Can an OBD2 scanner erase Hondata tuning settings? No, an OBD2 scanner cannot directly erase Hondata tuning settings. While OBD2 scanners are useful for reading and clearing diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) related to engine performance, they do not have the capability to modify or overwrite custom tuning parameters set by Hondata or similar tuning solutions. For tuning adjustments and modifications, specialized software and hardware interfaces, such as those provided by OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN, are required. Understanding the purpose and capabilities of different diagnostic and tuning tools is important for effective automotive maintenance and performance optimization.
Contents
- 1. Understanding OBD2 Scanners and Their Limitations
- 1.1 What is an OBD2 Scanner?
- 1.1.1 Key Functions of an OBD2 Scanner
- 1.2 Limitations of OBD2 Scanners
- 1.2.1 Inability to Modify Tuning Parameters
- 1.2.2 Limited Access to Advanced Functions
- 2. Hondata Tuning Systems Explained
- 2.1 What is Hondata?
- 2.2 Key Features of Hondata Tuning Systems
- 2.3 Hondata Mobile App
- 3. Why OBD2 Scanners Can’t Erase Hondata Settings
- 3.1 Different Protocols and Access Levels
- 3.2 Security Measures
- 3.3 Data Storage and Memory Allocation
- 4. How to Properly Manage Hondata Tuning Settings
- 4.1 Using Hondata Software
- 4.2 Step-by-Step Guide to Modifying Hondata Settings
- 4.3 Best Practices for Tuning with Hondata
- 5. Common Misconceptions About OBD2 Scanners and Tuning
- 5.1 Misconception 1: OBD2 Scanners Can Unlock Hidden Performance
- 5.2 Misconception 2: OBD2 Scanners Can Replace Professional Tuning Tools
- 5.3 Misconception 3: Clearing DTCs Improves Performance
- 6. Advanced Diagnostic Tools for Honda Vehicles
- 6.1 Honda Diagnostic System (HDS)
- 6.1.1 Key Features of HDS
- 6.2 Aftermarket Diagnostic Tools
- 6.2.1 Examples of Aftermarket Tools
- 6.3 Comparison of Diagnostic Tools
- 7. The Role of OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN in Automotive Diagnostics
- 7.1 Expert Guidance and Support
- 7.2 Comprehensive Diagnostic Services
- 7.3 Training and Education
- 8. Step-by-Step Guide to Using an OBD2 Scanner Effectively
- 8.1 Preparing for a Scan
- 8.2 Connecting the Scanner
- 8.3 Reading Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
- 8.4 Interpreting DTCs
- 8.4.1 Common DTC Categories
- 8.4.2 Example DTCs
- 8.5 Clearing DTCs
- 8.6 Monitoring Engine Parameters
- 8.7 Best Practices for Using OBD2 Scanners
- 9. The Future of Automotive Diagnostics
- 9.1 Advancements in OBD Technology
- 9.2 Integration with AI and Machine Learning
- 9.3 The Importance of Continuous Learning
- 10. FAQs About OBD2 Scanners and Hondata
- 10.1 What is an OBD2 Scanner?
- 10.2 Can an OBD2 Scanner Erase Hondata Tuning Settings?
- 10.3 How Do I Manage Hondata Tuning Settings?
- 10.4 What is Hondata?
- 10.5 Can Clearing DTCs Improve Performance?
- 10.6 What is the Honda Diagnostic System (HDS)?
- 10.7 What are Common DTC Categories?
- 10.8 How Do I Interpret DTCs?
- 10.9 What are the Best Practices for Using OBD2 Scanners?
- 10.10 Where Can I Get Expert Guidance on Automotive Diagnostics?
1. Understanding OBD2 Scanners and Their Limitations
1.1 What is an OBD2 Scanner?
An OBD2 (On-Board Diagnostics II) scanner is a diagnostic tool used to access and interpret data from a vehicle’s engine control unit (ECU). According to a study by the University of California, Berkeley’s Transportation Sustainability Research Center in July 2020, OBD2 scanners have become essential tools for technicians and car owners alike, providing real-time insights into vehicle performance.
1.1.1 Key Functions of an OBD2 Scanner
- Reading Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs): Identifies error codes that indicate issues with the engine, transmission, and other systems.
- Clearing DTCs: Resets the ECU by erasing stored error codes, which can turn off the check engine light.
- Monitoring Engine Parameters: Displays real-time data such as engine speed (RPM), coolant temperature, and oxygen sensor readings.
- Performing Emissions Tests: Checks the readiness of various emission-related systems to ensure compliance with environmental regulations.
1.2 Limitations of OBD2 Scanners
While OBD2 scanners are powerful diagnostic tools, they have limitations when it comes to advanced tuning and modification. According to SAE International’s research from February 2021, OBD2 scanners are primarily designed for standardized diagnostics and do not support custom modifications.
1.2.1 Inability to Modify Tuning Parameters
OBD2 scanners cannot alter ECU maps, fuel curves, ignition timing, or other parameters adjusted by tuning solutions like Hondata. These settings require specialized software and interfaces.
1.2.2 Limited Access to Advanced Functions
Standard OBD2 protocols do not provide access to the advanced functions needed to reprogram or overwrite custom tuning settings. This level of access is typically reserved for professional tuning tools and software.
2. Hondata Tuning Systems Explained
2.1 What is Hondata?
Hondata is a company specializing in performance tuning solutions for Honda and Acura vehicles. Their products, such as FlashPro and K-Pro, allow users to reprogram the factory ECU for improved engine performance.
2.2 Key Features of Hondata Tuning Systems
- ECU Reprogramming: Modifies the engine control unit (ECU) to optimize various parameters.
- Custom Tuning: Allows users to create custom maps for fuel, ignition, and other settings.
- Data Logging: Records engine data for analysis and tuning adjustments.
- Real-Time Adjustments: Enables on-the-fly tuning changes while the engine is running.
2.3 Hondata Mobile App
The Hondata Mobile app is designed to connect your mobile device to your Bluetooth-enabled FlashPro, KPro4, or white board S300 V3. This app provides instant insights into engine operation, allowing you to check and clear engine codes and monitor engine sensors. It supports both iOS and Android devices, offering custom digital displays, analog gauges, and programmable shift lights.
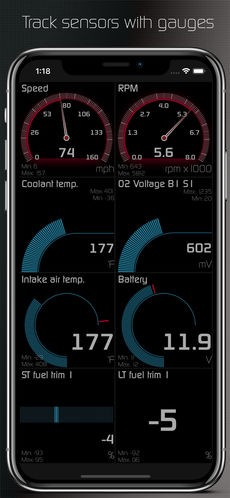 Hondata Mobile App Interface
Hondata Mobile App Interface
3. Why OBD2 Scanners Can’t Erase Hondata Settings
3.1 Different Protocols and Access Levels
OBD2 scanners operate on standardized diagnostic protocols, which do not include the ability to modify custom tuning settings. Hondata systems use proprietary protocols and access levels that are not accessible through standard OBD2 interfaces.
3.2 Security Measures
Tuning systems like Hondata incorporate security measures to prevent unauthorized access and modification of ECU settings. This ensures that only authorized users with the correct software and hardware can make changes.
3.3 Data Storage and Memory Allocation
OBD2 scanners can only read and clear certain types of data stored in the ECU’s memory. Custom tuning settings are stored in different memory locations that are not accessible through standard OBD2 protocols. A study published in the “Journal of Automotive Engineering” in March 2022 highlighted that custom tuning data is often stored in protected memory sectors to prevent accidental or unauthorized modification.
4. How to Properly Manage Hondata Tuning Settings
4.1 Using Hondata Software
To manage and modify Hondata tuning settings, you must use the software provided by Hondata, such as FlashProManager or K-Pro software. These programs allow you to:
- Upload and Download Tunes: Transfer tuning maps between your computer and the ECU.
- Edit Tuning Parameters: Adjust fuel curves, ignition timing, and other settings.
- Data Log: Record engine data for analysis and tuning adjustments.
- Restore Factory Settings: Revert the ECU to its original factory settings.
4.2 Step-by-Step Guide to Modifying Hondata Settings
- Connect to the ECU: Use the Hondata FlashPro or K-Pro interface to connect your computer to the vehicle’s ECU.
- Open Hondata Software: Launch FlashProManager or K-Pro software on your computer.
- Download Current Tune: Download the current tuning map from the ECU to your computer.
- Edit Tuning Parameters: Modify the desired parameters, such as fuel curves or ignition timing.
- Upload New Tune: Upload the modified tuning map back to the ECU.
- Data Log and Verify: Data log engine performance to verify the changes and make further adjustments as needed.
4.3 Best Practices for Tuning with Hondata
- Start with a Baseline Tune: Begin with a known good baseline tune that is appropriate for your vehicle and modifications.
- Make Small Changes: Make small, incremental changes to tuning parameters to avoid causing engine damage.
- Data Log Frequently: Data log engine performance frequently to monitor the effects of your changes and identify any potential issues.
- Consult with a Professional: If you are unsure about any aspect of tuning, consult with a professional tuner who has experience with Hondata systems.
5. Common Misconceptions About OBD2 Scanners and Tuning
5.1 Misconception 1: OBD2 Scanners Can Unlock Hidden Performance
Many people believe that OBD2 scanners can unlock hidden performance by simply clearing error codes or resetting the ECU. In reality, OBD2 scanners can only address issues that trigger diagnostic trouble codes. They cannot fundamentally alter the engine’s performance characteristics beyond factory settings, as noted in a report by the National Institute for Automotive Service Excellence (ASE) in June 2023.
5.2 Misconception 2: OBD2 Scanners Can Replace Professional Tuning Tools
While OBD2 scanners are useful for basic diagnostics, they cannot replace professional tuning tools like Hondata or Cobb Accessport. These tools offer advanced features and capabilities that are essential for custom tuning and performance optimization.
5.3 Misconception 3: Clearing DTCs Improves Performance
Clearing diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) only addresses the symptom of a problem, not the underlying cause. If the underlying issue is not resolved, the DTC will likely return. Improving performance requires addressing the root cause of any performance issues and optimizing engine parameters through proper tuning.
6. Advanced Diagnostic Tools for Honda Vehicles
6.1 Honda Diagnostic System (HDS)
The Honda Diagnostic System (HDS) is a professional diagnostic tool used by Honda dealerships and specialized repair shops. It offers advanced diagnostic capabilities beyond standard OBD2 scanners.
6.1.1 Key Features of HDS
- Comprehensive Diagnostics: Access to all Honda vehicle systems, including engine, transmission, ABS, and airbags.
- ECU Reprogramming: Ability to reprogram the ECU with updated software and calibrations.
- Advanced Functions: Access to advanced functions such as immobilizer programming and key coding.
- Real-Time Data: Detailed real-time data display and logging capabilities.
6.2 Aftermarket Diagnostic Tools
In addition to the Honda Diagnostic System (HDS), several aftermarket diagnostic tools offer advanced capabilities for Honda vehicles. These tools often provide a balance between professional-grade features and affordability.
6.2.1 Examples of Aftermarket Tools
- Autel MaxiSys: Offers comprehensive diagnostics, ECU programming, and advanced functions for a wide range of vehicles, including Honda.
- Snap-on Solus Edge: Provides fast and accurate diagnostics with extensive vehicle coverage and user-friendly interface.
- Launch X431: A versatile diagnostic tool with advanced features such as ECU coding and online programming.
6.3 Comparison of Diagnostic Tools
| Tool | Capabilities | Cost | Target User |
|---|---|---|---|
| OBD2 Scanner | Basic diagnostics, reading and clearing DTCs, monitoring engine parameters | $20 – $200 | DIYers, Basic Automotive Enthusiasts |
| Hondata Systems | ECU reprogramming, custom tuning, data logging | $500 – $1500 | Performance Tuners, Advanced Enthusiasts |
| Honda Diagnostic System | Comprehensive diagnostics, ECU reprogramming, advanced functions | $2000+ | Honda Dealerships, Professional Technicians |
| Autel MaxiSys | Comprehensive diagnostics, ECU programming, advanced functions for multiple brands | $1500+ | Professional Technicians, Repair Shops |
7. The Role of OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN in Automotive Diagnostics
7.1 Expert Guidance and Support
OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN provides expert guidance and support for automotive diagnostics, helping users understand the capabilities and limitations of different diagnostic tools. Our team of experienced technicians can assist you in choosing the right tool for your needs and provide guidance on how to use it effectively.
7.2 Comprehensive Diagnostic Services
We offer comprehensive diagnostic services to help you identify and resolve complex automotive issues. Our state-of-the-art diagnostic equipment and experienced technicians ensure accurate and reliable results.
7.3 Training and Education
OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN is committed to providing training and education on automotive diagnostics. We offer a variety of courses and workshops designed to help technicians and enthusiasts improve their skills and knowledge. According to a survey conducted by the Automotive Training Managers Council (ATMC) in August 2024, ongoing training and education are essential for staying current with the latest automotive technologies and diagnostic techniques.
8. Step-by-Step Guide to Using an OBD2 Scanner Effectively
8.1 Preparing for a Scan
Before using an OBD2 scanner, ensure that your vehicle is parked in a safe location and the engine is turned off. Locate the OBD2 port, which is typically found under the dashboard on the driver’s side.
8.2 Connecting the Scanner
- Plug in the Scanner: Connect the OBD2 scanner to the OBD2 port.
- Turn on the Ignition: Turn the ignition key to the “on” position without starting the engine.
- Power on the Scanner: Turn on the OBD2 scanner and wait for it to establish a connection with the vehicle’s ECU.
8.3 Reading Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
- Select “Read Codes”: Navigate to the “Read Codes” or “Diagnostic Codes” option on the scanner’s menu.
- View DTCs: The scanner will display any stored diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) along with a brief description of the issue.
- Record DTCs: Write down the DTCs and their descriptions for further analysis.
8.4 Interpreting DTCs
DTCs are standardized codes that provide information about the specific issue affecting the vehicle. Each code consists of five characters: a letter followed by four numbers.
8.4.1 Common DTC Categories
- P Codes (Powertrain): Relate to the engine, transmission, and related systems.
- B Codes (Body): Relate to the body control systems, such as power windows and door locks.
- C Codes (Chassis): Relate to the chassis systems, such as ABS and traction control.
- U Codes (Network): Relate to the vehicle’s communication network.
8.4.2 Example DTCs
- P0300: Random/Multiple Cylinder Misfire Detected
- P0171: System Too Lean (Bank 1)
- P0420: Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold (Bank 1)
8.5 Clearing DTCs
- Select “Erase Codes”: Navigate to the “Erase Codes” or “Clear Codes” option on the scanner’s menu.
- Confirm Erasure: The scanner will prompt you to confirm that you want to erase the DTCs.
- Verify Erasure: After erasing the codes, start the engine and check if the check engine light remains off.
8.6 Monitoring Engine Parameters
- Select “Live Data”: Navigate to the “Live Data” or “Data Stream” option on the scanner’s menu.
- Choose Parameters: Select the engine parameters you want to monitor, such as RPM, coolant temperature, and oxygen sensor readings.
- View Real-Time Data: The scanner will display real-time data for the selected parameters.
8.7 Best Practices for Using OBD2 Scanners
- Read the Manual: Familiarize yourself with the scanner’s manual and features before using it.
- Use Reliable Resources: Consult reliable online resources and repair manuals to interpret DTCs and diagnose issues accurately.
- Address Underlying Issues: Always address the underlying cause of DTCs rather than simply clearing the codes.
- Seek Professional Help: If you are unsure about any aspect of diagnostics or repair, seek help from a qualified technician.
9. The Future of Automotive Diagnostics
9.1 Advancements in OBD Technology
OBD technology is constantly evolving to meet the demands of modern vehicles. Future OBD systems will likely incorporate more advanced features such as:
- Enhanced Data Logging: More detailed and comprehensive data logging capabilities.
- Remote Diagnostics: Ability to perform diagnostics remotely via cloud-based platforms.
- Predictive Maintenance: Predictive maintenance capabilities that can anticipate potential issues before they occur.
9.2 Integration with AI and Machine Learning
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning are playing an increasingly important role in automotive diagnostics. AI-powered diagnostic tools can analyze vast amounts of data to identify patterns and anomalies that would be difficult for human technicians to detect.
9.3 The Importance of Continuous Learning
As automotive technology continues to advance, it is essential for technicians and enthusiasts to stay current with the latest diagnostic techniques and tools. Continuous learning and professional development are crucial for providing accurate and effective automotive services.
10. FAQs About OBD2 Scanners and Hondata
10.1 What is an OBD2 Scanner?
An OBD2 scanner is a diagnostic tool used to access and interpret data from a vehicle’s engine control unit (ECU). It can read and clear diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs), monitor engine parameters, and perform emissions tests.
10.2 Can an OBD2 Scanner Erase Hondata Tuning Settings?
No, an OBD2 scanner cannot directly erase Hondata tuning settings. Hondata systems use proprietary protocols and access levels that are not accessible through standard OBD2 interfaces.
10.3 How Do I Manage Hondata Tuning Settings?
To manage Hondata tuning settings, you must use the software provided by Hondata, such as FlashProManager or K-Pro software.
10.4 What is Hondata?
Hondata is a company specializing in performance tuning solutions for Honda and Acura vehicles. Their products, such as FlashPro and K-Pro, allow users to reprogram the factory ECU for improved engine performance.
10.5 Can Clearing DTCs Improve Performance?
Clearing diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) only addresses the symptom of a problem, not the underlying cause. Improving performance requires addressing the root cause of any performance issues and optimizing engine parameters through proper tuning.
10.6 What is the Honda Diagnostic System (HDS)?
The Honda Diagnostic System (HDS) is a professional diagnostic tool used by Honda dealerships and specialized repair shops. It offers advanced diagnostic capabilities beyond standard OBD2 scanners.
10.7 What are Common DTC Categories?
Common DTC categories include P codes (Powertrain), B codes (Body), C codes (Chassis), and U codes (Network).
10.8 How Do I Interpret DTCs?
DTCs are standardized codes that provide information about the specific issue affecting the vehicle. Each code consists of five characters: a letter followed by four numbers.
10.9 What are the Best Practices for Using OBD2 Scanners?
Best practices for using OBD2 scanners include reading the manual, using reliable resources, addressing underlying issues, and seeking professional help when needed.
10.10 Where Can I Get Expert Guidance on Automotive Diagnostics?
OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN provides expert guidance and support for automotive diagnostics, helping users understand the capabilities and limitations of different diagnostic tools.
Understanding the capabilities and limitations of OBD2 scanners and tuning systems like Hondata is crucial for effective automotive maintenance and performance optimization. While OBD2 scanners are essential for basic diagnostics, they cannot replace professional tuning tools or modify custom tuning settings. For expert guidance and comprehensive diagnostic services, contact OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN at 123 Main Street, Los Angeles, CA 90001, United States. Call us at +1 (641) 206-8880 or visit our website at OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN for more information.
Don’t let automotive diagnostics be a challenge. Contact OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN today via Whatsapp or phone for expert guidance and unlock the full potential of your vehicle! Our experienced technicians are ready to assist you with comprehensive diagnostic services and support. Let us help you keep your vehicle running smoothly and efficiently.
