Obd2 Connector Terminals are the crucial contact points within your car’s diagnostic port, and repairing them correctly is essential for accurate vehicle diagnostics; OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN is here to guide you through the process. This guide dives deep into identifying terminal issues, finding the right replacement parts, and ensuring a lasting repair using high-quality components. Discover how to confidently troubleshoot and fix your OBD2 connector, keeping your vehicle running smoothly with proper data communication, diagnostic port integrity, and automotive repair excellence.
Contents
- 1. Understanding the OBD2 Connector
- 1.1. OBD2 Connector Pinout
- 2. Common Causes of OBD2 Connector Damage
- 2.1. Blown Fuses and Improper Testing
- 2.2. Aftermarket Accessories
- 3. The Myth of Standardized OBD2 Connectors
- 3.1. Connector Variations
- 4. Avoiding Low-Quality Replacement Parts
- 4.1. Cost-Benefit Analysis
- 4.2. Warranty and Customer Satisfaction
- 5. Sourcing OEM Replacement Parts
- 5.1. Navigating Dealer Parts Systems
- 5.2. Identifying Terminals
- 5.3. Toyota Example
- 6. Exploring Aftermarket Connector and Terminal Suppliers
- 6.1. Connector Experts Example
- 6.2. Mouser Electronics
- 7. Crimping OBD2 Terminals Correctly
- 7.1. Engineer Crimpers
- 7.2. Crimping Technique
- 8. Step-by-Step Guide to Repairing OBD2 Connector Terminals
- 9. Understanding OBD2 Error Codes
- 10. The Importance of Regular Maintenance
- 10.1. Preventative Measures
- 11. The Future of OBD2 Technology
- 11.1. Enhanced Data Logging
- 11.2. Remote Diagnostics
- 12. Contact OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN for Expert Assistance
- 12.1. Benefits of Choosing OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN
- 12.2. Contact Information
- 13. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
- 13.1. What is an OBD2 Scanner?
- 13.2. How Do I Read OBD2 Error Codes?
- 13.3. What Are Common Car Problems and How Can They Be Fixed?
- 13.4. Can I Repair an OBD2 Connector Myself?
- 13.5. What Should I Do If My OBD2 Scanner Won’t Connect?
- 13.6. How Often Should I Scan My Car for OBD2 Codes?
- 13.7. What Does the Check Engine Light Mean?
- 13.8. How Can I Clear OBD2 Error Codes?
- 13.9. Are There Different Types of OBD2 Scanners?
- 13.10. Where Can I Find a Reliable OBD2 Repair Service?
1. Understanding the OBD2 Connector
What is the OBD2 connector, and why is it important for vehicle diagnostics? The OBD2 connector is a standardized 16-pin interface present in every car manufactured in 1996 or later, and it allows generic OBD2 scanners to access essential vehicle data. While the standard mandates access to specific data, automakers offer additional data beyond this standard, accessible with more advanced scan tools.
1.1. OBD2 Connector Pinout
What are the pin positions in an OBD2 connector? Here’s a breakdown:
- Pin 1: Manufacturer’s choice
- Pins 2 & 10: SAE J1850 (network)
- Pin 3: Manufacturer’s choice
- Pin 4: Chassis ground
- Pin 5: Signal ground
- Pins 6 & 14: CAN bus high and low (network)
- Pins 7 & 15: ISO9140 K-Line (network)
- Pins 8, 9, 11, 12, 13: Manufacturer’s choice
- Pin 16: Battery positive (key off power)
Understanding this pinout is crucial for diagnosing communication issues and ensuring proper scanner connectivity.
2. Common Causes of OBD2 Connector Damage
What factors commonly lead to OBD2 connector damage? Pin 16 is the most frequently damaged due to several reasons, including blown fuses and ill-advised testing methods.
2.1. Blown Fuses and Improper Testing
How do blown fuses and improper testing damage OBD2 terminals? Sometimes, the fuse for pin 16 blows due to poorly designed aftermarket accessories or overloads on shared circuits. Inexperienced individuals may damage the connector by jamming probes into it while testing for power.
 Damaged OBD2 terminal next to a new terminal under a microscope
Damaged OBD2 terminal next to a new terminal under a microscope
2.2. Aftermarket Accessories
Why can aftermarket accessories cause damage to OBD2 connectors? Aftermarket accessories, such as insurance dongles and aftermarket gauges, often lack the engineering and quality control of original equipment. Oversized male pins can stretch the female terminals, and devices drawing excessive current from pin 16 can overload the connector, which is only designed to supply power to a scan tool for short periods. Continuous high current draw can lead to premature wear and failure.
3. The Myth of Standardized OBD2 Connectors
Are all OBD2 connectors the same since OBDII is a standard? Despite the OBD2 standard, connectors vary significantly in how they attach to the car and how terminals are installed. Connector suppliers offer numerous options for both the plastic housings and the metal terminals.
3.1. Connector Variations
How do OBD2 connector attachments and terminal installations differ across vehicles? While any male OBD2 connector can plug into any female OBD2 connector, the mounting to the vehicle and the terminal installation methods vary widely. This lack of uniformity complicates repairs, as universal replacement parts are rare.
4. Avoiding Low-Quality Replacement Parts
Why should you avoid cheap OBD2 connectors from online marketplaces like Amazon? While inexpensive replacement OBD2 connectors are available, their terminal quality is often substandard. The metal used in these terminals is typically soft and lacks the springiness of OEM terminals, leading to short-term fixes that don’t last.
4.1. Cost-Benefit Analysis
What are the long-term cost implications of using substandard OBD2 connector parts? Although the initial cost of low-quality parts is appealing, the labor costs associated with replacing them quickly outweigh any savings. Replacing an OBD2 connector involves removing the lower dash, installing new terminals, soldering, and heat-shrinking wires. This process can take over an hour and a half, resulting in significant labor charges. Using substandard parts increases the risk of repeat repairs, costing more in the long run.
4.2. Warranty and Customer Satisfaction
How do substandard parts affect warranty claims and customer satisfaction? Using low-quality parts can lead to warranty claims and dissatisfied customers, and you risk damaging the vehicle’s sensitive electronic components with poorly made connectors. This can erode trust and damage your reputation. Investing in high-quality components from the start ensures a reliable repair, reducing the likelihood of comebacks and maintaining customer satisfaction.
5. Sourcing OEM Replacement Parts
Why is buying OBD2 connector parts directly from the dealer often the best option? Purchasing parts from the dealer ensures you receive high-quality, OEM components. However, obtaining the correct parts can be challenging.
5.1. Navigating Dealer Parts Systems
How can you find the correct OBD2 connector parts from a dealer when they’re not explicitly listed? While OBD2 connectors may not be listed as individual parts in the catalog, they can often be purchased in pieces. You can find the part number by consulting the electrical wiring diagrams on the vehicle’s service information system (e.g., Toyota TIS). Clicking on the OBD2 connector in the diagram typically reveals the part number for the plastic connector housing.
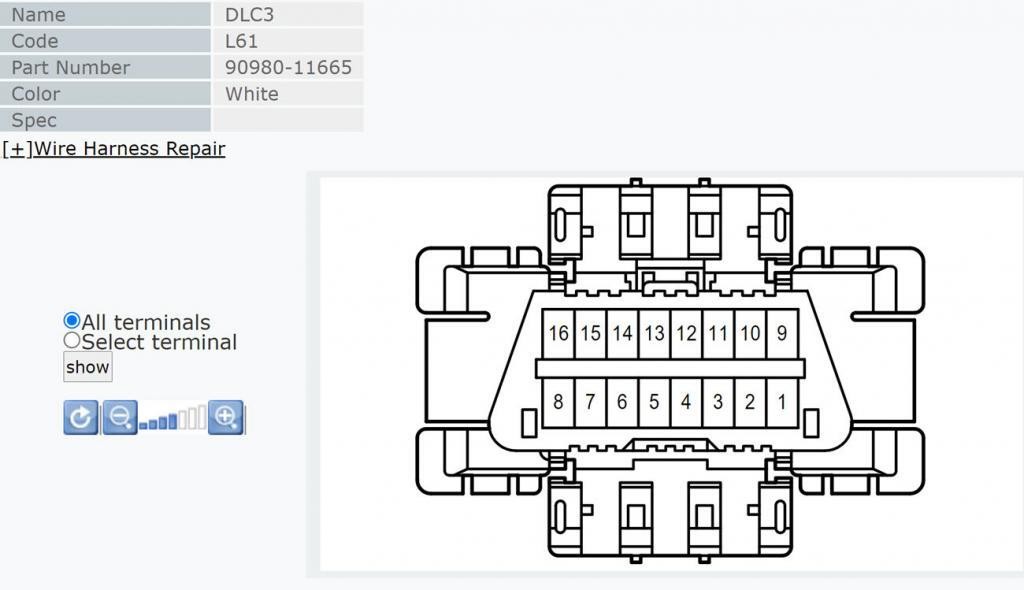 OBD2 connector picture and part number from the Toyota service manual
OBD2 connector picture and part number from the Toyota service manual
5.2. Identifying Terminals
What is the process for identifying the correct metal terminals for an OBD2 connector? Identifying the correct metal terminals can be more difficult. Dealership parts departments may not readily know which terminals fit a specific connector. Enlisting the help of experienced technicians or shop foremen who hoard used terminals can be invaluable.
5.3. Toyota Example
What is an example of a specific Toyota OBD2 repair terminal part number? For example, the correct part number for a Gen3 Prius OBDII connector terminal may be 82998-05010. While expensive at around $20 per terminal, it guarantees an exact fit and reliable connection.
6. Exploring Aftermarket Connector and Terminal Suppliers
What are the benefits of using specialized connector suppliers like Connector Experts? Companies like Connector Experts offer reproductions of OE connectors and terminals at a fraction of the cost. These suppliers often provide high-quality alternatives that match the performance and durability of OEM parts.
6.1. Connector Experts Example
How do Connector Experts’ terminals compare to OEM terminals in terms of quality and cost? Terminal part number TERM86 from Connector Experts has been found to be a suitable replacement for Toyota OBD2 connector terminals. These terminals are virtually indistinguishable from OEM terminals, with comparable hardness, springiness, and measurements, and they are significantly cheaper.
6.2. Mouser Electronics
What are the pros and cons of using electronics suppliers like Mouser for OBD2 connector parts? Mouser offers a wide selection of automotive connectors and terminals, but navigating their extensive catalog can be overwhelming. While they offer competitive pricing, finding the exact part you need requires careful research and technical knowledge.
7. Crimping OBD2 Terminals Correctly
What type of crimpers should you use for OBD2 terminals to ensure a secure connection? High-quality crimpers are essential for creating secure and reliable connections with small, open-barrel terminals used in OBD2 connectors. Standard wire crimpers designed for larger, old-school terminals are often inadequate.
7.1. Engineer Crimpers
Why are Engineer crimpers recommended for OBD2 terminal crimping? Engineer crimpers, made by a Japanese company, are specifically designed for small, open-barrel terminals. Despite their unassuming appearance, they are well-made and produce crimps that closely resemble factory crimps. These crimpers ensure a tight, reliable connection, crucial for maintaining proper communication through the OBD2 port.
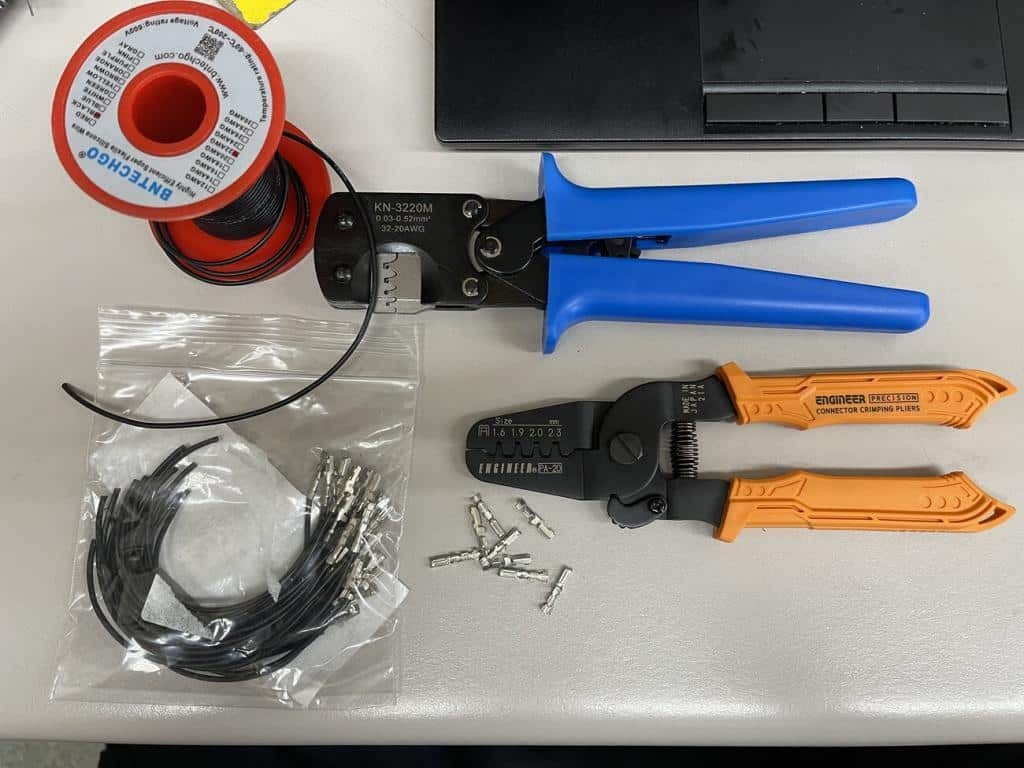 Wire crimpers, pigtails, terminals, and wire on a table
Wire crimpers, pigtails, terminals, and wire on a table
7.2. Crimping Technique
What is the proper technique for crimping OBD2 terminals? Proper crimping involves stripping the wire to the correct length, inserting it into the terminal, and using the crimpers to create a tight, gas-tight seal. A well-crimped terminal should securely grip the wire without damaging it, ensuring a reliable electrical connection.
8. Step-by-Step Guide to Repairing OBD2 Connector Terminals
How do you effectively repair OBD2 connector terminals? Follow these steps for a successful repair:
- Diagnose the Issue:
- Use a multimeter to check for continuity and voltage at the OBD2 connector.
- Inspect the terminals for damage, corrosion, or looseness.
- Use an OBD2 scanner to check for communication errors.
- Gather Necessary Tools and Materials:
- New OBD2 connector terminals (OEM or high-quality aftermarket)
- Wire crimpers (Engineer crimpers recommended)
- Wire stripper
- Soldering iron and solder
- Heat shrink tubing
- Heat gun
- Multimeter
- Wiring diagram for your vehicle
- Disconnect the Battery:
- Disconnect the negative terminal of the battery to prevent electrical shorts.
- Remove the Damaged Terminal:
- Carefully remove the damaged terminal from the OBD2 connector using a terminal removal tool or small pick.
- Take photos of the wiring configuration before removal to ensure correct reinstallation.
- Prepare the Wire:
- Strip about 1/4 inch of insulation from the end of the wire.
- If the wire is corroded, cut back to fresh, clean wire.
- Crimp the New Terminal:
- Insert the wire into the new terminal.
- Use the Engineer crimpers to crimp the terminal securely onto the wire.
- Ensure the crimp is tight and the wire is firmly held in place.
- Solder the Connection (Optional):
- For added security, solder the terminal to the wire.
- Apply a small amount of solder to the crimped connection.
- Allow the solder to flow and create a strong bond.
- Apply Heat Shrink Tubing:
- Slide a piece of heat shrink tubing over the terminal and wire.
- Use a heat gun to shrink the tubing, creating a protective seal.
- Reinstall the Terminal:
- Carefully reinsert the new terminal into the correct position in the OBD2 connector.
- Ensure the terminal locks securely into place.
- Test the Connection:
- Reconnect the battery.
- Use a multimeter to check for continuity and voltage at the repaired terminal.
- Plug in an OBD2 scanner to verify proper communication.
9. Understanding OBD2 Error Codes
What are some common OBD2 error codes and their potential causes? Here’s a table of common OBD2 error codes to help you understand potential issues:
| Error Code | Description | Possible Causes |
|---|---|---|
| P0101 | Mass Air Flow (MAF) Sensor Range/Performance | Dirty or faulty MAF sensor, vacuum leaks, damaged wiring |
| P0113 | Intake Air Temperature (IAT) Sensor Circuit High Input | Faulty IAT sensor, open circuit in wiring, poor connection |
| P0171 | System Too Lean (Bank 1) | Vacuum leaks, faulty O2 sensor, low fuel pressure, dirty fuel injectors |
| P0300 | Random/Multiple Cylinder Misfire Detected | Faulty spark plugs, ignition coils, fuel injectors, vacuum leaks, low compression |
| P0420 | Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold (Bank 1) | Faulty catalytic converter, O2 sensor issues, exhaust leaks |
| P0442 | Evaporative Emission Control System Leak Detected (Small Leak) | Loose or damaged fuel cap, cracked hoses, faulty purge valve |
| P0505 | Idle Air Control System Malfunction | Dirty or faulty IAC valve, vacuum leaks, throttle body issues |
| P0717 | Input/Turbine Speed Sensor Circuit No Signal | Faulty input speed sensor, wiring issues, transmission problems |
10. The Importance of Regular Maintenance
How can regular maintenance prevent OBD2 connector and terminal issues? Regular maintenance is crucial for preventing OBD2 connector and terminal issues. Keeping the connector clean and free from debris, ensuring proper installation of aftermarket accessories, and addressing electrical issues promptly can extend the life of your OBD2 port.
10.1. Preventative Measures
What are some preventative measures to protect your OBD2 connector?
- Regularly inspect the OBD2 connector for damage or corrosion.
- Use a protective cap when the connector is not in use.
- Ensure aftermarket accessories are properly installed and do not draw excessive current.
- Address any electrical issues promptly to prevent blown fuses and potential damage to the connector.
11. The Future of OBD2 Technology
How is OBD2 technology evolving to meet the demands of modern vehicles? OBD2 technology continues to evolve, with advancements in data logging, remote diagnostics, and integration with mobile devices. As vehicles become more complex, the OBD2 connector will remain a critical tool for diagnosing and repairing automotive issues.
11.1. Enhanced Data Logging
What advancements are being made in OBD2 data logging? Modern OBD2 scanners can log more data points and provide real-time monitoring of various vehicle parameters. This enhanced data logging capability enables technicians to diagnose intermittent issues and fine-tune vehicle performance.
11.2. Remote Diagnostics
How is remote diagnostics changing the automotive repair industry? Remote diagnostics allows technicians to access vehicle data and perform diagnostic tests remotely, reducing the need for physical inspections. This technology is particularly useful for fleet management and providing support to remote customers.
12. Contact OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN for Expert Assistance
Do you need help with your OBD2 connector or other automotive diagnostic issues? Contact us today for expert assistance! At OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN, we understand the challenges of diagnosing and repairing modern vehicles. Our team of experienced technicians is here to provide you with the knowledge and support you need to keep your vehicle running smoothly.
12.1. Benefits of Choosing OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN
What are the benefits of seeking assistance from OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN?
- Expert Technicians: Our technicians have years of experience diagnosing and repairing a wide range of automotive issues.
- High-Quality Parts: We use only the highest quality OEM and aftermarket parts to ensure reliable repairs.
- Advanced Diagnostic Tools: We utilize the latest OBD2 scanners and diagnostic equipment to accurately identify and resolve issues.
- Customer Satisfaction: We are committed to providing exceptional customer service and ensuring your satisfaction.
12.2. Contact Information
How can you reach OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN for assistance?
- Address: 123 Main Street, Los Angeles, CA 90001, United States
- WhatsApp: +1 (641) 206-8880
- Website: OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN
Don’t let OBD2 connector issues keep you off the road. Contact OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN today and experience the difference! We’re dedicated to providing top-notch information and services related to diagnostic port maintenance, OBDII terminal care, and car diagnostic solutions.
13. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
13.1. What is an OBD2 Scanner?
An OBD2 scanner is a diagnostic tool used to retrieve information from a vehicle’s onboard computer system, helping to identify potential issues and troubleshoot problems.
13.2. How Do I Read OBD2 Error Codes?
To read OBD2 error codes, plug an OBD2 scanner into the OBD2 port, turn on the ignition, and follow the scanner’s instructions to retrieve the stored codes.
13.3. What Are Common Car Problems and How Can They Be Fixed?
Common car problems include engine misfires, electrical issues, and sensor malfunctions. These can often be diagnosed using an OBD2 scanner and fixed by replacing faulty components or repairing damaged wiring.
13.4. Can I Repair an OBD2 Connector Myself?
Yes, repairing an OBD2 connector yourself is possible if you have the necessary tools and knowledge. However, it’s essential to follow proper procedures and use high-quality replacement parts to ensure a reliable repair.
13.5. What Should I Do If My OBD2 Scanner Won’t Connect?
If your OBD2 scanner won’t connect, check the OBD2 connector for damage or corrosion, ensure the ignition is turned on, and verify that the scanner is compatible with your vehicle.
13.6. How Often Should I Scan My Car for OBD2 Codes?
You should scan your car for OBD2 codes whenever you notice unusual symptoms, such as the check engine light illuminating, rough idling, or decreased fuel efficiency.
13.7. What Does the Check Engine Light Mean?
The check engine light indicates that the vehicle’s onboard computer has detected a problem. Scanning for OBD2 codes can help identify the specific issue triggering the light.
13.8. How Can I Clear OBD2 Error Codes?
You can clear OBD2 error codes using an OBD2 scanner. However, it’s important to address the underlying issue that caused the code before clearing it, as the code may reappear if the problem persists.
13.9. Are There Different Types of OBD2 Scanners?
Yes, there are various types of OBD2 scanners, ranging from basic code readers to advanced diagnostic tools with features like live data streaming and bi-directional control.
13.10. Where Can I Find a Reliable OBD2 Repair Service?
You can find a reliable OBD2 repair service by contacting OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN at 123 Main Street, Los Angeles, CA 90001, United States, via WhatsApp at +1 (641) 206-8880, or through our website at OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN.
By following these guidelines and seeking professional help when needed, you can effectively troubleshoot and repair OBD2 connector terminals, ensuring your vehicle remains in optimal condition.