Obd2 Alternator Test is possible but with some limitations. An OBD2 scanner like the Foxwell NT1009 can be a valuable tool to inspect your alternator, offering insights into your vehicle’s electrical health, and at OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN, we help you understand how to use it effectively. You can enhance your diagnostic capabilities by learning to interpret voltage readings and error codes related to your charging system, leading to better car maintenance and troubleshooting.
Contents
- 1. Understanding the Alternator’s Role in Your Vehicle’s Electrical System
- 2. How an OBD2 Scanner Can Assist in Diagnosing Alternator Issues
- 3. Step-by-Step Guide: Using an OBD2 Scanner for Alternator Checks
- 3.1. Prepare Your Vehicle and Scanner
- 3.2. Connect the Foxwell NT1009 Scanner
- 3.3. Navigating the Diagnostic Menu
- 3.4. Check Error Codes
- 3.5. Check Live Data for Voltage Output
- 3.6. Load Testing with Electrical Accessories
- 3.7. Take Advantage of Special Testing Functions
- 3.8. Analyze and Respond
- 3.9. Unplug and Store the Scanner Properly
- 4. Alternative Methods to Test Your Vehicle’s Alternator
- 4.1. Using a Multimeter
- 4.2. Performing a Load Test
- 5. Common OBD2 Codes Related to Alternator Issues
- 6. How to Interpret Voltage Readings for Accurate Diagnosis
- 6.1. Normal Voltage Range
- 6.2. Low Voltage Readings
- 6.3. High Voltage Readings
- 6.4. Voltage Drop Under Load
- 6.5. Using Live Data for Monitoring
- 7. The Importance of Regular Alternator Maintenance
- 8. Upgrading to Advanced OBD2 Scanners for Enhanced Diagnostics
- 8.1. Enhanced Features of Advanced Scanners
- 8.2. Benefits of Upgrading
- 8.3. Choosing the Right Scanner
- 9. The Role of OBD2 Scanners in Preventive Car Maintenance
- 9.1. Regular Monitoring
- 9.2. Tracking Performance
- 9.3. Identifying Potential Problems
- 9.4. Staying Informed
- 9.5. Integrating with Maintenance Schedules
- 10. Troubleshooting Common Issues Encountered During Alternator Testing
- 10.1. Scanner Compatibility Issues
- 10.2. Connection Problems
- 10.3. Incorrect Data Readings
- 10.4. Error Codes That Don’t Match Symptoms
- 10.5. Interference From Other Electrical Devices
- 11. Integrating OBD2 Scanner Data with Professional Diagnostic Tools
- 11.1. Enhanced Data Analysis
- 11.2. Bi-Directional Control
- 11.3. Access to Repair Information
- 11.4. Integration with Vehicle Databases
- 11.5. Collaboration with Mechanics
- 12. The Future of OBD2 Scanners in Automotive Diagnostics
- 12.1. Enhanced Connectivity
- 12.2. Artificial Intelligence (AI)
- 12.3. Integration with Advanced Driver-Assistance Systems (ADAS)
- 12.4. Over-the-Air Updates
- 12.5. User-Friendly Interfaces
- 13. Conclusion: The OBD2 Scanner as a Valuable Diagnostic Tool
- 14. Need Help with Your Alternator or OBD2 Scanner? Contact Us Today
- 15. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About OBD2 Alternator Testing
- 15.1. Can you test an alternator with an OBD2 scanner?
- 15.2. Will a bad alternator show up on a scan?
- 15.3. Is there an OBD code for alternator?
- 15.4. What voltage should I see when testing my alternator with an OBD2 scanner?
- 15.5. Can an OBD2 scanner detect a faulty voltage regulator?
- 15.6. How do I use live data to test my alternator with an OBD2 scanner?
- 15.7. What should I do if my OBD2 scanner shows a low voltage code?
- 15.8. Can I clear alternator-related codes with an OBD2 scanner?
- 15.9. Are there any specific tests for the charging system on an OBD2 scanner?
- 15.10. How often should I test my alternator with an OBD2 scanner?
1. Understanding the Alternator’s Role in Your Vehicle’s Electrical System
The alternator is a crucial component of your car’s electrical system, similar to how the heart functions in the human body. According to a study by the University of Michigan Transportation Research Institute, alternators are responsible for maintaining the charge of the battery and powering the electrical systems while the engine is running. They convert mechanical energy from the engine into electrical energy, which is then used to power components like headlights, the radio, and other accessories. Without a properly functioning alternator, your battery could quickly drain, leaving you stranded.
Common signs of a failing alternator include:
- Dimming headlights
- Slow engine start-up
- Dead battery
- Warning lights on the dashboard
Recognizing these symptoms early can save you from more significant headaches and repair bills in the future. Regular checks and proactive maintenance can keep your vehicle running smoothly.
2. How an OBD2 Scanner Can Assist in Diagnosing Alternator Issues
An OBD2 scanner, such as the Foxwell NT1009, can be an invaluable tool when diagnosing alternator issues, but it’s essential to understand its limitations. These tools read trouble codes stored by your car’s computer when something doesn’t function as expected, providing insight into potential problems under the hood.
According to research published in the SAE International Journal of Engines, OBD2 scanners have become increasingly sophisticated in detecting various automotive issues, including electrical system malfunctions.
While an OBD2 scanner won’t directly tell you if the alternator is faulty, it can identify related electrical issues such as:
- Low voltage (P0562)
- Problems in the field control circuit (P0622)
These clues can guide you toward determining if the alternator is the issue or if further investigation is needed. Remember, the scanner provides data, and it’s up to you to interpret it accurately.
3. Step-by-Step Guide: Using an OBD2 Scanner for Alternator Checks
To effectively use an OBD2 scanner like the Foxwell NT1009 to check for alternator problems, follow these steps:
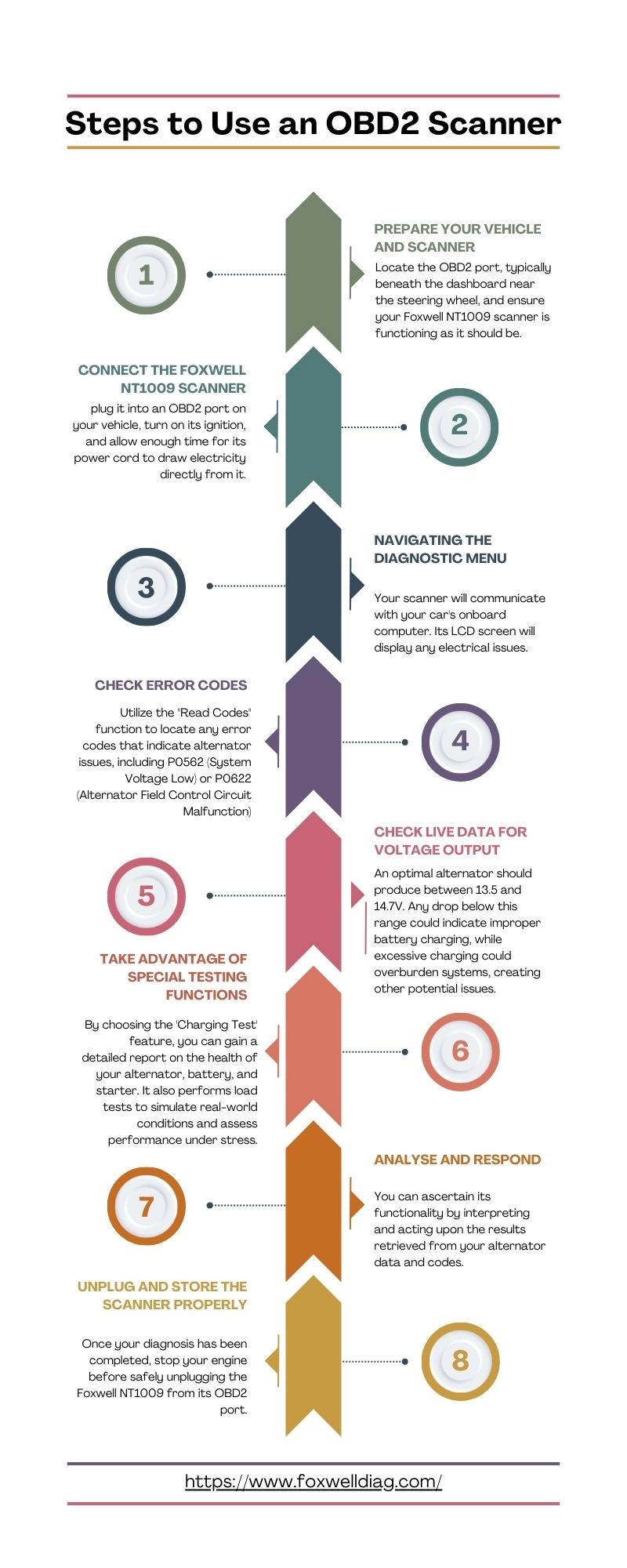
3.1. Prepare Your Vehicle and Scanner
Start by preparing your vehicle. Turn off all electronics, such as headlights and the radio, to avoid additional electrical load. Locate the OBD2 port, typically beneath the dashboard near the steering wheel, and ensure your Foxwell NT1009 scanner is functioning correctly.
3.2. Connect the Foxwell NT1009 Scanner
Plug the Foxwell NT1009 scanner into the OBD2 port on your vehicle. Turn on the ignition but don’t start the engine. Allow the scanner enough time to draw electricity directly from the car. Give it time to initialize and establish communication between itself and all systems within your car before testing begins.
3.3. Navigating the Diagnostic Menu
Access the diagnostic feature on the scanner. Navigate its menu until you find the “Diagnostic” section and choose it. When prompted, enter your vehicle’s make and model to provide accurate data. This step ensures the scanner communicates correctly with your car’s onboard computer.
3.4. Check Error Codes
Use the “Read Codes” function to locate any error codes that indicate alternator issues. Common codes include P0562 (System Voltage Low) or P0622 (Alternator Field Control Circuit Malfunction). These error messages could indicate potential alternator malfunction and should be noted for further investigation.
3.5. Check Live Data for Voltage Output
The Foxwell NT1009 allows you to monitor live data, which is essential for tracking an alternator’s performance. Start your engine and watch for voltage readings as soon as they appear. An optimal alternator should produce between 13.5 and 14.7V. Any drop below this range could indicate improper battery charging, while excessive charging could overburden systems, creating other potential issues.
According to a study by the Automotive Research Association of India, maintaining the correct voltage output is critical for the longevity and efficiency of automotive electrical systems.
3.6. Load Testing with Electrical Accessories
To further assess the alternator, turn on various electrical accessories, such as headlights and the air conditioner, to test how it handles an increased load. Signs of voltage dropping significantly under load could indicate an ineffective alternator. Monitor the voltage levels with the OBD2 scanner while these accessories are running.
3.7. Take Advantage of Special Testing Functions
The Foxwell NT1009 provides specific tests for your vehicle’s charging system. By choosing the ‘Charging Test’ feature, you can gain a detailed report on the health of your alternator, battery, and starter. It also performs load tests to simulate real-world conditions and assess performance under stress.
3.8. Analyze and Respond
Interpret and act upon the results retrieved from your alternator data and codes. If all readings fall within normal ranges, your alternator is probably functioning appropriately. However, if voltage readings consistently range low or high, this indicates repair or replacement is required. Using your scanner can clear any error codes left after making repairs.
3.9. Unplug and Store the Scanner Properly
Once your diagnosis has been completed, stop your engine before safely unplugging the Foxwell NT1009 from its OBD2 port. Store it away in a safe place to ensure its readiness for future use. Regular maintenance of your scanner will prolong its life and accuracy.
 Connecting Foxwell NT1009 to OBD2 port
Connecting Foxwell NT1009 to OBD2 port
4. Alternative Methods to Test Your Vehicle’s Alternator
If the OBD2 scanner cannot provide definitive answers, other methods exist for testing your alternator. These include using a multimeter or performing a load test.
4.1. Using a Multimeter
A multimeter is an efficient and straightforward approach. Connect it to the battery terminals while running the engine; readings between 13.5 and 14.7 V indicate proper alternator functioning. This method provides a quick snapshot of the alternator’s output voltage.
4.2. Performing a Load Test
A load test provides a more in-depth examination, using either a particular tool or professional mechanic, to gauge how well an alternator performs when the vehicle’s electrical load increases. This test measures its ability to provide consistent power when increased electrical loads come onto its circuits. It’s a more reliable method for assessing the alternator’s overall health.
According to a publication by the American Society of Automotive Engineers, load testing is a critical diagnostic step in evaluating alternator performance under real-world conditions.
5. Common OBD2 Codes Related to Alternator Issues
Understanding common OBD2 codes related to alternator issues can significantly aid in diagnosing problems. Here are some of the most frequent codes and what they indicate:
| OBD2 Code | Description | Possible Causes |
|---|---|---|
| P0562 | System Voltage Low | Faulty alternator, poor battery connection, short circuit in the electrical system |
| P0622 | Alternator Field Control Circuit Malfunction | Faulty alternator, wiring issues, problems with the engine control module (ECM) |
| P065A | Generator Performance | Failing alternator, worn brushes, internal component failure |
| P065B | Generator Control Circuit Range/Performance | Wiring problems, loose connections, faulty voltage regulator |
| P065C | Generator Control Circuit High | Short in the control circuit, faulty ECM, wiring issues |
| P065D | Generator Control Circuit Low | Open circuit, poor connection, faulty ECM |
| P065E | Generator Current Performance | Issues with the alternator’s ability to provide adequate current, internal failure |
| P065F | Generator Current Range/Performance | Problems with the alternator’s current regulation, wiring issues, faulty voltage regulator |
| P0660 | Intake Manifold Tuning Valve Control Circuit Open | Open or shorted generator tuning valve control circuit, poor electrical connection |
These codes can help you narrow down the potential issues and take appropriate action.
6. How to Interpret Voltage Readings for Accurate Diagnosis
Interpreting voltage readings from an OBD2 scanner is essential for accurately diagnosing alternator problems. Understanding what the readings indicate can help you determine the health of your alternator and take appropriate action.
6.1. Normal Voltage Range
A healthy alternator should produce between 13.5 and 14.7 volts when the engine is running. This range ensures that the battery is charging correctly and that the vehicle’s electrical systems are adequately powered.
6.2. Low Voltage Readings
If the voltage reading is below 13.5 volts, it could indicate that the alternator is not producing enough power to charge the battery and run the electrical systems. This can lead to a dead battery and other electrical issues.
Possible causes of low voltage include:
- A failing alternator
- Worn brushes
- Poor connections
- A faulty voltage regulator
6.3. High Voltage Readings
If the voltage reading is above 14.7 volts, it could indicate that the alternator is overcharging the battery. This can damage the battery and other electrical components.
Possible causes of high voltage include:
- A faulty voltage regulator
- Wiring issues
- A bad ground connection
6.4. Voltage Drop Under Load
When you turn on electrical accessories like headlights and the air conditioner, the voltage should not drop significantly. A significant drop in voltage under load indicates that the alternator is struggling to keep up with the electrical demand, which can be a sign of a failing alternator.
6.5. Using Live Data for Monitoring
The Foxwell NT1009 allows you to monitor live data, which is essential for tracking an alternator’s performance over time. By observing voltage readings under different conditions, you can get a more comprehensive understanding of the alternator’s health.
Interpreting voltage readings accurately requires attention to detail and an understanding of the factors that can affect voltage levels. Regular monitoring and prompt action can help prevent electrical problems and keep your vehicle running smoothly.
7. The Importance of Regular Alternator Maintenance
Regular alternator maintenance is crucial for ensuring the reliability and longevity of your vehicle. Neglecting maintenance can lead to unexpected breakdowns and costly repairs. Here are some essential maintenance tips:
- Inspect the Alternator Belt: Check the alternator belt for signs of wear and tear, such as cracks, fraying, or glazing. Replace the belt if it is damaged.
- Check Electrical Connections: Ensure that all electrical connections to the alternator are clean and tight. Loose or corroded connections can cause voltage drops and other electrical problems.
- Monitor Voltage Output: Use an OBD2 scanner or a multimeter to regularly monitor the alternator’s voltage output. This can help you detect problems early before they lead to more significant issues.
- Test the Battery: Have the battery tested regularly to ensure that it is in good condition. A weak battery can put extra strain on the alternator and shorten its lifespan.
- Keep the Alternator Clean: Keep the alternator clean and free of dirt and debris. A dirty alternator can overheat and fail prematurely.
By following these maintenance tips, you can extend the life of your alternator and avoid unexpected breakdowns. Regular maintenance not only saves you money in the long run but also ensures that your vehicle remains reliable and safe.
8. Upgrading to Advanced OBD2 Scanners for Enhanced Diagnostics
As technology advances, upgrading to more advanced OBD2 scanners can significantly enhance your diagnostic capabilities. Advanced scanners offer features that go beyond basic code reading and live data monitoring, providing a more comprehensive understanding of your vehicle’s health.
8.1. Enhanced Features of Advanced Scanners
- Bi-Directional Control: Allows you to send commands to the vehicle’s systems to test components and functions.
- Advanced Code Reading: Provides more detailed information about trouble codes, including possible causes and solutions.
- Data Logging: Allows you to record live data over time, which can be useful for diagnosing intermittent problems.
- Special Functions: Includes features such as ABS bleeding, throttle reset, and TPMS programming.
- Wireless Connectivity: Connects to your smartphone or tablet via Bluetooth or Wi-Fi, allowing you to view and analyze data on a larger screen.
8.2. Benefits of Upgrading
- More Accurate Diagnoses: Advanced features help you pinpoint problems more accurately, reducing the risk of misdiagnosis and unnecessary repairs.
- Faster Troubleshooting: Bi-directional control and data logging can speed up the troubleshooting process, saving you time and money.
- Comprehensive Vehicle Coverage: Many advanced scanners support a wide range of vehicle makes and models, ensuring compatibility with your car.
- User-Friendly Interface: Modern scanners often have intuitive interfaces and color displays, making them easier to use.
8.3. Choosing the Right Scanner
When choosing an advanced OBD2 scanner, consider your specific needs and budget. Look for a scanner that supports the features you need and is compatible with your vehicle. Read reviews and compare different models to find the best option for you.
Upgrading to an advanced OBD2 scanner can significantly improve your ability to diagnose and repair vehicle problems, ultimately saving you time and money.
9. The Role of OBD2 Scanners in Preventive Car Maintenance
OBD2 scanners play a crucial role in preventive car maintenance by allowing you to monitor your vehicle’s health and detect potential problems early. Regular use of an OBD2 scanner can help you avoid costly repairs and extend the life of your vehicle.
9.1. Regular Monitoring
By regularly scanning your vehicle for trouble codes, you can identify issues before they become major problems. Many minor issues can be resolved quickly and inexpensively if detected early.
9.2. Tracking Performance
OBD2 scanners allow you to track various performance parameters, such as engine temperature, fuel consumption, and O2 sensor readings. Monitoring these parameters can help you identify trends and detect anomalies that could indicate a problem.
9.3. Identifying Potential Problems
Even if your vehicle is not exhibiting any symptoms, an OBD2 scanner can detect hidden problems that could lead to future breakdowns. For example, a pending code might indicate a sensor that is starting to fail or a system that is not performing optimally.
9.4. Staying Informed
Using an OBD2 scanner can help you stay informed about your vehicle’s health and make informed decisions about maintenance and repairs. By understanding the data provided by the scanner, you can avoid unnecessary repairs and ensure that your vehicle is running efficiently.
9.5. Integrating with Maintenance Schedules
Combine regular OBD2 scanning with your vehicle’s recommended maintenance schedule to ensure comprehensive care. Address any issues detected by the scanner during routine maintenance to keep your vehicle in top condition.
10. Troubleshooting Common Issues Encountered During Alternator Testing
During alternator testing with an OBD2 scanner, you may encounter some common issues that can affect the accuracy of your diagnosis. Understanding these issues and how to troubleshoot them can help you get reliable results.
10.1. Scanner Compatibility Issues
Not all OBD2 scanners are compatible with all vehicles. Before starting the test, ensure that your scanner is compatible with your vehicle’s make and model. Check the scanner’s documentation or the manufacturer’s website for compatibility information.
10.2. Connection Problems
A poor connection between the scanner and the vehicle’s OBD2 port can prevent the scanner from reading data. Ensure that the scanner is securely plugged into the OBD2 port and that there are no loose connections. Clean the OBD2 port if necessary to ensure a good connection.
10.3. Incorrect Data Readings
Incorrect data readings can result from a faulty scanner or a problem with the vehicle’s electrical system. Verify the accuracy of the readings by comparing them to known values or by testing the alternator with a multimeter. If the readings are consistently incorrect, the scanner may need to be repaired or replaced.
10.4. Error Codes That Don’t Match Symptoms
Sometimes, the error codes displayed by the scanner may not match the symptoms that the vehicle is exhibiting. This can be due to a variety of factors, such as a misinterpretation of the codes or a problem with the vehicle’s computer. Consult a repair manual or a qualified mechanic to help you interpret the codes and diagnose the problem.
10.5. Interference From Other Electrical Devices
Other electrical devices in the vehicle can interfere with the scanner’s readings. Turn off any unnecessary electrical devices, such as headlights and the radio, during the test to minimize interference.
By understanding these common issues and how to troubleshoot them, you can ensure that you get accurate and reliable results when testing your alternator with an OBD2 scanner.
 Foxwell Full System Car Scanner
Foxwell Full System Car Scanner
11. Integrating OBD2 Scanner Data with Professional Diagnostic Tools
While OBD2 scanners are valuable for initial diagnostics, integrating their data with professional diagnostic tools can provide a more comprehensive and accurate assessment of alternator issues. Professional tools offer advanced features and capabilities that go beyond what a standard OBD2 scanner can provide.
11.1. Enhanced Data Analysis
Professional diagnostic tools can analyze data from the OBD2 scanner in more detail, providing insights into the root cause of the problem. They can also access additional data from the vehicle’s computer that is not available to standard OBD2 scanners.
11.2. Bi-Directional Control
Many professional tools offer bi-directional control, allowing you to send commands to the vehicle’s systems to test components and functions. This can be useful for testing the alternator’s voltage regulator or field control circuit.
11.3. Access to Repair Information
Professional diagnostic tools often provide access to repair information, such as wiring diagrams, technical service bulletins, and repair procedures. This information can help you troubleshoot and repair alternator issues more effectively.
11.4. Integration with Vehicle Databases
Some professional tools integrate with vehicle databases, providing detailed information about the vehicle’s systems and components. This can be useful for identifying potential problems and finding the right parts for the repair.
11.5. Collaboration with Mechanics
If you are unable to diagnose or repair the alternator issue yourself, integrating the OBD2 scanner data with a professional mechanic can help them troubleshoot the problem more quickly and accurately. Share the data from the scanner with the mechanic to provide them with a starting point for their diagnosis.
12. The Future of OBD2 Scanners in Automotive Diagnostics
The future of OBD2 scanners in automotive diagnostics looks promising, with ongoing advancements in technology and increasing integration with other automotive systems. As vehicles become more complex, OBD2 scanners will play an even more critical role in diagnosing and repairing problems.
12.1. Enhanced Connectivity
Future OBD2 scanners will likely feature enhanced connectivity options, such as wireless communication and cloud integration. This will allow for easier data sharing and remote diagnostics.
12.2. Artificial Intelligence (AI)
AI is expected to play a significant role in future OBD2 scanners, providing advanced data analysis and diagnostic capabilities. AI algorithms can analyze data from the scanner to identify patterns and predict potential problems before they occur.
12.3. Integration with Advanced Driver-Assistance Systems (ADAS)
As ADAS technologies become more prevalent, OBD2 scanners will need to integrate with these systems to diagnose and repair problems. This will require new diagnostic tools and procedures.
12.4. Over-the-Air Updates
Future OBD2 scanners will likely receive over-the-air updates, allowing them to stay up-to-date with the latest vehicle technologies and diagnostic procedures. This will ensure that the scanners remain compatible with new vehicles and can accurately diagnose problems.
12.5. User-Friendly Interfaces
OBD2 scanners are becoming more user-friendly, with intuitive interfaces and easy-to-understand data displays. This will make them accessible to a wider range of users, from professional mechanics to DIY enthusiasts.
13. Conclusion: The OBD2 Scanner as a Valuable Diagnostic Tool
An OBD2 scanner like Foxwell’s NT1009 is an invaluable tool for identifying alternator issues, but it shouldn’t be seen as your sole solution. While it provides valuable insights through live data feeds and special testing features, additional testing may still be necessary in certain instances. OBD2 scanners serve as an initial line of defense against car issues, helping detect problems early and providing enough data to decide whether you can repair it or need professional assistance.
At OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN, we believe that with regular use, Foxwell NT1009s can keep your electrical system under control and help avoid unexpected breakdowns or costly repairs. By understanding its capabilities and limitations, you can use it effectively to maintain your vehicle’s health and ensure reliable performance.
14. Need Help with Your Alternator or OBD2 Scanner? Contact Us Today
Are you experiencing alternator issues or need assistance using your OBD2 scanner? Don’t hesitate to reach out to us at OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN. Our team of expert technicians is ready to help you diagnose and resolve any problems you may be facing.
- Address: 123 Main Street, Los Angeles, CA 90001, United States
- WhatsApp: +1 (641) 206-8880
- Website: OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN
Whether you’re a seasoned mechanic or a DIY enthusiast, we can provide the guidance and support you need to keep your vehicle running smoothly. Contact us today for a consultation and let us help you get back on the road with confidence.
15. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About OBD2 Alternator Testing
15.1. Can you test an alternator with an OBD2 scanner?
Yes, an OBD2 scanner can help you test an alternator by reading trouble codes and monitoring live voltage data. However, it may not give a direct diagnosis, so you might need to combine it with other testing methods for a complete assessment.
15.2. Will a bad alternator show up on a scan?
A bad alternator can trigger related trouble codes on a scan, such as low system voltage or issues with the alternator’s circuit. While it won’t specifically say “bad alternator,” the codes can indicate a problem that requires further investigation.
15.3. Is there an OBD code for alternator?
Yes, there are OBD codes that relate to alternator issues. Common ones include P0562 (System Voltage Low) and P0622 (Alternator Field Control Circuit Malfunction), which can signal that your alternator isn’t working properly.
15.4. What voltage should I see when testing my alternator with an OBD2 scanner?
When testing your alternator with an OBD2 scanner, you should see a voltage reading between 13.5 and 14.7 volts. This range indicates that the alternator is functioning properly and charging the battery effectively.
15.5. Can an OBD2 scanner detect a faulty voltage regulator?
Yes, an OBD2 scanner can detect a faulty voltage regulator by monitoring the voltage output of the alternator. If the voltage is consistently too high or too low, it could indicate a problem with the voltage regulator.
15.6. How do I use live data to test my alternator with an OBD2 scanner?
To use live data to test your alternator, connect the OBD2 scanner to your vehicle, start the engine, and select the option to view live data. Look for the voltage reading and monitor it as you turn on electrical accessories like headlights and the air conditioner. The voltage should remain within the normal range, even under load.
15.7. What should I do if my OBD2 scanner shows a low voltage code?
If your OBD2 scanner shows a low voltage code, such as P0562, it could indicate a problem with the alternator, battery, or wiring. Check the battery connections, test the battery, and inspect the alternator. If necessary, consult a qualified mechanic for further diagnosis and repair.
15.8. Can I clear alternator-related codes with an OBD2 scanner?
Yes, you can clear alternator-related codes with an OBD2 scanner after you have addressed the underlying issue. However, it’s important to note that the codes may reappear if the problem is not fully resolved.
15.9. Are there any specific tests for the charging system on an OBD2 scanner?
Some OBD2 scanners, like the Foxwell NT1009, offer specific tests for the charging system. These tests can provide detailed information about the health of the alternator, battery, and starter.
15.10. How often should I test my alternator with an OBD2 scanner?
It’s a good practice to test your alternator with an OBD2 scanner as part of your regular vehicle maintenance routine. Testing it every few months can help you detect potential problems early and prevent unexpected breakdowns.