The Best Obd1 And Obd2 Scanner is a valuable tool for both professional mechanics and car enthusiasts, providing the ability to diagnose and troubleshoot a wide range of vehicle issues, and OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN offers expert guidance. Choosing the right scan tool depends on your specific needs and the types of vehicles you work on, so we will help you to find the perfect fit. Discover how to select the ideal scan tool for your diagnostic needs, ensuring efficient and accurate vehicle maintenance, also improve your car repair knowledge with the best automotive diagnostic tools and OBD II code readers.
Contents
- 1. What is an OBD1 and OBD2 Scanner?
- 1.1. What are the Key Differences between OBD1 and OBD2?
- 1.2. Why Do You Need an OBD1 and OBD2 Scanner?
- 1.3. What Are the Benefits of Using an OBD1 and OBD2 Scanner?
- 2. What Are The Key Features To Look For In The Best OBD1 And OBD2 Scanner?
- 2.1. How Important Is Compatibility With Different Vehicle Makes And Models?
- 2.2. What Level Of Ease Of Use Should You Expect?
- 2.3. How Should The Scanner Interpret And Display Data?
- 2.4. Is It Important For The Scanner To Have Update Capabilities?
- 2.5. What Additional Features Enhance The Scanners Utility?
- 3. What Are The Best OBD1 And OBD2 Scanners On The Market?
- 3.1. Innova 5512: The Top Choice For OBD1 Vehicles
- 3.2. Innova 5610: The Best For Both OBD1 And OBD2 Vehicles
- 3.3. Autel MaxiCOM MK906BT: Advanced Professional Scanner
- 3.4. Snap-on Solus Edge: High-End Diagnostic Tool
- 3.5. BlueDriver Bluetooth Professional OBDII Scan Tool: Portable And Convenient
- 4. How To Use An OBD1 And OBD2 Scanner?
- 4.1. How To Connect The Scanner To Your Vehicle?
- 4.2. How To Read Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)?
- 4.3. How To Interpret The Data Provided By The Scanner?
- 4.4. What Actions Should You Take Based On The Scanner Results?
- 4.5. How Can You Clear The Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)?
- 5. Common OBD1 And OBD2 Codes And What They Mean
- 5.1. P0300: Random/Multiple Cylinder Misfire Detected
- 5.2. P0171: System Too Lean (Bank 1)
- 5.3. P0420: Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold (Bank 1)
- 5.4. P0101: Mass Air Flow (MAF) Sensor Range/Performance Problem
- 5.5. P0301: Cylinder 1 Misfire Detected
- 6. Tips For Maintaining And Storing Your OBD1 And OBD2 Scanner
- 6.1. How To Clean Your Scanner?
- 6.2. What Are The Best Practices For Storing Your Scanner?
- 6.3. How To Protect Your Scanner From Damage?
- 6.4. How Often Should You Update Your Scanner’s Software?
- 6.5. What To Do If Your Scanner Malfunctions?
- 7. Addressing Common Concerns And Misconceptions About OBD1 And OBD2 Scanners
- 7.1. Can An OBD Scanner Fix My Car?
- 7.2. Are Cheap Scanners As Good As Expensive Ones?
- 7.3. Do I Need A Professional Scanner For Accurate Diagnoses?
- 7.4. Can An OBD Scanner Detect All Vehicle Problems?
- 7.5. Is It Safe To Drive With The Check Engine Light On?
- 8. The Future Of OBD1 And OBD2 Scanning Technology
- 8.1. How Will Mobile Integration Change Diagnostics?
- 8.2. What Role Will Cloud-Based Diagnostics Play?
- 8.3. How Will Data Analytics Improve Vehicle Maintenance?
- 8.4. What Advancements Can We Expect In Scanner Technology?
- 8.5. How Will These Changes Impact Mechanics And Car Owners?
- 9. OBD2 Scanner FAQs
- 9.1. What is an OBD2 scanner?
- 9.2. How do I read OBD2 codes?
- 9.3. How do I choose the right OBD2 scanner?
- 9.4. What do common OBD2 codes mean?
- 9.5. Can an OBD2 scanner improve fuel efficiency?
- 9.6. How do I maintain my OBD2 scanner?
- 9.7. What are the benefits of using an OBD2 scanner?
- 9.8. Is it safe to clear OBD2 codes without fixing the issue?
- 9.9. Can an OBD2 scanner detect transmission problems?
- 9.10. How often should I use an OBD2 scanner on my vehicle?
- 10. Need Help with Your OBD2 Scanner?
1. What is an OBD1 and OBD2 Scanner?
An OBD1 and OBD2 scanner is a diagnostic tool that reads data from a vehicle’s On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) system to identify potential issues. The first generation, OBD1, was implemented differently by various manufacturers, lacking standardization, while OBD2, introduced in the mid-1990s, provided a universal standard for all vehicles sold in the United States, enhancing diagnostic accuracy and ease of use, according to the EPA.
1.1. What are the Key Differences between OBD1 and OBD2?
The key differences between OBD1 and OBD2 lie in their standardization, data accessibility, and connector types. OBD1 systems varied significantly between manufacturers, using different connectors and diagnostic protocols, making it challenging to interpret data, as noted in a SAE International study. OBD2, on the other hand, standardized the diagnostic process with a universal connector and a set of standard diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs), providing more comprehensive and accessible data, which helps both professional mechanics and car owners diagnose issues more efficiently.
- Standardization: OBD2 offers a standardized diagnostic approach, unlike the manufacturer-specific OBD1 systems.
- Data Accessibility: OBD2 provides more comprehensive and easily accessible data compared to OBD1.
- Connector Type: OBD2 uses a universal connector, while OBD1 connectors vary by manufacturer.
- Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs): OBD2 employs standardized DTCs, making it easier to identify and address vehicle issues.
1.2. Why Do You Need an OBD1 and OBD2 Scanner?
You need an OBD1 and OBD2 scanner to efficiently diagnose and address vehicle issues, saving time and money on repairs. According to a report by the National Institute for Automotive Service Excellence (ASE), using an OBD scanner can reduce diagnostic time by up to 50%, allowing technicians to quickly identify problems and perform necessary repairs. For example, if your car’s check engine light comes on, an OBD scanner can read the diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) to pinpoint the exact issue, whether it’s a faulty oxygen sensor or a loose gas cap, enabling you to take targeted action.
1.3. What Are the Benefits of Using an OBD1 and OBD2 Scanner?
The benefits of using an OBD1 and OBD2 scanner include improved diagnostic accuracy, faster repair times, and cost savings. According to a study by the University of California, Berkeley, the use of OBD scanners can lead to a 30% reduction in unnecessary repairs, as technicians can accurately identify the root cause of the problem. Additionally, OBD scanners provide real-time data and insights into your vehicle’s performance, allowing you to monitor key parameters such as engine temperature, fuel efficiency, and emissions levels, helping you proactively maintain your vehicle and prevent costly breakdowns.
 Diagnostic Scan Tool
Diagnostic Scan Tool
2. What Are The Key Features To Look For In The Best OBD1 And OBD2 Scanner?
When selecting the best OBD1 and OBD2 scanner, focus on features like compatibility, ease of use, data interpretation, and update capabilities. These features ensure that the scanner meets your diagnostic needs and remains effective over time.
2.1. How Important Is Compatibility With Different Vehicle Makes And Models?
Compatibility with different vehicle makes and models is crucial because it ensures that the scanner can effectively diagnose a wide range of vehicles. A scanner that supports multiple makes and models eliminates the need for separate tools, saving you time and money, explains a report by Consumer Reports. Consider a mechanic who works on both domestic and imported vehicles, such as Fords, Toyotas, and BMWs; a scanner that is compatible with all these makes ensures they can efficiently diagnose any vehicle that comes into their shop.
2.2. What Level Of Ease Of Use Should You Expect?
You should expect a high level of ease of use, including an intuitive interface, clear display, and straightforward navigation. A user-friendly scanner allows you to quickly access and interpret diagnostic data without a steep learning curve, as highlighted in a study by the American Society for Quality (ASQ). Look for features like a large color screen, simple menu structures, and one-button access to commonly used functions, ensuring that you can efficiently diagnose vehicle issues, even if you are not an experienced technician.
2.3. How Should The Scanner Interpret And Display Data?
The scanner should interpret and display data in a clear, concise, and user-friendly format, including both numerical values and graphical representations. Effective data interpretation allows you to quickly identify abnormalities and understand the overall health of the vehicle, according to a study by SAE International. For example, the scanner should display live engine data, such as RPM, coolant temperature, and oxygen sensor readings, in real-time graphs, making it easier to spot trends and diagnose intermittent issues.
2.4. Is It Important For The Scanner To Have Update Capabilities?
It is important for the scanner to have update capabilities to ensure it remains compatible with new vehicle models and diagnostic protocols. Regular updates provide access to the latest diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs), enhanced system coverage, and software improvements, extending the lifespan and effectiveness of the scanner, according to a report by the Equipment and Tool Institute (ETI). Consider a scanner that offers free or low-cost updates via the internet, ensuring you always have the most current information for accurate diagnoses.
2.5. What Additional Features Enhance The Scanners Utility?
Additional features that enhance the scanner’s utility include bidirectional control, ABS/SRS diagnostics, and built-in code definitions. Bidirectional control allows you to send commands to the vehicle’s control modules, testing components like actuators and solenoids. ABS/SRS diagnostics enable you to diagnose and reset antilock braking and airbag systems, while built-in code definitions provide instant access to the meaning of diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs), saving time and effort. These features provide comprehensive diagnostic capabilities, making the scanner a more valuable tool for both professional mechanics and car enthusiasts.
3. What Are The Best OBD1 And OBD2 Scanners On The Market?
The best OBD1 and OBD2 scanners on the market combine compatibility, user-friendliness, and advanced features to provide comprehensive diagnostic capabilities. These scanners cater to a range of users, from DIY enthusiasts to professional mechanics, ensuring accurate and efficient vehicle maintenance.
3.1. Innova 5512: The Top Choice For OBD1 Vehicles
The Innova 5512 is the top choice for OBD1 vehicles because it includes an OBD1 kit, offering exceptional value for money. While retaining all the features of the Innova 5510, the Innova 5512 comes with an OBD-1 Kit that contains OBD1 adapters for General Motors, Ford, Toyota, Chrysler, and Honda vehicles from the 1980s and 1990s. This comprehensive kit allows you to diagnose a wide range of older vehicles, saving you the cost of purchasing adapters separately. For instance, the 5510 costs $249.99, while the 5512 costs $299.99, effectively giving you the OBD-1 Kit for just $50 rather than the full price of $117.64.
3.2. Innova 5610: The Best For Both OBD1 And OBD2 Vehicles
The Innova 5610 is ideal for owners of both OBD1 and OBD2 vehicles due to its advanced features like OEM live data and bi-directional controls. As Innova’s most advanced handheld tool, the 5610 provides a wide array of capabilities that enhance diagnostic accuracy and efficiency. Although it does not come with an OBD-1 Kit, this can be purchased separately, making it a versatile option for diagnosing a broad spectrum of vehicles, from vintage models to modern cars.
3.3. Autel MaxiCOM MK906BT: Advanced Professional Scanner
The Autel MaxiCOM MK906BT is an advanced professional scanner renowned for its comprehensive diagnostic capabilities and wireless connectivity. This scanner supports a wide range of vehicle makes and models, offering OE-level diagnostics, bi-directional control, and advanced functions like ECU coding and programming, according to a review by Diagnostic News. Its wireless Bluetooth connectivity allows you to move freely around the vehicle while performing tests, and its user-friendly interface makes it easy to navigate complex diagnostic procedures.
3.4. Snap-on Solus Edge: High-End Diagnostic Tool
The Snap-on Solus Edge is a high-end diagnostic tool praised for its fast performance, extensive vehicle coverage, and advanced features. This scanner offers comprehensive system coverage, including engine, transmission, ABS, and airbag systems, with detailed diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) and live data streams, according to a report by Professional Tool & Equipment News. Its intuitive touchscreen interface and guided diagnostics streamline the troubleshooting process, making it a favorite among professional technicians.
3.5. BlueDriver Bluetooth Professional OBDII Scan Tool: Portable And Convenient
The BlueDriver Bluetooth Professional OBDII Scan Tool is a portable and convenient option that turns your smartphone or tablet into a powerful diagnostic tool. This scanner connects wirelessly to your device via Bluetooth, providing access to a wide range of diagnostic information, including diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs), live data, and repair reports, as noted in a review by Popular Mechanics. Its user-friendly app offers enhanced diagnostics for a variety of vehicle makes and models, making it an excellent choice for DIY enthusiasts and light-duty professionals.
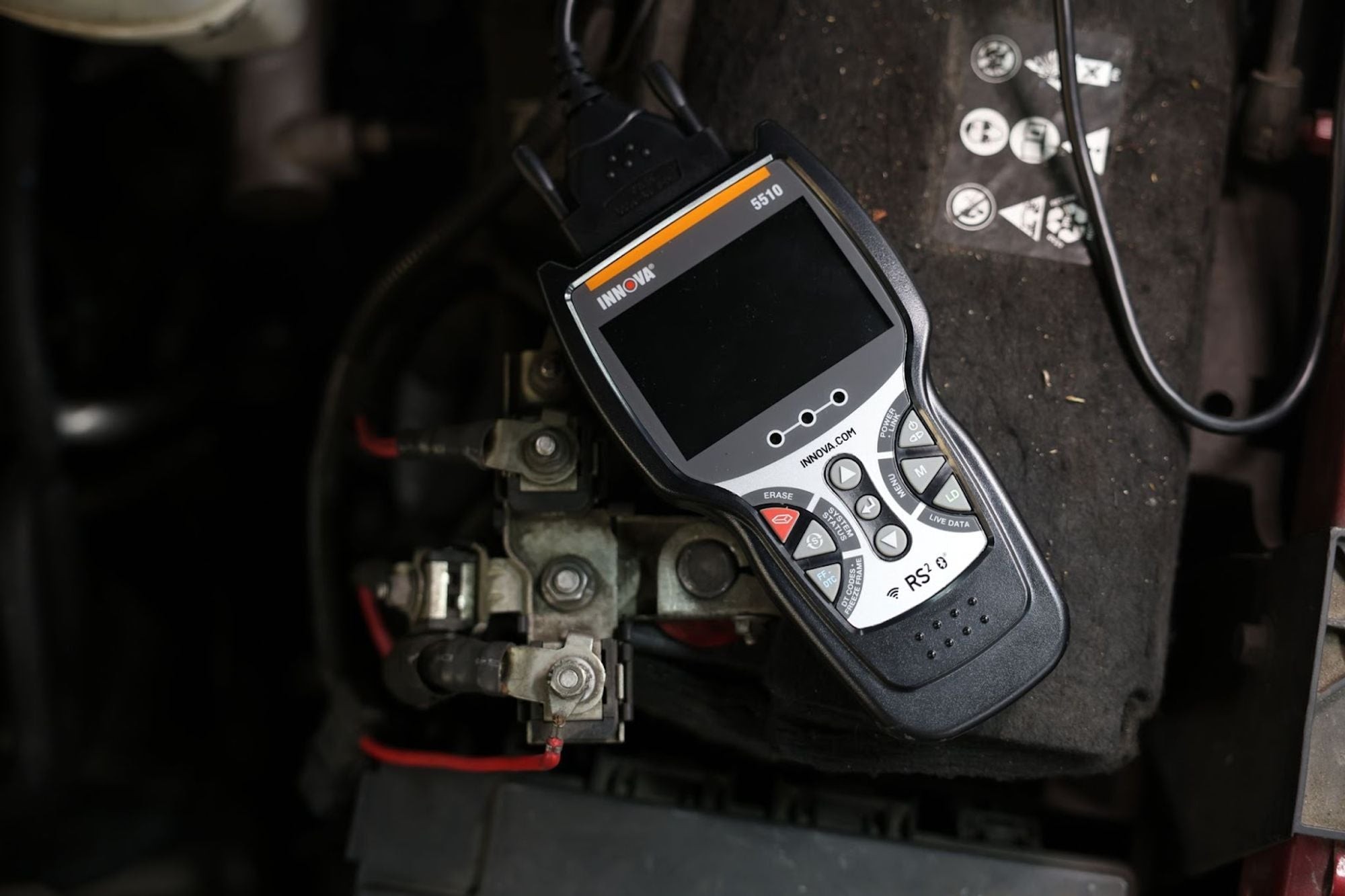 Innova OBD Scanner
Innova OBD Scanner
4. How To Use An OBD1 And OBD2 Scanner?
Using an OBD1 and OBD2 scanner involves connecting the scanner to your vehicle’s diagnostic port, reading diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs), interpreting the data, and taking appropriate action. This process can help you identify and address vehicle issues efficiently.
4.1. How To Connect The Scanner To Your Vehicle?
To connect the scanner to your vehicle, locate the diagnostic port, typically found under the dashboard on the driver’s side. For OBD2 vehicles, the port is a standard 16-pin connector. For OBD1 vehicles, you may need an adapter to match the specific connector type. Once located, plug the scanner cable into the port, ensuring a secure connection. Turn the vehicle’s ignition to the “on” position without starting the engine to power up the scanner and establish communication with the vehicle’s computer.
4.2. How To Read Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)?
To read diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs), power on the scanner and navigate to the “Read Codes” or “Diagnostic Codes” option in the main menu. The scanner will then communicate with the vehicle’s computer to retrieve any stored DTCs. These codes are typically displayed as a series of alphanumeric characters, such as P0300 (random misfire detected) or P0171 (system too lean, bank 1). Make note of each code, as they provide valuable information about potential issues affecting your vehicle.
4.3. How To Interpret The Data Provided By The Scanner?
Interpreting the data provided by the scanner involves understanding the meaning of the diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) and analyzing live data streams. Consult the scanner’s manual or a reputable online resource, like OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN, to look up the definition of each DTC, which provides insight into the affected system or component. Additionally, review live data parameters such as engine temperature, oxygen sensor readings, and fuel trim values to identify any abnormalities or out-of-range conditions that may indicate underlying problems.
4.4. What Actions Should You Take Based On The Scanner Results?
Based on the scanner results, take appropriate action to address the identified issues. If the scanner reveals a minor problem, such as a loose gas cap or a faulty sensor, you may be able to resolve it yourself by tightening the cap or replacing the sensor. For more complex issues, such as engine misfires or transmission problems, it’s best to consult a qualified mechanic. Provide the mechanic with the DTCs and any relevant data from the scanner to help them diagnose and repair the vehicle efficiently.
4.5. How Can You Clear The Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)?
You can clear the diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) after addressing the underlying issues by navigating to the “Clear Codes” or “Erase Codes” option on the scanner. Before clearing the codes, ensure that you have properly resolved the problem, as simply erasing the codes without fixing the issue will only result in the check engine light reappearing. After clearing the codes, take the vehicle for a test drive to confirm that the check engine light remains off and that no new DTCs are triggered.
5. Common OBD1 And OBD2 Codes And What They Mean
Understanding common OBD1 and OBD2 codes is essential for accurate vehicle diagnostics. These codes provide valuable information about potential issues, helping you take the appropriate steps for repair.
5.1. P0300: Random/Multiple Cylinder Misfire Detected
The P0300 code indicates that the engine is experiencing random or multiple cylinder misfires, which can result in rough idling, reduced power, and poor fuel economy. According to a study by the University of Michigan, common causes of P0300 include faulty spark plugs, ignition coils, fuel injectors, or vacuum leaks. Addressing this code involves inspecting and replacing any defective components, as well as performing a thorough engine tune-up to ensure optimal performance.
5.2. P0171: System Too Lean (Bank 1)
The P0171 code signifies that the engine is running too lean on bank 1, meaning there is an insufficient amount of fuel in the air-fuel mixture. Common causes of P0171 include vacuum leaks, a faulty mass airflow (MAF) sensor, a clogged fuel filter, or a weak fuel pump, explains a report by the National Institute for Automotive Service Excellence (ASE). Repairing this issue involves identifying and fixing any vacuum leaks, replacing the MAF sensor or fuel filter if necessary, and ensuring adequate fuel pressure.
5.3. P0420: Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold (Bank 1)
The P0420 code indicates that the catalytic converter on bank 1 is not functioning efficiently, failing to properly reduce harmful emissions. This code can be caused by a deteriorated catalytic converter, exhaust leaks, faulty oxygen sensors, or engine problems that are causing excessive emissions. Addressing the P0420 code may require replacing the catalytic converter, repairing any exhaust leaks, or replacing the oxygen sensors to restore proper emissions control.
5.4. P0101: Mass Air Flow (MAF) Sensor Range/Performance Problem
The P0101 code indicates that the mass air flow (MAF) sensor is not functioning within its specified range, resulting in inaccurate readings and potential engine performance issues. This code can be caused by a dirty or damaged MAF sensor, intake leaks, or wiring problems. Resolving the P0101 code typically involves cleaning or replacing the MAF sensor, inspecting and repairing any intake leaks, and checking the wiring connections to ensure proper sensor operation.
5.5. P0301: Cylinder 1 Misfire Detected
The P0301 code indicates that cylinder 1 is experiencing a misfire, meaning that the cylinder is not firing properly. Common causes of P0301 include a faulty spark plug, ignition coil, fuel injector, or vacuum leak in cylinder 1. Addressing this code involves inspecting and replacing any defective components in cylinder 1, such as the spark plug, ignition coil, or fuel injector, to restore proper combustion.
6. Tips For Maintaining And Storing Your OBD1 And OBD2 Scanner
Proper maintenance and storage of your OBD1 and OBD2 scanner ensure its longevity and reliability. Regular cleaning, careful handling, and appropriate storage conditions help prevent damage and maintain optimal performance.
6.1. How To Clean Your Scanner?
To clean your scanner, use a soft, lint-free cloth to wipe the screen and housing. Avoid using harsh chemicals or abrasive cleaners, as they can damage the screen or plastic components. For stubborn dirt or grime, dampen the cloth with a mild detergent solution, then gently wipe the affected areas. Ensure the scanner is completely dry before storing it.
6.2. What Are The Best Practices For Storing Your Scanner?
The best practices for storing your scanner involve keeping it in a cool, dry place away from direct sunlight and extreme temperatures. Store the scanner in its original case or a padded bag to protect it from dust and physical damage. Avoid placing heavy objects on top of the scanner, and ensure the cable is neatly coiled to prevent tangling or damage.
6.3. How To Protect Your Scanner From Damage?
To protect your scanner from damage, handle it with care and avoid dropping it or exposing it to excessive force. When connecting or disconnecting the scanner from the vehicle’s diagnostic port, do so gently to prevent damage to the connector pins. Keep the scanner away from liquids and moisture, and avoid using it in wet or damp conditions.
6.4. How Often Should You Update Your Scanner’s Software?
You should update your scanner’s software regularly to ensure it remains compatible with the latest vehicle models and diagnostic protocols. Check the manufacturer’s website for software updates at least every six months, or more frequently if you work with new vehicles regularly. Software updates provide access to new diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs), enhanced system coverage, and performance improvements.
6.5. What To Do If Your Scanner Malfunctions?
If your scanner malfunctions, first check the power source and cable connections to ensure they are functioning correctly. Consult the scanner’s manual for troubleshooting tips or contact the manufacturer’s customer support for assistance. Avoid attempting to repair the scanner yourself, as this could void the warranty or cause further damage. If the scanner is under warranty, follow the manufacturer’s instructions for repair or replacement.
7. Addressing Common Concerns And Misconceptions About OBD1 And OBD2 Scanners
Addressing common concerns and misconceptions about OBD1 and OBD2 scanners can help users make informed decisions and use these tools effectively. Understanding the capabilities and limitations of OBD scanners ensures accurate diagnoses and appropriate vehicle maintenance.
7.1. Can An OBD Scanner Fix My Car?
An OBD scanner cannot fix your car directly; it only identifies potential issues by reading diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs). While the scanner provides valuable information about the source of the problem, it does not perform the actual repairs. After identifying the issue, you must take appropriate action, such as replacing a faulty sensor or repairing a damaged component, to resolve the problem.
7.2. Are Cheap Scanners As Good As Expensive Ones?
Cheap scanners may not be as good as expensive ones in terms of features, vehicle coverage, and diagnostic accuracy. While basic scanners can read and clear diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs), they may lack advanced capabilities like live data streaming, bidirectional control, and ABS/SRS diagnostics, explains a study by Consumer Reports. Expensive scanners typically offer wider vehicle coverage, more detailed diagnostic information, and regular software updates, making them a better investment for professional mechanics and serious car enthusiasts.
7.3. Do I Need A Professional Scanner For Accurate Diagnoses?
You may not need a professional scanner for basic diagnoses, but advanced issues often require the capabilities of a professional-grade tool. A basic scanner can be sufficient for reading and clearing common diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs), but professional scanners offer enhanced diagnostics, wider vehicle coverage, and specialized functions like ECU coding and programming, according to a report by the Equipment and Tool Institute (ETI). For complex or intermittent problems, a professional scanner can provide more accurate and detailed information, leading to more effective repairs.
7.4. Can An OBD Scanner Detect All Vehicle Problems?
An OBD scanner cannot detect all vehicle problems, as it primarily focuses on issues related to the engine, emissions, and electronic control systems. While the scanner can identify many common problems, it may not detect mechanical issues, such as worn brakes, suspension problems, or fluid leaks. A comprehensive vehicle inspection by a qualified mechanic is necessary to identify all potential issues and ensure overall vehicle safety and reliability.
7.5. Is It Safe To Drive With The Check Engine Light On?
It may not be safe to drive with the check engine light on, as it can indicate a variety of potential problems, ranging from minor issues to serious mechanical failures. While some issues, such as a loose gas cap, may not pose an immediate threat, others, such as engine misfires or overheating, can cause significant damage if left unaddressed. Consult a qualified mechanic to diagnose and repair the issue as soon as possible to prevent further damage and ensure your safety.
8. The Future Of OBD1 And OBD2 Scanning Technology
The future of OBD1 and OBD2 scanning technology involves increased integration with mobile devices, cloud-based diagnostics, and advanced data analytics. These advancements promise to enhance diagnostic accuracy, streamline repair processes, and provide more comprehensive insights into vehicle health.
8.1. How Will Mobile Integration Change Diagnostics?
Mobile integration will change diagnostics by allowing users to access and interpret diagnostic data directly from their smartphones or tablets. Wireless OBD scanners, such as the BlueDriver Bluetooth Professional OBDII Scan Tool, connect to mobile devices via Bluetooth, providing real-time diagnostic information, repair reports, and access to online databases. Mobile integration enhances convenience, portability, and ease of use, making diagnostics more accessible to DIY enthusiasts and professional mechanics.
8.2. What Role Will Cloud-Based Diagnostics Play?
Cloud-based diagnostics will play a significant role by providing access to vast databases of diagnostic information, repair procedures, and expert knowledge. Cloud-based platforms can store and analyze diagnostic data from millions of vehicles, identifying patterns and trends that can help technicians diagnose complex issues more efficiently. Additionally, cloud-based diagnostics enable remote diagnostics, allowing experts to access and analyze vehicle data from anywhere in the world, facilitating faster and more accurate repairs.
8.3. How Will Data Analytics Improve Vehicle Maintenance?
Data analytics will improve vehicle maintenance by providing predictive insights into potential problems and optimizing maintenance schedules. By analyzing data from OBD scanners, vehicle sensors, and maintenance records, data analytics platforms can identify patterns and predict when certain components are likely to fail. This allows vehicle owners and fleet managers to proactively schedule maintenance, preventing costly breakdowns and extending the lifespan of their vehicles.
8.4. What Advancements Can We Expect In Scanner Technology?
We can expect advancements in scanner technology, including enhanced diagnostic capabilities, improved user interfaces, and wider vehicle coverage. Future scanners may incorporate artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning algorithms to automate diagnostic processes and provide more accurate and detailed information. Additionally, scanners will likely support new communication protocols and diagnostic standards, ensuring compatibility with the latest vehicle models and technologies.
8.5. How Will These Changes Impact Mechanics And Car Owners?
These changes will impact mechanics and car owners by providing them with more powerful and user-friendly diagnostic tools. Mechanics will be able to diagnose and repair vehicles more quickly and accurately, reducing labor costs and improving customer satisfaction. Car owners will have access to more information about their vehicle’s health, allowing them to make informed decisions about maintenance and repairs. Overall, these advancements will lead to more efficient and cost-effective vehicle maintenance.
9. OBD2 Scanner FAQs
Have questions about OBD2 scanners? Here are some frequently asked questions to help you understand their use and benefits better.
9.1. What is an OBD2 scanner?
An OBD2 scanner is a diagnostic tool used to retrieve information from a vehicle’s On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) system. It reads diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) that indicate potential issues with the vehicle’s engine, emissions, and other systems.
9.2. How do I read OBD2 codes?
To read OBD2 codes, connect the scanner to the vehicle’s diagnostic port, turn on the ignition, and follow the scanner’s prompts to retrieve the stored DTCs. The codes are displayed on the scanner’s screen.
9.3. How do I choose the right OBD2 scanner?
Choose the right OBD2 scanner by considering compatibility, ease of use, features, and budget. Ensure the scanner supports your vehicle’s make and model and offers the necessary diagnostic capabilities for your needs.
9.4. What do common OBD2 codes mean?
Common OBD2 codes indicate specific issues, such as P0300 (random misfire), P0171 (system too lean), and P0420 (catalyst system efficiency below threshold). Understanding these codes helps in diagnosing and addressing vehicle problems.
9.5. Can an OBD2 scanner improve fuel efficiency?
An OBD2 scanner can improve fuel efficiency by identifying issues that affect engine performance, such as faulty sensors or vacuum leaks. Addressing these issues can restore optimal engine operation and improve fuel economy.
9.6. How do I maintain my OBD2 scanner?
Maintain your OBD2 scanner by cleaning it regularly, storing it properly, and updating its software. This ensures its longevity and accuracy in diagnosing vehicle issues.
9.7. What are the benefits of using an OBD2 scanner?
The benefits of using an OBD2 scanner include faster diagnoses, cost savings on repairs, improved vehicle performance, and access to valuable diagnostic data. It empowers car owners and mechanics to maintain vehicles effectively.
9.8. Is it safe to clear OBD2 codes without fixing the issue?
It is not safe to clear OBD2 codes without fixing the issue. Clearing codes without addressing the underlying problem will only result in the check engine light reappearing, and the problem may worsen over time.
9.9. Can an OBD2 scanner detect transmission problems?
An OBD2 scanner can detect transmission problems by reading diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) related to the transmission control system. These codes can indicate issues such as slipping gears, incorrect gear ratios, or solenoid malfunctions.
9.10. How often should I use an OBD2 scanner on my vehicle?
You should use an OBD2 scanner on your vehicle whenever the check engine light comes on or if you notice any unusual symptoms, such as rough idling, reduced power, or poor fuel economy. Regular scanning can help identify and address potential issues before they become more serious.
10. Need Help with Your OBD2 Scanner?
Are you facing challenges using your OBD2 scanner or need expert advice on diagnosing and repairing your vehicle? At OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN, we are dedicated to providing you with the support and resources you need to ensure your vehicle runs smoothly. Our team of experienced technicians can guide you through the process of using your OBD2 scanner, interpreting diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs), and performing effective repairs. Whether you’re a DIY enthusiast or a professional mechanic, we’re here to help you get the most out of your diagnostic tools.
Contact us today for personalized assistance and expert guidance. Reach out via WhatsApp at +1 (641) 206-8880, visit our website at OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN, or stop by our location at 123 Main Street, Los Angeles, CA 90001, United States. Let OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN be your trusted partner in vehicle diagnostics and repair, ensuring you have the knowledge and support you need to keep your car in top condition.