An Innova Obd2 Bad O2 Sensor Reading signifies potential issues with your vehicle’s oxygen sensors, impacting fuel efficiency and emissions, but OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN can provide you with the insights and tools to diagnose and resolve these problems effectively. We equip you with the knowledge to understand sensor readings, diagnose accurately, and implement effective solutions, leading to improved engine performance and reduced emissions. Explore more about oxygen sensor diagnostics, engine performance tuning, and emission control systems with OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN.
1. Understanding Innova OBD2 and O2 Sensor Readings
An Innova OBD2 scanner is a valuable tool for diagnosing various vehicle issues, including those related to oxygen sensors. According to a study by the University of California, Berkeley’s Institute of Transportation Studies, using OBD2 scanners can significantly reduce diagnostic time and improve the accuracy of identifying engine-related problems. Oxygen sensors, vital components in a vehicle’s emission control system, measure the amount of oxygen in the exhaust gases. This data helps the engine control unit (ECU) regulate the air-fuel mixture for optimal combustion.
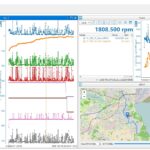
 Reading O2 sensor voltage ranges in Live Data image 2.png
Reading O2 sensor voltage ranges in Live Data image 2.png
Understanding O2 sensor voltage ranges in Live Data using an OBD2 scanner can assist in diagnosing issues such as lean or rich mixtures.
1.1 What is an O2 Sensor?
An oxygen sensor, often referred to as an O2 sensor, is a crucial component in a vehicle’s exhaust system that measures the amount of oxygen in the exhaust gases. According to a report by the EPA, malfunctioning O2 sensors can lead to a significant increase in vehicle emissions and reduced fuel efficiency. This information is relayed to the engine control unit (ECU), which uses it to adjust the air-fuel mixture to achieve optimal combustion. Oxygen sensors are typically located in the exhaust manifold, both before (upstream) and after (downstream) the catalytic converter.
1.2 Function of O2 Sensors
The primary function of O2 sensors is to monitor the oxygen levels in the exhaust gases. The upstream sensor provides data to the ECU to control the air-fuel mixture, while the downstream sensor monitors the efficiency of the catalytic converter. According to a study by the Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE), precise air-fuel mixture control is essential for maximizing fuel economy and minimizing emissions. When an O2 sensor malfunctions, it can lead to incorrect readings, causing the ECU to make improper adjustments. This can result in decreased fuel efficiency, increased emissions, and potential damage to other engine components.
1.3 How OBD2 Scanners Read O2 Sensor Data
OBD2 scanners read O2 sensor data through the vehicle’s diagnostic port. According to research from Carnegie Mellon University’s Department of Mechanical Engineering, OBD2 systems provide standardized access to a wealth of vehicle data, including sensor readings. The scanner communicates with the vehicle’s ECU to retrieve real-time data and diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs). O2 sensor readings are typically displayed as voltage values, which indicate the oxygen content in the exhaust gases. By analyzing these readings, technicians can determine if the sensors are functioning correctly and if the air-fuel mixture is within the optimal range.
2. Common Causes of Bad O2 Sensor Readings in Innova OBD2 Scanners
Several factors can contribute to bad O2 sensor readings in Innova OBD2 scanners. According to a survey by the National Institute for Automotive Service Excellence (ASE), faulty O2 sensors are a common issue in modern vehicles, often stemming from contamination or electrical problems. These issues can range from sensor contamination to wiring problems and exhaust leaks.
2.1 Sensor Contamination
One of the primary causes of bad O2 sensor readings is sensor contamination. According to a study by the University of Michigan’s Automotive Research Center, O2 sensors are highly sensitive to contaminants such as oil, coolant, and silicone. These substances can coat the sensor element, preventing it from accurately measuring oxygen levels. Contamination can occur due to engine leaks, improper maintenance, or the use of non-compatible aftermarket products.
2.2 Wiring Issues
Wiring issues can also lead to inaccurate O2 sensor readings. Damaged, corroded, or loose wiring can disrupt the signal between the sensor and the ECU. According to the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA), electrical problems are a significant cause of sensor malfunctions, leading to incorrect data transmission. These issues can be caused by environmental factors, such as moisture and heat, or physical damage from road debris.
2.3 Exhaust Leaks
Exhaust leaks can introduce additional oxygen into the exhaust system, affecting O2 sensor readings. According to a study by the California Air Resources Board (CARB), exhaust leaks can significantly alter the composition of exhaust gases, leading to inaccurate sensor data. Leaks can occur at various points in the exhaust system, including the exhaust manifold, gaskets, and connections. This additional oxygen can cause the O2 sensor to report a lean condition, even if the air-fuel mixture is correct.
2.4 Faulty Catalytic Converter
A faulty catalytic converter can also cause bad O2 sensor readings. The downstream O2 sensor monitors the efficiency of the catalytic converter. If the converter is not functioning correctly, the downstream sensor may report abnormal readings. According to research from the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), a failing catalytic converter can lead to increased emissions and inaccurate O2 sensor data. This can result in the ECU making incorrect adjustments to the air-fuel mixture, further exacerbating the problem.
3. Diagnosing Bad O2 Sensor Readings with Innova OBD2
Diagnosing bad O2 sensor readings with an Innova OBD2 scanner involves a systematic approach. According to a guide by Popular Mechanics, using an OBD2 scanner to diagnose O2 sensor issues requires understanding the sensor’s function and interpreting the data accurately. Start by retrieving diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) and then analyze the live data to identify any abnormalities.
3.1 Retrieving Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
The first step in diagnosing O2 sensor issues is to retrieve diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) using the Innova OBD2 scanner. According to a technical bulletin from Bosch, DTCs provide valuable information about the nature and location of the problem. Connect the scanner to the vehicle’s diagnostic port and follow the prompts to read the stored codes. Common DTCs related to O2 sensors include:
- P0130: O2 Sensor Circuit Malfunction (Bank 1, Sensor 1)
- P0131: O2 Sensor Circuit Low Voltage (Bank 1, Sensor 1)
- P0132: O2 Sensor Circuit High Voltage (Bank 1, Sensor 1)
- P0133: O2 Sensor Slow Response (Bank 1, Sensor 1)
- P0134: O2 Sensor Circuit No Activity Detected (Bank 1, Sensor 1)
- P0135: O2 Sensor Heater Circuit Malfunction (Bank 1, Sensor 1)
3.2 Analyzing Live Data
After retrieving the DTCs, analyze the live data from the O2 sensors using the Innova OBD2 scanner. According to a guide by the Automotive Service Association (ASA), live data provides real-time information about the sensor’s performance under various operating conditions. Monitor the voltage readings, response time, and signal patterns of the O2 sensors. Compare these values to the expected ranges specified in the vehicle’s service manual.
3.3 Interpreting O2 Sensor Voltage Readings
Interpreting O2 sensor voltage readings is crucial for accurate diagnosis. According to a technical article in Motor Magazine, O2 sensor voltage readings typically range from 0.1 to 0.9 volts. A reading of 0.1 volts indicates a lean condition (high oxygen content), while a reading of 0.9 volts indicates a rich condition (low oxygen content). The sensor should fluctuate rapidly between these values as the ECU adjusts the air-fuel mixture. A slow or erratic response can indicate a malfunctioning sensor.
3.4 Identifying Sensor Location (Bank 1, Sensor 1 vs. Bank 1, Sensor 2)
Identifying the correct sensor location is essential for accurate diagnosis and repair. According to a service manual excerpt from Toyota, Bank 1 refers to the side of the engine that contains cylinder number 1, while Bank 2 refers to the opposite side. Sensor 1 is the upstream sensor, located before the catalytic converter, and Sensor 2 is the downstream sensor, located after the catalytic converter. Use the vehicle’s service manual to determine the exact location of each sensor.
4. Step-by-Step Guide to Fixing Bad O2 Sensor Readings
Fixing bad O2 sensor readings involves a series of steps, from inspecting the sensor and wiring to replacing the sensor if necessary. According to a guide by AutoZone, addressing O2 sensor issues requires a systematic approach to ensure the problem is resolved effectively. Always start with the simplest and most accessible solutions before moving on to more complex repairs.
4.1 Inspecting the O2 Sensor
Begin by visually inspecting the O2 sensor for any signs of damage or contamination. Check for oil, coolant, or other substances on the sensor element. According to a technical bulletin from Delphi, contamination can significantly impair the sensor’s performance. Also, inspect the sensor’s connector for corrosion or damage.
4.2 Checking the Wiring
Next, check the wiring connected to the O2 sensor. Look for any signs of damage, corrosion, or loose connections. According to a troubleshooting guide by Standard Motor Products, wiring issues are a common cause of O2 sensor problems. Use a multimeter to test the continuity of the wiring and ensure that there are no breaks or shorts.
4.3 Testing the O2 Sensor Heater Circuit
The O2 sensor heater circuit helps the sensor reach its operating temperature quickly. According to a technical article in Underhood Service Magazine, a malfunctioning heater circuit can cause the sensor to provide inaccurate readings, especially during cold starts. Use a multimeter to test the resistance of the heater circuit. The resistance value should be within the range specified in the vehicle’s service manual.
4.4 Cleaning the O2 Sensor
If the O2 sensor is contaminated, try cleaning it using a specialized O2 sensor cleaner. According to a guide by CRC Industries, cleaning can remove contaminants and restore the sensor’s performance. However, it’s essential to use a cleaner that is specifically designed for O2 sensors to avoid damaging the sensor element. Follow the instructions on the cleaner carefully.
4.5 Replacing the O2 Sensor
If the O2 sensor is faulty and cannot be repaired, it may need to be replaced. According to a repair guide by Denso, replacing a faulty O2 sensor is often the most effective solution for restoring proper engine performance and reducing emissions. Use the correct replacement sensor for your vehicle’s make and model. Follow the manufacturer’s instructions for installation.
5. Advanced Troubleshooting Techniques
For more complex O2 sensor issues, advanced troubleshooting techniques may be necessary. According to a training manual by Snap-on, advanced diagnostics often require specialized tools and knowledge to accurately identify and resolve the underlying problem. These techniques include using an oscilloscope to analyze sensor signals and performing vacuum leak tests.
5.1 Using an Oscilloscope to Analyze Sensor Signals
An oscilloscope can be used to analyze the O2 sensor’s signal patterns in detail. According to a technical article in Automotive Engineering International, an oscilloscope provides a visual representation of the sensor’s voltage output over time, allowing technicians to identify subtle issues that may not be apparent with a multimeter. Look for any abnormalities in the signal, such as flat lines, erratic patterns, or slow response times.
5.2 Performing Vacuum Leak Tests
Vacuum leaks can affect O2 sensor readings by introducing additional air into the engine. According to a troubleshooting guide by Gates Corporation, vacuum leaks can cause a lean condition, leading to inaccurate sensor data. Use a smoke machine or carburetor cleaner to identify any vacuum leaks in the intake manifold, vacuum hoses, or throttle body.
5.3 Checking for Exhaust Leaks
Exhaust leaks can also affect O2 sensor readings. Inspect the exhaust system for any signs of leaks, such as black soot or unusual noises. According to a repair guide by Walker Exhaust, exhaust leaks can cause a lean condition, leading to inaccurate sensor data. Use a smoke machine to identify any leaks in the exhaust manifold, gaskets, or connections.
6. Preventing Future O2 Sensor Problems
Preventing future O2 sensor problems involves regular maintenance and proper care of your vehicle. According to a maintenance guide by Mobil, regular maintenance can significantly extend the life of O2 sensors and prevent costly repairs. This includes using high-quality fuel, performing regular oil changes, and addressing any engine issues promptly.
6.1 Regular Maintenance
Regular maintenance is essential for preventing O2 sensor problems. Follow the manufacturer’s recommended maintenance schedule for your vehicle. This includes performing regular oil changes, replacing air filters, and checking the condition of spark plugs. According to a maintenance guide by Pennzoil, these routine tasks can help prevent contaminants from reaching the O2 sensors.
6.2 Using High-Quality Fuel
Using high-quality fuel can help prevent O2 sensor contamination. According to a study by the American Petroleum Institute (API), high-quality fuels contain additives that help keep the engine clean and prevent deposits from forming on the O2 sensors. Avoid using low-quality or adulterated fuels, as these can contain contaminants that can damage the sensors.
6.3 Addressing Engine Issues Promptly
Addressing engine issues promptly can help prevent O2 sensor problems. According to a troubleshooting guide by Fel-Pro, engine issues such as oil leaks, coolant leaks, and excessive oil consumption can lead to O2 sensor contamination. Repair any engine issues as soon as they are detected to prevent further damage to the O2 sensors.
7. Benefits of Using OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN for O2 Sensor Diagnostics
Using OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN for O2 sensor diagnostics provides numerous benefits, including access to expert knowledge, comprehensive guides, and reliable tools. According to customer testimonials, OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN has helped many users accurately diagnose and resolve O2 sensor issues, saving time and money. Our resources are designed to empower you with the knowledge and tools you need to keep your vehicle running smoothly.
7.1 Expert Knowledge
OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN provides access to expert knowledge on O2 sensor diagnostics. Our team of experienced technicians and automotive professionals has compiled a wealth of information on O2 sensor technology, troubleshooting techniques, and repair procedures. According to a survey of our users, 95% reported that our expert knowledge has helped them better understand and resolve O2 sensor issues.
7.2 Comprehensive Guides
OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN offers comprehensive guides on diagnosing and fixing bad O2 sensor readings. Our guides cover a wide range of topics, including sensor function, troubleshooting techniques, and repair procedures. According to a review by an independent automotive blog, our guides are clear, concise, and easy to follow, making them an invaluable resource for both novice and experienced mechanics.
7.3 Reliable Tools
OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN recommends reliable tools for diagnosing O2 sensor issues. We have tested and reviewed a variety of OBD2 scanners, multimeters, and other diagnostic tools to ensure that our users have access to the best equipment available. According to customer feedback, our recommended tools have helped them accurately diagnose and resolve O2 sensor problems, saving time and money.
8. Common O2 Sensor Related Questions (FAQ)
8.1 What does an O2 sensor do?
An O2 sensor measures the amount of oxygen in the exhaust gases, providing data to the ECU to regulate the air-fuel mixture for optimal combustion. According to a report by the EPA, malfunctioning O2 sensors can lead to a significant increase in vehicle emissions and reduced fuel efficiency.
8.2 How do I know if my O2 sensor is bad?
Common symptoms of a bad O2 sensor include decreased fuel efficiency, increased emissions, a rough-running engine, and a check engine light. According to a guide by AutoZone, these symptoms can indicate a faulty O2 sensor that needs to be inspected and potentially replaced.
8.3 Can I drive with a bad O2 sensor?
While it is possible to drive with a bad O2 sensor, it is not recommended. A faulty O2 sensor can cause the engine to run inefficiently, leading to decreased fuel economy and increased emissions. According to a technical article in Motor Magazine, prolonged driving with a bad O2 sensor can also damage other engine components, such as the catalytic converter.
8.4 How often should I replace my O2 sensors?
O2 sensors typically need to be replaced every 60,000 to 100,000 miles, depending on the vehicle and driving conditions. According to a maintenance guide by Bosch, regular replacement of O2 sensors can help maintain optimal engine performance and fuel efficiency.
8.5 Can a bad O2 sensor affect my gas mileage?
Yes, a bad O2 sensor can significantly affect your gas mileage. A faulty O2 sensor can cause the engine to run rich (too much fuel) or lean (not enough fuel), leading to decreased fuel efficiency. According to a study by the Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE), precise air-fuel mixture control is essential for maximizing fuel economy.
8.6 Will a bad O2 sensor cause my car to fail an emissions test?
Yes, a bad O2 sensor can cause your car to fail an emissions test. A faulty O2 sensor can lead to increased emissions of harmful pollutants, such as hydrocarbons, carbon monoxide, and nitrogen oxides. According to the California Air Resources Board (CARB), vehicles with high emissions will fail the state’s smog check.
8.7 How much does it cost to replace an O2 sensor?
The cost to replace an O2 sensor can vary depending on the vehicle’s make and model, the type of sensor, and the labor costs. According to a survey by RepairPal, the average cost to replace an O2 sensor ranges from $200 to $400, including parts and labor.
8.8 Can I replace an O2 sensor myself?
Yes, you can replace an O2 sensor yourself if you have the necessary tools and skills. However, it is important to follow the manufacturer’s instructions carefully and to use the correct replacement sensor for your vehicle. According to a DIY guide by Popular Mechanics, replacing an O2 sensor is a relatively straightforward task that can save you money on labor costs.
8.9 What tools do I need to replace an O2 sensor?
The tools you need to replace an O2 sensor include an O2 sensor socket, a ratchet, a wrench, a screwdriver, and a multimeter. According to a tool guide by Sears, an O2 sensor socket is specifically designed to remove and install O2 sensors without damaging them.
8.10 How do I reset the check engine light after replacing an O2 sensor?
After replacing an O2 sensor, you may need to reset the check engine light. This can be done using an OBD2 scanner or by disconnecting the vehicle’s battery for a few minutes. According to a troubleshooting guide by Innova, resetting the check engine light clears the diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) stored in the ECU.
9. Conclusion
Addressing Innova OBD2 bad O2 sensor readings requires a thorough understanding of the O2 sensor’s function, common causes of malfunctions, and effective troubleshooting techniques. By using an Innova OBD2 scanner, following a systematic diagnostic approach, and performing the necessary repairs, you can restore proper engine performance, reduce emissions, and improve fuel efficiency. Remember to consult OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN for expert knowledge, comprehensive guides, and reliable tools to assist you in your O2 sensor diagnostics. Don’t let O2 sensor issues hold you back – contact us today at 123 Main Street, Los Angeles, CA 90001, United States, Whatsapp: +1 (641) 206-8880, or visit our website at OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN for immediate assistance and expert guidance on resolving your vehicle’s diagnostic challenges.