable than magnetic induction sensors, especially at low speeds.
1.3. D16Y8 Engine and OBD2 System
The D16Y8 engine is a 1.6-liter, single overhead cam (SOHC), VTEC engine commonly found in 1996-2000 Honda Civics. It is an OBD2-compliant engine, meaning it includes an onboard diagnostic system to monitor various engine parameters, including the crankshaft position sensor.
The OBD2 system enhances the diagnostic capabilities of the CKP sensor. When the sensor malfunctions or provides inaccurate readings, the OBD2 system generates a diagnostic trouble code (DTC) that can be read using an OBD2 scanner. This allows technicians and car owners to quickly identify and address issues related to the CKP sensor.
2. Common Symptoms of a Failing D16Y8 Crankshaft Positioning Sensor
Recognizing the symptoms of a failing D16Y8 crankshaft positioning sensor is crucial for timely diagnosis and repair. Here are some common signs to watch out for:
- Engine Stalling: A failing CKP sensor can cause the engine to stall intermittently, especially when it gets hot.
- Hard Starting or No Start: The engine may crank but fail to start if the CKP sensor is not providing accurate data to the ECU.
- Check Engine Light: The check engine light will often illuminate, indicating a problem with the engine management system. An OBD2 scanner can retrieve the specific diagnostic trouble code (DTC).
- Rough Idling: The engine may idle roughly or erratically due to incorrect ignition timing or fuel injection.
- Reduced Fuel Efficiency: Inaccurate data from the CKP sensor can lead to inefficient combustion, resulting in decreased fuel economy.
- Misfires: The engine may experience misfires, leading to a loss of power and rough running.
- Hesitation During Acceleration: The engine may hesitate or stumble when accelerating.
- Engine Surging: Unstable signals from the CKP sensor can cause the engine to speed up or slow down erratically.
Understanding these symptoms can help you identify a potential issue with your D16Y8 crankshaft positioning sensor early on, preventing further damage and ensuring your vehicle remains reliable. If you experience any of these symptoms, consider using an OBD2 scanner from OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN to diagnose the problem accurately.
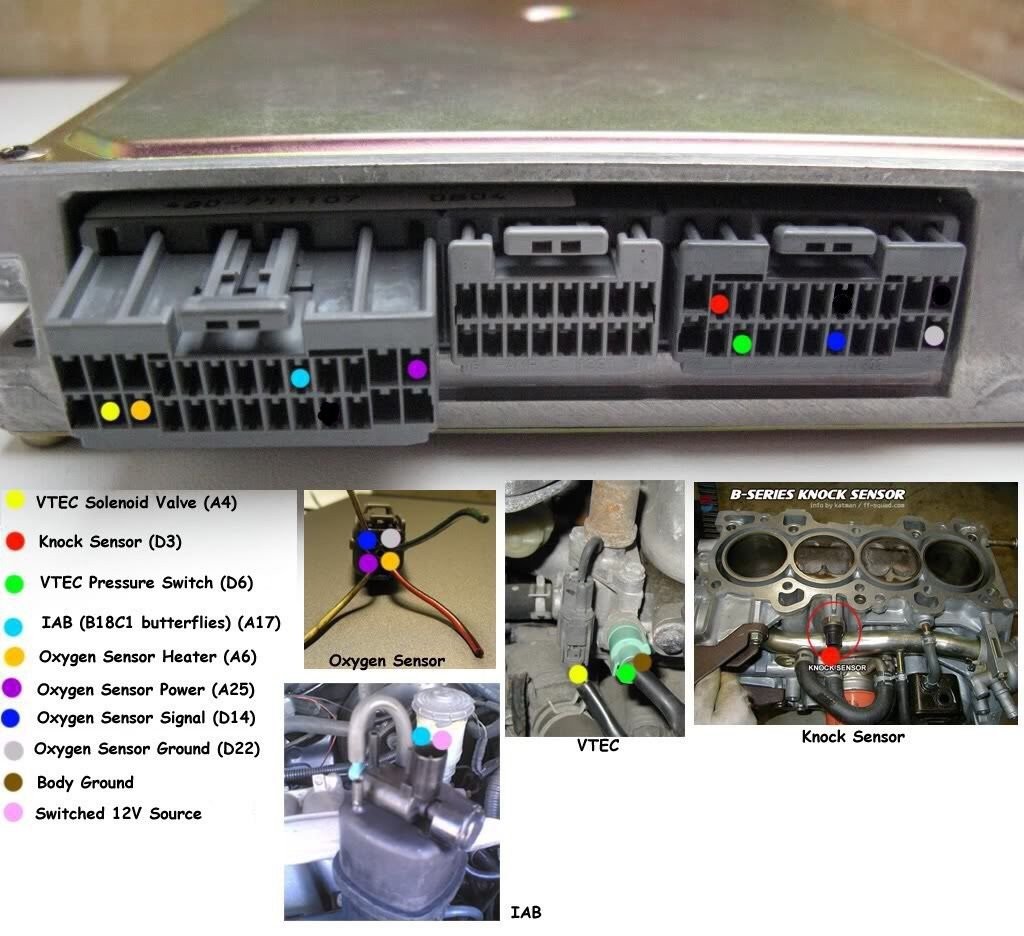 D16Y8 Crankshaft Position Sensor Location
D16Y8 Crankshaft Position Sensor Location
2.1. Diagnosing Sensor Failure
Diagnosing a failing crankshaft position sensor typically involves the following steps:
- Check Engine Light and OBD2 Codes: Use an OBD2 scanner to read any diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) stored in the ECU. Common codes related to the CKP sensor include P0335 (Crankshaft Position Sensor A Circuit Malfunction), P0336 (Crankshaft Position Sensor A Circuit Range/Performance), and P0337 (Crankshaft Position Sensor A Circuit Low Input).
- Visual Inspection: Inspect the sensor and its wiring for any signs of damage, such as frayed wires, corrosion, or loose connections.
- Continuity Test: Use a multimeter to check the continuity of the sensor’s wiring. Disconnect the sensor and check for continuity between the sensor terminals and the ECU.
- Resistance Test: Measure the resistance of the sensor. Compare the reading to the manufacturer’s specifications. An abnormal resistance reading indicates a faulty sensor.
- Voltage Test: With the engine running, use a multimeter to check the voltage output of the sensor. The voltage should fluctuate as the crankshaft rotates. A steady or absent voltage indicates a problem.
- Oscilloscope Test: An oscilloscope can provide a visual representation of the sensor’s signal. This can help identify intermittent problems or signal irregularities that may not be apparent with a multimeter.
- Inspect the Crankshaft Tone Ring: Ensure the crankshaft tone ring (reluctor ring) is clean and undamaged. A damaged or dirty tone ring can cause the sensor to produce inaccurate readings.
- Check for Interference: Ensure that there are no sources of electromagnetic interference (EMI) near the sensor that could disrupt its signal.
2.2. Common OBD2 Error Codes Related to the Crankshaft Positioning Sensor
When the crankshaft positioning sensor malfunctions, the OBD2 system will typically store one or more diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs). Here are some of the most common codes associated with CKP sensor issues:
| OBD2 Code | Description | Possible Causes |
|---|---|---|
| P0335 | Crankshaft Position Sensor A Circuit Malfunction | Faulty CKP sensor, wiring issues, loose connections, damaged crankshaft tone ring, ECU failure |
| P0336 | Crankshaft Position Sensor A Circuit Range/Performance | CKP sensor not providing accurate readings, timing misalignment, excessive crankshaft play, wiring issues |
| P0337 | Crankshaft Position Sensor A Circuit Low Input | Low voltage to the sensor, shorted wiring, faulty sensor |
| P0338 | Crankshaft Position Sensor A Circuit High Input | High voltage to the sensor, open wiring, faulty sensor |
| P0339 | Crankshaft Position Sensor A Circuit Intermittent | Intermittent wiring issues, loose connections, temperature-related sensor failure |
| P0320 | Ignition/Distributor Engine Speed Input Circuit Malfunction | Problems with the ignition system, faulty distributor, wiring issues, CKP sensor signal interference |
| P0725 | Engine Speed Input Circuit Malfunction | Issues with the engine speed signal, wiring problems, faulty CKP sensor, ECU failure |
| P1381 | Intermittent Interruption of Crankshaft Position Sensor | Loose connections, wiring issues, faulty CKP sensor, electromagnetic interference |
| P1382 | No Crankshaft Position Sensor Signal | Broken or disconnected wiring, faulty CKP sensor, ECU failure, damaged crankshaft tone ring |
By identifying these codes, you can narrow down the potential causes of the problem and take appropriate action. Use an OBD2 scanner from OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN to accurately read and interpret these codes, guiding your diagnostic process.
3. Step-by-Step Guide to Replacing the D16Y8 Crankshaft Positioning Sensor
Replacing the D16Y8 crankshaft positioning sensor is a straightforward process that can be accomplished with basic tools and a bit of mechanical knowledge. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you through the process:
3.1. Tools and Materials Needed
- New D16Y8 crankshaft positioning sensor (ensure it is compatible with your vehicle)
- OBD2 scanner (to clear any stored diagnostic trouble codes)
- Socket set and wrench set
- Screwdrivers (Phillips and flathead)
- Multimeter (for testing continuity and voltage)
- Jack and jack stands (for safely lifting the vehicle)
- Wheel chocks (for safety)
- Gloves and safety glasses
- Penetrating oil (if bolts are rusted)
- Shop towels or rags
3.2. Safety Precautions
Before starting any automotive repair, it’s essential to take the necessary safety precautions:
- Park on a Level Surface: Ensure your vehicle is parked on a level surface to prevent it from rolling.
- Engage the Parking Brake: Engage the parking brake firmly.
- Use Wheel Chocks: Place wheel chocks behind the rear wheels to prevent any movement.
- Disconnect the Battery: Disconnect the negative terminal of the battery to prevent electrical shocks and accidental activation of electrical components.
- Wear Safety Gear: Wear safety glasses to protect your eyes and gloves to protect your hands from dirt and chemicals.
- Work in a Well-Ventilated Area: If working indoors, ensure the area is well-ventilated to avoid inhaling harmful fumes.
3.3. Step-by-Step Replacement Process
- Locate the Crankshaft Positioning Sensor: The CKP sensor is typically located near the crankshaft pulley, often on the engine block. Refer to your vehicle’s service manual for the exact location.
- Lift the Vehicle: Use a jack to lift the front of the vehicle and securely place it on jack stands. Never work under a vehicle supported only by a jack.
- Access the Sensor: Depending on the vehicle model, you may need to remove the splash shield or other components to access the sensor. Use a socket or wrench to remove any necessary bolts or screws.
- Disconnect the Electrical Connector: Carefully disconnect the electrical connector from the CKP sensor. Press the release tab on the connector and gently pull it apart.
- Remove the Old Sensor: Use a socket or wrench to remove the bolt or screws securing the sensor to the engine block. Once the fasteners are removed, gently pull the sensor out.
- Inspect the Sensor Area: Before installing the new sensor, inspect the area for any dirt, debris, or corrosion. Clean the area with a shop towel if necessary.
- Install the New Sensor: Install the new CKP sensor in the reverse order of removal. Ensure it is properly aligned and securely fastened to the engine block.
- Reconnect the Electrical Connector: Reconnect the electrical connector to the new sensor. Ensure it clicks into place, indicating a secure connection.
- Reassemble Components: Reinstall any components that were removed to access the sensor, such as the splash shield.
- Lower the Vehicle: Carefully lower the vehicle from the jack stands.
- Reconnect the Battery: Reconnect the negative terminal of the battery.
- Clear Diagnostic Trouble Codes: Use an OBD2 scanner to clear any diagnostic trouble codes stored in the ECU.
- Start the Engine: Start the engine and check for any signs of problems, such as stalling, rough idling, or misfires.
- Test Drive: Take the vehicle for a test drive to ensure the issue is resolved and the engine is running smoothly.
3.4. Post-Replacement Checks
After replacing the crankshaft positioning sensor, perform these checks to ensure the repair was successful:
- Verify Engine Performance: Ensure the engine starts easily, idles smoothly, and accelerates without hesitation.
- Check for Diagnostic Trouble Codes: Use an OBD2 scanner to check for any new or recurring diagnostic trouble codes.
- Monitor Fuel Efficiency: Keep an eye on your fuel efficiency to ensure it returns to normal levels.
- Listen for Unusual Noises: Pay attention to any unusual noises coming from the engine.
- Inspect the Sensor Connection: Double-check the electrical connector to ensure it is securely connected.
By following these steps and performing the necessary checks, you can confidently replace the D16Y8 crankshaft positioning sensor and restore your vehicle’s performance. If you encounter any difficulties or are unsure about any step, consider seeking professional assistance from a qualified mechanic. Remember, OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN offers resources and support to help you with your automotive needs.
4. The Importance of Using an OBD2 Scanner
An OBD2 scanner is an indispensable tool for diagnosing and resolving automotive issues, particularly those related to the engine management system. Here are several reasons why using an OBD2 scanner is crucial for maintaining your vehicle:
4.1. Accurate Diagnostics
- Read Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs): An OBD2 scanner allows you to read the diagnostic trouble codes stored in the ECU. These codes provide valuable information about the nature and location of the problem.
- Pinpoint the Source of the Issue: By interpreting the DTCs, you can accurately pinpoint the source of the issue, whether it’s a faulty sensor, wiring problem, or other component failure.
- Avoid Guesswork: Using an OBD2 scanner eliminates the guesswork involved in diagnosing automotive problems, saving you time and money on unnecessary repairs.
4.2. Real-Time Data Monitoring
- Monitor Engine Parameters: OBD2 scanners can display real-time data from various sensors and components, allowing you to monitor engine performance in real-time.
- Identify Intermittent Problems: Real-time data monitoring can help identify intermittent problems that may not trigger a DTC.
- Verify Repairs: After performing a repair, you can use the OBD2 scanner to monitor the relevant parameters and ensure the issue has been resolved.
4.3. Cost Savings
- DIY Repairs: With an OBD2 scanner, you can diagnose and resolve many automotive issues yourself, saving on labor costs at a repair shop.
- Prevent Further Damage: Early diagnosis and repair can prevent minor issues from escalating into more significant and costly problems.
- Informed Decisions: An OBD2 scanner provides you with the information you need to make informed decisions about your vehicle’s maintenance and repairs.
4.4. User-Friendly Interface
Modern OBD2 scanners come equipped with user-friendly interfaces and intuitive software, making them easy to use for both professionals and DIY enthusiasts. Many scanners also offer additional features, such as code definitions, repair tips, and access to online resources.
4.5. Wide Compatibility
OBD2 scanners are compatible with a wide range of vehicles manufactured after 1996, making them a versatile tool for any car owner. Whether you drive a Honda Civic, Ford F-150, or BMW 3 Series, an OBD2 scanner can help you diagnose and resolve automotive issues.
4.6. Enhanced Vehicle Maintenance
By regularly scanning your vehicle for diagnostic trouble codes, you can proactively address potential issues before they cause significant problems. This helps ensure your vehicle remains reliable and performs optimally.
Investing in an OBD2 scanner is a smart decision for any car owner. It provides you with the tools and information you need to diagnose and resolve automotive issues efficiently, saving you time, money, and frustration. OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN offers a range of high-quality OBD2 scanners to suit your needs and budget.
5. Maintaining Your D16Y8 Engine
Proper maintenance is essential for keeping your D16Y8 engine running smoothly and reliably. Here are some key maintenance tasks to perform regularly:
5.1. Regular Oil Changes
- Importance: Regular oil changes are crucial for lubricating engine components, reducing friction, and preventing wear.
- Frequency: Change the oil and filter every 3,000 to 5,000 miles, or as recommended by the vehicle manufacturer.
- Type of Oil: Use the correct type of oil specified in your vehicle’s owner’s manual.
5.2. Air Filter Replacement
- Importance: A clean air filter ensures that the engine receives an adequate supply of clean air, improving performance and fuel efficiency.
- Frequency: Replace the air filter every 12,000 to 15,000 miles, or more frequently if driving in dusty conditions.
5.3. Spark Plug Replacement
- Importance: Spark plugs ignite the air-fuel mixture in the engine cylinders. Worn or fouled spark plugs can cause misfires, reduced power, and poor fuel economy.
- Frequency: Replace the spark plugs every 30,000 to 50,000 miles, or as recommended by the vehicle manufacturer.
- Type of Spark Plugs: Use the correct type of spark plugs specified in your vehicle’s owner’s manual.
5.4. Timing Belt Replacement
- Importance: The timing belt synchronizes the rotation of the crankshaft and camshaft. A broken timing belt can cause severe engine damage.
- Frequency: Replace the timing belt every 60,000 to 100,000 miles, or as recommended by the vehicle manufacturer.
- Inspection: Regularly inspect the timing belt for cracks, wear, or damage.
5.5. Coolant Flush
- Importance: Coolant helps regulate the engine’s temperature, preventing overheating and corrosion.
- Frequency: Flush and replace the coolant every 2 to 3 years, or as recommended by the vehicle manufacturer.
- Type of Coolant: Use the correct type of coolant specified in your vehicle’s owner’s manual.
5.6. Fluid Checks
- Importance: Regularly check the levels of various fluids, including engine oil, coolant, brake fluid, power steering fluid, and transmission fluid.
- Frequency: Check fluid levels at least once a month, or more frequently if you notice any leaks or unusual symptoms.
- Top Up as Needed: Top up fluids as needed to maintain the correct levels.
5.7. Visual Inspections
- Importance: Regularly inspect the engine compartment for any signs of leaks, damage, or wear.
- Check Hoses and Belts: Inspect hoses and belts for cracks, wear, or looseness.
- Look for Leaks: Check for leaks of oil, coolant, or other fluids.
- Inspect Wiring: Inspect wiring for damage or loose connections.
5.8. OBD2 Scanning
- Importance: Regularly scan your vehicle for diagnostic trouble codes using an OBD2 scanner.
- Early Detection: Early detection of problems can prevent minor issues from escalating into more significant and costly repairs.
- Proactive Maintenance: Proactive maintenance helps ensure your vehicle remains reliable and performs optimally.
By following these maintenance tips, you can keep your D16Y8 engine running smoothly and reliably for years to come. Regular maintenance not only extends the life of your engine but also improves fuel efficiency, reduces emissions, and enhances overall vehicle performance. OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN is here to support you with all your automotive diagnostic and maintenance needs.
 OBD2 Scanner Tool
OBD2 Scanner Tool
6. Troubleshooting Other Common D16Y8 Issues
Besides the crankshaft positioning sensor, the D16Y8 engine may encounter other common issues. Here’s how to troubleshoot some of them:
6.1. Misfires
- Symptoms: Rough idling, reduced power, poor fuel economy, check engine light.
- Possible Causes:
- Faulty spark plugs or wires
- Bad ignition coil
- Clogged fuel injectors
- Vacuum leaks
- Low compression
- Troubleshooting Steps:
- Check spark plugs and wires for wear or damage. Replace if necessary.
- Test ignition coils with a multimeter. Replace if faulty.
- Clean or replace fuel injectors.
- Check for vacuum leaks using a vacuum gauge or propane torch. Repair any leaks.
- Perform a compression test to check for low compression.
6.2. Idle Air Control (IAC) Valve Problems
- Symptoms: High or erratic idle, stalling, difficulty starting.
- Possible Causes:
- Dirty or clogged IAC valve
- Faulty IAC valve
- Vacuum leaks
- Wiring issues
- Troubleshooting Steps:
- Clean the IAC valve with carburetor cleaner.
- Test the IAC valve with a multimeter. Replace if faulty.
- Check for vacuum leaks around the IAC valve. Repair any leaks.
- Inspect wiring for damage or loose connections.
6.3. Oxygen Sensor Issues
- Symptoms: Poor fuel economy, check engine light, rough running.
- Possible Causes:
- Faulty oxygen sensor
- Exhaust leaks
- Wiring issues
- Troubleshooting Steps:
- Test the oxygen sensor with a multimeter. Replace if faulty.
- Check for exhaust leaks. Repair any leaks.
- Inspect wiring for damage or loose connections.
6.4. Catalytic Converter Failure
- Symptoms: Reduced power, poor fuel economy, check engine light, rattling noise from the exhaust.
- Possible Causes:
- Clogged or damaged catalytic converter
- Engine misfires
- Oil contamination
- Troubleshooting Steps:
- Inspect the catalytic converter for damage or clogs.
- Check for engine misfires. Repair any misfires.
- Address any oil leaks that may be contaminating the catalytic converter.
6.5. Fuel Pump Problems
- Symptoms: Hard starting, stalling, reduced power, check engine light.
- Possible Causes:
- Faulty fuel pump
- Clogged fuel filter
- Wiring issues
- Troubleshooting Steps:
- Check fuel pressure with a fuel pressure gauge.
- Replace the fuel filter.
- Inspect wiring for damage or loose connections.
By addressing these common D16Y8 engine issues promptly, you can ensure your vehicle remains reliable and performs optimally. OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN provides the resources and tools you need to diagnose and resolve these problems efficiently.
7. Benefits of Choosing OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN
Choosing OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN as your automotive diagnostic and repair resource offers numerous benefits. We are committed to providing high-quality products, expert advice, and exceptional customer service to meet all your automotive needs.
7.1. Wide Range of OBD2 Scanners
- Variety of Options: We offer a wide range of OBD2 scanners to suit different needs and budgets. Whether you’re a professional mechanic or a DIY enthusiast, we have the perfect scanner for you.
- Top Brands: Our scanners come from top brands known for their reliability, accuracy, and user-friendly features.
- Advanced Features: Many of our scanners offer advanced features such as real-time data monitoring, code definitions, and repair tips.
7.2. Expert Advice and Support
- Knowledgeable Staff: Our team of knowledgeable professionals is here to provide expert advice and support. We can help you choose the right scanner, diagnose automotive issues, and perform repairs.
- Online Resources: Our website features a wealth of online resources, including troubleshooting guides, repair tips, and FAQs.
- Customer Support: We offer exceptional customer support to answer your questions and address your concerns.
7.3. High-Quality Products
- Reliable Performance: Our OBD2 scanners are known for their reliable performance and accurate diagnostics.
- Durable Construction: Our products are built to last, with durable construction and high-quality components.
- Warranty: We stand behind our products with a comprehensive warranty.
7.4. Competitive Pricing
- Affordable Options: We offer competitive pricing on all our OBD2 scanners and automotive tools.
- Value for Money: Our products provide excellent value for money, with reliable performance and advanced features.
- Special Offers: We regularly offer special promotions and discounts to help you save even more.
7.5. Comprehensive Automotive Solutions
- Diagnostic Tools: We offer a wide range of diagnostic tools to help you identify and resolve automotive issues.
- Repair Parts: We can help you source high-quality repair parts for your vehicle.
- Maintenance Products: We offer a variety of maintenance products to help you keep your vehicle running smoothly.
7.6. Commitment to Customer Satisfaction
- Customer-Focused Approach: We are committed to providing exceptional customer service and ensuring your satisfaction.
- Easy Returns: We offer easy returns and exchanges if you’re not completely satisfied with your purchase.
- Positive Reviews: Our customers consistently give us positive reviews for our products and services.
Choosing OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN means you’re partnering with a trusted resource for all your automotive diagnostic and repair needs. We’re here to help you keep your vehicle running smoothly and reliably, saving you time, money, and frustration.
8. FAQ About D16Y8 OBD2 and Crankshaft Positioning Sensors
Here are some frequently asked questions about the D16Y8 OBD2 system and crankshaft positioning sensors:
Q1: What is an OBD2 scanner?
An OBD2 scanner is a diagnostic tool used to read and interpret diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) stored in a vehicle’s engine control unit (ECU). These codes help identify potential issues with the vehicle’s engine and other systems.
Q2: How do I read OBD2 codes on my D16Y8 engine?
To read OBD2 codes, plug an OBD2 scanner into the diagnostic port, typically located under the dashboard. Turn the ignition on, and follow the scanner’s instructions to read the stored codes.
Q3: What does the crankshaft positioning sensor do?
The crankshaft positioning sensor (CKP sensor) monitors the position and rotational speed of the crankshaft. This information is crucial for the ECU to manage ignition timing and fuel injection accurately.
Q4: What are the symptoms of a bad crankshaft positioning sensor?
Common symptoms include engine stalling, hard starting, check engine light, rough idling, reduced fuel efficiency, and misfires.
Q5: Can I replace the crankshaft positioning sensor myself?
Yes, replacing the crankshaft positioning sensor is a straightforward process that can be accomplished with basic tools and a bit of mechanical knowledge. Follow a step-by-step guide and take the necessary safety precautions.
Q6: How often should I replace my car’s crankshaft positioning sensor?
The crankshaft positioning sensor should be replaced when it fails or shows signs of malfunction. There is no specific replacement interval.
Q7: Can a bad crankshaft positioning sensor cause a no-start condition?
Yes, a faulty CKP sensor can prevent the engine from starting because the ECU needs accurate data from the sensor to time ignition and fuel injection correctly.
Q8: What is the difference between OBD1 and OBD2?
OBD1 (On-Board Diagnostics 1) is an earlier version of the onboard diagnostic system used in vehicles before 1996. OBD2 (On-Board Diagnostics 2) is a standardized system introduced in 1996 that provides more comprehensive monitoring and diagnostic capabilities.
Q9: How do I choose the right OBD2 scanner for my needs?
Consider factors such as your budget, the features you need, and the compatibility of the scanner with your vehicle. OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN offers a wide range of scanners to suit different needs and budgets.
Q10: Where can I get help with diagnosing and repairing my D16Y8 engine?
OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN provides expert advice, online resources, and high-quality products to help you diagnose and repair your D16Y8 engine efficiently.
9. Call to Action
Experiencing issues with your D16Y8 engine? Don’t let a faulty crankshaft positioning sensor or other engine problems keep you off the road. Contact OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN today for expert assistance!
- Get Expert Advice: Our knowledgeable team can help you diagnose and resolve any automotive issue.
- Find the Right OBD2 Scanner: We offer a wide range of high-quality OBD2 scanners to suit your needs and budget.
- Schedule a Consultation: Contact us to schedule a consultation and get personalized assistance.
Contact Information:
- Address: 123 Main Street, Los Angeles, CA 90001, United States
- WhatsApp: +1 (641) 206-8880
- Website: OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN
Let OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN be your trusted partner for all your automotive diagnostic and repair needs. Contact us today and experience the difference! We can help you use OBD2 scanner and auto repair services.