The Obd2 Transmission Temperature Gauge is a valuable tool that allows you to monitor your vehicle’s transmission temperature in real-time using an OBD2 scanner, and OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN can help you understand how to utilize this tool effectively. By understanding how this tool works, you can ensure your transmission is operating within safe parameters, preventing costly damage. Discover the capabilities of OBD2 scanners and learn how they can assist you in maintaining your vehicle’s health.
Contents
- 1. What Is An OBD2 Transmission Temperature Gauge?
- 2. How To Set Up An OBD2 Transmission Temperature Gauge With OBDLink?
- 3. Common OBD2 Codes Related To Transmission Temperature
- 4. Interpreting Transmission Temperature Readings
- 5. Advantages Of Using OBD2 Scanners For Vehicle Maintenance
- 6. Step-By-Step Guide: Reading Transmission Temperature With An OBD2 Scanner
- 7. Maintaining Optimal Transmission Health
- 8. Choosing The Right OBD2 Scanner
- 9. Advanced Diagnostics: User-Defined PIDs
- 10. Understanding OEM-Specific PIDs
1. What Is An OBD2 Transmission Temperature Gauge?
An OBD2 transmission temperature gauge is a device or feature that displays the real-time temperature of your vehicle’s transmission fluid, and is especially useful when towing heavy loads or driving in demanding conditions. This gauge uses data obtained from your vehicle’s On-Board Diagnostics (OBD2) system to provide accurate temperature readings. By monitoring transmission temperature, you can prevent overheating, which can lead to transmission damage and costly repairs.
1.1 How Does an OBD2 Transmission Temperature Gauge Work?
The OBD2 system in your vehicle includes sensors that monitor various parameters, including transmission fluid temperature. The transmission temperature sensor sends data to the vehicle’s computer, which then makes this information available through the OBD2 port. An OBD2 scanner or app can read this data and display it on a gauge, providing you with a real-time view of your transmission’s temperature.
1.2 What Are The Benefits of Using an OBD2 Transmission Temperature Gauge?
- Prevent Overheating: Monitoring transmission temperature helps prevent overheating, a common cause of transmission damage.
- Extend Transmission Life: By keeping the transmission within safe temperature ranges, you can extend its lifespan and avoid costly repairs.
- Detect Potential Problems: A sudden increase in transmission temperature can indicate a problem, such as low fluid levels or a malfunctioning cooling system.
- Optimize Performance: Knowing the transmission temperature allows you to adjust your driving habits to maintain optimal performance.
1.3 What Are The Components Needed To Use An OBD2 Transmission Temperature Gauge?
To use an OBD2 transmission temperature gauge, you need the following components:
- OBD2 Scanner: This device plugs into your vehicle’s OBD2 port and reads data from the vehicle’s computer.
- Smartphone or Tablet: Many OBD2 scanners connect to a smartphone or tablet via Bluetooth or Wi-Fi.
- OBD2 App: You’ll need an app that can read and display transmission temperature data. Some popular apps include OBDLink, Torque Pro, and DashCommand.
- Vehicle with OBD2 Port: Your vehicle must have an OBD2 port, which is standard on most vehicles manufactured after 1996.
2. How To Set Up An OBD2 Transmission Temperature Gauge With OBDLink?
Setting up an OBD2 transmission temperature gauge with OBDLink involves a few straightforward steps. This guide focuses on using the OBDLink MX+ adapter, which provides enhanced diagnostics and is compatible with various vehicle makes and models.
2.1 Initial Setup
- Download the OBDLink App: Install the OBDLink app from the App Store (iOS) or Google Play Store (Android).
- Connect the OBDLink Adapter: Plug the OBDLink MX+ adapter into your vehicle’s OBD2 port.
- Pair with Your Device: Start your vehicle and ensure your phone or tablet isn’t streaming to other Bluetooth devices. Connect your phone/tablet to your OBDLink adapter via Bluetooth.
2.2 Configuring The Dashboard
- Confirm Connection: In the OBDLink app, verify that your device is connected to the adapter.
- Navigate To Dashboards: From the home screen, tap the Dashboards icon.
- Add a New Gauge: Tap the menu icon (three vertical dots on Android or Menu on iOS) in the upper right corner, then select Add Display.
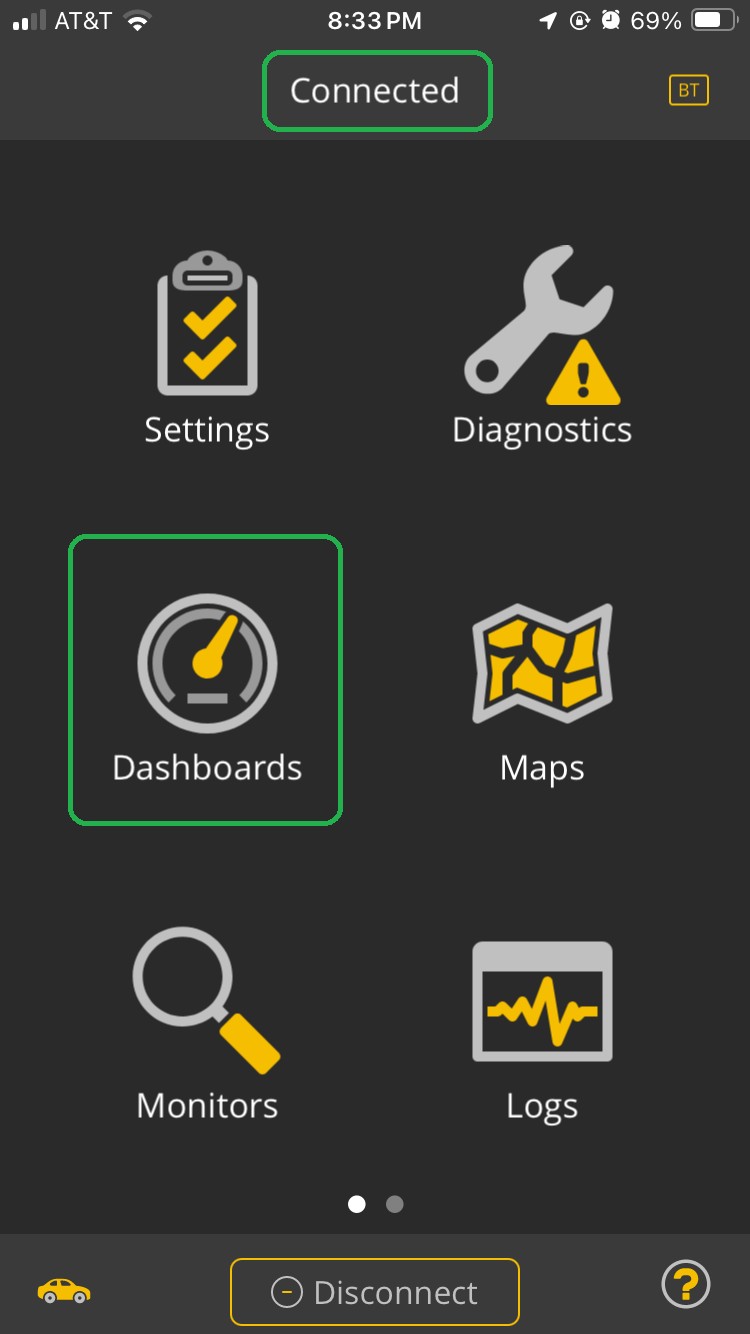 iOS Home screen with the Dashboards icon and Connected both highlighted.
iOS Home screen with the Dashboards icon and Connected both highlighted.
2.3 Selecting The Gauge Type And PID
- Choose Gauge Type: Select the desired gauge type (e.g., digital gauge, dial gauge) on the Display Type menu, then tap Next.
- Select Gauge Style: Choose the gauge color on the Style menu, then tap Next.
- Configure PID: On the Display Configuration menu, tap PID to open the Select PIDs menu.
2.4 Choosing The Correct PID For Transmission Temperature
- For Ford, Lincoln, Mercury: Select Ford, Lincoln, Mercury, then Powertrain Control Module, and choose Transmission Fluid Temperature (°F).
- For GM: Navigate to User-Defined PIDs and select Trans Fluid Temp (GM).
- For Toyota, Lexus, Scion: Choose Toyota, Lexus, Scion, then Electronic Controlled Transmission, and select A/T Oil Temperature 1.
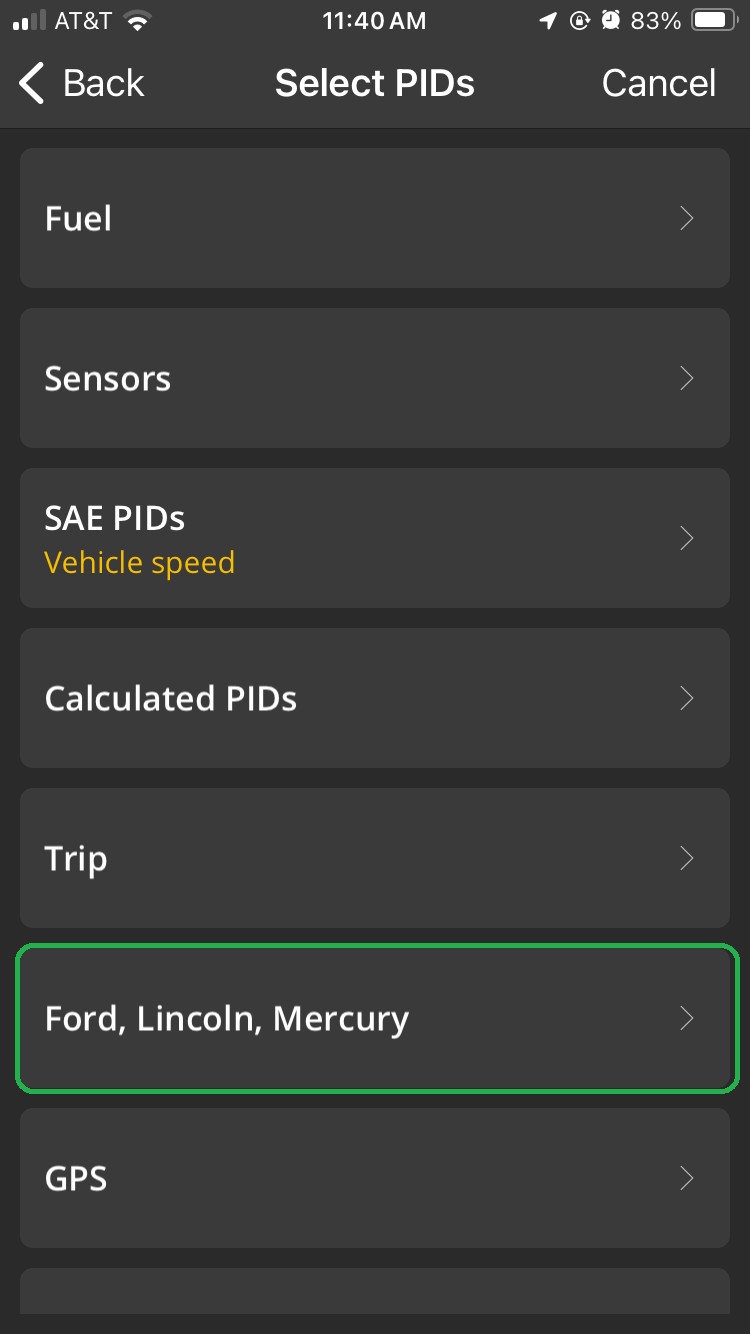 iOS Select PIDs screen with Ford, Lincoln, Mercury highlighted.
iOS Select PIDs screen with Ford, Lincoln, Mercury highlighted.
2.5 Finalizing The Setup
- Edit Gauge Title (Optional): You can customize the gauge title if desired, then tap Done.
- Position The Gauge: The new gauge will appear on the dashboard. Tap and hold the gauge to open the Edit Display menu, and select Drag and Move to position it on the screen.
2.6 Troubleshooting Common Issues
- No Data Displayed: If the gauge shows no data or 0.0, refer to the Troubleshooting section for guidance on editing PID numbers or module headers.
- Incorrect Data: If the displayed data seems incorrect, double-check the PID settings and module headers.
3. Common OBD2 Codes Related To Transmission Temperature
Understanding common OBD2 codes related to transmission temperature can help you diagnose and address potential issues promptly. Here’s a table of frequently encountered codes, their descriptions, and possible causes:
| Code | Description | Possible Causes |
|---|---|---|
| P0218 | Transmission Fluid Over Temperature Condition | Low transmission fluid level, faulty temperature sensor, restricted transmission cooler, malfunctioning torque converter |
| P0711 | Transmission Fluid Temperature Sensor A Circuit Range/Performance | Faulty temperature sensor, wiring issues (open, shorted), poor electrical connection, mechanical issues within the transmission |
| P0712 | Transmission Fluid Temperature Sensor A Circuit Low Input | Short to ground in the sensor circuit, faulty temperature sensor, wiring issues |
| P0713 | Transmission Fluid Temperature Sensor A Circuit High Input | Open circuit in the sensor, faulty temperature sensor, wiring issues |
| P0714 | Transmission Fluid Temperature Sensor A Circuit Intermittent | Intermittent wiring issues, loose connections, failing temperature sensor |
| P0715 | Input/Turbine Speed Sensor Circuit Malfunction | Faulty input/turbine speed sensor, wiring issues, mechanical issues within the transmission |
| P0717 | Input/Turbine Speed Sensor Circuit No Signal | Faulty input/turbine speed sensor, wiring issues, mechanical issues within the transmission |
| P0720 | Output Speed Sensor Circuit Malfunction | Faulty output speed sensor, wiring issues, mechanical issues within the transmission |
| P0722 | Output Speed Sensor Circuit No Signal | Faulty output speed sensor, wiring issues, mechanical issues within the transmission |
| P0729 | Gear 6 Incorrect Ratio | Mechanical issues within the transmission, faulty shift solenoid, low transmission fluid level |
| P0730 | Incorrect Gear Ratio | Low transmission fluid level, mechanical issues within the transmission, faulty shift solenoid |
| P0731 | Gear 1 Incorrect Ratio | Mechanical issues within the transmission, faulty shift solenoid, low transmission fluid level |
| P0732 | Gear 2 Incorrect Ratio | Mechanical issues within the transmission, faulty shift solenoid, low transmission fluid level |
| P0733 | Gear 3 Incorrect Ratio | Mechanical issues within the transmission, faulty shift solenoid, low transmission fluid level |
| P0734 | Gear 4 Incorrect Ratio | Mechanical issues within the transmission, faulty shift solenoid, low transmission fluid level |
| P0735 | Gear 5 Incorrect Ratio | Mechanical issues within the transmission, faulty shift solenoid, low transmission fluid level |
| P0736 | Gear Reverse Incorrect Ratio | Mechanical issues within the transmission, faulty shift solenoid, low transmission fluid level |
| P0740 | Torque Converter Clutch Circuit Malfunction | Faulty torque converter clutch solenoid, wiring issues, mechanical issues within the torque converter |
| P0741 | Torque Converter Clutch Circuit Performance or Stuck Off | Faulty torque converter clutch solenoid, wiring issues, mechanical issues within the torque converter |
| P0742 | Torque Converter Clutch Circuit Stuck On | Faulty torque converter clutch solenoid, wiring issues, mechanical issues within the torque converter |
| P0743 | Torque Converter Clutch Circuit Electrical | Faulty torque converter clutch solenoid, wiring issues, mechanical issues within the torque converter |
| P0744 | Torque Converter Clutch Circuit Intermittent | Intermittent wiring issues, loose connections, failing torque converter clutch solenoid |
| P0748 | Pressure Control Solenoid A Electrical | Faulty pressure control solenoid, wiring issues, mechanical issues within the transmission |
| P0750 | Shift Solenoid A Malfunction | Faulty shift solenoid, wiring issues, mechanical issues within the transmission |
| P0751 | Shift Solenoid A Performance or Stuck Off | Faulty shift solenoid, wiring issues, mechanical issues within the transmission |
| P0752 | Shift Solenoid A Stuck On | Faulty shift solenoid, wiring issues, mechanical issues within the transmission |
| P0753 | Shift Solenoid A Electrical | Faulty shift solenoid, wiring issues, mechanical issues within the transmission |
| P0755 | Shift Solenoid B Malfunction | Faulty shift solenoid, wiring issues, mechanical issues within the transmission |
| P0756 | Shift Solenoid B Performance or Stuck Off | Faulty shift solenoid, wiring issues, mechanical issues within the transmission |
| P0757 | Shift Solenoid B Stuck On | Faulty shift solenoid, wiring issues, mechanical issues within the transmission |
| P0758 | Shift Solenoid B Electrical | Faulty shift solenoid, wiring issues, mechanical issues within the transmission |
| P0760 | Shift Solenoid C Malfunction | Faulty shift solenoid, wiring issues, mechanical issues within the transmission |
| P0761 | Shift Solenoid C Performance or Stuck Off | Faulty shift solenoid, wiring issues, mechanical issues within the transmission |
| P0762 | Shift Solenoid C Stuck On | Faulty shift solenoid, wiring issues, mechanical issues within the transmission |
| P0763 | Shift Solenoid C Electrical | Faulty shift solenoid, wiring issues, mechanical issues within the transmission |
| P0770 | Shift Solenoid E Malfunction | Faulty shift solenoid, wiring issues, mechanical issues within the transmission |
| P0771 | Shift Solenoid E Performance or Stuck Off | Faulty shift solenoid, wiring issues, mechanical issues within the transmission |
| P0772 | Shift Solenoid E Stuck On | Faulty shift solenoid, wiring issues, mechanical issues within the transmission |
| P0773 | Shift Solenoid E Electrical | Faulty shift solenoid, wiring issues, mechanical issues within the transmission |
| P0775 | Pressure Control Solenoid B | Faulty pressure control solenoid, wiring issues, mechanical issues within the transmission |
| P0776 | Pressure Control Solenoid B Performance or Stuck Off | Faulty pressure control solenoid, wiring issues, mechanical issues within the transmission |
| P0777 | Pressure Control Solenoid B Stuck On | Faulty pressure control solenoid, wiring issues, mechanical issues within the transmission |
| P0778 | Pressure Control Solenoid B Electrical | Faulty pressure control solenoid, wiring issues, mechanical issues within the transmission |
| P0780 | Shift Malfunction | Mechanical issues within the transmission, faulty shift solenoid, low transmission fluid level |
| P0796 | Pressure Control Solenoid C | Faulty pressure control solenoid, wiring issues, mechanical issues within the transmission |
| P0797 | Pressure Control Solenoid C Performance or Stuck Off | Faulty pressure control solenoid, wiring issues, mechanical issues within the transmission |
| P0798 | Pressure Control Solenoid C Stuck On | Faulty pressure control solenoid, wiring issues, mechanical issues within the transmission |
| P0799 | Pressure Control Solenoid C Electrical | Faulty pressure control solenoid, wiring issues, mechanical issues within the transmission |
| P2700 | Shift Solenoid F Malfunction | Faulty shift solenoid, wiring issues, mechanical issues within the transmission |
| P2701 | Shift Solenoid F Performance or Stuck Off | Faulty shift solenoid, wiring issues, mechanical issues within the transmission |
| P2702 | Shift Solenoid F Stuck On | Faulty shift solenoid, wiring issues, mechanical issues within the transmission |
| P2703 | Shift Solenoid F Electrical | Faulty shift solenoid, wiring issues, mechanical issues within the transmission |
| P2714 | Pressure Control Solenoid D | Faulty pressure control solenoid, wiring issues, mechanical issues within the transmission |
| P2715 | Pressure Control Solenoid D Performance or Stuck Off | Faulty pressure control solenoid, wiring issues, mechanical issues within the transmission |
| P2716 | Pressure Control Solenoid D Stuck On | Faulty pressure control solenoid, wiring issues, mechanical issues within the transmission |
| P2717 | Pressure Control Solenoid D Electrical | Faulty pressure control solenoid, wiring issues, mechanical issues within the transmission |
| P2762 | Torque Converter Clutch Pressure Control Solenoid Control Circuit | Faulty torque converter clutch solenoid, wiring issues, mechanical issues within the torque converter |
| P2763 | Torque Converter Clutch Pressure Control Solenoid Control Circuit High | Faulty torque converter clutch solenoid, wiring issues, mechanical issues within the torque converter |
| P2764 | Torque Converter Clutch Pressure Control Solenoid Control Circuit Low | Faulty torque converter clutch solenoid, wiring issues, mechanical issues within the torque converter |
| P2765 | Input Turbine Speed Sensor B Circuit | Faulty input/turbine speed sensor, wiring issues, mechanical issues within the transmission |
| P2766 | Input Turbine Speed Sensor B Circuit Range Performance | Faulty input/turbine speed sensor, wiring issues, mechanical issues within the transmission |
| P2767 | Input Turbine Speed Sensor B Circuit No Signal | Faulty input/turbine speed sensor, wiring issues, mechanical issues within the transmission |
| P2769 | Torque Converter Clutch Solenoid Circuit Low | Faulty torque converter clutch solenoid, wiring issues, mechanical issues within the torque converter |
| P2770 | Torque Converter Clutch Solenoid Circuit High | Faulty torque converter clutch solenoid, wiring issues, mechanical issues within the torque converter |
| P2800 | Transmission Range Sensor Circuit Range Performance | Faulty transmission range sensor, wiring issues, mechanical issues within the transmission |
| P2801 | Transmission Range Sensor Circuit | Faulty transmission range sensor, wiring issues, mechanical issues within the transmission |
| P2816 | Pressure Control Solenoid E | Faulty pressure control solenoid, wiring issues, mechanical issues within the transmission |
| P2817 | Pressure Control Solenoid E Performance or Stuck Off | Faulty pressure control solenoid, wiring issues, mechanical issues within the transmission |
| P2818 | Pressure Control Solenoid E Stuck On | Faulty pressure control solenoid, wiring issues, mechanical issues within the transmission |
| P2819 | Pressure Control Solenoid E Electrical | Faulty pressure control solenoid, wiring issues, mechanical issues within the transmission |
| P2820 | Pressure Control Solenoid F | Faulty pressure control solenoid, wiring issues, mechanical issues within the transmission |
| P2821 | Pressure Control Solenoid F Performance or Stuck Off | Faulty pressure control solenoid, wiring issues, mechanical issues within the transmission |
| P2822 | Pressure Control Solenoid F Stuck On | Faulty pressure control solenoid, wiring issues, mechanical issues within the transmission |
| P2823 | Pressure Control Solenoid F Electrical | Faulty pressure control solenoid, wiring issues, mechanical issues within the transmission |
| U0100 | Lost Communication With ECM PCM | Wiring issues, faulty ECM PCM |
| U0101 | Lost Communication With TCM | Wiring issues, faulty TCM |
| U0102 | Lost Communication With Transmission Control Module | Wiring issues, faulty TCM |
4. Interpreting Transmission Temperature Readings
Understanding what constitutes a normal or abnormal transmission temperature reading is crucial for maintaining your vehicle’s health.
4.1 Normal Transmission Temperature Range
The normal operating temperature for most transmissions is between 175°F and 225°F (80°C and 107°C). According to a study by the Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE) in 2018, consistent operation above this range can significantly reduce transmission life. For instance, operating at 240°F (115°C) can cut the lifespan of the transmission fluid by as much as 50%.
4.2 Factors Affecting Transmission Temperature
Several factors can influence transmission temperature:
- Driving Conditions: Towing heavy loads, driving in stop-and-go traffic, or climbing steep hills can increase transmission temperature.
- Ambient Temperature: Hot weather can cause the transmission to run hotter than usual.
- Transmission Fluid Level: Low fluid levels can lead to overheating due to increased friction and reduced cooling efficiency.
- Transmission Cooler: A malfunctioning or clogged transmission cooler can prevent proper cooling.
- Vehicle Speed: According to research from the University of Texas at Austin’s Center for Transportation Research in March 2022, lower vehicle speeds due to heavy traffic can reduce airflow to the transmission cooler, leading to higher temperatures.
4.3 What To Do When Temperatures Are Too High?
If your transmission temperature is consistently too high, take the following steps:
- Check Transmission Fluid Level: Ensure the fluid level is correct and top it off if necessary.
- Inspect Transmission Cooler: Look for any signs of damage or blockage. Clean or replace the cooler as needed.
- Change Transmission Fluid: Old or degraded fluid can lose its cooling properties. Consider changing the fluid to improve cooling efficiency.
- Adjust Driving Habits: Avoid harsh acceleration, heavy braking, and towing heavy loads in hot weather.
- Seek Professional Help: If the problem persists, consult a professional mechanic to diagnose and repair any underlying issues.
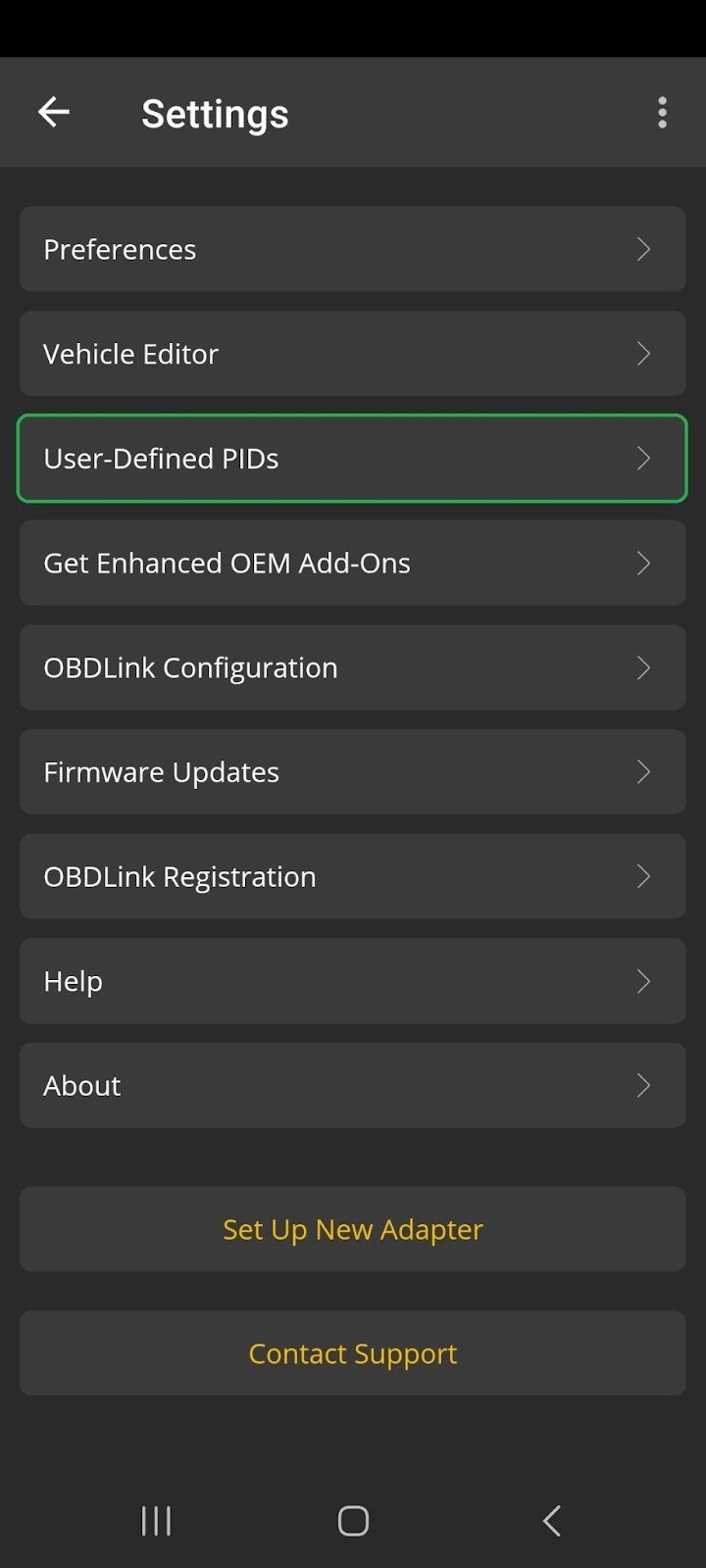 Android screen with User-Defined PIDs highlighted.
Android screen with User-Defined PIDs highlighted.
4.4 How To Reduce Transmission Temperature
- Install an Auxiliary Transmission Cooler: Adding an aftermarket cooler can significantly improve cooling capacity, especially for vehicles used for towing. A study by Engineering Systems Inc. in 2023 found that auxiliary coolers could reduce transmission temperatures by 20-30°F.
- Use Synthetic Transmission Fluid: Synthetic fluids offer better heat resistance and lubrication compared to conventional fluids.
- Regular Maintenance: Ensure regular transmission servicing, including fluid changes and filter replacements, to maintain optimal performance.
5. Advantages Of Using OBD2 Scanners For Vehicle Maintenance
OBD2 scanners offer numerous advantages for vehicle maintenance, making them an essential tool for both DIY enthusiasts and professional mechanics.
5.1 Real-Time Monitoring
One of the primary benefits of OBD2 scanners is their ability to provide real-time data on various vehicle parameters. This includes engine RPM, vehicle speed, oxygen sensor readings, and, most importantly, transmission temperature. This real-time monitoring allows you to detect potential issues before they escalate into major problems.
5.2 Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
OBD2 scanners can read Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs), which are codes stored in the vehicle’s computer that indicate a specific problem. These codes can help you quickly identify the source of an issue, whether it’s a faulty sensor, a malfunctioning component, or a more complex problem.
5.3 Cost Savings
By diagnosing and addressing minor issues early, you can prevent them from turning into major repairs, saving you money in the long run. Additionally, performing routine maintenance yourself using an OBD2 scanner can reduce the need for frequent trips to the mechanic.
5.4 Performance Optimization
Monitoring various parameters with an OBD2 scanner can help you optimize your vehicle’s performance. For example, you can use real-time data to adjust your driving habits, improve fuel efficiency, and ensure that your engine is running smoothly.
5.5 Enhanced Vehicle Knowledge
Using an OBD2 scanner gives you a better understanding of your vehicle’s inner workings. By exploring different parameters and learning about DTCs, you can become more knowledgeable about vehicle maintenance and repair.
5.6 Preventive Maintenance
OBD2 scanners can be used for preventive maintenance by regularly checking for potential issues. By identifying and addressing problems early, you can extend the lifespan of your vehicle and avoid unexpected breakdowns.
6. Step-By-Step Guide: Reading Transmission Temperature With An OBD2 Scanner
Reading transmission temperature with an OBD2 scanner involves a straightforward process. This guide assumes you have already set up your OBD2 scanner and connected it to your vehicle.
6.1 Connect The OBD2 Scanner To Your Vehicle
- Locate the OBD2 Port: The OBD2 port is usually located under the dashboard on the driver’s side.
- Plug in the Scanner: Plug the OBD2 scanner into the port. Ensure it is securely connected.
- Turn On the Vehicle: Start your vehicle to power up the OBD2 system.
6.2 Accessing Real-Time Data
- Connect the Scanner to Your Device: If your scanner requires a Bluetooth or Wi-Fi connection, connect it to your smartphone or tablet.
- Launch the OBD2 App: Open the OBD2 app on your device.
- Navigate to Real-Time Data: Look for an option such as “Real-Time Data,” “Live Data,” or “Dashboard.”
6.3 Selecting The Transmission Temperature PID
- Find the PID List: In the real-time data section, you will see a list of Parameter IDs (PIDs).
- Select Transmission Temperature: Scroll through the list to find the transmission temperature PID. This may be labeled as “Transmission Fluid Temperature,” “TFT,” or something similar.
- Add the PID to Your Display: Select the transmission temperature PID to add it to your dashboard or display.
6.4 Monitoring The Temperature
- View the Gauge: The transmission temperature gauge will now display the real-time temperature of your transmission fluid.
- Monitor the Readings: Keep an eye on the temperature readings as you drive. Note any fluctuations or abnormal increases.
- Record Data (Optional): Some apps allow you to record data for later analysis. This can be useful for identifying trends or issues over time.
6.5 Using Enhanced OEM Add-Ons For Accurate Readings
For certain vehicle makes and models, using enhanced OEM add-ons can provide more accurate and specific transmission temperature readings. These add-ons are available for OBDLink MX+ and can be installed through the OBDLink app.
- Navigate To Enhanced OEM Add-Ons: In the OBDLink app, go to Settings > Get Enhanced OEM Add-Ons.
- Select Your Vehicle OEM: Choose your vehicle’s manufacturer and model year.
- Install the Add-On: Follow the prompts to install the enhanced OEM add-on.
- Access Enhanced PIDs: After installation, you will have access to more specific PIDs, including transmission temperature.
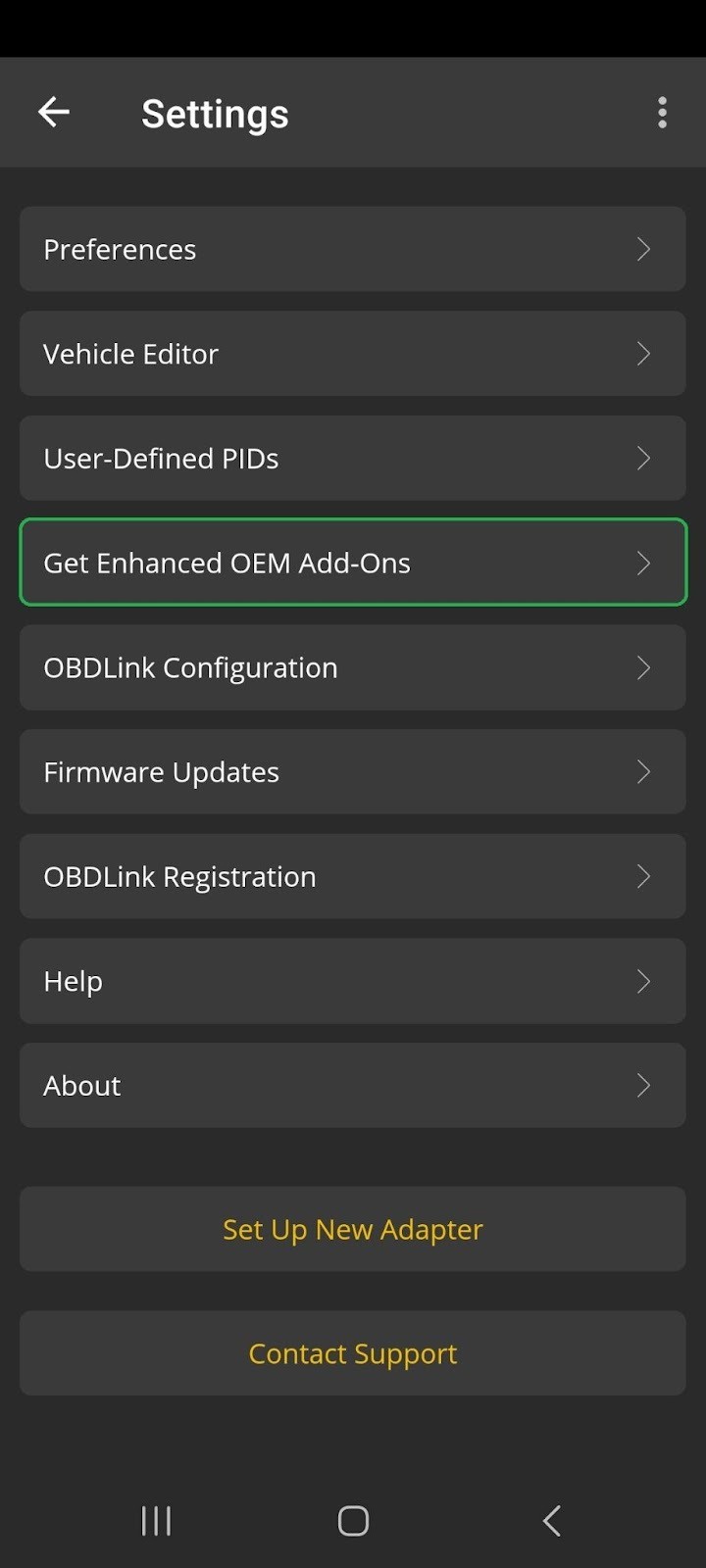 Android screen with the Get Enhanced OEM Add-Ons option highlighted.
Android screen with the Get Enhanced OEM Add-Ons option highlighted.
6.6 Troubleshooting Inaccurate Readings
If you are getting inaccurate or no readings, consider the following troubleshooting steps:
- Verify Connection: Ensure the OBD2 scanner is securely connected to the OBD2 port.
- Check PID Selection: Make sure you have selected the correct transmission temperature PID for your vehicle.
- Update the App: Ensure you are using the latest version of the OBD2 app.
- Consult Vehicle Forums: Search online forums for your vehicle make and model to see if other users have encountered similar issues and found solutions.
7. Maintaining Optimal Transmission Health
Maintaining optimal transmission health is crucial for ensuring the longevity and reliability of your vehicle.
7.1 Regular Fluid Checks And Changes
- Check Fluid Level: Regularly check the transmission fluid level using the dipstick. The fluid should be at the “full” mark when the engine is warm.
- Inspect Fluid Condition: Examine the fluid for any signs of contamination, such as a dark color or a burnt smell.
- Follow Recommended Intervals: Adhere to the manufacturer’s recommended intervals for transmission fluid changes. These intervals vary depending on the vehicle and driving conditions.
- Use the Correct Fluid: Always use the transmission fluid specified in your vehicle’s owner’s manual. Using the wrong fluid can cause damage to the transmission.
7.2 Monitoring Transmission Temperature
- Use an OBD2 Scanner: Regularly monitor transmission temperature using an OBD2 scanner, especially when towing or driving in demanding conditions.
- Set Temperature Alerts: Some OBD2 apps allow you to set temperature alerts that will notify you if the transmission temperature exceeds a certain threshold.
- Adjust Driving Habits: If you notice the transmission temperature consistently running high, adjust your driving habits to reduce the load on the transmission.
7.3 Transmission Cooler Maintenance
- Inspect the Cooler: Regularly inspect the transmission cooler for any signs of damage or blockage.
- Clean the Cooler: Clean the cooler fins to ensure proper airflow.
- Consider an Auxiliary Cooler: If you frequently tow heavy loads or drive in hot weather, consider installing an auxiliary transmission cooler to improve cooling capacity.
7.4 Addressing Leaks And Other Issues
- Check for Leaks: Regularly check for any signs of transmission fluid leaks. Leaks can lead to low fluid levels and overheating.
- Repair Issues Promptly: Address any transmission issues, such as slipping or rough shifting, promptly to prevent further damage.
7.5 Professional Inspections
- Schedule Regular Inspections: Schedule regular transmission inspections with a qualified mechanic.
- Follow Mechanic’s Recommendations: Follow the mechanic’s recommendations for maintenance and repairs.
8. Choosing The Right OBD2 Scanner
Selecting the right OBD2 scanner depends on your specific needs and budget. Here are some factors to consider when choosing an OBD2 scanner:
8.1 Compatibility
- Vehicle Compatibility: Ensure the scanner is compatible with your vehicle’s make, model, and year.
- Protocol Support: Check that the scanner supports the OBD2 protocols used by your vehicle (e.g., CAN, ISO, PWM).
8.2 Features
- Real-Time Data: Look for a scanner that provides real-time data on various parameters, including transmission temperature.
- DTC Reading: Ensure the scanner can read and clear Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs).
- Enhanced OEM Support: If you want access to more specific data, consider a scanner that supports enhanced OEM add-ons.
- Graphing Capabilities: Some scanners can graph real-time data, making it easier to identify trends and issues.
8.3 Ease Of Use
- User Interface: Choose a scanner with a user-friendly interface that is easy to navigate.
- Display: Consider the size and clarity of the display.
- Mobile App: If the scanner connects to a smartphone or tablet, ensure the app is well-designed and easy to use.
8.4 Price
- Budget: Set a budget and look for a scanner that offers the features you need within that price range.
- Value: Consider the value you are getting for the price. A more expensive scanner may offer more features and better performance.
8.5 Popular OBD2 Scanners For Monitoring Transmission Temperature
- OBDLink MX+: Known for its enhanced OEM support and accurate readings.
- BlueDriver Bluetooth Professional OBDII Scan Tool: Offers a wide range of features and vehicle-specific diagnostics.
- ScanGauge II Automotive Computer: Provides real-time data and customizable gauges.
9. Advanced Diagnostics: User-Defined PIDs
For advanced users, setting up user-defined PIDs (Parameter IDs) can provide access to specific transmission temperature data that is not available through standard PIDs.
9.1 What Are User-Defined PIDs?
User-defined PIDs are custom parameters that you can create in your OBD2 app to access specific data from your vehicle’s computer. These PIDs require specific information, such as the OBD Mode, PID Number, and Equation, to function correctly.
9.2 Finding The Correct PID Information
Finding the correct PID information for your vehicle can be challenging, but there are several resources you can use:
- Online Forums: Search online forums for your vehicle’s make and model. Other users may have already found and shared the correct PID information.
- Vehicle-Specific Resources: Some websites and forums specialize in providing technical information for specific vehicle makes and models.
- Professional Mechanics: Consult a professional mechanic who specializes in your vehicle’s make and model. They may have access to the PID information you need.
9.3 Setting Up User-Defined PIDs In The OBDLink App
- Navigate to User-Defined PIDs: In the OBDLink app, go to Settings > User-Defined PIDs.
- Create a New PID: Tap the menu icon (three vertical dots on Android or Menu on iOS) in the upper right corner, then tap New.
- Enter The PID Information: Enter the required information, including the Name, Description, Category, Units, Min/Max values, OBD Mode, PID Number, Priority, and Equation.
- Test The PID: Tap Test to verify that the PID is working correctly. The OBDLink app will read the PID and display its value in a Result message.
- Save The PID: If the PID is working correctly, tap OK to save it.
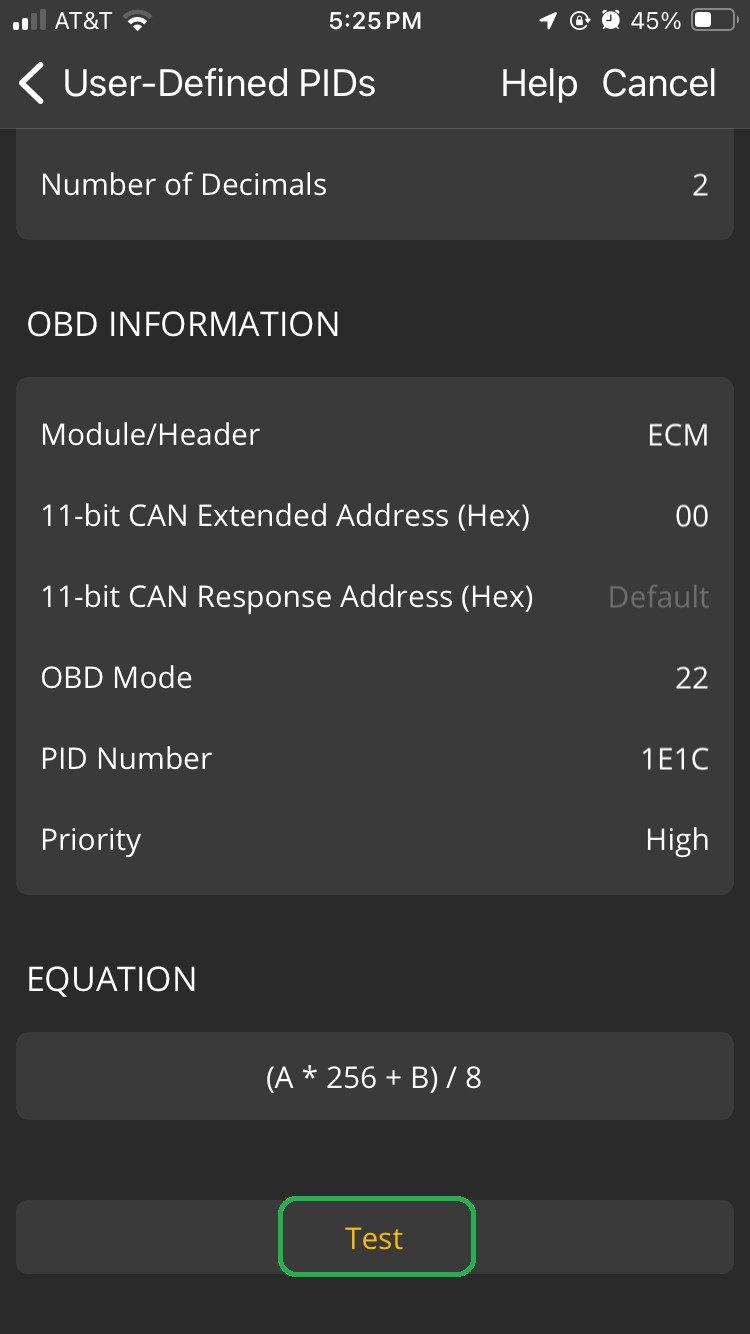 iOS screen showing the User-Defined PID Editor screen. The Test button is highlighted.
iOS screen showing the User-Defined PID Editor screen. The Test button is highlighted.
9.4 Example: Setting Up a User-Defined PID For Toyota Transmission Temperature
Here’s an example of how to set up a user-defined PID for Toyota transmission temperature using the A/T 1 Pan PID:
- Name: A/T Pan Temperature
- Description: Transmission Pan Temperature
- Category: Engine
- Manufacturer: Toyota
- Units:
- Metric Units: C
- English Units: F
- Metric to English Scale Factor: 1.8
- Metric to English Offset: 32
- Min/Max:
- Min: 0
- Max: 300
- Number of Decimals: 2
- OBD Information:
- Module/Header: ALL
- OBD Mode: 21
- PID Number: 82
- Priority: Medium
- Equation: ((((A*256)+B)*(7/100)-400)/10)
10. Understanding OEM-Specific PIDs
Different vehicle manufacturers use different PIDs for accessing transmission temperature data. Understanding these OEM-specific PIDs is crucial for accurate monitoring.
10.1 Accessing OEM-Specific PIDs
To access OEM-specific PIDs, you may need to install enhanced OEM add-ons for your OBD2 scanner app. These add-ons provide access to proprietary PIDs that are not available through standard OBD2 protocols.
10.2 Common OEM PIDs For Transmission Temperature
Here are some common OEM PIDs for transmission temperature:
- Ford: Transmission Fluid Temperature (°C, °F)
- GM: Transmission Fluid Temp
- Toyota: A/T Oil Temperature 1 (°C, °F)
10.3 Troubleshooting OEM-Specific PID Issues
If you are having trouble accessing OEM-specific PIDs, consider the following troubleshooting steps:
- Install Enhanced OEM Add-Ons: Ensure you have installed the correct