The 2013 Chevy Silverado Obd2 Fuse is essential for diagnosing and maintaining your truck’s performance. Understanding its location and function can save you time and money. At OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN, we provide comprehensive guides and services to help you with all your automotive diagnostic needs, ensuring your vehicle runs smoothly. Dive into this article to learn more about your Silverado’s OBD2 fuse, diagnostic procedures, and reliable solutions.
Contents
- 1. Understanding the Importance of the OBD2 Port and Fuse
- 1.1. What is the OBD2 Port?
- 1.2. Role of the OBD2 Fuse
- 1.3. Consequences of a Blown OBD2 Fuse
- 2. Locating the OBD2 Fuse in a 2013 Chevy Silverado
- 2.1. Identifying the Fuse Box Locations
- 2.2. Step-by-Step Guide to Finding the OBD2 Fuse
- 2.3. Common Fuse Box Diagrams for the 2013 Silverado
- 2.3.1. Instrument Panel Fuse Box Diagram
- 2.3.2. Engine Compartment Fuse Box Diagram
- 3. Identifying the Correct Fuse
- 3.1. Reading the Fuse Box Diagram
- 3.2. Typical Fuse Ratings for the OBD2 Port
- 3.3. Visual Inspection of the Fuse
- 4. Replacing a Blown OBD2 Fuse
- 4.1. Tools Needed for Fuse Replacement
- 4.2. Step-by-Step Fuse Replacement Guide
- 4.3. Safety Precautions During Fuse Replacement
- 5. Diagnosing Common Issues Related to the OBD2 Port
- 5.1. No Power to the OBD2 Port
- 5.2. Communication Errors with the Scanner
- 5.3. Intermittent Connectivity
- 6. When to Seek Professional Help
- 6.1. Identifying Complex Electrical Issues
- 6.2. Importance of Professional Diagnostics
- 6.3. How OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN Can Assist
- 7. Common OBD2 Codes for the 2013 Chevy Silverado
- 7.1. P0171 and P0174: System Too Lean
- 7.2. P0300: Random Misfire Detected
- 7.3. P0420: Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold
- 7.4. P0449: Evaporative Emission Control System Vent Valve/Solenoid Circuit Open
- 8. Using an OBD2 Scanner for Diagnostics
- 8.1. Connecting the Scanner to the OBD2 Port
- 8.2. Reading and Interpreting Diagnostic Codes
- 8.3. Clearing Codes and Resetting the Check Engine Light
- 9. Tips for Maintaining Your 2013 Chevy Silverado’s Electrical System
- 9.1. Regular Fuse Inspections
- 9.2. Battery Maintenance
- 9.3. Checking Wiring and Connections
- 10. Advanced Diagnostic Techniques
- 10.1. Using a Multimeter for Electrical Testing
- 10.2. Reading Live Data with an OBD2 Scanner
- 10.3. Performing Component Tests
- 11. Case Studies: OBD2 Fuse Issues in Chevy Silverados
- 11.1. Case Study 1: Intermittent Check Engine Light
- 11.2. Case Study 2: No Communication with the ECM
- 12. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- 12.1. What Does the OBD2 Fuse Protect?
- 12.2. Where Can I Find the Fuse Box Diagram for My Silverado?
- 12.3. Can I Use a Higher Amperage Fuse?
- 12.4. What Should I Do If the New Fuse Blows Immediately?
- 12.5. How Often Should I Check My Fuses?
- 12.6. Can a Blown OBD2 Fuse Affect My Vehicle’s Performance?
- 12.7. Is It Safe to Replace a Fuse Myself?
- 12.8. What Are the Common Causes of a Blown OBD2 Fuse?
- 12.9. How Can OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN Help with OBD2 Issues?
- 12.10. Where Is OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN Located?
- 13. Conclusion: Ensuring Your 2013 Chevy Silverado’s OBD2 Port is Functional
1. Understanding the Importance of the OBD2 Port and Fuse
The OBD2 (On-Board Diagnostics II) port is a standardized interface used to access your vehicle’s computer system. It allows mechanics and vehicle owners to retrieve diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) and monitor various parameters. According to a study by the National Institute for Automotive Service Excellence (ASE), accurate diagnostics can reduce repair times by up to 40%. The OBD2 fuse protects this critical system from electrical overloads, ensuring the scanner can communicate with the vehicle’s computer.
1.1. What is the OBD2 Port?
The OBD2 port, mandated in the United States since 1996, provides access to your vehicle’s engine control unit (ECU). This port allows technicians to read diagnostic codes, reset the check engine light, and monitor real-time data such as engine temperature, speed, and sensor readings. A properly functioning OBD2 system is vital for maintaining vehicle health and performance.
1.2. Role of the OBD2 Fuse
The OBD2 fuse protects the diagnostic port from electrical surges. A blown fuse can prevent the OBD2 scanner from powering on or communicating with the vehicle’s computer. Regular checks of this fuse can prevent unnecessary trips to the mechanic and allow for quicker diagnosis of issues.
1.3. Consequences of a Blown OBD2 Fuse
When the OBD2 fuse blows, several issues can arise:
- The OBD2 scanner won’t power on.
- Communication between the scanner and the vehicle’s computer is lost.
- Check engine light codes cannot be read.
- Emission testing might fail.
2. Locating the OBD2 Fuse in a 2013 Chevy Silverado
Finding the OBD2 fuse is the first step in diagnosing any issues with your OBD2 port. In the 2013 Chevy Silverado, the fuse is typically located in one of the vehicle’s fuse boxes.
2.1. Identifying the Fuse Box Locations
The 2013 Chevy Silverado has three main fuse box locations:
- Instrument Panel Fuse Box: Located on the driver’s side of the instrument panel, behind a cover.
- Center Instrument Panel Fuse Box: Situated underneath the instrument panel, to the left of the steering column.
- Engine Compartment Fuse Box: Found under the hood, usually near the battery.
2.2. Step-by-Step Guide to Finding the OBD2 Fuse
- Consult the Owner’s Manual: The owner’s manual is the best resource for locating the OBD2 fuse. It provides a detailed diagram of each fuse box and identifies the specific fuse for the OBD2 port.
- Check the Instrument Panel Fuse Box: This is the most common location for the OBD2 fuse.
- Inspect the Center Instrument Panel Fuse Box: If the fuse isn’t in the instrument panel fuse box, check here next.
- Examine the Engine Compartment Fuse Box: Although less common, the OBD2 fuse could be located in the engine compartment fuse box.
- Use a Fuse Puller: Use a fuse puller tool to safely remove the fuse for inspection. This tool helps prevent damage to the fuse box and other components.
2.3. Common Fuse Box Diagrams for the 2013 Silverado
Below are typical fuse box diagrams. Note that these can vary slightly based on the Silverado’s trim and options. Always refer to your owner’s manual for the most accurate information.
2.3.1. Instrument Panel Fuse Box Diagram
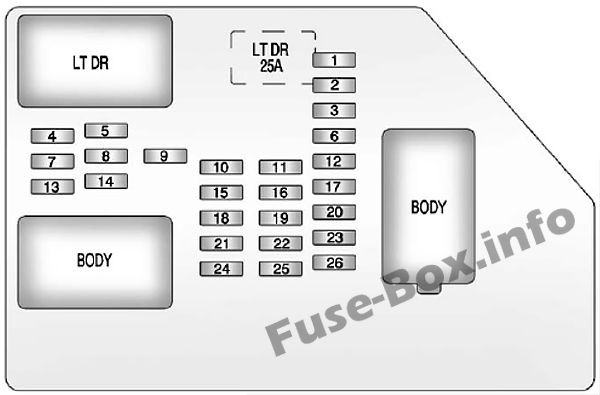 Instrument panel fuse box diagram: Chevrolet Silverado (2007, 2008, 2009, 2010, 2011, 2012, 2013)
Instrument panel fuse box diagram: Chevrolet Silverado (2007, 2008, 2009, 2010, 2011, 2012, 2013)
2.3.2. Engine Compartment Fuse Box Diagram
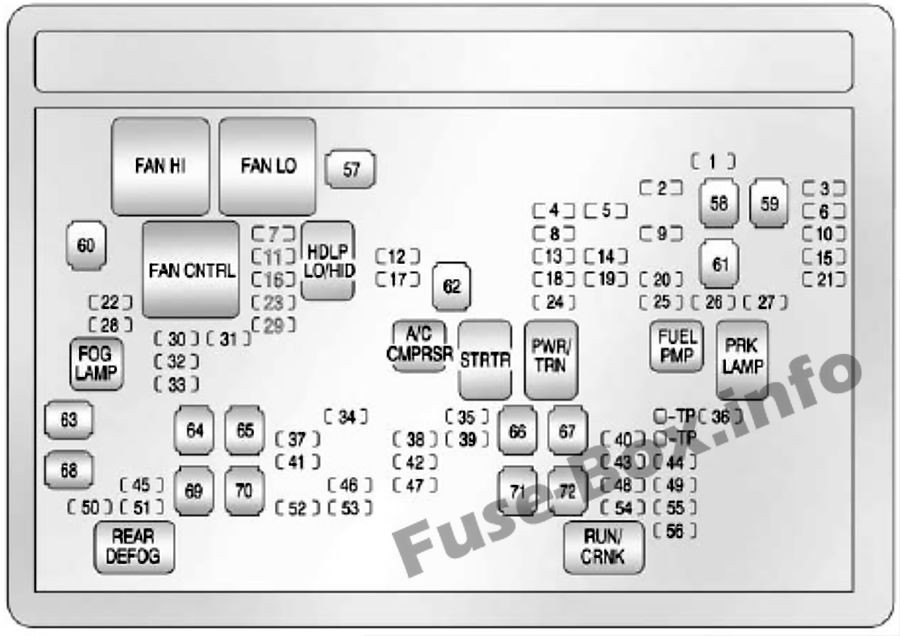 Under-hood fuse box diagram: Chevrolet Silverado (2007, 2008, 2009, 2010, 2011, 2012, 2013)
Under-hood fuse box diagram: Chevrolet Silverado (2007, 2008, 2009, 2010, 2011, 2012, 2013)
3. Identifying the Correct Fuse
Once you’ve located the fuse box, identifying the correct fuse is crucial. The fuse is typically labeled or identified in the fuse box diagram.
3.1. Reading the Fuse Box Diagram
The fuse box diagram provides a layout of each fuse and its corresponding function. Look for labels such as “OBD,” “DLC (Data Link Connector),” or “Diagnostic Port.”
3.2. Typical Fuse Ratings for the OBD2 Port
The OBD2 fuse typically has a rating between 10 and 20 amps. Check your owner’s manual for the specific amperage for your 2013 Chevy Silverado.
3.3. Visual Inspection of the Fuse
After locating the fuse, visually inspect it. A blown fuse will have a broken filament inside. If the filament is intact, the fuse is likely good.
4. Replacing a Blown OBD2 Fuse
Replacing a blown fuse is a straightforward process. Follow these steps to ensure a successful replacement.
4.1. Tools Needed for Fuse Replacement
- New fuse with the correct amperage
- Fuse puller tool
- Owner’s manual or fuse box diagram
4.2. Step-by-Step Fuse Replacement Guide
- Turn Off the Ignition: Ensure the vehicle’s ignition is turned off before replacing the fuse.
- Locate the Fuse Box: Find the fuse box containing the OBD2 fuse.
- Remove the Fuse Box Cover: Open the fuse box cover to access the fuses.
- Identify the Blown Fuse: Use the fuse box diagram to locate the OBD2 fuse.
- Remove the Blown Fuse: Use the fuse puller to carefully remove the blown fuse.
- Inspect the Fuse: Visually confirm that the filament is broken.
- Insert the New Fuse: Insert the new fuse with the correct amperage into the empty slot.
- Replace the Fuse Box Cover: Close the fuse box cover.
- Test the OBD2 Port: Plug in your OBD2 scanner to verify that it now powers on and communicates with the vehicle.
4.3. Safety Precautions During Fuse Replacement
- Always turn off the ignition before replacing a fuse.
- Use a fuse puller to avoid damaging the fuse box.
- Replace the fuse with one of the same amperage rating. Using a higher amperage fuse can damage the vehicle’s electrical system.
- If the new fuse blows immediately, there may be an underlying electrical issue that needs professional attention.
5. Diagnosing Common Issues Related to the OBD2 Port
If replacing the fuse doesn’t solve the problem, further diagnosis may be necessary. Several common issues can affect the OBD2 port’s functionality.
5.1. No Power to the OBD2 Port
If the OBD2 scanner still doesn’t power on after replacing the fuse, the issue might be with the wiring or the port itself.
- Check the Wiring: Inspect the wiring connected to the OBD2 port for any signs of damage or corrosion.
- Test the Port: Use a multimeter to check for voltage at the OBD2 port. There should be 12V between pin 16 (power) and pin 4 or 5 (ground).
5.2. Communication Errors with the Scanner
If the scanner powers on but can’t communicate with the vehicle, the problem might be with the scanner, the vehicle’s computer, or the wiring between them.
- Try a Different Scanner: Test the OBD2 port with a different scanner to rule out a scanner issue.
- Check the Vehicle’s Computer: A malfunctioning ECU can prevent communication with the scanner.
- Inspect the CAN Bus Wiring: The Controller Area Network (CAN) bus wiring is crucial for communication. Check for any breaks or shorts in the wiring.
5.3. Intermittent Connectivity
Intermittent connectivity issues can be frustrating. These are often caused by loose connections or corroded terminals.
- Clean the Terminals: Use aContact cleaner to clean the terminals in the OBD2 port and the scanner connector.
- Check for Loose Connections: Ensure all connections are tight and secure.
6. When to Seek Professional Help
While many OBD2 port issues can be resolved with simple troubleshooting, some problems require professional assistance.
6.1. Identifying Complex Electrical Issues
If you’re not comfortable working with electrical systems or if the problem persists after basic troubleshooting, it’s best to seek professional help. Complex electrical issues can be difficult to diagnose and repair without specialized tools and knowledge.
6.2. Importance of Professional Diagnostics
Professional mechanics have the expertise and equipment to accurately diagnose and repair complex automotive issues. They can identify problems that might be missed by a novice, preventing further damage to your vehicle. According to the Bureau of Labor Statistics, professionally trained automotive service technicians have a higher success rate in diagnosing and repairing vehicle issues.
6.3. How OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN Can Assist
At OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN, we offer comprehensive diagnostic services and support. Our team of experienced technicians can help you troubleshoot OBD2 port issues, read and interpret diagnostic codes, and provide expert repair advice. Contact us at +1 (641) 206-8880 or visit our location at 123 Main Street, Los Angeles, CA 90001, United States, for assistance.
7. Common OBD2 Codes for the 2013 Chevy Silverado
Understanding common OBD2 codes can help you diagnose issues more effectively. Here are some of the most frequent codes for the 2013 Chevy Silverado:
7.1. P0171 and P0174: System Too Lean
These codes indicate that the engine is running lean, meaning there is too much air and not enough fuel in the air-fuel mixture.
- Causes: Vacuum leaks, faulty oxygen sensors, defective mass airflow sensor, fuel delivery issues.
- Symptoms: Rough idling, poor acceleration, check engine light.
- Troubleshooting: Check for vacuum leaks, test the oxygen sensors and mass airflow sensor, inspect the fuel pump and fuel injectors.
7.2. P0300: Random Misfire Detected
This code indicates that the engine is experiencing random misfires, which can affect performance and fuel economy.
- Causes: Faulty spark plugs, defective ignition coils, vacuum leaks, low fuel pressure.
- Symptoms: Rough idling, poor acceleration, check engine light.
- Troubleshooting: Check the spark plugs and ignition coils, look for vacuum leaks, test the fuel pressure.
7.3. P0420: Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold
This code indicates that the catalytic converter is not functioning efficiently, which can lead to increased emissions.
- Causes: Faulty catalytic converter, defective oxygen sensors, exhaust leaks.
- Symptoms: Check engine light, reduced fuel economy, poor performance.
- Troubleshooting: Test the oxygen sensors, inspect the exhaust system for leaks, check the catalytic converter.
7.4. P0449: Evaporative Emission Control System Vent Valve/Solenoid Circuit Open
This code indicates a problem with the evaporative emission control system, which can affect fuel efficiency and emissions.
- Causes: Faulty vent valve/solenoid, damaged wiring, defective purge valve.
- Symptoms: Check engine light, fuel odor.
- Troubleshooting: Check the vent valve/solenoid and purge valve, inspect the wiring.
8. Using an OBD2 Scanner for Diagnostics
An OBD2 scanner is an essential tool for diagnosing automotive issues. Here’s how to use it effectively.
8.1. Connecting the Scanner to the OBD2 Port
- Locate the OBD2 Port: Find the OBD2 port under the dashboard on the driver’s side.
- Plug in the Scanner: Connect the OBD2 scanner to the port.
- Turn On the Ignition: Turn the ignition to the “on” position without starting the engine.
- Power On the Scanner: Turn on the OBD2 scanner and follow the on-screen instructions.
8.2. Reading and Interpreting Diagnostic Codes
- Read the Codes: Use the scanner to read any stored diagnostic codes.
- Record the Codes: Write down the codes for reference.
- Interpret the Codes: Use a reliable source, such as OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN, to interpret the meaning of each code.
- Troubleshoot the Issues: Follow the troubleshooting steps for each code to diagnose and repair the underlying issues.
8.3. Clearing Codes and Resetting the Check Engine Light
- Repair the Issues: Fix any problems identified by the diagnostic codes.
- Clear the Codes: Use the scanner to clear the stored diagnostic codes.
- Verify the Repair: Start the engine and monitor the vehicle to ensure the check engine light does not return.
9. Tips for Maintaining Your 2013 Chevy Silverado’s Electrical System
Proper maintenance of your vehicle’s electrical system can prevent many common issues.
9.1. Regular Fuse Inspections
Regularly inspect the fuses in your vehicle to ensure they are in good condition. Replace any blown or damaged fuses promptly.
9.2. Battery Maintenance
A healthy battery is crucial for the proper functioning of the electrical system.
- Clean the Terminals: Clean the battery terminals regularly to remove corrosion.
- Check the Voltage: Use a multimeter to check the battery voltage. It should be around 12.6 volts when the engine is off and between 13.7 and 14.7 volts when the engine is running.
- Replace as Needed: Replace the battery every 3-5 years or as needed.
9.3. Checking Wiring and Connections
Inspect the wiring and connections in your vehicle for any signs of damage or corrosion. Repair or replace any damaged wiring to prevent electrical issues.
10. Advanced Diagnostic Techniques
For more complex issues, advanced diagnostic techniques may be necessary.
10.1. Using a Multimeter for Electrical Testing
A multimeter is a versatile tool for testing electrical circuits. It can be used to measure voltage, current, and resistance.
- Voltage Testing: Use a multimeter to check for voltage at various points in the electrical system.
- Continuity Testing: Use a multimeter to check for continuity in wires and circuits.
- Resistance Testing: Use a multimeter to measure the resistance of components such as sensors and switches.
10.2. Reading Live Data with an OBD2 Scanner
OBD2 scanners can display live data from the vehicle’s sensors, providing valuable information for diagnosing issues.
- Monitor Sensor Readings: Use the scanner to monitor the readings from sensors such as the oxygen sensors, mass airflow sensor, and throttle position sensor.
- Analyze Data: Analyze the data to identify any anomalies or out-of-range values.
10.3. Performing Component Tests
Component tests involve testing individual components to verify that they are functioning correctly.
- Test Sensors: Use a multimeter or scanner to test the sensors in the vehicle.
- Test Actuators: Use a scanner to activate actuators such as the fuel injectors and solenoids.
11. Case Studies: OBD2 Fuse Issues in Chevy Silverados
Here are a couple of case studies to illustrate how OBD2 fuse issues can manifest and be resolved.
11.1. Case Study 1: Intermittent Check Engine Light
A 2013 Chevy Silverado owner experienced an intermittent check engine light. The OBD2 scanner would sometimes connect and sometimes not.
- Diagnosis: The OBD2 fuse was found to be loose in its socket, causing intermittent connectivity.
- Solution: The fuse was replaced and the socket was tightened, resolving the issue.
11.2. Case Study 2: No Communication with the ECM
A 2013 Chevy Silverado had no communication with the engine control module (ECM). The OBD2 scanner would not power on.
- Diagnosis: The OBD2 fuse was blown. Replacing the fuse allowed the scanner to power on, but communication with the ECM was still not possible. Further investigation revealed a short in the CAN bus wiring.
- Solution: The short in the CAN bus wiring was repaired, restoring communication with the ECM.
12. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
12.1. What Does the OBD2 Fuse Protect?
The OBD2 fuse protects the diagnostic port and the vehicle’s computer system from electrical overloads.
12.2. Where Can I Find the Fuse Box Diagram for My Silverado?
The fuse box diagram can be found in your vehicle’s owner’s manual or on a sticker inside the fuse box cover.
12.3. Can I Use a Higher Amperage Fuse?
No, never use a higher amperage fuse than specified. Doing so can damage the vehicle’s electrical system and create a fire hazard.
12.4. What Should I Do If the New Fuse Blows Immediately?
If the new fuse blows immediately, there may be an underlying electrical issue that needs professional attention.
12.5. How Often Should I Check My Fuses?
You should check your fuses regularly, especially if you experience any electrical issues or if your OBD2 scanner is not working.
12.6. Can a Blown OBD2 Fuse Affect My Vehicle’s Performance?
Yes, a blown OBD2 fuse can prevent you from diagnosing and addressing performance issues, which can indirectly affect your vehicle’s performance.
12.7. Is It Safe to Replace a Fuse Myself?
Yes, replacing a fuse is generally safe as long as you follow the proper precautions and use the correct amperage fuse.
12.8. What Are the Common Causes of a Blown OBD2 Fuse?
Common causes include electrical surges, short circuits, and faulty wiring.
12.9. How Can OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN Help with OBD2 Issues?
OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN offers comprehensive diagnostic services, expert repair advice, and a wide range of OBD2 scanners and tools to help you troubleshoot and resolve OBD2 issues.
12.10. Where Is OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN Located?
OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN is located at 123 Main Street, Los Angeles, CA 90001, United States. You can also contact us at +1 (641) 206-8880.
13. Conclusion: Ensuring Your 2013 Chevy Silverado’s OBD2 Port is Functional
Maintaining a functional OBD2 port is crucial for diagnosing and resolving issues with your 2013 Chevy Silverado. By understanding the location of the OBD2 fuse, knowing how to replace it, and recognizing common issues, you can keep your truck running smoothly. Trust OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN to provide the expertise, tools, and support you need to maintain your vehicle’s diagnostic capabilities.
If you encounter any issues with your OBD2 port or need assistance with diagnostics, don’t hesitate to contact us. Call us at +1 (641) 206-8880 or visit our website at OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN for more information. Our team is ready to help you keep your Chevy Silverado in top condition. We are located at 123 Main Street, Los Angeles, CA 90001, United States. Let OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN be your trusted partner in automotive diagnostics and repair.
