Installing WiFi in your car’s OBD2 port allows for wireless diagnostics and monitoring of your vehicle’s performance using a compatible scanner or app. OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN provides expert guidance on this process, ensuring a seamless connection for enhanced vehicle management. By understanding the steps involved, you can easily integrate this technology into your car. This integration offers real-time data, improves diagnostic accuracy, and streamlines automotive maintenance.
Contents
- 1. Understanding the Basics of OBD2 and WiFi Adapters
- 1.1. What is OBD2?
- 1.2. What is a WiFi OBD2 Adapter?
- 1.3. Benefits of Using WiFi OBD2
- 1.4. Common Applications for WiFi OBD2
- 2. Choosing the Right WiFi OBD2 Adapter
- 2.1. Compatibility with Your Vehicle
- 2.2. Compatibility with Your Device (Smartphone, Tablet, Computer)
- 2.3. Supported Protocols
- 2.4. Features and Functionality
- 2.5. Brand and Reviews
- 2.6. Budget
- 3. Step-by-Step Guide to Installing WiFi in Car OBD2
- 3.1. Locate the OBD2 Port in Your Car
- 3.2. Plug in the WiFi OBD2 Adapter
- 3.3. Turn on Your Car’s Ignition
- 3.4. Connect to the Adapter’s WiFi Network
- 3.5. Configure the OBD2 App
- 3.6. Test the Connection
- 3.7. Start Monitoring Vehicle Data
- 4. Troubleshooting Common Connection Issues
- 4.1. Check the Adapter’s Power
- 4.2. Verify WiFi Connectivity
- 4.3. Confirm the Adapter’s IP Address and Port Number
- 4.4. Restart Your Device and the Adapter
- 4.5. Check for App Updates
- 4.6. Test with a Different App
- 4.7. Contact the Adapter Manufacturer
- 5. Advanced Features and Usage Tips
- 5.1. Reading and Clearing Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
- 5.1.1. Understanding DTCs
- 5.1.2. Reading DTCs with an OBD2 App
- 5.1.3. Clearing DTCs with an OBD2 App
- 5.2. Monitoring Real-Time Data
- 5.2.1. Common Parameters to Monitor
- 5.2.2. Customizing the Dashboard
- 5.3. Data Logging and Analysis
- 5.3.1. Recording Data
- 5.3.2. Analyzing Data
- 5.4. Using Advanced Features
- 6. Choosing the Right OBD2 App
- 6.1. Compatibility
- 6.2. Features and Functionality
- 6.3. User Interface
- 6.4. Reviews and Ratings
- 6.5. Cost
- 7. Safety Precautions When Using OBD2 Adapters
- 7.1. Avoid Using While Driving
- 7.2. Monitor Battery Voltage
- 7.3. Be Aware of Potential Security Risks
- 7.4. Follow the Manufacturer’s Instructions
- 8. Maintaining Your WiFi OBD2 Adapter
- 8.1. Keep the Adapter Clean
- 8.2. Store the Adapter Properly
- 8.3. Update the Firmware
- 8.4. Inspect the Connector
- 9. The Future of OBD2 Technology
- 9.1. OBD3
- 9.2. Integration with Connected Car Services
- 9.3. Enhanced Cybersecurity
- 10. Why Choose OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN for Your OBD2 Needs?
- 10.1. Expert Guidance
- 10.2. Comprehensive Information
- 10.3. Wide Range of Products and Services
- 10.4. Contact Information
- FAQ: Installing WiFi in Car OBD2
- 1. What is an OBD2 scanner?
- 2. How do I read OBD2 fault codes?
- 3. What are common car errors and how can they be fixed?
- 4. Is installing a WiFi OBD2 adapter difficult?
- 5. What should I do if my OBD2 scanner won’t connect?
- 6. Can a WiFi OBD2 adapter drain my car battery?
- 7. Are there security risks associated with using a WiFi OBD2 adapter?
- 8. How can OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN help me with my car diagnostics?
- 9. What are the benefits of using a WiFi OBD2 adapter over a wired one?
- 10. What advanced features can I access with a WiFi OBD2 adapter?
1. Understanding the Basics of OBD2 and WiFi Adapters
The On-Board Diagnostics II (OBD2) system is standardized across most modern vehicles, providing access to various engine and performance data. A WiFi OBD2 adapter acts as a bridge, transmitting this data wirelessly to your smartphone, tablet, or computer. This eliminates the need for cumbersome cables and allows for greater flexibility in data monitoring and analysis.
1.1. What is OBD2?
OBD2 is a standardized system that allows you to access data from your vehicle’s computer. The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) mandated it in 1996 for all cars sold in the United States to monitor emissions. Over time, its capabilities have expanded to include various performance metrics. According to a study by the National Institute for Automotive Service Excellence (ASE) in 2022, understanding OBD2 systems is crucial for effective vehicle diagnostics. The OBD2 port is typically located under the dashboard on the driver’s side.
1.2. What is a WiFi OBD2 Adapter?
A WiFi OBD2 adapter is a device that plugs into your car’s OBD2 port and transmits data wirelessly via WiFi. This allows you to connect your smartphone, tablet, or computer to your car’s diagnostic system without the need for cables. These adapters are compatible with various apps and software, providing a user-friendly interface for accessing and interpreting vehicle data.
 WiFi OBD2 adapter
WiFi OBD2 adapter
1.3. Benefits of Using WiFi OBD2
Using a WiFi OBD2 adapter offers several advantages:
- Wireless Connectivity: Eliminates the need for physical cables, providing greater flexibility and convenience.
- Real-Time Data: Access real-time data on your vehicle’s performance, including engine temperature, speed, and fuel efficiency.
- Diagnostic Capabilities: Read and clear diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs), helping you identify and resolve issues quickly.
- Cost-Effective: Often more affordable than professional diagnostic tools, making it accessible to a wider range of users.
1.4. Common Applications for WiFi OBD2
WiFi OBD2 adapters are used in various applications, including:
- Vehicle Diagnostics: Identifying and troubleshooting vehicle issues.
- Performance Monitoring: Tracking engine performance and efficiency.
- Data Logging: Recording vehicle data for later analysis.
- Custom Dashboards: Creating custom displays of vehicle data on your smartphone or tablet.
2. Choosing the Right WiFi OBD2 Adapter
Selecting the right WiFi OBD2 adapter is crucial for ensuring compatibility and performance. Consider the following factors when making your choice.
2.1. Compatibility with Your Vehicle
Ensure that the adapter is compatible with your vehicle’s make, model, and year. While OBD2 is standardized, some adapters may have compatibility issues with certain vehicles. Check the adapter’s specifications and read user reviews to confirm compatibility.
2.2. Compatibility with Your Device (Smartphone, Tablet, Computer)
Verify that the adapter is compatible with your smartphone, tablet, or computer’s operating system (iOS, Android, Windows). Some adapters are designed to work with specific operating systems, so it’s essential to choose one that matches your device.
2.3. Supported Protocols
OBD2 uses several communication protocols, including:
- CAN (Controller Area Network): The most common protocol in modern vehicles.
- ISO 9141-2: Used in many European and Asian vehicles.
- SAE J1850 VPW: Used in some older GM vehicles.
- SAE J1850 PWM: Used in some older Ford vehicles.
Ensure that the adapter supports the protocols used by your vehicle. According to a 2023 report by the Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE), CAN is the dominant protocol in most new vehicles.
2.4. Features and Functionality
Consider the features and functionality offered by the adapter, such as:
- Reading and Clearing DTCs: Essential for diagnosing and resolving vehicle issues.
- Real-Time Data Monitoring: Allows you to monitor various engine parameters in real-time.
- Data Logging: Records vehicle data for later analysis.
- Support for Advanced Parameters: Some adapters support advanced parameters, such as oxygen sensor readings and fuel trim.
2.5. Brand and Reviews
Research different brands and read user reviews to get an idea of the adapter’s reliability and performance. Popular brands include:
- OBDLink: Known for their high-quality and reliable adapters.
- BlueDriver: Offers a comprehensive app with advanced diagnostic features.
- Veepeak: Provides affordable and reliable adapters for basic diagnostics.
2.6. Budget
WiFi OBD2 adapters range in price from around $20 to $200. Determine your budget and choose an adapter that offers the best features and performance within your price range.
3. Step-by-Step Guide to Installing WiFi in Car OBD2
Follow these steps to successfully install and connect your WiFi OBD2 adapter.
3.1. Locate the OBD2 Port in Your Car
The OBD2 port is typically located under the dashboard on the driver’s side. It is a 16-pin connector. Refer to your vehicle’s owner’s manual if you have trouble locating the port.
3.2. Plug in the WiFi OBD2 Adapter
Plug the WiFi OBD2 adapter into the OBD2 port. Ensure that it is securely connected. Some adapters have a power button that you may need to press to turn on the adapter.
3.3. Turn on Your Car’s Ignition
Turn on your car’s ignition without starting the engine. This provides power to the OBD2 port and allows the adapter to communicate with the vehicle’s computer.
3.4. Connect to the Adapter’s WiFi Network
On your smartphone, tablet, or computer, go to the WiFi settings and search for available networks. The WiFi OBD2 adapter should appear as a network with a name like “OBDII,” “WiFi_OBDII,” or something similar. Connect to this network. Most adapters do not require a password, but if prompted, refer to the adapter’s documentation.
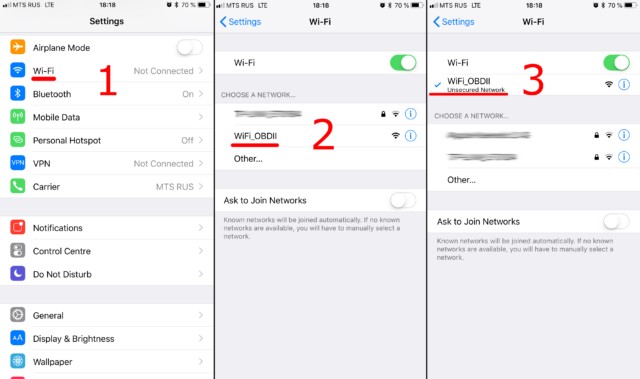 Connect to WiFi Network
Connect to WiFi Network
3.5. Configure the OBD2 App
Download and install an OBD2 app on your device. Popular apps include:
- Car Scanner ELM OBD2
- Torque Pro
- OBD Fusion
- DashCommand
Open the app and go to the settings menu. Select “WiFi” as the connection type. Enter the adapter’s IP address and port number. The default IP address is typically 192.168.0.10, and the port number is 35000. Refer to the adapter’s documentation for the correct settings.
3.6. Test the Connection
In the app, select the option to connect to the OBD2 adapter. The app should establish a connection and begin displaying vehicle data. If the connection fails, double-check the WiFi settings and adapter configuration.
3.7. Start Monitoring Vehicle Data
Once connected, you can start monitoring various vehicle parameters, read and clear DTCs, and perform other diagnostic functions.
4. Troubleshooting Common Connection Issues
If you encounter issues connecting to the WiFi OBD2 adapter, try the following troubleshooting steps.
4.1. Check the Adapter’s Power
Ensure that the adapter is receiving power. Some adapters have a power indicator light that you can check. If the adapter does not have a power button, try unplugging it and plugging it back in.
4.2. Verify WiFi Connectivity
Make sure that your device is connected to the adapter’s WiFi network. Check the WiFi settings on your device to confirm the connection.
4.3. Confirm the Adapter’s IP Address and Port Number
Double-check the adapter’s IP address and port number in the OBD2 app settings. Ensure that they match the settings specified in the adapter’s documentation.
4.4. Restart Your Device and the Adapter
Try restarting your smartphone, tablet, or computer and the OBD2 adapter. This can resolve temporary connectivity issues.
4.5. Check for App Updates
Ensure that you have the latest version of the OBD2 app installed on your device. App updates often include bug fixes and performance improvements that can resolve connectivity issues.
4.6. Test with a Different App
Try using a different OBD2 app to see if the issue is with the app or the adapter. This can help you isolate the problem.
4.7. Contact the Adapter Manufacturer
If you have tried all of the above steps and are still unable to connect, contact the adapter manufacturer for assistance. They may be able to provide specific troubleshooting steps or recommend a replacement adapter.
5. Advanced Features and Usage Tips
Once you have successfully installed and connected your WiFi OBD2 adapter, you can explore advanced features and usage tips to get the most out of your device.
5.1. Reading and Clearing Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
One of the primary functions of an OBD2 adapter is to read and clear DTCs. These codes provide valuable information about potential issues with your vehicle.
5.1.1. Understanding DTCs
DTCs are standardized codes that identify specific issues with your vehicle’s engine, transmission, and other systems. The codes are typically five characters long and follow a specific format. For example, P0300 indicates a random or multiple cylinder misfire. According to a 2021 study by AAA, misfires are a common issue that can be easily diagnosed with an OBD2 scanner.
5.1.2. Reading DTCs with an OBD2 App
Most OBD2 apps allow you to read DTCs with a simple tap of a button. The app will display the codes along with a brief description of the issue.
5.1.3. Clearing DTCs with an OBD2 App
After addressing the issue, you can clear the DTCs using the OBD2 app. This will reset the check engine light and clear the codes from the vehicle’s computer. However, it’s important to note that if the underlying issue is not resolved, the codes may reappear.
5.2. Monitoring Real-Time Data
WiFi OBD2 adapters allow you to monitor various engine parameters in real-time, providing valuable insights into your vehicle’s performance.
5.2.1. Common Parameters to Monitor
- Engine RPM: Revolutions per minute, indicating how fast the engine is running.
- Vehicle Speed: Your current speed in miles per hour or kilometers per hour.
- Engine Temperature: The temperature of the engine coolant.
- Fuel Consumption: The amount of fuel being used by the engine.
- Oxygen Sensor Readings: The readings from the oxygen sensors, which help monitor the air-fuel mixture.
- Fuel Trim: Adjustments made by the engine control unit (ECU) to optimize the air-fuel mixture.
5.2.2. Customizing the Dashboard
Many OBD2 apps allow you to customize the dashboard to display the parameters that are most important to you. You can choose from a variety of gauges, graphs, and digital displays.
5.3. Data Logging and Analysis
Some WiFi OBD2 adapters and apps support data logging, allowing you to record vehicle data for later analysis.
5.3.1. Recording Data
You can record data while driving, capturing various engine parameters over time. This data can be used to identify trends, diagnose issues, and optimize performance.
5.3.2. Analyzing Data
The recorded data can be analyzed using specialized software or the OBD2 app itself. This can help you identify patterns and anomalies that may indicate potential problems.
5.4. Using Advanced Features
Some WiFi OBD2 adapters and apps offer advanced features, such as:
- Performance Testing: Measure your vehicle’s acceleration, braking, and horsepower.
- Fuel Efficiency Analysis: Analyze your driving habits to optimize fuel efficiency.
- Custom PID Support: Access custom parameters specific to your vehicle.
6. Choosing the Right OBD2 App
Selecting the right OBD2 app is crucial for maximizing the functionality of your WiFi OBD2 adapter. Consider the following factors when making your choice.
6.1. Compatibility
Ensure that the app is compatible with your smartphone, tablet, or computer’s operating system (iOS, Android, Windows).
6.2. Features and Functionality
Consider the features and functionality offered by the app, such as:
- Reading and Clearing DTCs: Essential for diagnosing and resolving vehicle issues.
- Real-Time Data Monitoring: Allows you to monitor various engine parameters in real-time.
- Data Logging: Records vehicle data for later analysis.
- Custom Dashboard: Allows you to customize the display of vehicle data.
- Advanced Features: Some apps offer advanced features, such as performance testing and fuel efficiency analysis.
6.3. User Interface
Choose an app with a user-friendly interface that is easy to navigate and understand.
6.4. Reviews and Ratings
Read user reviews and ratings to get an idea of the app’s reliability and performance.
6.5. Cost
OBD2 apps range in price from free to $100 or more. Determine your budget and choose an app that offers the best features and performance within your price range.
7. Safety Precautions When Using OBD2 Adapters
While using an OBD2 adapter is generally safe, it’s important to take certain precautions to avoid potential issues.
7.1. Avoid Using While Driving
Avoid using the OBD2 adapter and app while driving. This can be distracting and increase the risk of an accident. Instead, pull over to a safe location before using the adapter.
7.2. Monitor Battery Voltage
Some OBD2 adapters can drain your car’s battery if left plugged in for extended periods. Monitor your battery voltage and unplug the adapter when not in use.
7.3. Be Aware of Potential Security Risks
Be aware of potential security risks associated with using WiFi OBD2 adapters. Some adapters may be vulnerable to hacking, which could allow unauthorized access to your vehicle’s computer. Choose a reputable brand and keep the adapter’s firmware up to date to minimize these risks. According to a 2020 report by the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA), cybersecurity is a growing concern in the automotive industry.
7.4. Follow the Manufacturer’s Instructions
Always follow the manufacturer’s instructions when using an OBD2 adapter. This will help ensure that you are using the adapter safely and effectively.
8. Maintaining Your WiFi OBD2 Adapter
Proper maintenance can extend the lifespan and performance of your WiFi OBD2 adapter.
8.1. Keep the Adapter Clean
Keep the adapter clean and free of dirt and debris. Use a soft cloth to wipe the adapter regularly.
8.2. Store the Adapter Properly
Store the adapter in a safe and dry location when not in use. Avoid exposing the adapter to extreme temperatures or humidity.
8.3. Update the Firmware
Keep the adapter’s firmware up to date. Firmware updates often include bug fixes and performance improvements.
8.4. Inspect the Connector
Regularly inspect the connector for damage or wear. Replace the adapter if the connector is damaged.
9. The Future of OBD2 Technology
OBD2 technology is constantly evolving, with new features and capabilities being added all the time.
9.1. OBD3
OBD3 is the next generation of on-board diagnostics. It is expected to include more advanced monitoring capabilities and improved security features.
9.2. Integration with Connected Car Services
OBD2 technology is increasingly being integrated with connected car services, allowing for remote diagnostics, vehicle tracking, and other advanced features.
9.3. Enhanced Cybersecurity
As vehicles become more connected, cybersecurity is becoming increasingly important. Future OBD2 systems are expected to include enhanced security features to protect against hacking and unauthorized access.
10. Why Choose OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN for Your OBD2 Needs?
OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN is your trusted resource for all things OBD2. We offer expert guidance, comprehensive information, and a wide range of OBD2 products and services.
10.1. Expert Guidance
Our team of experienced automotive technicians and engineers provides expert guidance on all aspects of OBD2 technology. We can help you choose the right adapter, troubleshoot connection issues, and interpret vehicle data.
10.2. Comprehensive Information
Our website features a wealth of information on OBD2 technology, including detailed articles, step-by-step guides, and troubleshooting tips.
10.3. Wide Range of Products and Services
We offer a wide range of OBD2 products and services, including:
- WiFi OBD2 Adapters: Choose from a variety of high-quality adapters from leading brands.
- OBD2 Apps: Discover the best OBD2 apps for your smartphone, tablet, or computer.
- Diagnostic Services: Get expert diagnostic services from our team of experienced technicians.
At OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN, we are committed to helping you get the most out of your OBD2 system. Contact us today to learn more.
10.4. Contact Information
- Address: 123 Main Street, Los Angeles, CA 90001, United States
- Whatsapp: +1 (641) 206-8880
- Website: OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN
Are you facing challenges with your car’s diagnostics? Do you want to understand your vehicle better and ensure its optimal performance? Contact OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN today via WhatsApp at +1 (641) 206-8880 for expert advice and support on using OBD2 scanners and automotive repair services. Let us help you diagnose and fix your car issues efficiently.
FAQ: Installing WiFi in Car OBD2
1. What is an OBD2 scanner?
An OBD2 scanner is a device used to diagnose issues with your vehicle by reading data from its onboard computer system.
2. How do I read OBD2 fault codes?
Connect the OBD2 scanner to your car’s OBD2 port, turn on the ignition, and use the scanner to read the diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) displayed.
3. What are common car errors and how can they be fixed?
Common car errors include engine misfires, oxygen sensor failures, and catalytic converter issues. Solutions vary but often involve replacing faulty parts or repairing wiring.
4. Is installing a WiFi OBD2 adapter difficult?
No, installing a WiFi OBD2 adapter is straightforward. Plug it into the OBD2 port, connect to its WiFi network, and configure your OBD2 app.
5. What should I do if my OBD2 scanner won’t connect?
Check the adapter’s power, verify WiFi connectivity, confirm the IP address and port number, and ensure the app is updated.
6. Can a WiFi OBD2 adapter drain my car battery?
Yes, if left plugged in for extended periods. Monitor your battery voltage and unplug the adapter when not in use.
7. Are there security risks associated with using a WiFi OBD2 adapter?
Yes, some adapters may be vulnerable to hacking. Choose a reputable brand and keep the adapter’s firmware updated to minimize these risks.
8. How can OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN help me with my car diagnostics?
OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN offers expert guidance, comprehensive information, and a wide range of OBD2 products and diagnostic services.
9. What are the benefits of using a WiFi OBD2 adapter over a wired one?
WiFi OBD2 adapters offer wireless connectivity, greater flexibility, and convenience, eliminating the need for physical cables.
10. What advanced features can I access with a WiFi OBD2 adapter?
You can access real-time data monitoring, data logging, performance testing, and fuel efficiency analysis, depending on the adapter and app.
