Connecting your PC to OBD2 allows you to diagnose car issues and monitor performance, and OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN offers the knowledge and tools to make it simple. This article will guide you through the process of setting up your PC with an OBD2 scanner, understanding diagnostic data, and performing basic troubleshooting with access to the latest technology and expert advice for successful car diagnostics and maintenance. In this guide, you’ll also learn about vehicle diagnostics, scan tool, and car maintenance.
Contents
- 1. Understanding OBD2 and Its Importance
- What is OBD2?
- Why Connect Your PC to OBD2?
- 2. Essential Equipment You’ll Need
- OBD2 Scanner/Adapter
- Software
- A Windows-Based PC
- 3. Step-by-Step Guide to Connecting Your PC to OBD2
- Step 1: Download and Install the Necessary Software
- Step 2: Locate the OBD2 Port in Your Vehicle
- Step 3: Plug in the OBD2 Scanner/Adapter
- Step 4: Turn On Your Vehicle’s Ignition
- Step 5: Establish a Connection
- For Bluetooth Adapters:
- For USB Adapters:
- Step 6: Configure the Software
- Step 7: Test the Connection
- 4. Understanding OBD2 Data
- Reading Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
- Interpreting Real-Time Data
- 5. Troubleshooting Common Connection Issues
- Issue: Cannot Establish Connection
- Potential Causes:
- Troubleshooting Steps:
- Issue: No Data Displayed
- Potential Causes:
- Troubleshooting Steps:
- 6. Advanced Tips and Tricks
- Using Android Emulators for Torque Pro
- Data Logging and Analysis
- Customizing Dashboards
- 7. Benefits of Using OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN
- Expert Guidance
- Up-to-Date Information
- Comprehensive Support
- 8. Real-World Applications of OBD2 Diagnostics
- Improving Fuel Efficiency
- Preventing Costly Repairs
- Ensuring Emissions Compliance
- 9. Choosing the Right OBD2 Software
- Key Considerations When Selecting OBD2 Software
- Compatibility
- Features
- User Interface
- Updates and Support
- Cost
- Popular OBD2 Software Options
- OBDWiz
- ScanTool.net
- Torque Pro (with Android Emulator)
- Tips for Making Your Selection
- 10. Understanding Vehicle Recalls and TSBs Through OBD2 Connection
- Importance of Staying Informed About Recalls and TSBs
- Vehicle Recalls
- Technical Service Bulletins (TSBs)
- Utilizing Your OBD2 Connection for Recall and TSB Information
- Monitoring Vehicle Performance
- Reading Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
- Resources for Finding Recall and TSB Information
- National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA)
- Vehicle Manufacturer Websites
- Online Databases
- Automotive Forums
- Interpreting Recall and TSB Information
- Recalls
- TSBs
- Taking Action
- Recalls
- TSBs
- 11. Safety Precautions and Best Practices
- General Safety Precautions
- Best Practices for OBD2 Diagnostics
- 12. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- What is an OBD2 scanner?
- How do I read OBD2 fault codes?
- What are common car malfunctions and how to fix them?
- Can I damage my car by using an OBD2 scanner?
- How often should I perform an OBD2 scan?
- What is the “Check Engine” light?
- Can I reset the “Check Engine” light with an OBD2 scanner?
- What does real-time data mean?
- What is a DTC?
- Can I use an OBD2 scanner on any car?
- 13. Contact OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN for Expert Assistance
1. Understanding OBD2 and Its Importance
What is OBD2?
OBD2, or On-Board Diagnostics II, is a standardized system used in most vehicles since 1996. According to the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), OBD2 was implemented to monitor the performance of a vehicle’s engine and emissions systems. It provides valuable data that can help identify issues and ensure your car runs efficiently. This system is crucial for technicians and car enthusiasts alike for maintaining vehicle health.
Why Connect Your PC to OBD2?
Connecting your PC to the OBD2 port unlocks a wealth of information about your vehicle. Instead of relying solely on dashboard warning lights, you can:
- Diagnose Issues: Read diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) to pinpoint problems.
- Monitor Performance: Track real-time data like engine RPM, speed, and temperature.
- Reset Codes: Clear the “Check Engine” light after addressing the issue.
- Customize Settings: Some advanced software allows you to adjust certain vehicle settings.
According to a study by AAA, vehicle owners who proactively address maintenance issues save an average of $100 annually in repair costs. Connecting your PC to OBD2 enables this proactive approach, improving vehicle longevity and decreasing unexpected repairs.
2. Essential Equipment You’ll Need
OBD2 Scanner/Adapter
This device plugs into your vehicle’s OBD2 port and communicates with your PC. Several types are available:
- Bluetooth OBD2 Adapters: These connect wirelessly to your PC, offering convenience and flexibility.
- USB OBD2 Scanners: These provide a wired connection, ensuring a stable and reliable data stream.
Software
You’ll need software on your PC to interpret the data from the OBD2 scanner. Several options are available:
- OBDwiz: A comprehensive software package designed to work seamlessly with OBDLink adapters.
- ScanTool.net: Offers a variety of software solutions for OBD2 diagnostics.
- Torque Pro (Android Emulator): Allows you to use the popular Torque Pro app on your PC through an Android emulator.
A Windows-Based PC
While some OBD2 scanners work with smartphones, a Windows PC offers a larger screen and more robust software options for in-depth analysis. Ensure your PC meets the minimum system requirements for the chosen software.
3. Step-by-Step Guide to Connecting Your PC to OBD2
Step 1: Download and Install the Necessary Software
Before connecting anything, download and install the software you’ve chosen. OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN recommends OBDwiz for its comprehensive features and user-friendly interface.
Step 2: Locate the OBD2 Port in Your Vehicle
The OBD2 port is typically located under the dashboard on the driver’s side. Consult your vehicle’s manual if you have trouble finding it.
Step 3: Plug in the OBD2 Scanner/Adapter
 Vehicle OBD2 Port Location
Vehicle OBD2 Port Location
Carefully plug the OBD2 scanner into the port. Ensure it fits snugly, but don’t force it.
Alt Text: Locating the OBD2 diagnostic port in a vehicle.
Step 4: Turn On Your Vehicle’s Ignition
Turn the ignition key to the “ON” position. This provides power to the OBD2 port and allows the scanner to communicate with the vehicle’s computer.
The position is sometimes marked with the Roman numeral ‘II.’ Stop just before you start the engine.
Step 5: Establish a Connection
For Bluetooth Adapters:
- Enable Bluetooth on your PC:
- Go to Settings > Devices > Bluetooth & other devices.
- Turn the Bluetooth toggle switch to “On.”
- Make the OBDLink discoverable: Press the ‘Connect’ button on the device.
- Pair the Adapter with Your PC:
- Click “Add Bluetooth or other device.”
- Select “Bluetooth.”
- Choose your OBDLink device from the list.
- Enter the PIN if prompted (usually “1234” or “0000”).
For USB Adapters:
- Connect the USB Cable: Plug the USB cable from the adapter into an available USB port on your PC.
- Install Drivers (if necessary): Windows should automatically detect the device and install the necessary drivers. If not, you may need to download them from the manufacturer’s website.
Step 6: Configure the Software
- Launch the OBD2 Software: Open the software you installed (e.g., OBDwiz).
- Select the Correct COM Port (for USB Adapters):
- Go to the software settings or preferences.
- Identify the COM port assigned to your OBD2 adapter (you can find this in Device Manager).
- Select the appropriate COM port in the software.
- Auto-Detect (if available): Some software, like OBDwiz, has an “Auto Detect” feature that automatically configures the connection settings.
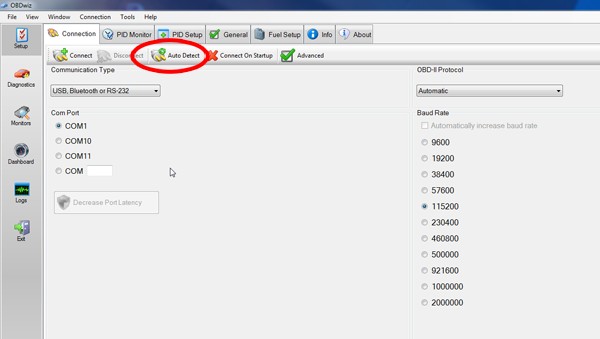 OBDwiz Auto Detect
OBDwiz Auto Detect
Step 7: Test the Connection
In the software, look for an option to “Connect” or “Test Connection.” This will verify that your PC is communicating with the OBD2 scanner and your vehicle’s computer.
4. Understanding OBD2 Data
Reading Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
DTCs are codes stored by the vehicle’s computer when it detects a problem. They consist of five characters:
- The first character indicates the system:
- P: Powertrain (engine, transmission)
- B: Body (interior, lights)
- C: Chassis (brakes, suspension)
- U: Network (communication)
- The second character indicates whether the code is generic (0) or manufacturer-specific (1).
- The third character indicates the subsystem:
- 1: Fuel and air metering
- 2: Fuel and air metering (injector circuit)
- 3: Ignition system
- 4: Auxiliary emission controls
- 5: Vehicle speed controls and idle control system
- 6: Computer output system
- 7: Transmission
- 8: Transmission
- The last two characters are specific to the fault.
For example, P0300 indicates a random/multiple cylinder misfire detected in the powertrain system.
Interpreting Real-Time Data
Your OBD2 software can display real-time data from various sensors in your vehicle. Common parameters include:
- Engine RPM
- Vehicle Speed
- Coolant Temperature
- Intake Air Temperature
- Mass Air Flow (MAF)
- Oxygen Sensor Readings
- Fuel Trim
Monitoring these parameters can help you identify trends and potential problems before they trigger a DTC.
5. Troubleshooting Common Connection Issues
Issue: Cannot Establish Connection
Potential Causes:
- Incorrect COM port selected
- Faulty OBD2 scanner
- Damaged OBD2 port in the vehicle
- Bluetooth pairing problems
Troubleshooting Steps:
- Verify the COM port: Ensure the correct COM port is selected in your software.
- Test the OBD2 scanner: Try the scanner on another vehicle to rule out a faulty device.
- Inspect the OBD2 port: Check for damage or corrosion in the vehicle’s OBD2 port.
- Re-pair Bluetooth: Remove the pairing from your PC and repeat the pairing process.
Issue: No Data Displayed
Potential Causes:
- Vehicle not supported
- Incorrect protocol selected
- Faulty sensor
Troubleshooting Steps:
- Check Vehicle Compatibility: Ensure that your vehicle is OBD2 compliant and supported by the software.
- Verify Protocol: Some software allows you to manually select the OBD2 protocol. Consult your vehicle’s manual for the correct protocol.
- Inspect Sensors: If you suspect a faulty sensor, use the OBD2 scanner to check for DTCs related to that sensor.
6. Advanced Tips and Tricks
Using Android Emulators for Torque Pro
Torque Pro is a popular OBD2 app for Android devices. You can use an Android emulator like BlueStacks or NoxPlayer to run Torque Pro on your PC.
- Download and install an Android emulator.
- Download and install Torque Pro within the emulator.
- Pair your Bluetooth OBD2 adapter with the emulator.
- Configure Torque Pro to connect to the adapter.
Data Logging and Analysis
Most OBD2 software allows you to log data over time. This can be useful for:
- Diagnosing intermittent problems
- Monitoring vehicle performance under different conditions
- Tracking fuel economy
Customizing Dashboards
Customize your software dashboard to display the parameters most important to you. This allows you to quickly monitor the data you need without sifting through irrelevant information.
7. Benefits of Using OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN
Expert Guidance
OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN provides expert guidance on selecting the right OBD2 scanner and software for your needs. Our team of experienced technicians can help you navigate the complexities of OBD2 diagnostics.
Up-to-Date Information
We stay up-to-date with the latest OBD2 standards, DTCs, and diagnostic techniques. Our resources are continually updated to ensure you have the most accurate and relevant information.
Comprehensive Support
From initial setup to advanced troubleshooting, OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN offers comprehensive support to help you get the most out of your OBD2 scanner.
8. Real-World Applications of OBD2 Diagnostics
Improving Fuel Efficiency
By monitoring parameters like fuel trim and oxygen sensor readings, you can identify issues that are negatively impacting your fuel economy. Addressing these issues can save you money at the pump and reduce your carbon footprint. According to the U.S. Department of Energy, optimizing your vehicle’s fuel efficiency can save you hundreds of dollars per year.
Preventing Costly Repairs
Regular OBD2 diagnostics can help you catch minor issues before they escalate into major repairs. By addressing problems early, you can prevent damage to critical components and extend the life of your vehicle. A study by the National Institute for Automotive Service Excellence (ASE) found that preventative maintenance can reduce the likelihood of major repairs by up to 50%.
Ensuring Emissions Compliance
OBD2 systems are designed to monitor emissions-related components. Using an OBD2 scanner, you can verify that your vehicle is operating within acceptable emissions standards and avoid failing an emissions test.
9. Choosing the Right OBD2 Software
Selecting the appropriate OBD2 software is crucial for maximizing the effectiveness of your diagnostic efforts. Different software packages offer varying features, compatibility, and user interfaces. Here’s a detailed guide to help you make an informed decision.
Key Considerations When Selecting OBD2 Software
Compatibility
Ensure the software is compatible with your computer’s operating system (Windows, macOS, Linux) and supports your OBD2 adapter (Bluetooth or USB). Some software may require specific hardware configurations or drivers.
Features
Assess the range of features offered by the software. Basic features include reading and clearing DTCs, displaying real-time data, and generating reports. Advanced features may include:
- Enhanced Diagnostics: Access to manufacturer-specific codes and parameters.
- Bi-Directional Control: Ability to send commands to the vehicle’s computer to test components.
- Data Logging: Recording and analyzing data over time.
- Customizable Dashboards: Creating personalized displays of real-time data.
- Freeze Frame Data: Capturing data at the moment a DTC is triggered.
User Interface
A user-friendly interface can significantly enhance your diagnostic experience. Look for software with intuitive menus, clear data displays, and easy-to-navigate features.
Updates and Support
Regular software updates are essential to ensure compatibility with new vehicles and access to the latest features and bug fixes. Check if the software provider offers reliable customer support in case you encounter any issues.
Cost
OBD2 software ranges from free to several hundred dollars. Determine your budget and compare the features offered by different software packages within your price range.
Popular OBD2 Software Options
Here are some of the most popular OBD2 software options, each offering unique features and capabilities:
OBDWiz
Overview: OBDWiz is a comprehensive software package designed to work seamlessly with OBDLink adapters. It offers a wide range of features for reading and clearing DTCs, displaying real-time data, and generating reports.
Key Features:
- User-friendly interface
- Automatic adapter detection
- Support for all OBD2 protocols
- Enhanced diagnostics for select vehicles
- Data logging and graphing
Pros: - Easy to use
- Reliable performance
- Excellent customer support
Cons: - Primarily designed for use with OBDLink adapters
- Limited advanced features compared to some other options
ScanTool.net
Overview: ScanTool.net offers a variety of software solutions for OBD2 diagnostics, catering to both novice and experienced users. Their software is compatible with a wide range of OBD2 adapters and offers a comprehensive set of features.
Key Features:
- Support for multiple OBD2 adapters
- Comprehensive DTC database
- Real-time data display
- Data logging and playback
- Customizable dashboards
Pros: - Versatile and compatible with various adapters
- Extensive features for diagnostics and analysis
- Affordable pricing
Cons: - The interface may not be as intuitive as some other options
- Advanced features may require additional purchases
Torque Pro (with Android Emulator)
Overview: Torque Pro is a popular OBD2 app for Android devices, known for its extensive features and customizable interface. By using an Android emulator, you can run Torque Pro on your Windows PC and access its capabilities on a larger screen.
Key Features:
- Real-time data display
- Customizable dashboards
- DTC reading and clearing
- GPS tracking
- Plugin support for enhanced functionality
Pros: - Extensive features and customization options
- Large community and active development
- Affordable pricing
Cons: - Requires an Android emulator to run on Windows
- May require some technical knowledge to set up and configure
Tips for Making Your Selection
- Read Reviews: Research user reviews and ratings to get insights into the software’s performance and reliability.
- Try Free Trials: Many software providers offer free trials or demo versions. Take advantage of these opportunities to test the software before making a purchase.
- Consider Your Needs: Evaluate your specific diagnostic needs and choose software that offers the features you require.
- Seek Recommendations: Ask for recommendations from experienced technicians or car enthusiasts who have used OBD2 software extensively.
By carefully considering these factors and exploring the available options, you can select the OBD2 software that best suits your needs and helps you unlock the full potential of your vehicle’s diagnostic system.
10. Understanding Vehicle Recalls and TSBs Through OBD2 Connection
Importance of Staying Informed About Recalls and TSBs
Vehicle recalls and Technical Service Bulletins (TSBs) are crucial for maintaining the safety, reliability, and performance of your vehicle. Understanding how to access and interpret this information can help you address potential issues proactively and prevent costly repairs.
Vehicle Recalls
A vehicle recall is issued when a manufacturer determines that a specific vehicle model or component has a safety-related defect or fails to comply with federal safety standards. Recalls are typically initiated by the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) or the vehicle manufacturer. When a recall is issued, the manufacturer is responsible for notifying vehicle owners and providing a free remedy for the defect.
Technical Service Bulletins (TSBs)
Technical Service Bulletins (TSBs) are issued by vehicle manufacturers to provide guidance to technicians on how to address common issues or problems that may arise with specific vehicle models. Unlike recalls, TSBs are not safety-related and do not require manufacturers to notify vehicle owners or provide free repairs. Instead, TSBs serve as a resource for technicians to diagnose and repair issues more effectively.
Utilizing Your OBD2 Connection for Recall and TSB Information
While an OBD2 connection cannot directly provide recall or TSB information, it can assist you in identifying potential issues that may be related to a recall or TSB. By monitoring your vehicle’s performance and reading diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs), you can detect symptoms or problems that may be addressed in a recall or TSB.
Monitoring Vehicle Performance
Regularly monitor your vehicle’s performance using your OBD2 scanner and software. Pay attention to any unusual symptoms, such as:
- Engine misfires
- Transmission slipping
- Erratic sensor readings
- Unexplained warning lights
- Decreased fuel efficiency
Reading Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
When your vehicle experiences an issue, it will often store a DTC in its computer system. Use your OBD2 scanner to read and interpret these codes. Research the codes online to determine if they are related to a known recall or TSB.
Resources for Finding Recall and TSB Information
National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA)
The NHTSA website (www.nhtsa.gov/recalls) is the primary source for recall information in the United States. You can search for recalls by vehicle make, model, and year. The NHTSA website also provides information on how to report a safety-related defect.
Vehicle Manufacturer Websites
Vehicle manufacturers typically have a recall lookup tool on their websites. You can enter your vehicle’s VIN (Vehicle Identification Number) to check for any open recalls.
Online Databases
Several online databases compile TSB information from various sources. These databases can be valuable resources for identifying potential issues and troubleshooting problems. Some popular TSB databases include:
- ALLDATA
- Mitchell 1
- Identifix
Automotive Forums
Automotive forums and online communities can be valuable sources of information on recalls and TSBs. Other vehicle owners may have experienced similar issues and can provide insights and recommendations.
Interpreting Recall and TSB Information
Recalls
When checking for recalls, pay attention to the following information:
- Recall Number: The unique identifier assigned to the recall.
- Affected Vehicles: The specific vehicle models and years affected by the recall.
- Description of the Defect: A detailed explanation of the safety-related defect.
- Remedy: The corrective action that will be taken to address the defect.
- Notification Instructions: Information on how vehicle owners will be notified and how to schedule the repair.
TSBs
When reviewing TSBs, look for the following information:
- TSB Number: The unique identifier assigned to the TSB.
- Affected Vehicles: The specific vehicle models and years affected by the TSB.
- Subject: A brief description of the issue addressed in the TSB.
- Symptom/Condition: A detailed explanation of the symptoms or conditions that may indicate the issue.
- Cause: The underlying cause of the issue.
- Correction: The recommended repair procedure or solution.
Taking Action
Recalls
If your vehicle is subject to a recall, contact your local dealership to schedule the free repair. Provide the dealership with the recall number and your vehicle’s VIN.
TSBs
If you suspect that your vehicle may be affected by a TSB, consult with a qualified technician. Provide the technician with the TSB number and a description of the symptoms you are experiencing. The technician can diagnose the issue and perform the recommended repair procedure.
By staying informed about vehicle recalls and TSBs and utilizing your OBD2 connection to monitor your vehicle’s performance, you can proactively address potential issues and ensure the safety, reliability, and longevity of your vehicle.
11. Safety Precautions and Best Practices
General Safety Precautions
- Always work in a well-ventilated area.
- Wear safety glasses to protect your eyes.
- Disconnect the negative battery terminal before working on electrical components.
- Avoid touching hot engine parts.
- Use caution when working around moving parts.
Best Practices for OBD2 Diagnostics
- Read the vehicle’s manual before performing any diagnostics.
- Use high-quality OBD2 scanners and software.
- Follow the manufacturer’s instructions for using the scanner and software.
- Double-check all connections before starting the diagnostic process.
- Record all DTCs and data readings for future reference.
- Clear DTCs only after addressing the underlying issue.
- Consult with a qualified technician if you are unsure about any aspect of the diagnostic process.
12. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is an OBD2 scanner?
An OBD2 scanner is a tool used to read diagnostic information from a vehicle’s computer system.
How do I read OBD2 fault codes?
Connect the scanner to the OBD2 port, turn on the ignition, and use the software to read the codes.
What are common car malfunctions and how to fix them?
Common malfunctions include engine misfires, faulty oxygen sensors, and transmission problems. The fix depends on the specific issue.
Can I damage my car by using an OBD2 scanner?
No, using an OBD2 scanner correctly will not damage your car.
How often should I perform an OBD2 scan?
Perform a scan whenever you notice a warning light or suspect a problem.
What is the “Check Engine” light?
The “Check Engine” light indicates that the vehicle’s computer has detected a problem.
Can I reset the “Check Engine” light with an OBD2 scanner?
Yes, you can reset the light after addressing the underlying issue.
What does real-time data mean?
Real-time data is information from various sensors displayed as it happens.
What is a DTC?
DTC stands for Diagnostic Trouble Code.
Can I use an OBD2 scanner on any car?
Most cars manufactured after 1996 are OBD2 compliant.
13. Contact OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN for Expert Assistance
Do you need help connecting your PC to OBD2 or interpreting diagnostic data? Contact OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN today! Our team of expert technicians is ready to provide the guidance and support you need.
Address: 123 Main Street, Los Angeles, CA 90001, United States
WhatsApp: +1 (641) 206-8880
Website: OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN
By connecting your PC to OBD2, you can unlock a wealth of information about your vehicle and take control of your car’s health. With the right equipment, software, and guidance from OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN, you can diagnose problems, monitor performance, and save money on costly repairs. Contact us today to get started!
With OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN, understanding and maintaining your vehicle has never been easier.