The best 2004 Cr V Obd2 Torque Applications are diagnostic tools that empower you to understand your vehicle’s health, identify issues, and potentially save on repair costs, and you can find detailed guidance and assistance at OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN. By utilizing the appropriate OBD2 scanner and torque application, you can effectively monitor engine performance, read diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs), and gain valuable insights into your 2004 CR-V. These tools can also provide real-time data, which is helpful for troubleshooting and maintaining your vehicle’s optimal performance.
Contents
- 1. Understanding OBD2 and Your 2004 CR-V
- 1.1. What is OBD2?
- 1.2. How Does OBD2 Work in a 2004 CR-V?
- 1.3. Benefits of Using OBD2 with Your CR-V
- 2. Key Features to Look for in an OBD2 Scanner
- 2.1. Compatibility with 2004 CR-V
- 2.2. Reading and Clearing DTCs
- 2.3. Real-Time Data Monitoring
- 2.4. Freeze Frame Data
- 2.5. User-Friendliness
- 2.6. Wireless Connectivity (Bluetooth/Wi-Fi)
- 3. Top OBD2 Scanners for the 2004 CR-V
- 3.1. BlueDriver Bluetooth Professional OBDII Scan Tool
- 3.2. Innova 3100j Diagnostic Scan Tool
- 3.3. Autel MaxiCOM MK808
- 3.4. Foxwell NT301 OBD2 Scanner
- 3.5. Launch CRP129E OBD2 Scanner
- 4. Torque Pro App and OBD2 Adapters
- 4.1. What is Torque Pro?
- 4.2. Recommended OBD2 Adapters for Torque Pro
- 4.3. Setting Up Torque Pro with Your 2004 CR-V
- 5. Common OBD2 Codes for the 2004 CR-V
- 5.1. P0171 – System Too Lean (Bank 1)
- 5.2. P0300 – Random Misfire Detected
- 5.3. P0420 – Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold (Bank 1)
- 5.4. P0135 – O2 Sensor Heater Circuit Malfunction (Bank 1, Sensor 1)
- 5.5. P0401 – Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) Flow Insufficient Detected
- 6. Step-by-Step Guide to Diagnosing Issues with OBD2
- 6.1. Connect the OBD2 Scanner
- 6.2. Turn on the Ignition
- 6.3. Read the Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
- 6.4. Research the Codes
- 6.5. Inspect the Vehicle
- 6.6. Test the Components
- 6.7. Repair or Replace Faulty Components
- 7. Advanced OBD2 Functions and Capabilities
- 7.1. Bidirectional Control
- 7.2. Actuation Tests
- 7.3. Special Functions
- 7.4. Live Data Streaming
- 8. Maintaining Your 2004 CR-V with OBD2
- 8.1. Regular Scanning for DTCs
- 8.2. Monitoring Engine Performance
- 8.3. Performing Routine Maintenance
- 8.4. Keeping Records of DTCs and Repairs
- 9. Choosing the Right OBD2 Software
- 9.1. Key Considerations for OBD2 Software
- 9.2. Popular OBD2 Software Options
- 10. Tips for Interpreting OBD2 Data
- 10.1. Understanding Sensor Readings
- 10.2. Identifying Patterns
- 10.3. Using Freeze Frame Data
- 10.4. Consulting Repair Manuals
- 10.5. Seeking Professional Help
- 11. Common Mistakes to Avoid When Using OBD2 Scanners
- 11.1. Ignoring Basic Maintenance
- 11.2. Misinterpreting DTCs
- 11.3. Failing to Clear DTCs After Repairs
- 11.4. Neglecting Software Updates
- 11.5. Using Incompatible Adapters
- 12. OBD2 and Emissions Testing
- 12.1. How OBD2 Systems Aid in Emissions Testing
- 12.2. Preparing Your 2004 CR-V for Emissions Testing
- 12.3. What Happens if Your CR-V Fails the Emissions Test?
- 13. OBD2 and Fuel Efficiency
- 13.1. Monitoring Fuel-Related Parameters
- 13.2. Identifying Issues Affecting Fuel Economy
- 13.3. Optimizing Driving Habits
- 14. OBD2 Resources and Communities
- 14.1. Online Forums
- 14.2. Repair Manuals
- 14.3. Diagnostic Software
- 14.4. Professional Mechanics
- 15. The Future of OBD2 Technology
- 15.1. Enhanced Diagnostics
- 15.2. Wireless Connectivity
- 15.3. Cloud-Based Diagnostics
- 15.4. Integration with Advanced Driver-Assistance Systems (ADAS)
- 16. Understanding Generic vs. Enhanced OBD2 Codes
- 16.1. What are Generic OBD2 Codes?
- 16.2. What are Enhanced OBD2 Codes?
- 16.3. How to Use Both Types of Codes Effectively
- 17. The Role of Oxygen Sensors in OBD2 Diagnostics
- 17.1. How Oxygen Sensors Work
- 17.2. Common Oxygen Sensor Codes
- 17.3. Diagnosing Oxygen Sensor Issues
- 18. Using Freeze Frame Data for Intermittent Problems
- 18.1. What is Freeze Frame Data?
- 18.2. How to Access Freeze Frame Data
- 18.3. Interpreting Freeze Frame Data
- 19. Resetting the Check Engine Light with OBD2
- 19.1. When to Reset the Check Engine Light
- 19.2. How to Reset the Check Engine Light
- 19.3. What to Do If the Light Comes Back On
- 20. OBD2 and Vehicle Security
- 20.1. How OBD2 Can Be Used for Security
- 20.2. Potential Security Risks
- 20.3. Protecting Your Vehicle from OBD2-Related Security Threats
- FAQ: 2004 CR V OBD2 Torque Applications
- What exactly is an OBD2 scanner, and how does it benefit me?
- How do I choose the right OBD2 scanner for my 2004 CR-V?
- What are some common OBD2 codes I might encounter with my 2004 CR-V, and what do they mean?
- Can I use the Torque Pro app with my OBD2 scanner on my 2004 CR-V?
- How do I interpret the data from my OBD2 scanner to diagnose problems accurately?
- What is freeze frame data, and how can it help with diagnosing intermittent issues in my 2004 CR-V?
- How do I reset the check engine light on my 2004 CR-V after fixing a problem?
- What are the potential security risks associated with using an OBD2 port, and how can I protect my vehicle?
- How can OBD2 scanners help me improve my 2004 CR-V’s fuel efficiency?
- Where can I find reliable resources and communities to learn more about OBD2 systems and automotive repair?
1. Understanding OBD2 and Your 2004 CR-V
The On-Board Diagnostics II (OBD2) system is a standardized system in most vehicles manufactured after 1996, including your 2004 Honda CR-V. It monitors various components of your car, such as the engine, transmission, and emissions systems. When a problem is detected, the system generates a diagnostic trouble code (DTC) that can be read using an OBD2 scanner, offering valuable insights into your vehicle’s operational status.
1.1. What is OBD2?
OBD2, or On-Board Diagnostics II, is a standardized system that monitors a vehicle’s engine, transmission, and emissions systems. According to a study by the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) from the Office of Transportation and Air Quality, OBD2 systems were mandated in all cars and light trucks sold in the United States starting in 1996 to ensure vehicles meet emissions standards and to allow for easier diagnosis and repair. When a problem is detected, the OBD2 system generates a diagnostic trouble code (DTC).
1.2. How Does OBD2 Work in a 2004 CR-V?
In your 2004 CR-V, the OBD2 system uses sensors to monitor different parameters, such as engine temperature, oxygen levels, and throttle position. If any of these parameters fall outside the acceptable range, the system stores a DTC. The engine control unit (ECU) illuminates the check engine light on the dashboard to alert the driver.
1.3. Benefits of Using OBD2 with Your CR-V
Using an OBD2 scanner with your 2004 CR-V offers several benefits:
- Early Detection of Problems: Identifies issues before they become major problems.
- Cost Savings: Reduces repair costs by allowing you to diagnose and fix issues yourself or provide accurate information to a mechanic.
- Performance Monitoring: Monitors engine performance and ensures optimal fuel efficiency.
2. Key Features to Look for in an OBD2 Scanner
When choosing an OBD2 scanner for your 2004 CR-V, consider the following features to ensure it meets your needs:
2.1. Compatibility with 2004 CR-V
Ensure the scanner is compatible with your specific vehicle model and year. Most OBD2 scanners support a wide range of vehicles, but it’s always best to verify.
2.2. Reading and Clearing DTCs
The scanner should be able to read and clear diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs). This allows you to identify the problem and reset the check engine light after making repairs.
2.3. Real-Time Data Monitoring
Real-time data monitoring allows you to view live sensor data, such as engine temperature, RPM, and oxygen sensor readings. This is helpful for diagnosing intermittent issues and monitoring engine performance.
2.4. Freeze Frame Data
Freeze frame data captures the sensor data at the moment a DTC is triggered. This information can help you understand the conditions under which the problem occurred.
2.5. User-Friendliness
Choose a scanner with an intuitive interface and clear instructions. A user-friendly scanner will save you time and frustration.
2.6. Wireless Connectivity (Bluetooth/Wi-Fi)
Some scanners offer wireless connectivity, allowing you to connect to your smartphone or tablet. This can be convenient for viewing data and generating reports.
3. Top OBD2 Scanners for the 2004 CR-V
Here are some of the top OBD2 scanners that work well with the 2004 Honda CR-V, offering a range of features and capabilities:
3.1. BlueDriver Bluetooth Professional OBDII Scan Tool
The BlueDriver scanner is a popular choice due to its comprehensive features and user-friendly interface. It connects to your smartphone via Bluetooth and provides detailed diagnostic reports.
 BlueDriver Bluetooth Professional OBDII Scan Tool, capturing detailed diagnostic reports via Bluetooth
BlueDriver Bluetooth Professional OBDII Scan Tool, capturing detailed diagnostic reports via Bluetooth
- Pros:
- Comprehensive diagnostic reports
- Bluetooth connectivity
- User-friendly app
- Cons:
- Requires a smartphone or tablet
- Some advanced features may require a subscription
3.2. Innova 3100j Diagnostic Scan Tool
The Innova 3100j is a reliable and easy-to-use scan tool that provides basic OBD2 functionality. It’s a good option for DIYers who need to read and clear DTCs.
- Pros:
- Affordable
- Easy to use
- Reads and clears DTCs
- Cons:
- Limited advanced features
- No wireless connectivity
3.3. Autel MaxiCOM MK808
The Autel MaxiCOM MK808 is an advanced scan tool that offers a wide range of features, including bidirectional control, actuation tests, and special functions. It’s suitable for professional mechanics and advanced DIYers.
- Pros:
- Advanced diagnostic features
- Bidirectional control
- Actuation tests
- Cons:
- Higher price point
- May be overwhelming for beginners
3.4. Foxwell NT301 OBD2 Scanner
The Foxwell NT301 is a budget-friendly option that offers a good balance of features and performance. It reads and clears DTCs, displays freeze frame data, and performs I/M readiness tests.
- Pros:
- Affordable
- Reads and clears DTCs
- Displays freeze frame data
- Cons:
- Limited advanced features
- No wireless connectivity
3.5. Launch CRP129E OBD2 Scanner
The Launch CRP129E is a versatile scanner that supports OBD2 diagnostics as well as ABS, SRS, transmission, and engine systems. It also offers features like oil reset, brake reset, and throttle adaptation.
- Pros:
- Supports multiple systems
- Special reset functions
- Color display
- Cons:
- Mid-range price point
- Some features may require updates
4. Torque Pro App and OBD2 Adapters
Torque Pro is a popular Android app that turns your smartphone or tablet into a powerful diagnostic tool. When paired with an OBD2 adapter, it can read DTCs, monitor real-time data, and perform other diagnostic functions.
4.1. What is Torque Pro?
Torque Pro is an Android app that connects to your vehicle’s OBD2 system via an OBD2 adapter. It allows you to monitor various parameters, read DTCs, and customize dashboards to display the data you’re most interested in.
4.2. Recommended OBD2 Adapters for Torque Pro
To use Torque Pro with your 2004 CR-V, you’ll need an OBD2 adapter that is compatible with the app. Here are some recommended adapters:
- BAFX Products Bluetooth OBD2 Adapter: This adapter is known for its reliability and compatibility with Torque Pro.
- Veepeak Mini Bluetooth OBD2 Scanner: A compact and affordable adapter that works well with Torque Pro.
- OBDLink MX+ Bluetooth OBD2 Scanner: A high-performance adapter that offers advanced features and fast data transfer.
4.3. Setting Up Torque Pro with Your 2004 CR-V
Setting up Torque Pro with your 2004 CR-V is a straightforward process:
- Plug in the OBD2 Adapter: Connect the OBD2 adapter to the OBD2 port in your CR-V.
- Pair with Your Device: Pair the adapter with your Android smartphone or tablet via Bluetooth.
- Configure Torque Pro: Open Torque Pro and configure the app to connect to the adapter.
- Start Monitoring: Begin monitoring real-time data and reading DTCs.
5. Common OBD2 Codes for the 2004 CR-V
Understanding common OBD2 codes for your 2004 CR-V can help you diagnose and fix issues more effectively. Here are some of the most common codes and their meanings:
5.1. P0171 – System Too Lean (Bank 1)
This code indicates that the engine is running lean, meaning there is too much air and not enough fuel in the air-fuel mixture. Possible causes include vacuum leaks, a faulty oxygen sensor, or a malfunctioning fuel injector.
5.2. P0300 – Random Misfire Detected
This code indicates that the engine is misfiring randomly. Possible causes include faulty spark plugs, ignition coils, or a vacuum leak.
5.3. P0420 – Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold (Bank 1)
This code indicates that the catalytic converter is not functioning efficiently. Possible causes include a faulty catalytic converter, oxygen sensor issues, or exhaust leaks.
5.4. P0135 – O2 Sensor Heater Circuit Malfunction (Bank 1, Sensor 1)
This code indicates that the oxygen sensor heater circuit is malfunctioning. Possible causes include a faulty oxygen sensor or wiring issues.
5.5. P0401 – Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) Flow Insufficient Detected
This code indicates that the EGR system is not flowing enough exhaust gas. Possible causes include a clogged EGR valve or a faulty EGR solenoid.
6. Step-by-Step Guide to Diagnosing Issues with OBD2
Diagnosing issues with your 2004 CR-V using an OBD2 scanner involves a systematic approach. Follow these steps to effectively identify and address problems:
6.1. Connect the OBD2 Scanner
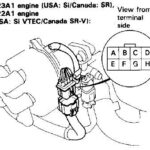
Plug the OBD2 scanner into the OBD2 port, typically located under the dashboard on the driver’s side.
6.2. Turn on the Ignition
Turn the ignition key to the “on” position without starting the engine.
6.3. Read the Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
Use the scanner to read the DTCs stored in the vehicle’s computer. Record the codes and their descriptions.
6.4. Research the Codes
Research the meaning of each DTC using online resources, repair manuals, or diagnostic software. Understand the potential causes and symptoms associated with each code.
6.5. Inspect the Vehicle
Inspect the vehicle for any obvious signs of damage or malfunction. Check for vacuum leaks, loose connections, and damaged components.
6.6. Test the Components
Use a multimeter or other diagnostic tools to test the components related to the DTCs. Verify that the sensors and actuators are functioning properly.
6.7. Repair or Replace Faulty Components
Repair or replace any faulty components as needed. Clear the DTCs and test the vehicle to ensure the problem is resolved.
 Inspecting the vehicle for any obvious signs of damage or malfunction
Inspecting the vehicle for any obvious signs of damage or malfunction
7. Advanced OBD2 Functions and Capabilities
Beyond reading and clearing DTCs, advanced OBD2 scanners offer additional functions and capabilities that can help you diagnose and repair complex issues.
7.1. Bidirectional Control
Bidirectional control allows you to send commands to the vehicle’s computer to activate or deactivate certain components. This can be useful for testing actuators, solenoids, and other devices.
7.2. Actuation Tests
Actuation tests allow you to activate specific components to verify their functionality. For example, you can activate the fuel pump, EGR valve, or cooling fan to check if they are working properly.
7.3. Special Functions
Special functions include features like oil reset, brake reset, and throttle adaptation. These functions can help you perform routine maintenance tasks and reset the vehicle’s computer after making repairs.
7.4. Live Data Streaming
Live data streaming allows you to view real-time sensor data and monitor engine performance. This can be helpful for diagnosing intermittent issues and identifying performance problems.
8. Maintaining Your 2004 CR-V with OBD2
Using an OBD2 scanner can help you maintain your 2004 CR-V and ensure it runs smoothly for years to come. Here are some tips for using OBD2 to maintain your vehicle:
8.1. Regular Scanning for DTCs
Scan your vehicle for DTCs regularly, even if the check engine light is not illuminated. This can help you identify potential issues before they become major problems.
8.2. Monitoring Engine Performance
Use the OBD2 scanner to monitor engine performance and ensure optimal fuel efficiency. Check parameters like engine temperature, RPM, and oxygen sensor readings.
8.3. Performing Routine Maintenance
Use the OBD2 scanner to perform routine maintenance tasks, such as resetting the oil life monitor and performing throttle adaptation.
8.4. Keeping Records of DTCs and Repairs
Keep records of all DTCs and repairs performed on your vehicle. This can help you track recurring issues and identify patterns.
9. Choosing the Right OBD2 Software
Selecting the right OBD2 software is crucial for maximizing the capabilities of your OBD2 scanner. There are numerous software options available, each offering unique features and benefits.
9.1. Key Considerations for OBD2 Software
- Compatibility: Ensure the software is compatible with your OBD2 scanner and operating system.
- Features: Consider the features offered by the software, such as DTC lookup, live data monitoring, and advanced diagnostics.
- User Interface: Choose software with an intuitive and user-friendly interface.
- Updates: Ensure the software is regularly updated to support new vehicles and features.
- Cost: Compare the cost of different software options and choose one that fits your budget.
9.2. Popular OBD2 Software Options
- Torque Pro: A popular Android app that offers a wide range of features for OBD2 diagnostics.
- OBD Auto Doctor: A versatile software that supports multiple platforms and offers advanced diagnostic features.
- ScanXL Pro: A professional-grade software that offers advanced diagnostics and customization options.
- FORScan: A powerful software designed specifically for Ford, Lincoln, and Mercury vehicles.
- DashCommand: A customizable app that allows you to create personalized dashboards and monitor real-time data.
10. Tips for Interpreting OBD2 Data
Interpreting OBD2 data can be challenging, but with the right knowledge and tools, you can gain valuable insights into your vehicle’s health. Here are some tips for interpreting OBD2 data:
10.1. Understanding Sensor Readings
Learn how to interpret sensor readings, such as oxygen sensor voltages, engine temperature, and RPM. Understand the normal ranges for these parameters and identify any deviations.
10.2. Identifying Patterns
Look for patterns in the data that may indicate a problem. For example, a consistently high oxygen sensor voltage may indicate a lean condition.
10.3. Using Freeze Frame Data
Use freeze frame data to understand the conditions under which a DTC was triggered. This information can help you identify the root cause of the problem.
10.4. Consulting Repair Manuals
Consult repair manuals and online resources for information on interpreting OBD2 data and diagnosing specific issues.
10.5. Seeking Professional Help
If you are unsure about interpreting OBD2 data or diagnosing a problem, seek professional help from a qualified mechanic.
 Consulting repair manuals and online resources for information on interpreting OBD2 data
Consulting repair manuals and online resources for information on interpreting OBD2 data
11. Common Mistakes to Avoid When Using OBD2 Scanners
Using OBD2 scanners can be incredibly helpful, but it’s easy to make mistakes that can lead to misdiagnosis or further problems. Here are some common mistakes to avoid:
11.1. Ignoring Basic Maintenance
Don’t rely solely on the OBD2 scanner to diagnose problems. Perform regular maintenance tasks, such as checking fluid levels, inspecting belts and hoses, and changing spark plugs.
11.2. Misinterpreting DTCs
Don’t assume that a DTC always points directly to the faulty component. Research the code and consider all possible causes before making repairs.
11.3. Failing to Clear DTCs After Repairs
Always clear the DTCs after making repairs to ensure the check engine light is turned off and the vehicle’s computer is reset.
11.4. Neglecting Software Updates
Keep your OBD2 scanner’s software updated to ensure it supports the latest vehicles and features.
11.5. Using Incompatible Adapters
Ensure that the OBD2 adapter you are using is compatible with your vehicle and the diagnostic software.
12. OBD2 and Emissions Testing
OBD2 systems play a crucial role in emissions testing. During an emissions test, the vehicle’s OBD2 system is checked to ensure that all emissions-related components are functioning properly.
12.1. How OBD2 Systems Aid in Emissions Testing
OBD2 systems monitor the performance of emissions-related components, such as the catalytic converter, oxygen sensors, and EGR valve. If any of these components are not functioning properly, the OBD2 system will generate a DTC, which can cause the vehicle to fail the emissions test.
12.2. Preparing Your 2004 CR-V for Emissions Testing
To prepare your 2004 CR-V for emissions testing, make sure that the check engine light is not illuminated and that all emissions-related components are functioning properly. You can use an OBD2 scanner to check for DTCs and monitor the performance of these components.
12.3. What Happens if Your CR-V Fails the Emissions Test?
If your CR-V fails the emissions test, you will need to repair the issues that caused the failure and retest the vehicle. Common repairs include replacing the catalytic converter, oxygen sensors, or EGR valve.
13. OBD2 and Fuel Efficiency
Using an OBD2 scanner can help you improve your 2004 CR-V’s fuel efficiency by monitoring engine performance and identifying issues that may be affecting fuel economy.
13.1. Monitoring Fuel-Related Parameters
Use the OBD2 scanner to monitor fuel-related parameters, such as fuel trim, oxygen sensor readings, and mass airflow (MAF) sensor data. These parameters can provide insights into the engine’s fuel efficiency.
13.2. Identifying Issues Affecting Fuel Economy
Identify issues that may be affecting fuel economy, such as vacuum leaks, faulty oxygen sensors, and clogged fuel injectors. Repair these issues to improve fuel efficiency.
13.3. Optimizing Driving Habits
Optimize your driving habits to improve fuel efficiency. Avoid aggressive acceleration and braking, and maintain a steady speed.
14. OBD2 Resources and Communities
There are numerous OBD2 resources and communities available online where you can learn more about OBD2 systems and get help with diagnosing and repairing your vehicle.
14.1. Online Forums
Join online forums dedicated to OBD2 and automotive repair. These forums can provide valuable information and support from other enthusiasts and professionals.
14.2. Repair Manuals
Consult repair manuals for detailed information on diagnosing and repairing your vehicle. Repair manuals typically include OBD2 code definitions, troubleshooting procedures, and wiring diagrams.
14.3. Diagnostic Software
Use diagnostic software to access advanced OBD2 features and capabilities. Diagnostic software can provide detailed information on sensor data, actuation tests, and special functions.
14.4. Professional Mechanics
Seek professional help from a qualified mechanic if you are unsure about diagnosing or repairing your vehicle.
15. The Future of OBD2 Technology
OBD2 technology is constantly evolving, with new features and capabilities being developed all the time. Here are some trends to watch for in the future of OBD2 technology:
15.1. Enhanced Diagnostics
Future OBD2 systems will offer enhanced diagnostics, with more detailed information on vehicle performance and potential issues.
15.2. Wireless Connectivity
Wireless connectivity will become more common, allowing for seamless integration with smartphones, tablets, and other devices.
15.3. Cloud-Based Diagnostics
Cloud-based diagnostics will allow for remote monitoring and diagnosis of vehicle issues.
15.4. Integration with Advanced Driver-Assistance Systems (ADAS)
OBD2 systems will be integrated with ADAS to provide enhanced safety and performance.
16. Understanding Generic vs. Enhanced OBD2 Codes
When using an OBD2 scanner, you’ll encounter both generic and enhanced codes. Knowing the difference can significantly aid in accurate diagnostics.
16.1. What are Generic OBD2 Codes?
Generic OBD2 codes are standardized codes that apply to all vehicles manufactured after 1996. They cover basic engine and emissions-related issues.
16.2. What are Enhanced OBD2 Codes?
Enhanced OBD2 codes are manufacturer-specific codes that provide more detailed information about vehicle systems and components. These codes can vary between different makes and models.
16.3. How to Use Both Types of Codes Effectively
Start with generic codes to get a general idea of the problem, then use enhanced codes for more specific diagnostics. This approach can help you pinpoint the exact cause of an issue.
17. The Role of Oxygen Sensors in OBD2 Diagnostics
Oxygen sensors are critical components of the OBD2 system, providing data that helps monitor engine performance and emissions.
17.1. How Oxygen Sensors Work
Oxygen sensors measure the amount of oxygen in the exhaust gases. This data is used by the engine control unit (ECU) to adjust the air-fuel mixture for optimal combustion.
17.2. Common Oxygen Sensor Codes
Common oxygen sensor codes include P0135 (O2 Sensor Heater Circuit Malfunction) and P0171 (System Too Lean). These codes can indicate a faulty oxygen sensor or issues with the air-fuel mixture.
17.3. Diagnosing Oxygen Sensor Issues
Use an OBD2 scanner to monitor oxygen sensor readings and check for any abnormalities. If the readings are outside the normal range, the oxygen sensor may need to be replaced.
18. Using Freeze Frame Data for Intermittent Problems
Freeze frame data is a snapshot of the vehicle’s sensor data at the moment a DTC is triggered. This information can be invaluable for diagnosing intermittent problems.
18.1. What is Freeze Frame Data?
Freeze frame data captures sensor readings such as engine speed, coolant temperature, and fuel trim at the time a DTC is set.
18.2. How to Access Freeze Frame Data
Most OBD2 scanners can display freeze frame data. Simply connect the scanner to your vehicle and select the option to view freeze frame data.
18.3. Interpreting Freeze Frame Data
Analyze the freeze frame data to identify any unusual conditions that may have contributed to the problem. This can help you narrow down the possible causes and focus your diagnostic efforts.
19. Resetting the Check Engine Light with OBD2
One of the most common uses for an OBD2 scanner is to reset the check engine light after making repairs.
19.1. When to Reset the Check Engine Light
Reset the check engine light after you have diagnosed and repaired the underlying issue. Do not reset the light without addressing the problem, as it will likely return.
19.2. How to Reset the Check Engine Light
Connect the OBD2 scanner to your vehicle and select the option to clear DTCs. This will reset the check engine light and clear the stored codes.
19.3. What to Do If the Light Comes Back On
If the check engine light comes back on after resetting it, there is likely still an issue that needs to be addressed. Use the OBD2 scanner to read the DTCs and diagnose the problem.
20. OBD2 and Vehicle Security
OBD2 ports can also be used for vehicle security purposes, such as disabling the engine or tracking the vehicle’s location.
20.1. How OBD2 Can Be Used for Security
Some security systems use the OBD2 port to communicate with the vehicle’s computer and control certain functions, such as the ignition system.
20.2. Potential Security Risks
The OBD2 port can also be a potential security risk, as it can be used by thieves to bypass the vehicle’s security system.
20.3. Protecting Your Vehicle from OBD2-Related Security Threats
Consider using an OBD2 port lock or other security devices to protect your vehicle from OBD2-related security threats.
By understanding how to use an OBD2 scanner and torque applications effectively, you can keep your 2004 CR-V running smoothly and avoid costly repairs. Remember to always consult your vehicle’s repair manual and seek professional help when needed. For expert guidance and assistance, visit OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN or contact us at 123 Main Street, Los Angeles, CA 90001, United States. You can also reach us via Whatsapp at +1 (641) 206-8880.
 OBD2 scanner displaying live data and diagnostic trouble codesIf you are facing challenges in diagnosing or repairing your 2004 CR-V, don’t hesitate to seek expert help. Contact OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN today for professional advice and services. Our team is ready to assist you with all your OBD2 and automotive repair needs. Reach us at 123 Main Street, Los Angeles, CA 90001, United States, or through Whatsapp at +1 (641) 206-8880. Visit our website at OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN for more information.
OBD2 scanner displaying live data and diagnostic trouble codesIf you are facing challenges in diagnosing or repairing your 2004 CR-V, don’t hesitate to seek expert help. Contact OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN today for professional advice and services. Our team is ready to assist you with all your OBD2 and automotive repair needs. Reach us at 123 Main Street, Los Angeles, CA 90001, United States, or through Whatsapp at +1 (641) 206-8880. Visit our website at OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN for more information.
 A technician using an OBD2 scanner to diagnose a vehicle issue
A technician using an OBD2 scanner to diagnose a vehicle issue
FAQ: 2004 CR V OBD2 Torque Applications
What exactly is an OBD2 scanner, and how does it benefit me?
An OBD2 scanner is a diagnostic tool that accesses your vehicle’s computer to read diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs), offering insights into potential issues. It benefits you by enabling early detection of problems, reducing repair costs through DIY diagnostics, and monitoring overall engine performance.
How do I choose the right OBD2 scanner for my 2004 CR-V?
To choose the right OBD2 scanner, ensure it’s compatible with your 2004 CR-V, reads and clears DTCs, monitors real-time data, and has a user-friendly interface. Consider additional features like wireless connectivity for added convenience.
What are some common OBD2 codes I might encounter with my 2004 CR-V, and what do they mean?
Common OBD2 codes for a 2004 CR-V include P0171 (System Too Lean), P0300 (Random Misfire Detected), and P0420 (Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold). These codes indicate potential issues with the engine, fuel system, or emissions components.
Can I use the Torque Pro app with my OBD2 scanner on my 2004 CR-V?
Yes, Torque Pro is a popular Android app that can be used with compatible OBD2 adapters to monitor real-time data, read DTCs, and perform other diagnostic functions on your 2004 CR-V.
How do I interpret the data from my OBD2 scanner to diagnose problems accurately?
To interpret OBD2 data accurately, understand sensor readings, identify patterns in the data, use freeze frame data, and consult repair manuals. If unsure, seek professional help from a qualified mechanic.
What is freeze frame data, and how can it help with diagnosing intermittent issues in my 2004 CR-V?
Freeze frame data captures sensor data at the moment a DTC is triggered, providing a snapshot of the conditions under which the problem occurred. It helps diagnose intermittent issues by showing what was happening when the code was set.
How do I reset the check engine light on my 2004 CR-V after fixing a problem?
To reset the check engine light, connect the OBD2 scanner to your vehicle and select the option to clear DTCs. Ensure the underlying issue has been resolved before resetting the light.
What are the potential security risks associated with using an OBD2 port, and how can I protect my vehicle?
Potential security risks include unauthorized access to your vehicle’s computer system. Protect your vehicle by using an OBD2 port lock or other security devices.
How can OBD2 scanners help me improve my 2004 CR-V’s fuel efficiency?
OBD2 scanners can help improve fuel efficiency by monitoring fuel-related parameters, identifying issues affecting fuel economy, and allowing you to optimize your driving habits.
Where can I find reliable resources and communities to learn more about OBD2 systems and automotive repair?
Reliable resources include online forums, repair manuals, diagnostic software, and professional mechanics. Joining OBD2-focused communities can also provide valuable insights and support.