The Slingshot Obd2 Port location is typically under the steering column, providing easy access for diagnostics. OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN offers resources and tools to help you effectively utilize this port for vehicle maintenance. By using an OBD2 scanner, you gain access to crucial data such as engine codes, live sensor readings, and performance metrics. This knowledge empowers you with the insights needed for efficient vehicle diagnostics and maintenance, enhancing the reliability and performance of your slingshot.
Contents
- 1. What is the Slingshot OBD2 Port?
- 1.1. Key Features of the OBD2 Port
- 1.2. Benefits of Using the OBD2 Port
- 2. Where is the OBD2 Port Located on a Polaris Slingshot?
- 2.1. Step-by-Step Guide to Finding the OBD2 Port
- 2.2. Visual Aids and Diagrams
- 3. How to Use an OBD2 Scanner with Your Slingshot
- 3.1. Step-by-Step Guide to Using an OBD2 Scanner
- 3.2. Interpreting Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
- 3.3. Common Mistakes to Avoid When Using an OBD2 Scanner
- 4. What Kind of OBD2 Scanner Should You Use for a Slingshot?
- 4.1. Basic OBD2 Scanners
- 4.2. Advanced OBD2 Scanners
- 4.3. Wireless OBD2 Adapters
- 4.4. Recommended OBD2 Scanners for Slingshot
- 5. Common Issues Diagnosed Using the Slingshot OBD2 Port
- 5.1. Engine Misfires
- 5.2. Oxygen Sensor Issues
- 5.3. Catalytic Converter Problems
- 5.4. Fuel System Issues
- 5.5. ABS and Traction Control Issues
- 6. Advantages of Regular OBD2 Scanning for Your Slingshot
- 6.1. Early Problem Detection
- 6.2. Cost Savings
- 6.3. Improved Vehicle Performance
- 6.4. Preventive Maintenance
- 7. OBD2 Port and Polaris Slingshot Performance Tuning
- 7.1. ECU Tuning
- 7.2. Performance Monitoring
- 7.3. Data Logging
- 8. Advanced Diagnostic Procedures Using Slingshot OBD2 Port
- 8.1. Performing Sensor Tests
- 8.2. Reading Freeze Frame Data
- 8.3. Using Bidirectional Control
- 8.4. Retrieving Enhanced Codes
- 9. Safety Precautions When Working with the Slingshot OBD2 Port
- 9.1. Disconnect the Battery (If Necessary)
- 9.2. Use Proper Grounding Techniques
- 9.3. Follow the Scanner’s Instructions
- 9.4. Wear Appropriate Safety Gear
- 10. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About the Slingshot OBD2 Port
- 10.1. What is an OBD2 Scanner?
- 10.2. Why Should I Use an OBD2 Scanner on My Slingshot?
- 10.3. Where is the OBD2 Port Located on a Slingshot?
- 10.4. Can I Damage My Slingshot by Using an OBD2 Scanner?
- 10.5. What Do the Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) Mean?
- 10.6. How Often Should I Scan My Slingshot with an OBD2 Scanner?
- 10.7. Can I Clear the Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) Myself?
- 10.8. What if I Don’t Understand the DTCs?
- 10.9. Are Wireless OBD2 Scanners Reliable?
- 10.10. Can I Use an OBD2 Scanner to Improve My Slingshot’s Performance?
1. What is the Slingshot OBD2 Port?
The slingshot OBD2 port, or On-Board Diagnostics II port, is a standardized interface in Polaris Slingshot vehicles that allows access to the vehicle’s computer system for diagnostic and monitoring purposes. This port enables mechanics and vehicle owners to retrieve diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs), monitor live data, and assess the overall health of the engine and other systems.
According to the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), all cars and light trucks manufactured after 1996 are mandated to have an OBD2 port. This regulation was implemented to standardize vehicle diagnostics, making it easier to identify and address issues related to emissions and engine performance.
1.1. Key Features of the OBD2 Port
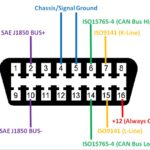
The OBD2 port is a 16-pin connector, typically trapezoidal, found inside the car’s cabin. The Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE) standardized its shape and function to ensure compatibility across different vehicle manufacturers.
- Standardized Connector: Ensures that any OBD2 scanner can connect to any vehicle equipped with an OBD2 port.
- Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs): Provides access to codes that indicate specific problems with the vehicle’s systems.
- Live Data Monitoring: Allows real-time monitoring of various engine parameters, such as RPM, temperature, and sensor readings.
- Emission-Related Diagnostics: Primarily designed to monitor and diagnose emission-related issues to comply with environmental regulations.
1.2. Benefits of Using the OBD2 Port
Using the OBD2 port offers several benefits for vehicle maintenance and diagnostics:
- Early Problem Detection: Identifies potential issues before they escalate into major problems.
- Cost Savings: Reduces the need for expensive diagnostic services at a mechanic.
- Informed Decision-Making: Provides data to make informed decisions about vehicle repairs and maintenance.
- Performance Monitoring: Allows monitoring of the vehicle’s performance to ensure it is running optimally.
2. Where is the OBD2 Port Located on a Polaris Slingshot?
The OBD2 port in a Polaris Slingshot is typically located under the steering column. Specifically, it is often found on the driver’s side, near the center console. Locating the OBD2 port is straightforward, allowing easy access for diagnostic tools.
2.1. Step-by-Step Guide to Finding the OBD2 Port
To locate the OBD2 port on your Polaris Slingshot, follow these steps:
- Locate the Steering Column: Sit in the driver’s seat and identify the steering column.
- Check Underneath the Column: Reach under the steering column towards the center console.
- Feel for the Connector: Feel for a trapezoidal, 16-pin connector. It is usually exposed and easily accessible.
- Use a Flashlight (if needed): If the area is dark, use a flashlight to get a better view.
- Identify the Port: Once found, you will see the OBD2 port ready for your diagnostic tool.
2.2. Visual Aids and Diagrams
To help you find the OBD2 port, consider using visual aids:
- Online Images: Search online for images of the Polaris Slingshot OBD2 port location.
- Vehicle Manual: Consult your vehicle’s manual, which usually includes a diagram showing the location of the OBD2 port.
- Forums and Communities: Check online forums and communities for specific advice and images from other Slingshot owners.
3. How to Use an OBD2 Scanner with Your Slingshot
Using an OBD2 scanner with your Polaris Slingshot is a straightforward process. An OBD2 scanner can read and clear engine codes on all year Slingshots from 2015 to current year. By following the steps below, you can retrieve valuable diagnostic information and maintain your vehicle effectively.
3.1. Step-by-Step Guide to Using an OBD2 Scanner
- Purchase an OBD2 Scanner: Buy a compatible OBD2 scanner. Options range from basic code readers to advanced diagnostic tools.
- Locate the OBD2 Port: Find the OBD2 port under the steering column, as described in Section 2.
- Plug in the Scanner: Turn off the ignition. Plug the OBD2 scanner into the port. Ensure it is securely connected.
- Turn on the Ignition: Turn the ignition to the “on” position, but do not start the engine.
- Power on the Scanner: The scanner should power on automatically. If not, follow the scanner’s instructions to turn it on.
- Read Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs): Navigate the scanner’s menu to “Read Codes” or a similar option. The scanner will display any stored DTCs.
- Interpret the Codes: Use the scanner’s manual or online resources to understand the meaning of each DTC.
- Clear the Codes (Optional): If you have addressed the issues indicated by the codes, you can clear them by selecting “Clear Codes” in the scanner’s menu.
- Monitor Live Data (Optional): Some scanners allow you to monitor live data, such as engine temperature, RPM, and sensor readings.
- Unplug the Scanner: Once you are finished, turn off the ignition and unplug the scanner.
3.2. Interpreting Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
DTCs are alphanumeric codes that provide information about specific issues detected by the vehicle’s computer system. Understanding these codes is crucial for effective vehicle maintenance.
-
Code Structure: DTCs typically consist of five characters: a letter followed by four numbers.
- The letter indicates the system:
- P: Powertrain (engine, transmission)
- B: Body (airbags, power windows)
- C: Chassis (ABS, suspension)
- U: Network (communication systems)
- The first number indicates whether the code is generic (0) or manufacturer-specific (1).
- The remaining three numbers specify the exact fault.
- The letter indicates the system:
-
Common DTCs: Some common DTCs include:
- P0300: Random/Multiple Cylinder Misfire Detected
- P0171: System Too Lean (Bank 1)
- P0420: Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold (Bank 1)
-
Resources for Interpretation: Use the following resources to interpret DTCs:
- Scanner’s Manual: Many scanners come with a manual that lists common DTCs and their meanings.
- Online Databases: Websites like OBD-Codes.com offer comprehensive databases of DTCs.
- Vehicle-Specific Forums: Online forums dedicated to your vehicle model can provide insights and solutions from other owners.
3.3. Common Mistakes to Avoid When Using an OBD2 Scanner
To ensure accurate and reliable diagnostics, avoid these common mistakes when using an OBD2 scanner:
- Ignoring Codes: Never ignore DTCs. Address them promptly to prevent further damage.
- Clearing Codes Without Addressing the Issue: Clearing codes without fixing the underlying problem will only result in the codes reappearing.
- Using Incompatible Scanners: Ensure that the scanner is compatible with your vehicle’s make and model.
- Misinterpreting Codes: Always verify the meaning of a DTC before taking action.
- Forgetting to Turn Off the Ignition: Always turn off the ignition before plugging or unplugging the scanner to avoid electrical issues.
4. What Kind of OBD2 Scanner Should You Use for a Slingshot?
Choosing the right OBD2 scanner for your Polaris Slingshot depends on your needs and budget. Different scanners offer various features and capabilities, ranging from basic code reading to advanced diagnostics.
4.1. Basic OBD2 Scanners
Basic OBD2 scanners are designed for simple tasks such as reading and clearing diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs). These scanners are typically inexpensive and easy to use, making them suitable for vehicle owners who want to perform basic diagnostics.
-
Features:
- Read DTCs
- Clear DTCs
- Display DTC definitions
-
Pros:
- Affordable
- Easy to use
- Compact and portable
-
Cons:
- Limited functionality
- May not support advanced features like live data monitoring
4.2. Advanced OBD2 Scanners
Advanced OBD2 scanners offer a wider range of features, including live data monitoring, enhanced diagnostics, and the ability to perform specialized tests. These scanners are suitable for experienced mechanics and vehicle owners who require more detailed information about their vehicle’s performance.
-
Features:
- Read and clear DTCs
- Display DTC definitions
- Monitor live data (e.g., RPM, temperature, sensor readings)
- Perform O2 sensor tests
- Reset service lights
-
Pros:
- Comprehensive functionality
- Detailed diagnostic information
- Support for various vehicle systems
-
Cons:
- More expensive
- May require technical knowledge to use effectively
4.3. Wireless OBD2 Adapters
Wireless OBD2 adapters, also known as Bluetooth or Wi-Fi OBD2 scanners, connect to your smartphone or tablet via Bluetooth or Wi-Fi. These adapters work with OBD2 apps to provide diagnostic information and live data monitoring.
-
Features:
- Read and clear DTCs
- Display DTC definitions via app
- Monitor live data via app
- Wireless connectivity
-
Pros:
- Convenient and portable
- Affordable
- User-friendly apps
-
Cons:
- Relies on smartphone or tablet for display
- May require purchasing a compatible OBD2 app
4.4. Recommended OBD2 Scanners for Slingshot
Here are some recommended OBD2 scanners for Polaris Slingshot vehicles:
| Scanner | Type | Features | Price Range |
|---|---|---|---|
| Autel MaxiCOM MK808 | Advanced | Read/Clear DTCs, Live Data, O2 Sensor Test, Service Resets | $200-$300 |
| BlueDriver | Wireless (Bluetooth) | Read/Clear DTCs, Live Data, Vehicle-Specific Reports via App | $100-$120 |
| Innova 3100i | Basic | Read/Clear DTCs, ABS Codes, Battery Voltage | $50-$70 |
| DDMWorks | Basic | Read/Clear DTCs, Displays live data from the ECM | $100-$150 |
5. Common Issues Diagnosed Using the Slingshot OBD2 Port
The OBD2 port in your Polaris Slingshot can help diagnose a wide range of issues, from minor sensor malfunctions to more serious engine problems.
5.1. Engine Misfires
Engine misfires occur when one or more cylinders in the engine fail to fire properly. This can result in rough idling, reduced power, and poor fuel economy.
- Common DTCs: P0300 (Random/Multiple Cylinder Misfire Detected), P0301-P0306 (Cylinder Specific Misfire Detected)
- Possible Causes: Faulty spark plugs, ignition coils, fuel injectors, vacuum leaks, low compression
- How to Diagnose: Use an OBD2 scanner to read DTCs and identify the affected cylinder(s). Check spark plugs, ignition coils, and fuel injectors for proper function.
5.2. Oxygen Sensor Issues
Oxygen sensors monitor the amount of oxygen in the exhaust gases to ensure the engine is running efficiently. Faulty oxygen sensors can lead to poor fuel economy, increased emissions, and engine performance issues.
- Common DTCs: P0130-P0167 (Oxygen Sensor Circuit Malfunction), P0171 (System Too Lean), P0174 (System Too Rich)
- Possible Causes: Damaged oxygen sensors, exhaust leaks, vacuum leaks, faulty mass airflow (MAF) sensor
- How to Diagnose: Use an OBD2 scanner to read DTCs and monitor oxygen sensor readings. Check for exhaust leaks and vacuum leaks. Test the oxygen sensors for proper function.
5.3. Catalytic Converter Problems
The catalytic converter reduces harmful emissions by converting pollutants into less harmful substances. A failing catalytic converter can result in increased emissions, poor engine performance, and eventual engine damage.
- Common DTCs: P0420 (Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold)
- Possible Causes: Damaged catalytic converter, exhaust leaks, faulty oxygen sensors, engine misfires
- How to Diagnose: Use an OBD2 scanner to read DTCs. Inspect the catalytic converter for damage and exhaust leaks. Check oxygen sensor readings.
5.4. Fuel System Issues
Fuel system issues can cause a variety of problems, including poor fuel economy, rough idling, and engine performance issues.
- Common DTCs: P0087 (Fuel Rail/System Pressure Too Low), P0171 (System Too Lean), P0174 (System Too Rich)
- Possible Causes: Faulty fuel pump, fuel filter, fuel injectors, fuel pressure regulator
- How to Diagnose: Use an OBD2 scanner to read DTCs. Check fuel pressure and fuel injector function. Inspect the fuel filter for clogs.
5.5. ABS and Traction Control Issues
ABS (Anti-lock Braking System) and traction control issues can affect the vehicle’s braking and handling capabilities.
- Common DTCs: C0031 (Left Front Wheel Speed Sensor Circuit Malfunction), C0034 (Right Front Wheel Speed Sensor Circuit Malfunction)
- Possible Causes: Faulty wheel speed sensors, damaged ABS module, hydraulic issues
- How to Diagnose: Use an OBD2 scanner to read DTCs. Check wheel speed sensors for proper function. Inspect the ABS module for damage.
6. Advantages of Regular OBD2 Scanning for Your Slingshot
Regular use of an OBD2 scanner on your Polaris Slingshot offers several advantages, including early problem detection, cost savings, and improved vehicle performance.
6.1. Early Problem Detection
Regular OBD2 scanning allows you to identify potential issues before they escalate into major problems. By monitoring DTCs and live data, you can detect minor malfunctions and address them promptly, preventing further damage.
6.2. Cost Savings
By identifying and addressing issues early, you can avoid costly repairs and maintenance. Regular OBD2 scanning reduces the need for expensive diagnostic services at a mechanic, saving you money in the long run.
6.3. Improved Vehicle Performance
Monitoring live data and addressing DTCs helps ensure that your vehicle is running optimally. Regular OBD2 scanning allows you to maintain peak performance, improve fuel economy, and extend the lifespan of your Slingshot.
6.4. Preventive Maintenance
OBD2 scanning supports preventive maintenance by providing insights into the health of various vehicle systems. By addressing potential issues before they become critical, you can prevent breakdowns and ensure the reliability of your Slingshot.
7. OBD2 Port and Polaris Slingshot Performance Tuning
The OBD2 port can also be used for performance tuning and customization. By accessing the vehicle’s computer system, you can modify various parameters to improve performance and enhance the driving experience.
7.1. ECU Tuning
ECU (Engine Control Unit) tuning involves modifying the software that controls the engine’s operation. This can be done to increase horsepower, improve throttle response, and optimize fuel economy.
-
Benefits:
- Increased horsepower and torque
- Improved throttle response
- Optimized fuel economy
-
Considerations:
- Requires specialized knowledge and equipment
- May void the vehicle’s warranty
- Can affect emissions compliance
7.2. Performance Monitoring
The OBD2 port allows you to monitor various performance parameters in real-time, such as:
- Engine RPM
- Vehicle speed
- Intake air temperature
- Manifold pressure
- Throttle position
- Oxygen sensor voltage
This information can be used to assess the vehicle’s performance, identify potential issues, and fine-tune the engine for optimal results.
7.3. Data Logging
Data logging involves recording performance data over time. This data can be analyzed to identify trends, diagnose problems, and evaluate the effectiveness of performance modifications.
-
Benefits:
- Identify performance bottlenecks
- Monitor the effects of tuning modifications
- Diagnose intermittent issues
8. Advanced Diagnostic Procedures Using Slingshot OBD2 Port
For experienced mechanics and advanced users, the OBD2 port can be used for more sophisticated diagnostic procedures.
8.1. Performing Sensor Tests
Advanced OBD2 scanners allow you to perform specific tests on various sensors to verify their functionality. This can include:
- Oxygen sensor tests
- Throttle position sensor tests
- Mass airflow (MAF) sensor tests
- Coolant temperature sensor tests
8.2. Reading Freeze Frame Data
Freeze frame data captures a snapshot of the vehicle’s operating conditions at the moment a DTC was triggered. This information can provide valuable clues about the cause of the problem.
-
Benefits:
- Identify the conditions that triggered the DTC
- Troubleshoot intermittent issues
- Understand the context of the fault
8.3. Using Bidirectional Control
Bidirectional control allows you to send commands to the vehicle’s computer system to activate specific components and perform tests. This can include:
- Activating fuel injectors
- Controlling the cooling fan
- Operating the throttle
8.4. Retrieving Enhanced Codes
Some advanced OBD2 scanners can retrieve enhanced codes that are specific to the vehicle manufacturer. These codes provide more detailed information about the fault and can help narrow down the possible causes.
9. Safety Precautions When Working with the Slingshot OBD2 Port
When working with the OBD2 port, it is important to follow safety precautions to avoid damaging the vehicle or causing personal injury.
9.1. Disconnect the Battery (If Necessary)
In some cases, it may be necessary to disconnect the vehicle’s battery before performing certain diagnostic procedures. This can prevent electrical damage and ensure your safety.
9.2. Use Proper Grounding Techniques
When working with electrical components, it is important to use proper grounding techniques to avoid electrical shock.
9.3. Follow the Scanner’s Instructions
Always follow the instructions provided with the OBD2 scanner to ensure proper usage and avoid damaging the vehicle’s computer system.
9.4. Wear Appropriate Safety Gear
Wear appropriate safety gear, such as gloves and eye protection, to protect yourself from potential hazards.
10. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About the Slingshot OBD2 Port
Here are some frequently asked questions about the Polaris Slingshot OBD2 port:
10.1. What is an OBD2 Scanner?
An OBD2 scanner is a diagnostic tool used to read and interpret data from a vehicle’s onboard computer system. It helps identify issues by reading diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) and monitoring live data.
10.2. Why Should I Use an OBD2 Scanner on My Slingshot?
Using an OBD2 scanner helps you diagnose and address vehicle issues early, potentially saving on costly repairs. It also helps monitor vehicle performance and ensure it runs efficiently.
10.3. Where is the OBD2 Port Located on a Slingshot?
The OBD2 port on a Polaris Slingshot is typically located under the steering column, near the center console on the driver’s side.
10.4. Can I Damage My Slingshot by Using an OBD2 Scanner?
When used correctly, an OBD2 scanner will not damage your Slingshot. However, it’s crucial to follow the scanner’s instructions and safety precautions.
10.5. What Do the Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) Mean?
Diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) are alphanumeric codes that indicate specific issues detected by the vehicle’s computer system. Each code corresponds to a specific problem, such as engine misfires or sensor malfunctions.
10.6. How Often Should I Scan My Slingshot with an OBD2 Scanner?
You should scan your Slingshot whenever you notice any performance issues or warning lights. Regular scanning, even without apparent problems, can help detect potential issues early.
10.7. Can I Clear the Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) Myself?
Yes, you can clear DTCs using an OBD2 scanner. However, it’s important to address the underlying issue causing the code to appear. Clearing the code without fixing the problem will likely result in its reappearance.
10.8. What if I Don’t Understand the DTCs?
If you are unsure about the meaning of DTCs, consult your scanner’s manual, online databases, or a professional mechanic for interpretation and guidance.
10.9. Are Wireless OBD2 Scanners Reliable?
Wireless OBD2 scanners can be reliable, but their performance depends on the quality of the adapter and the app used. Ensure you choose reputable brands and read reviews before purchasing.
10.10. Can I Use an OBD2 Scanner to Improve My Slingshot’s Performance?
Yes, an OBD2 scanner can help improve performance by monitoring engine parameters and identifying issues affecting efficiency. Additionally, some scanners support ECU tuning for performance enhancements.
_6446-wm.jpg)
Understanding where the slingshot OBDII port is located and how to use an OBD2 scanner can greatly enhance your vehicle’s maintenance and performance. Whether you’re a seasoned mechanic or a new Slingshot owner, the insights gained from regular OBD2 scanning can save you time and money.
If you’re facing challenges interpreting OBD2 data or need assistance with repairs, don’t hesitate to reach out. Contact us at OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN. Our experts are here to help you navigate the complexities of vehicle diagnostics and ensure your Slingshot runs smoothly. Visit us at 123 Main Street, Los Angeles, CA 90001, United States. You can also connect with us via WhatsApp at +1 (641) 206-8880 for immediate support and guidance.