Resetting your OBD2 scanner and check engine light involves diagnosing and clearing trouble codes, allowing you to address minor issues or confirm successful repairs; OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN provides detailed guides and resources to help you confidently navigate this process. By understanding how to clear codes and interpret the results, you can save time and money while ensuring your vehicle operates efficiently with our diagnostic tools and auto repair information.
Contents
- 1. What is an OBD2 Reset and Why is it Important?
- 2. Understanding the Check Engine Light and OBD2 System
- 3. Identifying the Need for an OBD2 Reset
- 4. Essential Tools for Resetting Your OBD2 Scanner
- 5. Step-by-Step Guide: How to Reset Your OBD2 Scanner
- 5.1. Locate the OBD2 Port
- 5.2. Connect the OBD2 Scanner
- 5.3. Turn On the Ignition
- 5.4. Read the Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
- 5.5. Record the Codes
- 5.6. Clear the Codes
- 5.7. Verify the Reset
- 5.8. Disconnect the Scanner
- 5.9. Start the Engine
- 6. Interpreting OBD2 Codes
- 7. Common OBD2 Codes and Their Meanings
- 8. When to Seek Professional Help
- 9. Tips for Maintaining Your Vehicle’s OBD2 System
- 10. Advanced OBD2 Scanner Features
- 11. OBD2 Scanner Brands and Models
- 12. Common Mistakes to Avoid When Resetting Your OBD2 Scanner
- 13. OBD2 Reset and Vehicle Emissions Testing
- 14. OBD2 Reset and Battery Disconnection
- 15. The Future of OBD2 Technology
- 16. How to Find Reliable OBD2 Information Online
- 17. Safety Precautions When Working with OBD2 Scanners
- 18. Troubleshooting Common OBD2 Scanner Issues
- 19. OBD2 Reset and Vehicle Resale Value
- 20. Contact OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN for Expert Assistance
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
- What is an OBD2 scanner?
- How do I read OBD2 codes?
- What does the check engine light mean?
- Can I reset the OBD2 system without a scanner?
- How often should I scan my car with an OBD2 scanner?
- Is it safe to drive with the check engine light on?
- How long does it take for OBD2 monitors to reset?
- What are OBD2 readiness monitors?
- What is the difference between generic and manufacturer-specific OBD2 codes?
- Where can I find the OBD2 port in my car?
1. What is an OBD2 Reset and Why is it Important?
An OBD2 reset refers to clearing stored diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) from your vehicle’s onboard computer using an OBD2 scanner. This process is crucial for several reasons:
- Clearing the Check Engine Light: The most common reason is to turn off the check engine light after addressing the underlying issue.
- Verifying Repairs: Resetting the OBD2 system allows you to confirm whether a repair was successful. If the problem persists, the check engine light will reappear, indicating further attention is needed.
- System Readiness: Resetting the OBD2 system can help prepare your vehicle for emissions testing. Some states require that your vehicle’s OBD2 system has completed certain diagnostic cycles to ensure it is functioning correctly.
- Improved Vehicle Performance: While resetting the OBD2 system doesn’t directly improve performance, it allows you to identify and fix underlying issues that may be affecting your vehicle’s efficiency and power.
- Preventing Unnecessary Repairs: Sometimes, a temporary glitch can trigger the check engine light. Resetting the system can clear the light if the issue is resolved, preventing unnecessary trips to the mechanic.
According to the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), all cars and light trucks sold in the United States since 1996 are required to have an OBD2 system. The Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE) developed the standards for OBD2, ensuring consistency across different vehicle makes and models.
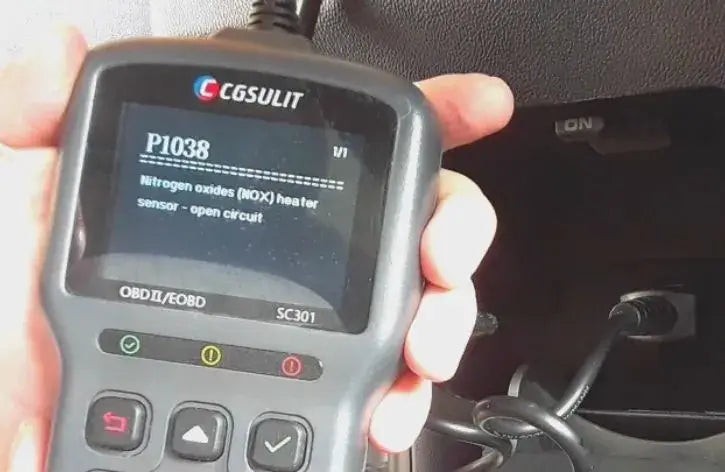 OBD2 Scanner displaying diagnostic codes
OBD2 Scanner displaying diagnostic codes
2. Understanding the Check Engine Light and OBD2 System
The check engine light (CEL), also known as the malfunction indicator lamp (MIL), is a signal from your vehicle’s onboard diagnostic (OBD) system indicating a potential issue. The OBD2 system monitors various sensors and components throughout your vehicle, and if it detects a problem, it stores a diagnostic trouble code (DTC) and illuminates the CEL.
The OBD2 system is standardized across all vehicles sold in the US since 1996, providing a universal way to access diagnostic information. This standardization allows technicians and vehicle owners to use a variety of OBD2 scanners to read and interpret DTCs.
According to a study by AAA, 75 million Americans have admitted to ignoring their check engine light. While not all CELs indicate serious problems, ignoring them can lead to more significant and costly repairs down the road.
3. Identifying the Need for an OBD2 Reset
Before performing an OBD2 reset, it’s crucial to understand when it’s appropriate. Here are some scenarios where a reset is necessary:
- After Repairing a Fault: If you’ve fixed a problem that triggered the check engine light, resetting the OBD2 system clears the code and turns off the light.
- Verifying Diagnostic Tests: After performing diagnostic tests, a reset can help confirm whether the issue has been resolved.
- Addressing Minor Issues: For minor, intermittent issues that don’t affect vehicle performance, a reset can clear the code. However, if the issue persists, the light will reappear.
- Preparing for Emissions Testing: Some states require that your vehicle’s OBD2 system has completed certain diagnostic cycles before an emissions test. Resetting the system can help initiate these cycles.
It’s important to note that resetting the OBD2 system without addressing the underlying problem is not a solution. The check engine light will likely reappear if the issue persists. Always diagnose and repair the fault before performing a reset.
4. Essential Tools for Resetting Your OBD2 Scanner
To reset your OBD2 scanner and clear the check engine light, you’ll need the following tools:
- OBD2 Scanner: An OBD2 scanner is essential for reading and clearing diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs).
- Vehicle’s Repair Manual: Consult your vehicle’s repair manual for specific instructions and diagnostic information.
- Basic Hand Tools: Depending on the repair needed, you may require basic hand tools such as wrenches, screwdrivers, and pliers.
- Safety Gear: Always wear safety glasses and gloves when working on your vehicle to protect yourself from potential hazards.
OBD2 scanners come in various forms, from basic code readers to advanced diagnostic tools with features like live data streaming and bidirectional control. Choose a scanner that meets your needs and budget. CGSULIT SC301 is an affordable option that will help you to read and erase codes.
 CGSULIT SC301 OBDII/EOBD Code Reader
CGSULIT SC301 OBDII/EOBD Code Reader
5. Step-by-Step Guide: How to Reset Your OBD2 Scanner
Resetting your OBD2 scanner involves a series of steps to ensure you’re clearing the codes correctly and safely. Here’s a detailed guide:
5.1. Locate the OBD2 Port
The OBD2 port is usually located under the dashboard on the driver’s side. It’s typically near the steering column or in the center console area.
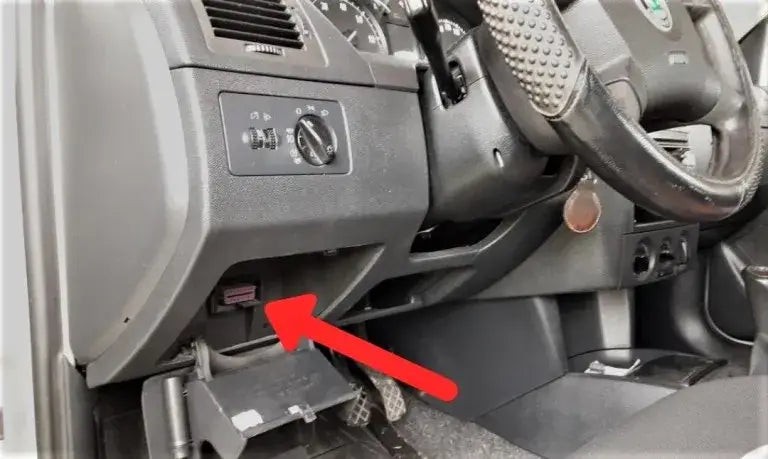 Locating the OBDII port under the dashboard
Locating the OBDII port under the dashboard
5.2. Connect the OBD2 Scanner
Plug the OBD2 scanner into the port. Ensure it’s securely connected.
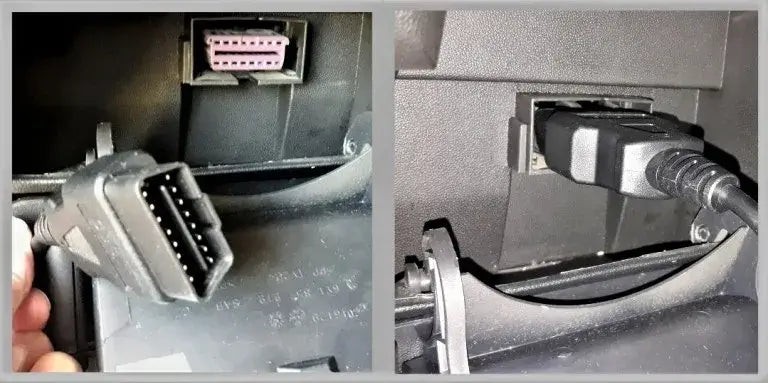 Connecting the OBDII code reader to the vehicle's port
Connecting the OBDII code reader to the vehicle's port
5.3. Turn On the Ignition
Turn the ignition to the “ON” position without starting the engine. This provides power to the OBD2 system.
 Turning on the ignition of the car
Turning on the ignition of the car
5.4. Read the Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
Follow the scanner’s instructions to read the DTCs. The scanner will display a list of codes stored in the vehicle’s computer.
 OBDII scan tool scanning for error codes
OBDII scan tool scanning for error codes
5.5. Record the Codes
Write down each code and its description. This information will be helpful for diagnosing and repairing the underlying issues.
5.6. Clear the Codes
Navigate to the “Clear Codes” or “Erase Codes” option on the scanner. Confirm that you want to clear the codes.
 Accessing the DTC library for clearing codes
Accessing the DTC library for clearing codes
5.7. Verify the Reset
Turn off the ignition and then turn it back on. Check if the check engine light is off. If it’s still on, repeat the process or investigate the underlying issue.
5.8. Disconnect the Scanner
Once you’ve verified that the codes have been cleared, disconnect the OBD2 scanner from the port.
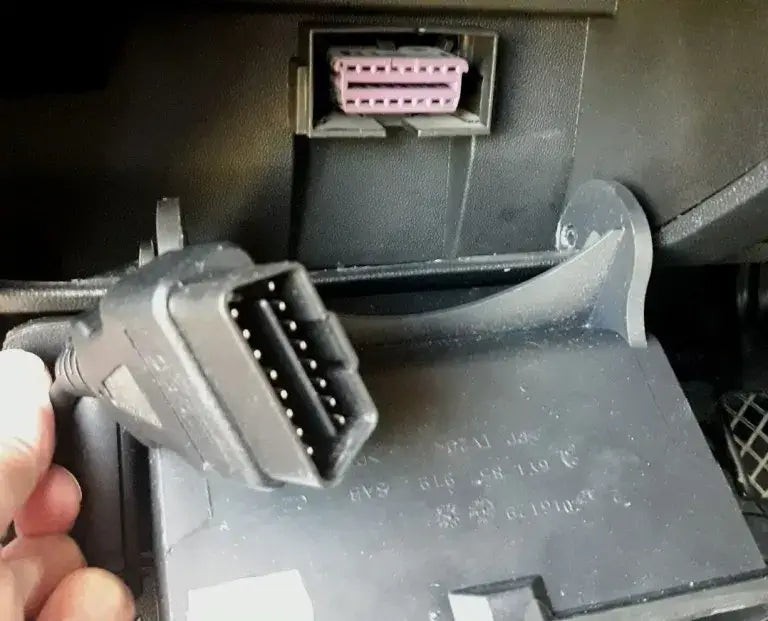 Disconnecting the OBDII reader from the port
Disconnecting the OBDII reader from the port
5.9. Start the Engine
Start the engine to ensure everything is working correctly. If the check engine light remains off, the reset was successful.
 Starting the engine to check if the light is gone
Starting the engine to check if the light is gone
6. Interpreting OBD2 Codes
OBD2 codes are standardized five-character alphanumeric codes that provide information about the nature and location of a problem within your vehicle’s systems. Here’s how to interpret them:
- First Character:
- P: Powertrain (engine, transmission)
- B: Body (airbags, power windows)
- C: Chassis (ABS, suspension)
- U: Network (communication systems)
- Second Character:
- 0: Generic (SAE-defined)
- 1: Manufacturer-specific
- Third Character: Indicates the system involved:
- 1: Fuel and air metering
- 2: Fuel and air metering (injector circuit)
- 3: Ignition system
- 4: Auxiliary emission controls
- 5: Vehicle speed and idle control
- 6: Computer output circuit
- 7: Transmission
- 8: Transmission
- Fourth and Fifth Characters: Specific fault code number
For example, the code P0300 indicates a random/multiple cylinder misfire in the engine. Refer to your vehicle’s repair manual or online resources for a complete list of OBD2 codes and their meanings.
7. Common OBD2 Codes and Their Meanings
Here’s a list of common OBD2 codes and their meanings:
| Code | Description | Possible Causes |
|---|---|---|
| P0171 | System Too Lean (Bank 1) | Vacuum leak, faulty O2 sensor, MAF sensor issue |
| P0300 | Random/Multiple Cylinder Misfire | Faulty spark plugs, ignition coils, fuel injectors |
| P0420 | Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold (Bank 1) | Faulty catalytic converter, O2 sensor issue |
| P0442 | Evaporative Emission Control System Leak Detected (Small Leak) | Loose gas cap, faulty purge valve, cracked hoses |
| P0505 | Idle Air Control System Malfunction | Faulty IAC valve, vacuum leak |
This table provides a general overview. Always consult your vehicle’s repair manual for specific diagnostic information.
8. When to Seek Professional Help
While resetting your OBD2 scanner and clearing the check engine light can be a simple task, there are situations where it’s best to seek professional help. Consider consulting a qualified mechanic if:
- The Check Engine Light Returns Quickly: If the check engine light reappears shortly after resetting the system, it indicates a persistent issue that requires professional diagnosis and repair.
- You’re Unsure About the Diagnosis: If you’re not confident in your ability to diagnose the underlying problem based on the OBD2 codes, it’s best to seek expert assistance.
- The Problem Seems Complex: For complex issues involving multiple systems or components, professional mechanics have the knowledge and tools to accurately diagnose and repair the problem.
- You Lack the Necessary Tools or Expertise: If you don’t have the necessary tools or experience to perform the required repairs, it’s safer to entrust the job to a qualified mechanic.
According to the National Institute for Automotive Service Excellence (ASE), certified mechanics have demonstrated their knowledge and skills through rigorous testing and training. Seeking help from an ASE-certified mechanic ensures that your vehicle is in capable hands.
9. Tips for Maintaining Your Vehicle’s OBD2 System
Maintaining your vehicle’s OBD2 system involves regular checks and proactive measures to prevent potential issues. Here are some tips:
- Regularly Check the Check Engine Light: Pay attention to the check engine light and address any issues promptly.
- Perform Routine Maintenance: Follow your vehicle’s recommended maintenance schedule to keep all systems in good working order.
- Use Quality Parts: When replacing components, use high-quality parts that meet or exceed OEM specifications.
- Keep Your Vehicle Clean: Regularly clean your vehicle, including the engine compartment, to prevent corrosion and damage to sensors and wiring.
- Monitor Fuel Efficiency: Keep track of your vehicle’s fuel efficiency, as a sudden drop in mileage can indicate a problem with the engine or fuel system.
By following these tips, you can help keep your vehicle’s OBD2 system in optimal condition and prevent costly repairs down the road.
10. Advanced OBD2 Scanner Features
Advanced OBD2 scanners offer a range of features beyond reading and clearing codes. Some of these features include:
- Live Data Streaming: Allows you to monitor real-time data from various sensors and components, providing valuable insights into your vehicle’s performance.
- Bidirectional Control: Enables you to send commands to specific components, such as turning on the fuel pump or activating the EGR valve, to test their functionality.
- Freeze Frame Data: Captures a snapshot of sensor data at the moment a DTC is triggered, helping you diagnose intermittent issues.
- Oxygen Sensor Testing: Allows you to test the performance of your vehicle’s oxygen sensors, which are crucial for fuel efficiency and emissions control.
- EVAP System Testing: Enables you to test the integrity of your vehicle’s evaporative emission control system, which prevents fuel vapors from escaping into the atmosphere.
These advanced features can provide valuable diagnostic information and help you troubleshoot complex issues. However, they also require a deeper understanding of vehicle systems and diagnostic procedures.
11. OBD2 Scanner Brands and Models
Several reputable brands offer high-quality OBD2 scanners. Some popular options include:
- CGSULIT: Known for affordable and reliable code readers like the SC301.
- Autel: Offers a wide range of scanners, from basic code readers to advanced diagnostic tools.
- Launch: Specializes in professional-grade diagnostic equipment for automotive technicians.
- BlueDriver: A popular Bluetooth scanner that pairs with your smartphone or tablet.
- Actron: Offers a variety of affordable and user-friendly scanners.
When choosing an OBD2 scanner, consider your needs, budget, and the features that are most important to you. Read reviews and compare specifications to find the best option for your vehicle.
12. Common Mistakes to Avoid When Resetting Your OBD2 Scanner
Resetting your OBD2 scanner is generally straightforward, but here are some common mistakes to avoid:
- Resetting Without Addressing the Underlying Issue: Resetting the OBD2 system without fixing the problem will only temporarily turn off the check engine light. The light will likely reappear if the issue persists.
- Using an Incompatible Scanner: Ensure that your OBD2 scanner is compatible with your vehicle’s make and model.
- Ignoring Warning Signs: Pay attention to any warning signs or symptoms your vehicle is exhibiting, even if the check engine light is not on.
- Damaging the OBD2 Port: Be careful when connecting and disconnecting the OBD2 scanner to avoid damaging the port.
- Failing to Record the Codes: Always write down the DTCs before clearing them, as this information can be valuable for diagnosing and repairing the underlying issues.
By avoiding these common mistakes, you can ensure a smooth and successful OBD2 reset.
13. OBD2 Reset and Vehicle Emissions Testing
In many states, vehicles are required to undergo emissions testing to ensure they meet air quality standards. The OBD2 system plays a crucial role in this process.
Before an emissions test, your vehicle’s OBD2 system must have completed certain diagnostic cycles, known as “readiness monitors.” These monitors test various systems, such as the catalytic converter, oxygen sensors, and evaporative emission control system.
Resetting the OBD2 system clears these readiness monitors, so it’s important to allow your vehicle to complete these cycles before undergoing an emissions test. This typically involves driving the vehicle for a certain period under specific conditions, such as highway driving and city driving.
Consult your vehicle’s repair manual or local emissions testing guidelines for specific instructions on completing the readiness monitors.
14. OBD2 Reset and Battery Disconnection
Disconnecting your vehicle’s battery can also reset the OBD2 system, but this method is not recommended. Disconnecting the battery can erase other important data stored in your vehicle’s computer, such as radio presets and seat memory settings.
Using an OBD2 scanner to clear the codes is a safer and more reliable method, as it only clears the DTCs and leaves other settings intact.
15. The Future of OBD2 Technology
OBD2 technology continues to evolve, with new features and capabilities being added to meet the demands of modern vehicles. Some trends in OBD2 technology include:
- Wireless OBD2 Scanners: Bluetooth and Wi-Fi enabled scanners that can connect to your smartphone or tablet, providing greater convenience and flexibility.
- Cloud-Based Diagnostics: Scanners that can upload diagnostic data to the cloud for analysis and remote support.
- Integration with Telematics Systems: OBD2 data integrated with telematics systems for fleet management and vehicle tracking.
- Advanced Driver-Assistance Systems (ADAS) Diagnostics: OBD2 scanners that can diagnose and calibrate ADAS features, such as lane departure warning and adaptive cruise control.
These advancements will continue to make OBD2 technology more powerful and user-friendly, providing vehicle owners and technicians with valuable diagnostic information.
16. How to Find Reliable OBD2 Information Online
Finding reliable OBD2 information online can be challenging, as there are many sources of varying quality. Here are some tips for finding trustworthy information:
- Consult Official Sources: Refer to your vehicle’s repair manual, manufacturer websites, and government agencies like the EPA for accurate and up-to-date information.
- Use Reputable Websites: Stick to well-known automotive websites and forums that are known for their expertise and accuracy.
- Check for Credentials: Look for authors and contributors who have relevant qualifications and experience in the automotive industry.
- Be Wary of Unsubstantiated Claims: Be skeptical of information that seems too good to be true or lacks supporting evidence.
- Cross-Reference Information: Compare information from multiple sources to ensure consistency and accuracy.
By following these tips, you can find reliable OBD2 information online and make informed decisions about your vehicle’s maintenance and repair.
17. Safety Precautions When Working with OBD2 Scanners
Working with OBD2 scanners involves certain safety precautions to protect yourself and your vehicle. Here are some important guidelines:
- Read the Instructions: Always read and follow the manufacturer’s instructions for your OBD2 scanner.
- Wear Safety Gear: Wear safety glasses and gloves when working on your vehicle to protect yourself from potential hazards.
- Work in a Well-Ventilated Area: If you’re working on your vehicle in a garage, ensure that it’s well-ventilated to prevent the buildup of harmful fumes.
- Disconnect the Battery: Disconnect the negative battery terminal before performing any electrical repairs to prevent electrical shock.
- Avoid Distractions: Stay focused and avoid distractions when working on your vehicle to prevent accidents.
By following these safety precautions, you can minimize the risk of injury or damage when working with OBD2 scanners.
18. Troubleshooting Common OBD2 Scanner Issues
Even with the best equipment, you may encounter issues when using an OBD2 scanner. Here are some common problems and troubleshooting tips:
- Scanner Won’t Connect: Ensure that the scanner is securely plugged into the OBD2 port and that the ignition is turned on. Check the scanner’s power source and wiring.
- Scanner Won’t Read Codes: Verify that the scanner is compatible with your vehicle’s make and model. Try updating the scanner’s software.
- Scanner Displays Incorrect Codes: Ensure that you’re using the correct diagnostic procedures and that the scanner is functioning properly. Cross-reference the codes with your vehicle’s repair manual.
- Scanner Freezes or Crashes: Try restarting the scanner. If the problem persists, contact the manufacturer for support.
- Scanner Won’t Clear Codes: Ensure that you’ve addressed the underlying issue and that the scanner is properly connected. Try clearing the codes multiple times.
If you’re unable to resolve the issue, consult a qualified mechanic or contact the scanner manufacturer for assistance.
19. OBD2 Reset and Vehicle Resale Value
Maintaining a clean OBD2 system can positively impact your vehicle’s resale value. Potential buyers may be hesitant to purchase a vehicle with a check engine light on, as it can indicate underlying problems.
By addressing any issues and ensuring that the OBD2 system is functioning correctly, you can increase buyer confidence and potentially command a higher resale price.
20. Contact OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN for Expert Assistance
Do you need help with your OBD2 scanner or require automotive repair advice? Contact OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN today! Our team of experienced technicians can provide expert guidance and support to help you diagnose and resolve any automotive issues.
Contact Information:
- Address: 123 Main Street, Los Angeles, CA 90001, United States
- WhatsApp: +1 (641) 206-8880
- Website: OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN
Let OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN be your trusted resource for all your automotive diagnostic and repair needs. Whether you’re a seasoned mechanic or a DIY enthusiast, we’re here to help you keep your vehicle running smoothly.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What is an OBD2 scanner?
An OBD2 scanner is a diagnostic tool used to read and clear diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) from a vehicle’s onboard computer. It helps identify potential issues and monitor vehicle performance.
How do I read OBD2 codes?
Connect the OBD2 scanner to the vehicle’s OBD2 port, turn on the ignition, and follow the scanner’s instructions to read the DTCs. The scanner will display a list of codes and their descriptions.
What does the check engine light mean?
The check engine light indicates a potential issue with your vehicle’s systems. It could be a minor problem or a more serious issue that requires immediate attention.
Can I reset the OBD2 system without a scanner?
While disconnecting the battery can reset the OBD2 system, it’s not recommended. Using an OBD2 scanner is a safer and more reliable method.
How often should I scan my car with an OBD2 scanner?
You should scan your car with an OBD2 scanner whenever the check engine light comes on or if you notice any unusual symptoms or performance issues.
Is it safe to drive with the check engine light on?
It depends on the severity of the issue. If the check engine light is flashing, it indicates a serious problem that requires immediate attention. If the light is on but not flashing, you can usually drive the car for a short period, but it’s best to get it checked as soon as possible.
How long does it take for OBD2 monitors to reset?
The time it takes for OBD2 monitors to reset depends on the vehicle and driving conditions. It typically involves driving the vehicle for a certain period under specific conditions, such as highway driving and city driving.
What are OBD2 readiness monitors?
OBD2 readiness monitors are diagnostic cycles that test various systems, such as the catalytic converter, oxygen sensors, and evaporative emission control system. They must be completed before an emissions test.
What is the difference between generic and manufacturer-specific OBD2 codes?
Generic OBD2 codes are standardized codes that apply to all vehicles. Manufacturer-specific codes are unique to a particular vehicle make and model and provide more detailed information about the issue.
Where can I find the OBD2 port in my car?
The OBD2 port is typically located under the dashboard on the driver’s side. It’s usually near the steering column or in the center console area.