Is your OBD2 port not working, leaving you unable to diagnose your car’s problems? The 05 Ion Obd2 Fuse, along with wiring issues or a faulty ECU, can cause this frustrating problem. At OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN, we help you quickly identify and resolve these issues, ensuring your vehicle is back on the road promptly. Our expert guidance and resources, focusing on diagnostic interface tools and auto repair solutions, make car maintenance straightforward and efficient.
Contents
- 1. Understanding the OBD2 System and the 05 Ion OBD2 Fuse
- 1.1 The Importance of the OBD2 System
- 1.2 The Function of the 05 Ion OBD2 Fuse
- 1.3 Common Symptoms of a Blown 05 Ion OBD2 Fuse
- 2. Locating and Inspecting the 05 Ion OBD2 Fuse
- 2.1 Finding the Fuse Box
- 2.2 Identifying the 05 Ion OBD2 Fuse
- 2.3 Steps to Inspect the Fuse
- 2.4 Tools Needed for Fuse Inspection
- 3. Causes of a Blown 05 Ion OBD2 Fuse
- 3.1 Short Circuits in the OBD2 Port Wiring
- 3.2 Faulty OBD2 Scanners and Devices
- 3.3 Overloading the Circuit
- 3.4 Corrosion and Damage to the OBD2 Port
- 4. Step-by-Step Guide to Replacing the 05 Ion OBD2 Fuse
- 4.1 Preparing to Replace the Fuse
- 4.2 Removing the Blown Fuse
- 4.3 Installing the New Fuse
- 4.4 Testing the OBD2 Port After Fuse Replacement
- 5. Troubleshooting Steps If the OBD2 Port Still Doesn’t Work
- 5.1 Checking for Wiring Damage
- 5.2 Inspecting the OBD2 Port for Corrosion
- 5.3 Testing with a Different Scan Tool
- 5.4 Evaluating the Possibility of a Faulty ECU
- 6. Advanced Diagnostic Techniques for OBD2 Port Issues
- 6.1 Using an Oscilloscope
- 6.2 Performing Voltage Drop Tests
- 6.3 Utilizing Specialized Diagnostic Software
- 7. Preventive Measures to Avoid Future OBD2 Port Problems
- 7.1 Regular Inspection and Cleaning
- 7.2 Using High-Quality Scan Tools
- 7.3 Avoiding Overloading the Circuit
- 7.4 Protecting the Wiring from Damage
- 8. Common OBD2 Error Codes and Their Meanings
- 8.1 P0171: System Too Lean (Bank 1)
- 8.2 P0300: Random Misfire Detected
- 8.3 P0420: Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold (Bank 1)
- 9. The Role of OBD2 Scanners in Modern Automotive Repair
- 9.1 Reading Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
- 9.2 Accessing Live Data
- 9.3 Performing System Tests
- 10. Choosing the Right OBD2 Scanner for Your Needs
- 10.1 Compatibility
- 10.2 Features
- 10.3 Ease of Use
- 10.4 Price
- 11. How OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN Can Help You
- 11.1 Expert Guidance and Support
- 11.2 Comprehensive Resources and Information
- 11.3 Professional Diagnostic Services
- 11.4 Contact Us Today
- FAQ: Frequently Asked Questions About OBD2 Port Issues
- What is an OBD2 scanner and what does it do?
- How do I read an OBD2 error code?
- What are some common OBD2 error codes?
- Can a blown fuse affect the OBD2 port?
- Where is the OBD2 fuse located in my car?
- What should I do if my OBD2 scanner won’t connect?
- How can I clean the OBD2 port?
- Is it safe to leave an OBD2 scanner plugged in all the time?
- Can a faulty oxygen sensor cause OBD2 port issues?
- What is the difference between a basic and an advanced OBD2 scanner?
1. Understanding the OBD2 System and the 05 Ion OBD2 Fuse
What is the OBD2 system and what role does the 05 ion OBD2 fuse play?
The On-Board Diagnostics II (OBD2) system is a standardized system used in vehicles to monitor and diagnose engine and emissions-related problems. The 05 ion OBD2 fuse protects the OBD2 port and related circuits from electrical overloads. It ensures that the scan tool can properly communicate with the vehicle’s computer, which is essential for diagnosing issues. If this fuse blows, the OBD2 port may not function.
1.1 The Importance of the OBD2 System
Why is the OBD2 system vital for modern vehicles?
The OBD2 system is essential because it monitors a vehicle’s critical systems, including the engine, transmission, and emissions controls. When a problem is detected, the OBD2 system generates a Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC), which can be read using a scan tool. This allows technicians and car owners to quickly identify and address issues, preventing further damage and ensuring the vehicle operates efficiently. According to a study by the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), effective use of OBD2 systems can reduce vehicle emissions by up to 25%.
1.2 The Function of the 05 Ion OBD2 Fuse
What is the specific function of the 05 ion OBD2 fuse within the system?
The 05 ion OBD2 fuse specifically protects the OBD2 port and its associated wiring from power surges and short circuits. This fuse is typically located in the vehicle’s fuse box and is designed to blow (break the electrical circuit) if there is an overcurrent, preventing damage to the OBD2 port and the vehicle’s computer. A blown fuse means no power to the OBD2 port, rendering it useless for diagnostics until the fuse is replaced.
1.3 Common Symptoms of a Blown 05 Ion OBD2 Fuse
How can you tell if the 05 ion OBD2 fuse has blown?
Common symptoms of a blown 05 ion OBD2 fuse include:
- The OBD2 scanner does not power on when connected to the port.
- The scanner powers on but cannot establish a connection with the vehicle’s computer.
- The check engine light may or may not be illuminated, but no diagnostic data can be retrieved.
For example, if you plug in your OBD2 scanner and it doesn’t light up or show any signs of power, the first thing to check is the 05 ion OBD2 fuse.
2. Locating and Inspecting the 05 Ion OBD2 Fuse
Where can you find the 05 ion OBD2 fuse and how should you inspect it?
The 05 ion OBD2 fuse is typically located in one of the vehicle’s fuse boxes, either under the dashboard or in the engine compartment. To inspect the fuse, visually check for a broken filament inside the fuse. A multimeter can also be used to test the fuse for continuity.
2.1 Finding the Fuse Box
Where are the fuse boxes typically located in a vehicle?
Fuse boxes are commonly found in two locations:
- Under the Dashboard: Often located on the driver’s side, near the steering column or behind a small panel.
- In the Engine Compartment: Usually near the battery or along the fender walls.
Consult your vehicle’s owner’s manual for the exact location of the fuse boxes.
2.2 Identifying the 05 Ion OBD2 Fuse
How can you identify which fuse is the correct one to check?
Refer to the fuse box diagram, usually printed on the inside of the fuse box cover or in the vehicle’s owner’s manual. The diagram will label each fuse and its function. Look for a fuse labeled “OBD,” “Diagnostic,” or “Cigar Lighter” (as some vehicles share this fuse). The fuse number may vary by vehicle model, but it is often a low-amperage fuse (e.g., 5A, 7.5A, 10A).
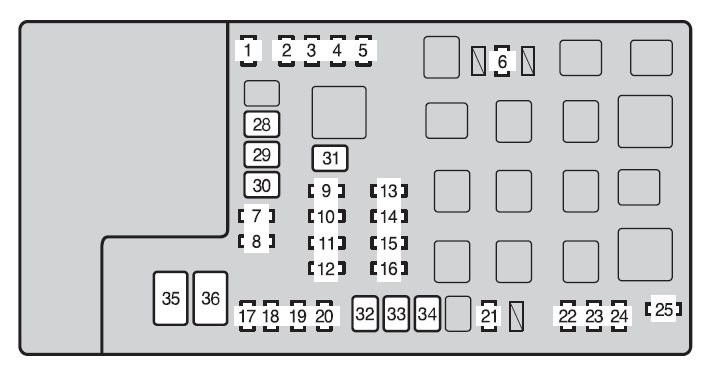 Toyota Tacoma MK2 fuse box engine compartment type a 2012
Toyota Tacoma MK2 fuse box engine compartment type a 2012
2.3 Steps to Inspect the Fuse
What is the proper procedure for inspecting the 05 ion OBD2 fuse?
Follow these steps to inspect the fuse:
- Turn Off the Vehicle: Ensure the ignition is off to prevent electrical shock or damage.
- Open the Fuse Box: Remove the fuse box cover.
- Locate the Fuse: Use the fuse box diagram to find the 05 ion OBD2 fuse.
- Visually Inspect: Look at the fuse. If the small wire inside is broken or the plastic is blackened, the fuse is blown.
- Test with a Multimeter (Optional): Set the multimeter to the continuity setting. Touch one probe to each of the fuse’s metal contacts. If the multimeter beeps or shows continuity (usually a reading close to 0 ohms), the fuse is good. If there is no continuity, the fuse is blown.
- Replace if Necessary: If the fuse is blown, replace it with a new fuse of the same amperage.
2.4 Tools Needed for Fuse Inspection
What tools are required for inspecting and replacing the fuse?
- Fuse Puller: A small plastic tool designed to safely remove fuses.
- Multimeter (Optional): For testing continuity.
- Replacement Fuse: Ensure it is the same amperage as the original.
- Flashlight: To provide better visibility in the fuse box.
3. Causes of a Blown 05 Ion OBD2 Fuse
Why does the 05 ion OBD2 fuse blow in the first place?
A blown 05 ion OBD2 fuse typically results from an electrical overload or short circuit in the OBD2 port or connected devices. Common causes include faulty scan tools, damaged wiring, or issues with accessories that draw power from the OBD2 port.
3.1 Short Circuits in the OBD2 Port Wiring
How can damaged wiring lead to a blown fuse?
Damaged or frayed wiring can create a short circuit, where the electrical current bypasses the intended path and flows directly to ground. This sudden surge of current exceeds the fuse’s capacity, causing it to blow and protect the circuit from further damage.
3.2 Faulty OBD2 Scanners and Devices
Can a malfunctioning scanner cause the fuse to blow?
Yes, a faulty OBD2 scanner or any device plugged into the OBD2 port can cause the fuse to blow. Internal electrical problems within the scanner can draw excessive current, leading to an overload. Always ensure that your scan tool is in good working condition and compatible with your vehicle.
3.3 Overloading the Circuit
Is it possible to overload the OBD2 circuit by using multiple devices?
Connecting multiple high-draw devices to the OBD2 port simultaneously can overload the circuit, causing the fuse to blow. The OBD2 port is not designed to handle a large amount of power draw, so avoid using multiple adapters or devices at the same time.
3.4 Corrosion and Damage to the OBD2 Port
How can physical damage or corrosion affect the fuse?
Corrosion or physical damage to the OBD2 port can create a short circuit. Corrosion can build up on the connector pins, creating a path for electricity to flow where it shouldn’t. Physical damage, such as bent pins or a cracked housing, can also lead to electrical shorts. Regular inspection and cleaning of the OBD2 port can help prevent these issues.
4. Step-by-Step Guide to Replacing the 05 Ion OBD2 Fuse
What is the correct procedure for replacing a blown 05 ion OBD2 fuse?
Replacing the 05 ion OBD2 fuse is a straightforward process: turn off the ignition, locate the fuse box, identify the blown fuse, remove it with a fuse puller, and replace it with a new fuse of the same amperage. Test the OBD2 port with a scanner to ensure it now functions correctly.
4.1 Preparing to Replace the Fuse
What steps should you take before starting the replacement process?
- Turn Off the Ignition: Ensure the vehicle’s ignition is completely off.
- Gather Your Tools: Have a fuse puller, replacement fuse, and flashlight ready.
- Locate the Fuse Box: Identify the fuse box containing the 05 ion OBD2 fuse.
- Consult the Fuse Diagram: Verify the fuse location using the fuse box diagram.
4.2 Removing the Blown Fuse
How should you safely remove the blown fuse from the fuse box?
Use the fuse puller to gently grip the fuse and pull it straight out of the fuse box. Avoid using pliers or other metal tools, as they can damage the fuse box or create a short circuit.
4.3 Installing the New Fuse
What precautions should you take when installing the replacement fuse?
Ensure the replacement fuse has the same amperage rating as the original. Align the fuse with the terminals in the fuse box and press it firmly into place. Do not force the fuse, as this can damage the fuse box.
4.4 Testing the OBD2 Port After Fuse Replacement
How can you verify that the OBD2 port is working after replacing the fuse?
Plug your OBD2 scanner into the port and turn on the vehicle’s ignition. The scanner should power on and establish a connection with the vehicle’s computer. If the scanner still does not work, there may be another underlying issue, such as damaged wiring or a faulty OBD2 port.
5. Troubleshooting Steps If the OBD2 Port Still Doesn’t Work
What should you do if replacing the fuse doesn’t solve the problem?
If the OBD2 port still doesn’t work after replacing the fuse, further troubleshooting is necessary. Check the wiring for damage, inspect the OBD2 port for corrosion, and test the port with a different scan tool. A faulty ECU may also be the cause.
5.1 Checking for Wiring Damage
How should you inspect the wiring connected to the OBD2 port?
Visually inspect the wiring harness connected to the OBD2 port for any signs of damage, such as frayed wires, cracks, or exposed conductors. Use a multimeter to check for continuity in the wires. If you find any damaged wires, repair or replace them as needed. According to a study by the National Institute for Automotive Service Excellence (ASE), faulty wiring is a common cause of OBD2 port issues.
5.2 Inspecting the OBD2 Port for Corrosion
How can corrosion affect the OBD2 port’s functionality?
Corrosion on the OBD2 port’s connector pins can prevent proper communication between the scan tool and the vehicle’s computer. Use a wire brush or electrical contact cleaner to carefully clean the pins. Ensure the port is completely dry before reconnecting any devices.
5.3 Testing with a Different Scan Tool
Why is it important to test with another scan tool?
Testing with a different scan tool can help determine if the issue is with the original scanner or the vehicle’s OBD2 port. If the second scanner works, the original scanner is likely faulty and needs to be repaired or replaced.
5.4 Evaluating the Possibility of a Faulty ECU
When should you suspect a problem with the Engine Control Unit (ECU)?
If you have checked the fuse, wiring, and OBD2 port, and the port still does not work, a faulty ECU may be the cause. The ECU is the vehicle’s main computer and controls various functions, including OBD2 communication. Consult a professional mechanic to diagnose and repair ECU issues.
6. Advanced Diagnostic Techniques for OBD2 Port Issues
What are some advanced methods for diagnosing OBD2 port problems?
Advanced diagnostic techniques include using an oscilloscope to analyze signal waveforms, performing voltage drop tests, and using specialized diagnostic software. These methods require advanced technical knowledge and should be performed by a qualified technician.
6.1 Using an Oscilloscope
How can an oscilloscope help diagnose OBD2 port issues?
An oscilloscope can display the electrical signals within the OBD2 system, allowing technicians to identify issues such as signal interference, voltage irregularities, and communication errors. By analyzing the waveforms, technicians can pinpoint the source of the problem and make targeted repairs.
6.2 Performing Voltage Drop Tests
What is a voltage drop test and how is it performed?
A voltage drop test measures the voltage loss across a circuit. Excessive voltage drop indicates high resistance, which can be caused by corroded connections, damaged wiring, or faulty components. To perform a voltage drop test, connect a multimeter in series with the circuit and measure the voltage while the circuit is operating.
6.3 Utilizing Specialized Diagnostic Software
What types of diagnostic software are available for OBD2 systems?
Specialized diagnostic software provides advanced features such as enhanced code reading, live data streaming, and bi-directional control. These tools can access deeper levels of the vehicle’s computer system, allowing technicians to diagnose complex issues that are not accessible with standard OBD2 scanners. Examples include AutoEnginuity, Snap-on diagnostic tools, and dealer-level diagnostic software.
7. Preventive Measures to Avoid Future OBD2 Port Problems
How can you prevent OBD2 port issues from recurring?
Preventive measures include regularly inspecting the OBD2 port for damage and corrosion, using high-quality scan tools, avoiding overloading the circuit, and protecting the wiring from damage. Regular maintenance can help ensure the OBD2 port remains functional and reliable.
7.1 Regular Inspection and Cleaning
How often should you inspect and clean the OBD2 port?
Inspect the OBD2 port at least twice a year for any signs of damage or corrosion. Clean the connector pins with a wire brush or electrical contact cleaner to remove any buildup. This helps ensure a good electrical connection and prevents communication issues.
7.2 Using High-Quality Scan Tools
Why is it important to use a reputable scan tool?
Using a high-quality scan tool reduces the risk of electrical issues and ensures accurate diagnostic information. Low-quality or counterfeit scan tools may not meet industry standards and can potentially damage the vehicle’s computer system. Invest in a reputable brand with positive reviews and a solid warranty.
7.3 Avoiding Overloading the Circuit
What precautions should you take to avoid overloading the OBD2 circuit?
Avoid plugging multiple devices into the OBD2 port simultaneously. Each device draws power from the circuit, and overloading it can cause the fuse to blow or damage the port. If you need to use multiple devices, consider using a powered splitter or adapter that provides its own power source.
7.4 Protecting the Wiring from Damage
How can you protect the OBD2 port wiring from physical damage?
Protect the wiring harness connected to the OBD2 port by securing it away from moving parts and sharp edges. Use zip ties or electrical tape to bundle the wires and prevent them from rubbing against other components. Regular inspection and maintenance can help identify and address potential wiring issues before they cause problems.
8. Common OBD2 Error Codes and Their Meanings
What are some frequent OBD2 error codes and what do they indicate?
Common OBD2 error codes include P0171 (System Too Lean), P0300 (Random Misfire Detected), and P0420 (Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold). These codes provide valuable information about the nature and location of the problem, helping technicians to diagnose and repair the vehicle efficiently.
8.1 P0171: System Too Lean (Bank 1)
What does this code indicate and what are the possible causes?
Code P0171 indicates that the engine is running lean, meaning there is too much air and not enough fuel in the air-fuel mixture. Possible causes include:
- Vacuum leaks
- Faulty oxygen sensor
- Dirty or clogged fuel injectors
- Low fuel pressure
- Mass airflow (MAF) sensor issues
8.2 P0300: Random Misfire Detected
What does a P0300 code signify and how should it be addressed?
P0300 indicates that the engine is experiencing random misfires, meaning one or more cylinders are not firing properly. Potential causes include:
- Faulty spark plugs
- Bad ignition coils
- Vacuum leaks
- Low fuel pressure
- Internal engine problems
8.3 P0420: Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold (Bank 1)
What does code P0420 mean and what steps should be taken?
P0420 indicates that the catalytic converter is not functioning efficiently and is not properly reducing emissions. Possible causes include:
- Faulty catalytic converter
- Exhaust leaks
- Damaged oxygen sensors
- Engine running rich or lean
9. The Role of OBD2 Scanners in Modern Automotive Repair
How do OBD2 scanners contribute to effective automotive repair?
OBD2 scanners are indispensable tools for modern automotive repair. They allow technicians and car owners to quickly read diagnostic trouble codes, access live data, and perform system tests, enabling accurate and efficient diagnoses. According to a report by the Automotive Aftermarket Industry Association (AAIA), the use of OBD2 scanners has reduced diagnostic time by up to 40%.
9.1 Reading Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
How do OBD2 scanners help in identifying DTCs?
OBD2 scanners read the diagnostic trouble codes stored in the vehicle’s computer. These codes provide specific information about the nature and location of the problem, helping technicians to quickly identify the issue and begin the repair process.
9.2 Accessing Live Data
What kind of real-time information can OBD2 scanners provide?
OBD2 scanners can access live data from various sensors and systems in the vehicle, including engine speed, coolant temperature, oxygen sensor readings, and fuel trim values. This real-time data helps technicians to monitor the performance of the engine and identify any abnormalities.
9.3 Performing System Tests
What types of system tests can be performed with an OBD2 scanner?
OBD2 scanners can perform system tests such as oxygen sensor tests, EVAP system tests, and misfire monitoring. These tests help technicians to verify the functionality of individual components and systems and ensure they are operating within acceptable parameters.
10. Choosing the Right OBD2 Scanner for Your Needs
How do you select the most appropriate OBD2 scanner for your specific requirements?
When choosing an OBD2 scanner, consider factors such as compatibility, features, ease of use, and price. Basic scanners are suitable for reading and clearing codes, while advanced scanners offer features such as live data streaming, bi-directional control, and access to manufacturer-specific codes.
10.1 Compatibility
What compatibility factors should be considered when selecting an OBD2 scanner?
Ensure the scanner is compatible with your vehicle’s make and model. Some scanners are designed to work with specific vehicle types, while others offer broader compatibility. Check the scanner’s specifications to verify it supports the OBD2 protocols used by your vehicle.
10.2 Features
What features should you look for in an OBD2 scanner?
Consider the features that are most important to you. Basic scanners offer code reading and clearing, while advanced scanners provide live data, graphing, bi-directional control, and access to manufacturer-specific codes. Choose a scanner that offers the features you need for your diagnostic and repair tasks.
10.3 Ease of Use
How important is user-friendliness when choosing an OBD2 scanner?
Opt for a scanner that is easy to use, with a clear display, intuitive menus, and helpful documentation. Some scanners offer smartphone or tablet integration, which can provide a more user-friendly interface. Consider reading reviews and watching videos to get a sense of the scanner’s usability before making a purchase.
10.4 Price
How does price factor into the selection of an OBD2 scanner?
OBD2 scanners range in price from basic models under $50 to advanced professional-grade tools costing several thousand dollars. Set a budget and choose a scanner that offers the features and compatibility you need within your price range. Keep in mind that investing in a higher-quality scanner can save you time and money in the long run by providing more accurate and comprehensive diagnostic information.
11. How OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN Can Help You
Looking for reliable solutions for your car’s diagnostic needs? At OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN, we offer comprehensive guidance and support to help you resolve OBD2 port issues and ensure your vehicle runs smoothly. Our expert team provides detailed troubleshooting steps, advanced diagnostic techniques, and personalized advice tailored to your specific vehicle and situation.
11.1 Expert Guidance and Support
Struggling with a non-functional OBD2 port or perplexing error codes? Our team of experienced technicians is here to provide expert guidance and support every step of the way. We offer detailed troubleshooting steps, advanced diagnostic techniques, and personalized advice tailored to your specific vehicle and situation.
11.2 Comprehensive Resources and Information
Navigating the complexities of automotive diagnostics can be overwhelming. That’s why we offer a wealth of comprehensive resources and information to empower you with the knowledge you need to tackle OBD2 port issues effectively. From detailed articles and step-by-step guides to informative videos and interactive tools, we provide the resources you need to diagnose and resolve problems with confidence.
11.3 Professional Diagnostic Services
Sometimes, even with the best tools and resources, diagnosing and repairing OBD2 port issues can be challenging. That’s where our professional diagnostic services come in. Our team of skilled technicians utilizes state-of-the-art equipment and advanced diagnostic techniques to accurately identify and resolve even the most complex OBD2 port problems.
11.4 Contact Us Today
Ready to get your OBD2 port working again and ensure your vehicle runs smoothly? Contact us today at:
- Address: 123 Main Street, Los Angeles, CA 90001, United States
- WhatsApp: +1 (641) 206-8880
- Website: OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN
Let OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN be your trusted partner in automotive diagnostics and repair!
FAQ: Frequently Asked Questions About OBD2 Port Issues
What is an OBD2 scanner and what does it do?
An OBD2 scanner is a diagnostic tool used to read and interpret data from a vehicle’s onboard computer system, helping to identify potential issues.
How do I read an OBD2 error code?
Connect the OBD2 scanner to the OBD2 port, turn on the ignition, and follow the scanner’s instructions to read the stored error codes.
What are some common OBD2 error codes?
Common codes include P0171 (System Too Lean), P0300 (Random Misfire Detected), and P0420 (Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold).
Can a blown fuse affect the OBD2 port?
Yes, a blown fuse can prevent the OBD2 port from functioning by cutting off its power supply.
Where is the OBD2 fuse located in my car?
The OBD2 fuse is typically located in the vehicle’s fuse box, either under the dashboard or in the engine compartment. Consult your vehicle’s owner’s manual for the exact location.
What should I do if my OBD2 scanner won’t connect?
Check the OBD2 fuse, inspect the port for damage, and ensure the scanner is compatible with your vehicle.
How can I clean the OBD2 port?
Use a wire brush or electrical contact cleaner to carefully clean the connector pins, ensuring the port is dry before reconnecting any devices.
Is it safe to leave an OBD2 scanner plugged in all the time?
Leaving an OBD2 scanner plugged in can drain the battery, so it’s generally not recommended unless the device has a low-power mode.
Can a faulty oxygen sensor cause OBD2 port issues?
While a faulty oxygen sensor won’t directly cause OBD2 port issues, it can trigger error codes that can be read using an OBD2 scanner.
What is the difference between a basic and an advanced OBD2 scanner?
Basic scanners read and clear codes, while advanced scanners offer live data, graphing, bi-directional control, and access to manufacturer-specific codes.