Obd2 Code Meaning refers to the specific diagnostic information provided by your vehicle’s onboard computer system when it detects a problem. Understanding OBD2 code meaning is crucial for diagnosing car issues, and OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN provides the tools and expertise to decipher these codes accurately. This knowledge can help you address car troubles effectively, reduce repair costs, and ensure your vehicle operates smoothly. Think of it as your car speaking to you, telling you exactly what’s wrong so you can fix it.
Contents
- 1. Demystifying OBD2 Codes: What They Are and Why They Matter
- 1.1 The Purpose of OBD2 Codes
- 1.2 How OBD2 Systems Work
- 1.3 Why OBD2 Codes Are Important
- 1.4 Common Misconceptions About OBD2 Codes
- 2. Decoding the Anatomy of OBD2 Codes
- 2.1 The First Character: Identifying the System
- 2.2 The Second Character: Code Type
- 2.3 The Third Character: Identifying the Subsystem
- 2.4 The Fourth and Fifth Characters: Specific Issue
- 2.5 Examples of OBD2 Code Anatomy
- 3. Essential OBD2 Codes Every Car Owner Should Know
- 3.1 P0171: System Too Lean (Bank 1)
- 3.2 P0300: Random/Multiple Cylinder Misfire Detected
- 3.3 P0420: Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold (Bank 1)
- 3.4 P0442: Evaporative Emission Control System Leak Detected (Small Leak)
- 3.5 P0500: Vehicle Speed Sensor A
- 3.6 P0700: Transmission Control System Malfunction
- 3.7 P0101: Mass Air Flow (MAF) Sensor Circuit Range/Performance Problem
- 3.8 P0113: Intake Air Temperature Circuit High Input
- 3.9 P0118: Engine Coolant Temperature Circuit High Input
- 3.10 P0301 – P0306: Cylinder 1-6 Misfire Detected
- 4. Step-by-Step Guide: Using an OBD2 Scanner
- 4.1 Step 1: Locate the OBD2 Port
- 4.2 Step 2: Plug in the OBD2 Scanner
- 4.3 Step 3: Power On the Scanner
- 4.4 Step 4: Read the Codes
- 4.5 Step 5: Interpret the Codes
- 4.6 Step 6: Clear the Codes (Optional)
- 4.7 Step 7: Verify the Repair
- 4.8 Choosing the Right OBD2 Scanner
- 5. Advanced Diagnostics: Beyond Basic OBD2 Code Meaning
- 5.1 Live Data Streaming
- 5.2 Freeze Frame Data
- 5.3 Component Testing
- 5.4 Bi-Directional Control
- 5.5 Smoke Testing
- 5.6 Oscilloscope Diagnostics
- 5.7 When to Seek Professional Help
- 6. Common Mistakes to Avoid When Interpreting OBD2 Codes
- 6.1 Replacing Parts Without Proper Diagnosis
- 6.2 Ignoring Underlying Issues
- 6.3 Not Considering All Possible Causes
- 6.4 Overlooking Related Symptoms
- 6.5 Using Inaccurate or Unreliable Information
- 6.6 Failing to Perform a Thorough Inspection
- 6.7 Neglecting Basic Maintenance
- 7. Preventative Maintenance: Keeping OBD2 Codes at Bay
- 7.1 Follow the Manufacturer’s Recommended Maintenance Schedule
- 7.2 Check and Replace Fluids Regularly
- 7.3 Inspect and Replace Filters
- 7.4 Check and Replace Spark Plugs
- 7.5 Inspect and Maintain Belts and Hoses
- 7.6 Check Tire Pressure and Alignment
- 7.7 Keep the Engine Clean
- 7.8 Use Quality Fuel and Additives
- 8. The Future of OBD2: What’s on the Horizon
- 8.1 Enhanced Data Logging and Analysis
- 8.2 Wireless OBD2 Scanners
- 8.3 Integration with Telematics Systems
- 8.4 Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML)
- 8.5 Over-the-Air (OTA) Updates
- 8.6 Cybersecurity Enhancements
- 9. Real-World Examples: OBD2 Code Meaning in Action
- 9.1 Case Study 1: Diagnosing a P0171 Code
- 9.2 Case Study 2: Identifying a Misfire with a P0300 Code
- 9.3 Case Study 3: Resolving an EVAP Leak with a P0442 Code
- 9.4 How OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN Can Help
- 10. FAQs About OBD2 Code Meaning
- 10.1 What is an OBD2 scanner?
- 10.2 Where is the OBD2 port located?
- 10.3 Can I clear OBD2 codes myself?
- 10.4 What does the check engine light mean?
- 10.5 Are all OBD2 codes serious?
- 10.6 How do I find the meaning of an OBD2 code?
- 10.7 Can I drive my car with the check engine light on?
- 10.8 How often should I check for OBD2 codes?
- 10.9 What if I can’t find the OBD2 port in my car?
- 10.10 Are OBD2 scanners compatible with all vehicles?
1. Demystifying OBD2 Codes: What They Are and Why They Matter
OBD2 (On-Board Diagnostics II) codes are standardized diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) used in vehicles to identify potential issues within various systems. According to the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), all cars and light trucks manufactured in the United States since 1996 are required to support OBD2 diagnostics. These codes are essential for car owners and mechanics because they provide valuable information about the health and performance of a vehicle, making diagnosing and repairing problems more efficient and accurate. At OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN, we help you understand these codes, making car maintenance more transparent and manageable.
1.1 The Purpose of OBD2 Codes
OBD2 codes serve as a standardized way for a vehicle’s computer to communicate problems to mechanics and car owners. When a sensor detects an issue, the computer generates a specific code that corresponds to that problem. According to a study by the National Institute for Automotive Service Excellence (ASE), using OBD2 codes can reduce diagnostic time by as much as 50%. This standardization helps ensure that any mechanic can understand the problem, regardless of the car’s make or model.
1.2 How OBD2 Systems Work
OBD2 systems work by monitoring various components and systems within a vehicle, such as the engine, transmission, and emissions systems. These systems use sensors to collect data, which is then analyzed by the car’s computer. If any reading falls outside the normal range, the computer generates an OBD2 code. For example, if the oxygen sensor detects that the air-fuel mixture is too rich or lean, it will trigger a corresponding code.
1.3 Why OBD2 Codes Are Important
Understanding OBD2 code meaning is important for several reasons:
- Early Detection of Problems: OBD2 codes can help you identify potential problems before they become severe, saving you money on costly repairs.
- Accurate Diagnosis: These codes provide specific information about the issue, making it easier for mechanics to diagnose the problem accurately.
- Cost Savings: By addressing problems early and accurately, you can reduce the overall cost of car maintenance and repairs.
- Improved Fuel Efficiency: Addressing issues identified by OBD2 codes can improve your vehicle’s fuel efficiency.
- Reduced Emissions: Fixing problems related to emissions can help reduce your vehicle’s environmental impact.
1.4 Common Misconceptions About OBD2 Codes
There are several common misconceptions about OBD2 codes that can lead to confusion and misdiagnosis:
- OBD2 Codes Always Indicate a Major Problem: While some codes indicate severe issues, others may be related to minor problems that are easy to fix.
- Clearing an OBD2 Code Fixes the Problem: Clearing a code without addressing the underlying issue will only temporarily turn off the check engine light. The code will likely reappear if the problem persists.
- All OBD2 Scanners Are Created Equal: The quality and features of OBD2 scanners can vary significantly. Some scanners provide more detailed information and advanced diagnostic capabilities than others.
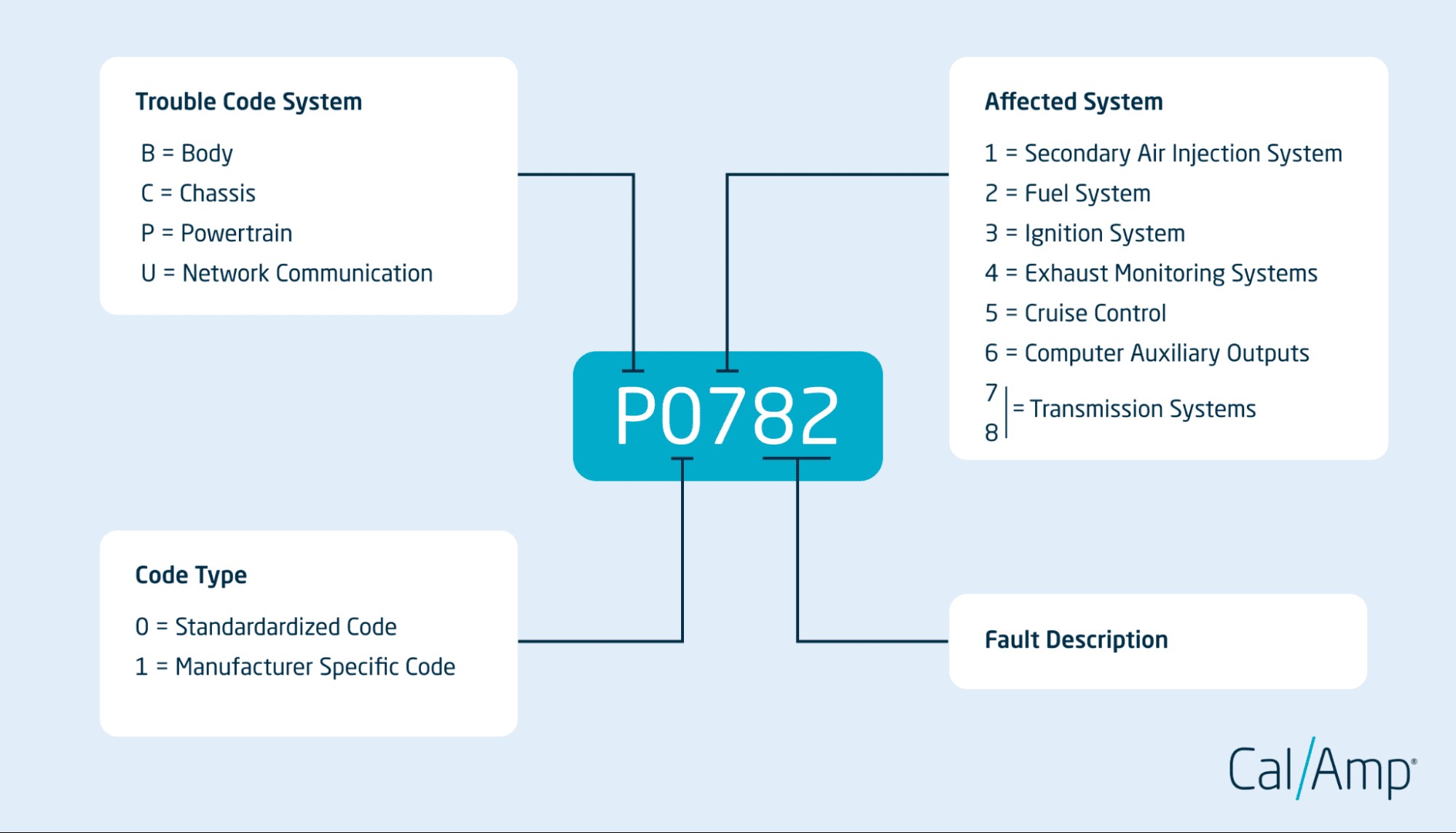
2. Decoding the Anatomy of OBD2 Codes
OBD2 codes are structured in a specific format that provides information about the system and nature of the problem. Understanding the anatomy of these codes is crucial for accurate diagnosis and repair. The code consists of five characters: a letter followed by four digits. Each character provides a specific piece of information.
2.1 The First Character: Identifying the System
The first character of an OBD2 code indicates the primary system affected by the problem:
- P (Powertrain): This indicates issues with the engine, transmission, or related components.
- B (Body): This indicates problems with the vehicle’s body systems, such as airbags, lights, or power windows.
- C (Chassis): This indicates issues with the chassis systems, such as brakes, suspension, or steering.
- U (Network): This indicates problems with the vehicle’s communication network.
2.2 The Second Character: Code Type
The second character of an OBD2 code specifies whether the code is standardized or manufacturer-specific:
- 0: This indicates a generic, standardized code that applies to all vehicles.
- 1, 2, or 3: This indicates a manufacturer-specific code that is unique to a particular car make or model.
2.3 The Third Character: Identifying the Subsystem
The third character of an OBD2 code indicates the specific subsystem affected by the problem:
- 0: Fuel and air metering and auxiliary emission controls.
- 1: Fuel and air metering.
- 2: Fuel injector circuit.
- 3: Ignition system or misfires.
- 4: Auxiliary emission controls.
- 5: Vehicle speed controls and idle control system.
- 6: Computer and output circuit.
- 7: Transmission.
- 8: Transmission.
2.4 The Fourth and Fifth Characters: Specific Issue
The fourth and fifth characters of an OBD2 code provide specific information about the nature of the problem within the identified system and subsystem. These characters can range from 00 to 99, with each combination corresponding to a particular issue. For example, the code P0301 indicates a misfire in cylinder 1.
2.5 Examples of OBD2 Code Anatomy
To further illustrate the anatomy of OBD2 codes, here are a few examples:
- P0300: This code indicates a random or multiple cylinder misfire in the engine (Powertrain, generic code, ignition system or misfires).
- B0100: This code indicates a fault in the driver’s side airbag circuit (Body, generic code).
- C1234: This code indicates a problem with the right front wheel speed sensor (Chassis, generic code).
- U0100: This code indicates a loss of communication with the Engine Control Module (ECM) (Network, generic code).
Understanding the structure of OBD2 codes enables you to quickly identify the system and nature of the problem, which is crucial for accurate diagnosis and repair. OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN offers resources and tools to help you interpret these codes effectively.
3. Essential OBD2 Codes Every Car Owner Should Know
While there are thousands of possible OBD2 codes, some are more common than others. Knowing these common codes can help you quickly identify potential problems with your vehicle and take appropriate action. Here are some essential OBD2 codes every car owner should know:
3.1 P0171: System Too Lean (Bank 1)
This code indicates that the engine is running too lean, meaning there is too much air and not enough fuel in the air-fuel mixture. According to a study by AAA, P0171 is one of the most common OBD2 codes, often caused by a vacuum leak, faulty oxygen sensor, or a dirty mass airflow (MAF) sensor.
3.2 P0300: Random/Multiple Cylinder Misfire Detected
This code indicates that the engine is experiencing misfires in one or more cylinders. Misfires can be caused by faulty spark plugs, ignition coils, fuel injectors, or a compression issue. A misfire can lead to reduced engine power, poor fuel economy, and potential damage to the catalytic converter.
3.3 P0420: Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold (Bank 1)
This code indicates that the catalytic converter is not functioning efficiently. The catalytic converter is responsible for reducing harmful emissions from the exhaust. This code can be caused by a faulty catalytic converter, exhaust leaks, or problems with the oxygen sensors.
3.4 P0442: Evaporative Emission Control System Leak Detected (Small Leak)
This code indicates that there is a small leak in the evaporative emission control system (EVAP). The EVAP system prevents fuel vapors from escaping into the atmosphere. A small leak can be caused by a loose or faulty gas cap, a cracked EVAP hose, or a faulty purge valve.
3.5 P0500: Vehicle Speed Sensor A
This code indicates a problem with the vehicle speed sensor (VSS). The VSS measures the speed of the vehicle and provides this information to the car’s computer. A faulty VSS can cause problems with the speedometer, cruise control, and transmission shifting.
3.6 P0700: Transmission Control System Malfunction
This code indicates a general problem with the transmission control system. There may be other transmission-related codes, but this one simply says that the computer has detected a generic issue.
3.7 P0101: Mass Air Flow (MAF) Sensor Circuit Range/Performance Problem
 OBD2 Codes and Sensor Testing
OBD2 Codes and Sensor Testing
This code indicates a problem with the mass air flow (MAF) sensor. The MAF sensor measures the amount of air entering the engine, helping the vehicle’s computer determine the right fuel-air mixture for optimal performance.
3.8 P0113: Intake Air Temperature Circuit High Input
This code indicates that the intake air temperature (IAT) sensor is reading too high. The IAT sensor measures the temperature of the air entering the engine, which is used to adjust the air-fuel mixture.
3.9 P0118: Engine Coolant Temperature Circuit High Input
This code indicates that the engine coolant temperature (ECT) sensor is reading too high. The ECT sensor measures the temperature of the engine coolant, which is used to adjust the air-fuel mixture and control the cooling fan.
3.10 P0301 – P0306: Cylinder 1-6 Misfire Detected
These codes indicate a misfire in the specific cylinder. It is important to check spark plugs, ignition coils and fuel injectors.
4. Step-by-Step Guide: Using an OBD2 Scanner
Using an OBD2 scanner is a straightforward process that can provide valuable insights into your vehicle’s health. Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to use an OBD2 scanner:
4.1 Step 1: Locate the OBD2 Port
The OBD2 port is typically located under the dashboard on the driver’s side. It is a 16-pin connector that is usually easily accessible. If you have trouble locating the port, consult your vehicle’s owner’s manual.
4.2 Step 2: Plug in the OBD2 Scanner
Once you have located the OBD2 port, plug in the scanner. Make sure the connection is secure. Some scanners may require you to turn the ignition on (but not start the engine) to power on the scanner.
4.3 Step 3: Power On the Scanner
Turn the ignition key to the “on” position without starting the engine. This will provide power to the OBD2 scanner. Follow the scanner’s instructions to power it on. Some scanners will power on automatically once connected to the OBD2 port.
4.4 Step 4: Read the Codes
Navigate the scanner’s menu to find the option to read codes. The scanner will then communicate with the vehicle’s computer and retrieve any stored OBD2 codes. The codes will be displayed on the scanner’s screen.
4.5 Step 5: Interpret the Codes
Once you have retrieved the codes, interpret them using a code reader or a reliable online database. Note the code and the corresponding description. Some scanners may provide a brief description of the code, but it’s always a good idea to research the code further to understand the potential causes and solutions. OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN offers an extensive database of OBD2 codes and their meanings to help you with this step.
4.6 Step 6: Clear the Codes (Optional)
After addressing the underlying issue, you can clear the codes using the scanner. Navigate to the option to clear codes and follow the scanner’s instructions. Keep in mind that clearing the codes without fixing the problem will only temporarily turn off the check engine light. The code will likely reappear if the issue persists.
4.7 Step 7: Verify the Repair
After clearing the codes and performing the necessary repairs, it’s important to verify that the problem has been resolved. Drive the vehicle under the conditions that triggered the code initially. Use the OBD2 scanner to monitor the vehicle’s systems and ensure that the code does not reappear.
4.8 Choosing the Right OBD2 Scanner
Selecting the right OBD2 scanner depends on your needs and budget. There are several factors to consider when choosing a scanner:
- Features: Look for a scanner that provides detailed code definitions, live data streaming, and the ability to clear codes.
- Compatibility: Make sure the scanner is compatible with your vehicle’s make and model.
- Ease of Use: Choose a scanner with a user-friendly interface and clear instructions.
- Price: OBD2 scanners range in price from around $20 to several hundred dollars. Consider your budget and the features you need when making your decision.
5. Advanced Diagnostics: Beyond Basic OBD2 Code Meaning
While basic OBD2 code meaning can provide a starting point for diagnosing vehicle problems, advanced diagnostics often require more sophisticated tools and techniques. Here are some advanced diagnostic methods that go beyond basic OBD2 code reading:
5.1 Live Data Streaming
Live data streaming allows you to monitor various parameters in real-time as the vehicle is running. This can provide valuable insights into how the engine and other systems are performing. For example, you can monitor the oxygen sensor readings, fuel trim values, and engine temperature to identify potential problems.
5.2 Freeze Frame Data
Freeze frame data captures a snapshot of the vehicle’s operating conditions at the moment a code was triggered. This can help you understand the circumstances that led to the problem and identify the root cause. Freeze frame data typically includes parameters such as engine speed, load, and temperature.
5.3 Component Testing
Component testing involves using specialized tools to test individual components, such as sensors, actuators, and circuits. This can help you determine whether a component is functioning properly or needs to be replaced. Component testing often requires a multimeter, oscilloscope, or other diagnostic tools.
5.4 Bi-Directional Control
Bi-directional control allows you to send commands to the vehicle’s computer to activate or deactivate certain components. This can be useful for testing systems such as the cooling fan, fuel pump, or throttle actuator. Bi-directional control requires a more advanced OBD2 scanner or diagnostic tool.
5.5 Smoke Testing
Smoke testing is a technique used to detect leaks in the intake, exhaust, or EVAP systems. It involves introducing smoke into the system and looking for areas where the smoke escapes. Smoke testing can help identify hard-to-find leaks that can cause various problems.
5.6 Oscilloscope Diagnostics
Using an oscilloscope for diagnostics allows you to view the electrical signals from various sensors and actuators. This can help you identify problems with the signal pattern, such as shorts, opens, or intermittent issues. Oscilloscope diagnostics requires specialized training and equipment.
5.7 When to Seek Professional Help
While advanced diagnostics can be helpful for identifying complex problems, it’s important to know when to seek professional help. If you’re not comfortable performing advanced diagnostic procedures or if you’re unable to resolve the issue, it’s best to consult a qualified mechanic. Mechanics have the training, experience, and equipment to accurately diagnose and repair a wide range of vehicle problems.
6. Common Mistakes to Avoid When Interpreting OBD2 Codes
Interpreting OBD2 codes can be tricky, and it’s important to avoid common mistakes that can lead to misdiagnosis and unnecessary repairs. Here are some common mistakes to avoid:
6.1 Replacing Parts Without Proper Diagnosis
One of the most common mistakes is replacing parts without properly diagnosing the problem. Just because an OBD2 code points to a specific component doesn’t mean that component is necessarily faulty. It’s important to perform thorough testing to confirm that the component is indeed the cause of the problem.
6.2 Ignoring Underlying Issues
Clearing an OBD2 code without addressing the underlying issue will only temporarily turn off the check engine light. The code will likely reappear if the problem persists. It’s important to identify and address the root cause of the problem, rather than just clearing the code.
6.3 Not Considering All Possible Causes
An OBD2 code can have multiple possible causes, and it’s important to consider all of them. Don’t assume that the first possible cause you find is the correct one. Perform thorough testing and research to narrow down the possibilities and identify the true cause of the problem.
6.4 Overlooking Related Symptoms
OBD2 codes are often accompanied by other symptoms, such as poor engine performance, reduced fuel economy, or unusual noises. It’s important to consider these related symptoms when diagnosing the problem. The symptoms can provide valuable clues about the nature and location of the issue.
6.5 Using Inaccurate or Unreliable Information
There is a lot of information available online about OBD2 codes, but not all of it is accurate or reliable. Be sure to use trusted sources, such as repair manuals, technical service bulletins, and reputable online databases. OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN provides reliable and accurate information about OBD2 codes and their meanings.
6.6 Failing to Perform a Thorough Inspection
A visual inspection can often reveal obvious problems, such as broken wires, loose connections, or damaged components. Before diving into advanced diagnostics, perform a thorough visual inspection of the affected system.
6.7 Neglecting Basic Maintenance
Many OBD2 codes are caused by neglected maintenance, such as dirty air filters, worn spark plugs, or low fluid levels. Be sure to keep up with your vehicle’s maintenance schedule to prevent these types of problems.
7. Preventative Maintenance: Keeping OBD2 Codes at Bay
Preventative maintenance is key to keeping OBD2 codes at bay and ensuring the long-term health of your vehicle. Regular maintenance can help identify and address potential problems before they trigger a code and cause more serious damage. Here are some preventative maintenance tips to help keep your vehicle running smoothly:
7.1 Follow the Manufacturer’s Recommended Maintenance Schedule
Your vehicle’s owner’s manual outlines a recommended maintenance schedule based on mileage or time intervals. This schedule includes tasks such as oil changes, filter replacements, fluid checks, and inspections. Following this schedule can help prevent many common problems that trigger OBD2 codes.
7.2 Check and Replace Fluids Regularly
Fluids such as engine oil, coolant, brake fluid, and transmission fluid play a crucial role in the proper functioning of your vehicle. Check these fluids regularly and replace them according to the manufacturer’s recommendations. Low or contaminated fluids can lead to various problems that trigger OBD2 codes.
7.3 Inspect and Replace Filters
Filters such as the air filter, fuel filter, and cabin air filter help keep contaminants out of your vehicle’s systems. Inspect these filters regularly and replace them as needed. Dirty filters can reduce engine performance, fuel economy, and air quality.
7.4 Check and Replace Spark Plugs
Spark plugs are responsible for igniting the air-fuel mixture in the engine. Worn or fouled spark plugs can cause misfires, reduced engine power, and poor fuel economy. Check and replace your spark plugs according to the manufacturer’s recommendations.
7.5 Inspect and Maintain Belts and Hoses
Belts and hoses are essential for the proper functioning of various systems, such as the cooling system, power steering system, and air conditioning system. Inspect these components regularly for cracks, leaks, or wear. Replace them as needed to prevent system failures.
7.6 Check Tire Pressure and Alignment
Proper tire pressure and alignment are important for vehicle handling, fuel economy, and tire wear. Check your tire pressure regularly and inflate your tires to the recommended pressure. Have your vehicle’s alignment checked periodically to ensure proper handling and prevent uneven tire wear.
7.7 Keep the Engine Clean
A clean engine can run cooler and more efficiently. Periodically clean the engine compartment to remove dirt, grease, and debris. This can help prevent overheating and other problems.
7.8 Use Quality Fuel and Additives
Using high-quality fuel and fuel additives can help keep your engine clean and prevent fuel system problems. Choose a reputable gas station and use fuel that meets or exceeds the manufacturer’s recommendations. Consider using a fuel additive periodically to clean fuel injectors and remove deposits.
8. The Future of OBD2: What’s on the Horizon
The field of OBD2 diagnostics is constantly evolving, with new technologies and features being developed to improve accuracy and efficiency. Here are some trends and developments to watch for in the future of OBD2:
8.1 Enhanced Data Logging and Analysis
Future OBD2 systems are likely to offer more advanced data logging and analysis capabilities. This will allow mechanics and car owners to monitor vehicle performance over time and identify subtle problems before they become major issues. Enhanced data logging may include features such as trend analysis, predictive maintenance, and remote diagnostics.
8.2 Wireless OBD2 Scanners
Wireless OBD2 scanners are already becoming more common, and this trend is likely to continue. Wireless scanners offer greater flexibility and convenience, allowing you to diagnose vehicle problems from a smartphone, tablet, or computer. Wireless scanners may also offer features such as cloud storage, remote access, and automatic updates.
8.3 Integration with Telematics Systems
Telematics systems, which combine GPS tracking and vehicle diagnostics, are becoming increasingly popular. In the future, OBD2 systems are likely to be more tightly integrated with telematics systems. This will allow fleet managers and car owners to monitor vehicle health remotely, track vehicle location, and receive alerts for potential problems.
8.4 Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML)
AI and ML are being used increasingly in vehicle diagnostics. These technologies can analyze large amounts of data to identify patterns, predict failures, and provide more accurate diagnoses. AI-powered diagnostic tools may be able to identify problems that would be difficult or impossible for a human mechanic to detect.
8.5 Over-the-Air (OTA) Updates
Over-the-air (OTA) updates are becoming more common in modern vehicles. These updates allow manufacturers to remotely update vehicle software, fix bugs, and add new features. In the future, OBD2 systems may be able to receive OTA updates to improve diagnostic capabilities and add support for new codes and protocols.
8.6 Cybersecurity Enhancements
As vehicles become more connected, cybersecurity is becoming an increasingly important concern. Future OBD2 systems are likely to include enhanced security features to protect against hacking and unauthorized access. These features may include encryption, authentication, and intrusion detection.
9. Real-World Examples: OBD2 Code Meaning in Action
To further illustrate the importance and practical application of OBD2 code meaning, here are a few real-world examples of how understanding these codes can help diagnose and resolve vehicle problems:
9.1 Case Study 1: Diagnosing a P0171 Code
A car owner noticed that their vehicle’s check engine light was on and that the car was experiencing poor fuel economy. They used an OBD2 scanner and retrieved a P0171 code, indicating that the system was running too lean (Bank 1). After researching the code, they learned that it could be caused by a vacuum leak, a faulty oxygen sensor, or a dirty MAF sensor.
They visually inspected the engine compartment and found a cracked vacuum hose. They replaced the hose and cleared the code. After driving the car for a few days, they noticed that the check engine light did not come back on and that the fuel economy had improved. In this case, understanding the OBD2 code and its possible causes helped the car owner quickly diagnose and resolve the problem.
9.2 Case Study 2: Identifying a Misfire with a P0300 Code
A driver noticed that their car was running rough and that the check engine light was flashing. They used an OBD2 scanner and retrieved a P0300 code, indicating a random or multiple cylinder misfire. They knew that misfires can be caused by faulty spark plugs, ignition coils, or fuel injectors.
They started by inspecting the spark plugs and found that one of them was fouled. They replaced all of the spark plugs and cleared the code. After driving the car for a while, they noticed that the misfire was gone and that the engine was running smoothly. By understanding the OBD2 code and its potential causes, the driver was able to identify and fix the misfire.
9.3 Case Study 3: Resolving an EVAP Leak with a P0442 Code
A car owner noticed that their vehicle’s check engine light was on but didn’t notice any other symptoms. They used an OBD2 scanner and retrieved a P0442 code, indicating a small leak in the evaporative emission control system (EVAP). After researching the code, they learned that it could be caused by a loose gas cap or a cracked EVAP hose.
They checked the gas cap and found that it was loose. They tightened the gas cap and cleared the code. After driving the car for a few days, they noticed that the check engine light did not come back on. In this case, understanding the OBD2 code and its possible causes helped the car owner quickly resolve the EVAP leak.
9.4 How OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN Can Help
These real-world examples demonstrate the practical value of understanding OBD2 code meaning. OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN provides the resources and tools you need to effectively diagnose and resolve vehicle problems. Our extensive database of OBD2 codes, combined with our expert advice and diagnostic tools, can help you save time and money on car repairs.
10. FAQs About OBD2 Code Meaning
Here are some frequently asked questions about OBD2 code meaning:
10.1 What is an OBD2 scanner?
An OBD2 scanner is a diagnostic tool that connects to a vehicle’s onboard computer system to retrieve diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs). These codes provide information about potential problems within the vehicle’s systems.
10.2 Where is the OBD2 port located?
The OBD2 port is typically located under the dashboard on the driver’s side. It is a 16-pin connector that is usually easily accessible.
10.3 Can I clear OBD2 codes myself?
Yes, you can clear OBD2 codes using an OBD2 scanner. However, it’s important to address the underlying issue before clearing the code. Clearing the code without fixing the problem will only temporarily turn off the check engine light.
10.4 What does the check engine light mean?
The check engine light indicates that the vehicle’s computer has detected a problem within one of the monitored systems. It’s important to have the code read and diagnosed to determine the cause of the problem.
10.5 Are all OBD2 codes serious?
No, not all OBD2 codes are serious. Some codes indicate minor problems that are easy to fix, while others indicate more severe issues that require professional attention.
10.6 How do I find the meaning of an OBD2 code?
You can find the meaning of an OBD2 code using an OBD2 scanner or a reliable online database. OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN offers an extensive database of OBD2 codes and their meanings.
10.7 Can I drive my car with the check engine light on?
It depends on the nature of the problem. If the check engine light is flashing, it indicates a more serious problem that could damage the engine. In this case, it’s best to avoid driving the car and have it towed to a mechanic. If the check engine light is solid, you can usually drive the car, but it’s important to have the code read and diagnosed as soon as possible.
10.8 How often should I check for OBD2 codes?
You should check for OBD2 codes whenever the check engine light comes on or if you notice any unusual symptoms, such as poor engine performance, reduced fuel economy, or unusual noises.
10.9 What if I can’t find the OBD2 port in my car?
Consult your vehicle’s owner’s manual for the location of the OBD2 port. If you still can’t find it, consult a qualified mechanic.
10.10 Are OBD2 scanners compatible with all vehicles?
OBD2 scanners are compatible with all cars and light trucks manufactured in the United States since 1996. However, some scanners may not be compatible with certain makes or models. Check the scanner’s compatibility before purchasing.
Understanding OBD2 code meaning is essential for maintaining the health and performance of your vehicle. With the right tools and knowledge, you can effectively diagnose and resolve vehicle problems, saving time and money on repairs.
Are you struggling to understand the OBD2 codes your car is throwing? Don’t let those mysterious codes leave you stranded! Contact us at OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN for expert advice and top-notch service. Call us at +1 (641) 206-8880 or visit our location at 123 Main Street, Los Angeles, CA 90001, United States, and let our team help you decode your car’s issues today. Whether you need help deciphering a specific code or want to schedule a diagnostic check, we’re here to ensure your vehicle runs smoothly and efficiently. Reach out now and take the first step towards a healthier, more reliable ride!