OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN understands your curiosity about the Hdmi To Obd2 Pinout. While a direct HDMI to OBD2 connection isn’t typically used in automotive diagnostics, exploring alternative solutions will help you achieve your goal. This article will explain common ways to access vehicle data using OBD2 scanners and related technologies. If you’re eager to get started and need immediate assistance, feel free to contact us via WhatsApp at +1 (641) 206-8880, or visit our website, OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN. We provide guidance, support, and services to ensure your automotive diagnostic needs are met effectively. Let’s dive into the details and get you the information you need.
Contents
- 1. Understanding OBD2 and Its Functionality
- 1.1 What Is the OBD2 Port?
- 1.2 Key Functions of the OBD2 System
- 1.3 OBD2 Protocols
- 2. Exploring HDMI and Its Applications
- 2.1 What Is HDMI?
- 2.2 Common Uses of HDMI
- 2.3 HDMI Versions and Capabilities
- 3. Why an HDMI to OBD2 Pinout Is Uncommon
- 3.1 Differences in Signal Types
- 3.2 Voltage and Protocol Incompatibilities
- 3.3 Lack of Standardized Use
- 4. Alternatives for Accessing Vehicle Data
- 4.1 Using an OBD2 Scanner with a Display
- 4.2 Connecting an OBD2 Scanner to a Computer via USB
- 4.3 Using Bluetooth or Wi-Fi OBD2 Adapters with Smartphones or Tablets
- 4.4 Utilizing Head-Up Displays (HUDs) with OBD2 Connectivity
- 5. Step-by-Step Guide: Using an OBD2 Scanner
- 5.1 Locating the OBD2 Port in Your Vehicle
- 5.2 Connecting the OBD2 Scanner
- 5.3 Reading Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
- 5.4 Interpreting the Codes and Diagnosing Issues
- 5.5 Clearing the Codes (If Applicable)
- 6. Common OBD2 Trouble Codes and Their Meanings
- 7. Advanced OBD2 Functions and Capabilities
- 7.1 Live Data Streaming
- 7.2 Freeze Frame Data
- 7.3 Oxygen Sensor Testing
- 7.4 EVAP System Testing
- 7.5 I/M Readiness Monitoring
- 8. Choosing the Right OBD2 Scanner for Your Needs
- 8.1 Basic OBD2 Scanners
- 8.2 Mid-Range OBD2 Scanners
- 8.3 Professional-Grade OBD2 Scanners
- 8.4 Considerations for Compatibility
- 8.5 Budget and Features
- 9. OBD2 and Vehicle Maintenance: Best Practices
- 9.1 Regular Code Scanning
- 9.2 Monitoring Live Data
- 9.3 Addressing Issues Promptly
- 9.4 Keeping Records
- 9.5 Staying Updated
- 10. The Future of OBD2 Technology
- 10.1 Enhanced Diagnostics
- 10.2 Remote Diagnostics
- 10.3 Integration with Telematics
- 10.4 Cybersecurity Measures
- 10.5 Standardized Data Formats
- 11. Call to Action: Get Expert Assistance from OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN
1. Understanding OBD2 and Its Functionality
OBD2, or On-Board Diagnostics II, is a standardized system used in modern vehicles to monitor and report on various engine and vehicle parameters. It is crucial for vehicle diagnostics, maintenance, and repair.
OBD2 systems provide a wealth of data, offering insights into your vehicle’s health and performance. This data helps technicians quickly identify and address issues, ensuring your car runs smoothly and efficiently. According to the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), OBD2 systems have been mandatory in all cars sold in the United States since 1996, helping to reduce emissions and improve vehicle reliability.
1.1 What Is the OBD2 Port?
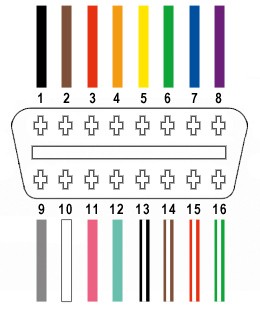
The OBD2 port is a standardized 16-pin connector found in most vehicles manufactured after 1996. It provides access to the vehicle’s computer, allowing users to read diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) and monitor various parameters.
This port is usually located under the dashboard on the driver’s side, making it easily accessible for technicians and vehicle owners. The standardized nature of the OBD2 port ensures compatibility across different vehicle makes and models, simplifying diagnostics and maintenance.
1.2 Key Functions of the OBD2 System
The OBD2 system performs several vital functions, including:
- Monitoring engine performance
- Detecting emission control system faults
- Providing diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs)
- Enabling real-time data monitoring
These functions help maintain vehicle health, reduce emissions, and provide valuable information for diagnosing and repairing issues. Modern OBD2 scanners can even reset the check engine light after repairs are completed.
1.3 OBD2 Protocols
OBD2 uses several communication protocols, including:
- SAE J1850 PWM
- SAE J1850 VPW
- ISO 9141-2
- ISO 14230-4 (KWP2000)
- ISO 15765-4 (CAN)
These protocols ensure that diagnostic tools can communicate effectively with the vehicle’s computer, regardless of the manufacturer. CAN (Controller Area Network) is the most common protocol in modern vehicles.
2. Exploring HDMI and Its Applications
HDMI, or High-Definition Multimedia Interface, is a digital interface used for transmitting high-resolution video and audio signals between devices. It is commonly used in home entertainment systems, computers, and gaming consoles.
HDMI offers a single-cable solution for high-quality audio and video, simplifying connections and reducing cable clutter. Its widespread adoption in consumer electronics has made it a standard for connecting various devices.
2.1 What Is HDMI?
HDMI is a digital interface standard for connecting high-definition devices such as TVs, Blu-ray players, and computers. It supports uncompressed video and audio data.
The HDMI standard has evolved over the years, with newer versions supporting higher resolutions, refresh rates, and advanced features like HDR (High Dynamic Range). This makes it ideal for modern entertainment systems.
2.2 Common Uses of HDMI
HDMI is used in a variety of applications, including:
- Connecting gaming consoles to TVs
- Connecting Blu-ray players to home theater systems
- Connecting computers to monitors
- Connecting streaming devices (e.g., Roku, Apple TV) to TVs
Its ability to transmit high-quality audio and video signals makes it a versatile connection option for various devices.
2.3 HDMI Versions and Capabilities
Different HDMI versions offer varying capabilities, such as:
- HDMI 1.4: Supports 4K resolution at 30Hz
- HDMI 2.0: Supports 4K resolution at 60Hz
- HDMI 2.1: Supports 8K resolution at 60Hz and 4K resolution at 120Hz
Choosing the right HDMI version ensures optimal performance and compatibility between devices. Newer versions also support advanced features like eARC (Enhanced Audio Return Channel) for improved audio quality.
3. Why an HDMI to OBD2 Pinout Is Uncommon
Directly connecting an HDMI interface to an OBD2 port is not a standard practice in automotive diagnostics due to fundamental differences in their purposes and signal types. While both are interfaces, they serve entirely different functions.
HDMI is designed for transmitting high-definition video and audio, while OBD2 is for transmitting vehicle diagnostic data. The protocols, voltage levels, and pin configurations are incompatible.
3.1 Differences in Signal Types
HDMI transmits digital video and audio signals, while OBD2 transmits diagnostic data using protocols like CAN, KWP2000, and others. These signal types are fundamentally different.
The data transmitted via OBD2 is typically low-bandwidth and focused on vehicle parameters, such as engine temperature, speed, and diagnostic trouble codes. In contrast, HDMI transmits high-bandwidth data for video and audio.
3.2 Voltage and Protocol Incompatibilities
HDMI operates at different voltage levels and uses a different communication protocol than OBD2. Directly connecting them could damage the vehicle’s electronic control unit (ECU) or the HDMI device.
OBD2 systems typically use 12V for power, while HDMI devices operate at lower voltages. The communication protocols also differ significantly, making direct communication impossible without specialized conversion hardware.
3.3 Lack of Standardized Use
There are no standardized or widely adopted devices that directly convert HDMI to OBD2. The market demand for such a conversion is limited due to the availability of more practical alternatives.
Instead of trying to force an HDMI connection, most automotive diagnostic tools use OBD2 scanners with USB, Bluetooth, or Wi-Fi connectivity to interface with computers, smartphones, or dedicated diagnostic devices.
4. Alternatives for Accessing Vehicle Data
While an HDMI to OBD2 pinout isn’t feasible, several effective alternatives exist for accessing and displaying vehicle data. These alternatives utilize standard OBD2 connections and various display technologies to provide the information you need.
These alternatives range from basic OBD2 scanners with simple displays to advanced diagnostic tools that can stream data to smartphones or tablets. Understanding these options will help you find the best solution for your needs.
4.1 Using an OBD2 Scanner with a Display
OBD2 scanners with built-in displays are a common and straightforward way to access vehicle data. These scanners plug directly into the OBD2 port and display diagnostic trouble codes and real-time data on a small screen.
 OBD2 Scanner with Display
OBD2 Scanner with Display
These scanners are user-friendly and do not require additional devices, making them ideal for quick diagnostics and troubleshooting. Many models also offer features like code definitions, freeze frame data, and the ability to clear DTCs.
4.2 Connecting an OBD2 Scanner to a Computer via USB
Many OBD2 scanners can connect to a computer via USB, allowing you to view and analyze vehicle data using specialized software. This provides a more detailed and comprehensive view of your vehicle’s performance.
The software often includes advanced features like data logging, graphing, and customized reports. This option is suitable for users who need in-depth analysis and diagnostics.
4.3 Using Bluetooth or Wi-Fi OBD2 Adapters with Smartphones or Tablets
Bluetooth or Wi-Fi OBD2 adapters can wirelessly connect to smartphones or tablets, allowing you to monitor vehicle data using dedicated apps. This is a convenient and versatile option for modern diagnostics.
 Bluetooth OBD2 Adapter
Bluetooth OBD2 Adapter
These adapters pair with apps that can display real-time data, read diagnostic trouble codes, and perform various diagnostic tests. Some apps also offer advanced features like customizable dashboards and performance monitoring.
4.4 Utilizing Head-Up Displays (HUDs) with OBD2 Connectivity
Head-Up Displays (HUDs) that connect to the OBD2 port can project vehicle data onto the windshield, providing real-time information without obstructing the driver’s view. This enhances safety and convenience.
HUDs can display information such as speed, engine RPM, coolant temperature, and diagnostic trouble codes. They are a popular choice for drivers who want to monitor their vehicle’s performance without taking their eyes off the road.
5. Step-by-Step Guide: Using an OBD2 Scanner
Using an OBD2 scanner is a straightforward process that can help you diagnose and troubleshoot vehicle issues. Here’s a step-by-step guide to get you started.
This guide covers the basic steps for using an OBD2 scanner, from connecting the device to interpreting the data. Whether you’re a seasoned mechanic or a first-time user, these steps will help you effectively use an OBD2 scanner.
5.1 Locating the OBD2 Port in Your Vehicle
The OBD2 port is typically located under the dashboard on the driver’s side. Consult your vehicle’s manual if you’re having trouble finding it.
 Locating the OBD2 Port
Locating the OBD2 Port
The port is usually easily accessible, but in some vehicles, it may be hidden behind a panel or cover. Once located, ensure that the port is clean and free from obstructions.
5.2 Connecting the OBD2 Scanner
Plug the OBD2 scanner into the OBD2 port. Ensure it is securely connected.
 Connecting the OBD2 Scanner
Connecting the OBD2 Scanner
The scanner should power on automatically once connected. If not, check the vehicle’s ignition and ensure that it is in the “ON” position.
5.3 Reading Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
Follow the scanner’s instructions to read diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs). These codes indicate specific issues with your vehicle.
 Reading DTCs
Reading DTCs
The scanner will display a list of DTCs, along with a brief description of each code. Record these codes for further investigation and troubleshooting.
5.4 Interpreting the Codes and Diagnosing Issues
Use the DTCs to research and diagnose the underlying issues. Online resources and repair manuals can provide detailed information about each code.
 Interpreting Codes
Interpreting Codes
Understanding the meaning of the codes will help you identify the specific components or systems that are malfunctioning. This will guide your repair efforts and ensure that you address the root cause of the problem.
5.5 Clearing the Codes (If Applicable)
After addressing the issues, you can use the OBD2 scanner to clear the diagnostic trouble codes. This will reset the check engine light.
 Clearing Codes
Clearing Codes
Clearing the codes does not fix the underlying problem, so ensure that you have properly repaired the issue before clearing the codes. If the problem persists, the check engine light will reappear.
6. Common OBD2 Trouble Codes and Their Meanings
Understanding common OBD2 trouble codes is essential for effective vehicle diagnostics. Here’s a table of frequently encountered codes and their meanings.
This table provides a quick reference for common OBD2 codes, helping you understand the potential issues with your vehicle. Refer to your vehicle’s repair manual for detailed troubleshooting steps.
| Code | Description | Possible Causes |
|---|---|---|
| P0101 | Mass Air Flow (MAF) Sensor Range/Performance | Dirty or faulty MAF sensor, vacuum leaks, wiring issues |
| P0171 | System Too Lean (Bank 1) | Vacuum leaks, faulty oxygen sensor, low fuel pressure, MAF sensor issues |
| P0300 | Random/Multiple Cylinder Misfire Detected | Faulty spark plugs, ignition coils, fuel injectors, vacuum leaks, low compression |
| P0420 | Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold | Faulty catalytic converter, oxygen sensor issues, exhaust leaks |
| P0442 | Evaporative Emission Control System Leak | Loose or faulty gas cap, damaged EVAP lines, faulty purge valve |
| P0741 | Torque Converter Clutch Circuit Performance | Faulty torque converter, solenoid issues, transmission problems |
| P0113 | Intake Air Temperature Sensor Circuit High Input | Faulty IAT sensor, wiring issues, connector problems |
7. Advanced OBD2 Functions and Capabilities
Modern OBD2 scanners offer advanced functions beyond basic code reading. These capabilities can provide deeper insights into your vehicle’s performance and health.
These advanced functions are valuable for diagnosing complex issues and optimizing vehicle performance. Understanding these capabilities can help you make the most of your OBD2 scanner.
7.1 Live Data Streaming
Live data streaming allows you to monitor real-time parameters such as engine RPM, coolant temperature, and oxygen sensor readings. This data can help you identify intermittent issues and diagnose performance problems.
 Live Data Streaming
Live Data Streaming
Monitoring live data can provide valuable insights into how your vehicle is performing under different conditions. This can help you pinpoint the exact moment when a problem occurs.
7.2 Freeze Frame Data
Freeze frame data captures a snapshot of the vehicle’s operating conditions at the moment a diagnostic trouble code is triggered. This information can help you recreate the conditions that led to the fault.
Freeze frame data includes parameters such as engine speed, load, and fuel trim. This information can be invaluable for diagnosing elusive problems that are difficult to reproduce.
7.3 Oxygen Sensor Testing
OBD2 scanners can perform oxygen sensor tests to ensure they are functioning correctly. Faulty oxygen sensors can cause poor fuel economy and emissions issues.
Oxygen sensor tests can measure the sensor’s response time and voltage output. This can help you determine if the sensor is providing accurate readings and functioning within the specified range.
7.4 EVAP System Testing
EVAP (Evaporative Emission Control System) testing helps identify leaks in the fuel vapor recovery system. These leaks can cause emissions issues and trigger the check engine light.
EVAP system tests can pressurize the system and monitor for leaks. This can help you identify faulty components such as gas caps, purge valves, and vapor lines.
7.5 I/M Readiness Monitoring
I/M (Inspection/Maintenance) readiness monitoring checks whether the vehicle’s emission control systems are ready for state emissions testing. This can help you avoid failing an emissions test.
I/M readiness monitors check the status of various emission control systems, such as the catalytic converter, oxygen sensors, and EVAP system. This ensures that your vehicle meets the required emissions standards.
8. Choosing the Right OBD2 Scanner for Your Needs
Selecting the right OBD2 scanner depends on your specific needs and budget. Consider the features, compatibility, and ease of use when making your decision.
This section provides guidance on choosing the best OBD2 scanner for your needs. Whether you’re a DIY enthusiast or a professional mechanic, understanding the different types of scanners will help you make an informed decision.
8.1 Basic OBD2 Scanners
Basic OBD2 scanners are affordable and easy to use. They typically offer code reading and clearing capabilities, making them suitable for simple diagnostics.
 Basic OBD2 Scanner
Basic OBD2 Scanner
These scanners are ideal for vehicle owners who want to quickly diagnose and clear common trouble codes. They are a cost-effective solution for basic troubleshooting.
8.2 Mid-Range OBD2 Scanners
Mid-range OBD2 scanners offer additional features such as live data streaming, freeze frame data, and enhanced code definitions. They provide more detailed information for diagnosing complex issues.
These scanners are suitable for DIY enthusiasts and amateur mechanics who need more advanced diagnostic capabilities. They offer a good balance of features and affordability.
8.3 Professional-Grade OBD2 Scanners
Professional-grade OBD2 scanners offer advanced functions such as bi-directional control, advanced sensor testing, and access to manufacturer-specific codes. They are designed for professional mechanics and advanced users.
 Professional OBD2 Scanner
Professional OBD2 Scanner
These scanners are equipped with the latest technology and offer comprehensive diagnostic capabilities. They are an essential tool for professional automotive repair shops.
8.4 Considerations for Compatibility
Ensure that the OBD2 scanner is compatible with your vehicle’s make, model, and year. Some scanners may not support all vehicles or protocols.
Check the scanner’s compatibility list before making a purchase to ensure that it will work with your vehicle. Some scanners may require software updates to support newer vehicles.
8.5 Budget and Features
Balance your budget with the features you need. Consider whether you need advanced functions such as live data streaming, bi-directional control, or access to manufacturer-specific codes.
Determine your diagnostic needs and prioritize the features that are most important to you. This will help you find an OBD2 scanner that meets your requirements without exceeding your budget.
9. OBD2 and Vehicle Maintenance: Best Practices
Regularly using an OBD2 scanner can help you proactively maintain your vehicle and prevent costly repairs. Here are some best practices for using OBD2 in vehicle maintenance.
This section outlines how to integrate OBD2 scanning into your regular vehicle maintenance routine. By following these best practices, you can keep your vehicle running smoothly and efficiently.
9.1 Regular Code Scanning
Scan your vehicle for diagnostic trouble codes regularly, even if the check engine light is not on. This can help you identify potential issues before they become serious.
Regular code scanning can detect pending codes, which indicate that a problem is developing. Addressing these issues early can prevent more significant damage and costly repairs.
9.2 Monitoring Live Data
Monitor live data parameters such as engine RPM, coolant temperature, and oxygen sensor readings to assess your vehicle’s performance. This can help you identify abnormalities and potential problems.
Monitoring live data can provide valuable insights into how your vehicle is performing under different conditions. This can help you identify issues that may not trigger a diagnostic trouble code.
9.3 Addressing Issues Promptly
Address any diagnostic trouble codes or performance issues promptly. Ignoring these problems can lead to more significant damage and costly repairs.
Promptly addressing issues can prevent them from escalating and causing further damage. This can save you time and money in the long run.
9.4 Keeping Records
Keep a record of all diagnostic trouble codes, repairs, and maintenance performed on your vehicle. This can help you track your vehicle’s history and identify recurring issues.
Keeping detailed records can help you and your mechanic understand your vehicle’s maintenance history. This can assist in diagnosing and resolving complex issues.
9.5 Staying Updated
Stay updated on the latest OBD2 technology and diagnostic techniques. This can help you make the most of your OBD2 scanner and improve your diagnostic skills.
Staying informed about the latest advancements in OBD2 technology can help you stay ahead of potential problems. This can ensure that you are using the most effective diagnostic methods.
10. The Future of OBD2 Technology
OBD2 technology is continuously evolving, with new features and capabilities being developed to meet the demands of modern vehicles.
This section explores the future trends and advancements in OBD2 technology. Understanding these trends can help you prepare for the next generation of automotive diagnostics.
10.1 Enhanced Diagnostics
Future OBD2 systems will offer enhanced diagnostic capabilities, including more detailed data and advanced troubleshooting tools. This will enable more accurate and efficient vehicle diagnostics.
Enhanced diagnostics will provide mechanics with more comprehensive information about vehicle performance. This will help them diagnose and resolve complex issues more effectively.
10.2 Remote Diagnostics
Remote diagnostics will allow mechanics to diagnose and troubleshoot vehicles remotely, using telematics and cloud-based data. This can improve efficiency and reduce downtime.
Remote diagnostics can enable mechanics to diagnose problems without physically inspecting the vehicle. This can save time and money for both the mechanic and the vehicle owner.
10.3 Integration with Telematics
OBD2 systems will increasingly integrate with telematics systems, providing real-time data and insights for vehicle tracking, performance monitoring, and predictive maintenance.
Integration with telematics systems can provide vehicle owners with valuable information about their vehicle’s health and performance. This can help them make informed decisions about maintenance and repairs.
10.4 Cybersecurity Measures
Future OBD2 systems will incorporate advanced cybersecurity measures to protect against hacking and unauthorized access. This is essential to ensure the safety and security of modern vehicles.
Cybersecurity measures are crucial to prevent malicious actors from accessing and manipulating vehicle systems. This can protect against theft, damage, and other security threats.
10.5 Standardized Data Formats
Efforts are underway to standardize OBD2 data formats, making it easier for different diagnostic tools and systems to communicate and share information. This will improve compatibility and interoperability.
Standardized data formats will simplify the process of accessing and analyzing vehicle data. This will benefit mechanics, vehicle owners, and other stakeholders in the automotive industry.
11. Call to Action: Get Expert Assistance from OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN
While an HDMI to OBD2 pinout is not a viable option, OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN offers a range of solutions and expert guidance to meet your automotive diagnostic needs. Don’t let complex car issues keep you guessing.
Contact us today via WhatsApp at +1 (641) 206-8880, or visit our website, OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN, for personalized support and services. Our team of experienced technicians is ready to help you diagnose and resolve any vehicle issue. We provide comprehensive guidance, support, and services to ensure your automotive diagnostic needs are met effectively. Located at 123 Main Street, Los Angeles, CA 90001, United States, we are committed to providing top-notch service and support to our customers. Get in touch now and let us help you get back on the road with confidence.
