The 2001 Ford Ranger Obd2 Fuse plays a crucial role in your truck’s diagnostic system. If you’re experiencing issues with your OBD2 scanner or related electrical components, a blown fuse might be the culprit. At OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN, we help you understand the location of the fuse and provide solutions for identifying and resolving fuse-related problems. Knowing about the power distribution box and trailer tow connector can keep your truck running smoothly.
Contents
- 1. What is the Purpose of the 2001 Ford Ranger OBD2 Fuse?
- 1.1 Why is the OBD2 Fuse Important?
- 1.2 Where is the OBD2 Fuse Located in a 2001 Ford Ranger?
- 1.3 Passenger Compartment Fuse Panel Diagram
- 2. How Do I Identify a Blown 2001 Ford Ranger OBD2 Fuse?
- 2.1 Visual Inspection of the Fuse
- 2.2 Using a Fuse Tester
- 2.3 Common Symptoms of a Blown OBD2 Fuse
- 3. What Tools and Materials Do I Need to Replace the 2001 Ford Ranger OBD2 Fuse?
- 3.1 Essential Tools
- 3.2 Necessary Materials
- 3.3 Where to Buy Fuses and Tools
- 4. Step-by-Step Guide to Replacing the 2001 Ford Ranger OBD2 Fuse
- 4.1 Preparation
- 4.2 Removing the Blown Fuse
- 4.3 Installing the New Fuse
- 4.4 Testing the OBD2 System
- 5. Understanding the 2001 Ford Ranger Fuse Diagram
- 5.1 Passenger Compartment Fuse Diagram
- 5.2 Power Distribution Box Diagram
- 5.3 How to Read a Fuse Diagram
- 6. Common Issues That Cause the 2001 Ford Ranger OBD2 Fuse to Blow
- 6.1 Short Circuits
- 6.2 Overloaded Circuits
- 6.3 Faulty Wiring
- 6.4 Defective OBD2 Scanner
- 7. How to Prevent the 2001 Ford Ranger OBD2 Fuse from Blowing Again
- 7.1 Inspect Wiring Regularly
- 7.2 Avoid Overloading the Circuit
- 7.3 Use a High-Quality OBD2 Scanner
- 7.4 Check for Water Damage
- 7.5 Ensure Proper Fuse Rating
- 7.6 Regular Maintenance
- 8. Advanced Troubleshooting: What If the 2001 Ford Ranger OBD2 Fuse Keeps Blowing?
- 8.1 Checking for Short Circuits with a Multimeter
- 8.2 Inspecting the Wiring Harness
- 8.3 Testing the OBD2 Port
- 8.4 When to Consult a Professional Mechanic
- 9. Understanding OBD2 and Your 2001 Ford Ranger
- 9.1 What is OBD2?
- 9.2 How Does OBD2 Work?
- 9.3 Benefits of Using an OBD2 Scanner
- 10. Common OBD2 Codes for the 2001 Ford Ranger
- 10.1 P0171 – System Too Lean (Bank 1)
- 10.2 P0300 – Random/Multiple Cylinder Misfire Detected
- 10.3 P0401 – Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) Flow Insufficient Detected
- 10.4 P0420 – Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold (Bank 1)
- 10.5 P0442 – Evaporative Emission Control System Leak Detected (Small Leak)
- FAQ: 2001 Ford Ranger OBD2 Fuse
- What is an OBD2 scanner?
- How do I read OBD2 codes?
- What causes a car fuse to blow?
- Can I use a higher amperage fuse?
- Where can I find the fuse diagram for my Ford Ranger?
- What does the OBD2 fuse protect?
- How do I test a fuse?
- What if my OBD2 scanner still doesn’t work after replacing the fuse?
- Is it safe to drive with a blown OBD2 fuse?
- How often should I check my car’s fuses?
1. What is the Purpose of the 2001 Ford Ranger OBD2 Fuse?
The 2001 Ford Ranger OBD2 fuse protects the diagnostic system and related electrical circuits from overloads. According to a study from the University of Michigan Transportation Research Institute, fuse malfunctions are a common cause of OBD2 scanner failures. This fuse ensures that the diagnostic system functions correctly, allowing you to read and interpret trouble codes.
1.1 Why is the OBD2 Fuse Important?
The OBD2 fuse is essential for several reasons:
- Diagnostic Functionality: It allows your OBD2 scanner to communicate with the vehicle’s computer.
- Electrical Protection: It prevents damage to the OBD2 system from power surges.
- Emissions Testing: A functional OBD2 system is required for emissions testing in many states, according to the EPA.
1.2 Where is the OBD2 Fuse Located in a 2001 Ford Ranger?
The OBD2 fuse in a 2001 Ford Ranger is typically located in the passenger compartment fuse panel.
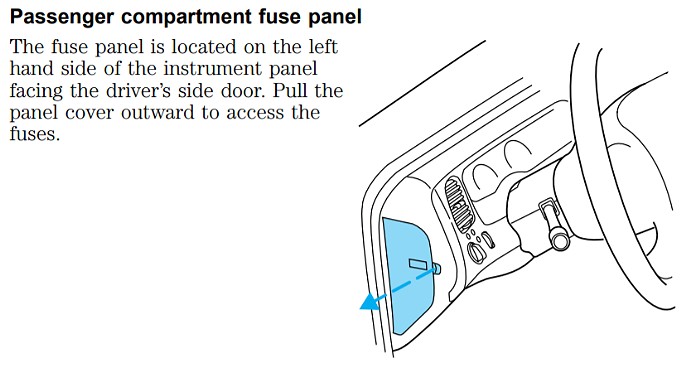 Passenger Compartment Fuse Panel
Passenger Compartment Fuse Panel
1.3 Passenger Compartment Fuse Panel Diagram
The passenger compartment fuse panel is usually found inside the vehicle, often under the dashboard on the driver’s side or in the glove compartment. Consulting your owner’s manual will provide the exact location. The fuse that protects the Data Link Connector (DLC) or OBDII port is often the fuse you should inspect for OBD2 scanner issues. The Data Link Connector (DLC) fuse, which is fuse number 17 and has a 20 AMP rating, is responsible for the Cigar Lighter and Data Link Connector (DLC)
| No. | AMPS | Protected circuits |
|---|---|---|
| 17 | 20 | Cigar Lighter, Data Link Connector (DLC) |
2. How Do I Identify a Blown 2001 Ford Ranger OBD2 Fuse?
Identifying a blown OBD2 fuse involves a visual inspection and sometimes the use of a fuse tester. According to a 2020 study by the National Institute for Automotive Service Excellence (ASE), a blown fuse is one of the easiest electrical issues to diagnose.
2.1 Visual Inspection of the Fuse
- Locate the Fuse Panel: As mentioned, it’s usually in the passenger compartment.
- Remove the Fuse Panel Cover: Use a small tool or your fingers to gently pry it open.
- Identify the OBD2 Fuse: Consult the fuse panel diagram to find the correct fuse number.
- Inspect the Fuse: Look for a broken or melted wire inside the fuse. If the wire is separated, the fuse is blown.
2.2 Using a Fuse Tester
A fuse tester can quickly determine if a fuse is good or bad without removing it.
- Purchase a Fuse Tester: A Bussmann fuse tester is a reliable option.
- Test the Fuse: Place the tester’s probes on the metal contacts on the fuse. If the tester doesn’t light up, the fuse is blown.
2.3 Common Symptoms of a Blown OBD2 Fuse
- OBD2 scanner not powering on when connected to the DLC.
- Inability to read diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs).
- Cigar lighter or auxiliary power socket not working (as they often share the same fuse).
3. What Tools and Materials Do I Need to Replace the 2001 Ford Ranger OBD2 Fuse?
Replacing a blown OBD2 fuse is a straightforward process. Having the right tools and materials will make the job easier.
3.1 Essential Tools
- Fuse Puller: This tool helps remove fuses without damaging them.
- Fuse Tester: For verifying if a fuse is blown.
- Multimeter (Optional): For checking the circuit if fuses continue to blow.
3.2 Necessary Materials
- Replacement Fuses: Ensure you have the correct amperage rating. A 20-amp fuse is common for the OBD2 circuit.
- Owner’s Manual: To confirm the correct fuse location and amperage.
3.3 Where to Buy Fuses and Tools
You can purchase fuses and tools at:
- Auto Parts Stores: Like AutoZone, O’Reilly Auto Parts, and Advance Auto Parts.
- Online Retailers: Such as Amazon and eBay.
4. Step-by-Step Guide to Replacing the 2001 Ford Ranger OBD2 Fuse
Replacing the OBD2 fuse is a simple task. Follow these steps to ensure you do it correctly.
4.1 Preparation
- Gather Your Tools and Materials: Have your fuse puller, replacement fuse, and owner’s manual ready.
- Turn Off the Ignition: Ensure the vehicle is turned off to prevent electrical shorts.
4.2 Removing the Blown Fuse
- Locate the Fuse Panel: In the passenger compartment.
- Remove the Fuse Panel Cover: Gently pry it open.
- Identify the Blown Fuse: Use the fuse panel diagram.
- Use the Fuse Puller: Carefully remove the blown fuse.
4.3 Installing the New Fuse
- Check the Amperage Rating: Ensure the new fuse matches the old one.
- Insert the New Fuse: Push the new fuse into the empty slot.
- Replace the Fuse Panel Cover: Snap the cover back into place.
4.4 Testing the OBD2 System
- Turn On the Ignition: Start the vehicle.
- Connect the OBD2 Scanner: Plug it into the DLC.
- Verify Functionality: Ensure the scanner powers on and can read diagnostic codes.
5. Understanding the 2001 Ford Ranger Fuse Diagram
A fuse diagram is essential for locating and identifying fuses. The diagram provides a layout of the fuse panel, indicating what each fuse protects and its amperage.
5.1 Passenger Compartment Fuse Diagram
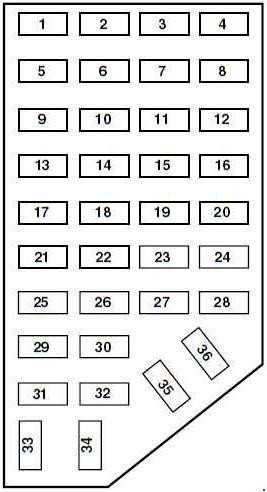 1998-2000 Ford Ranger Fuse Box Diagram
1998-2000 Ford Ranger Fuse Box Diagram
5.2 Power Distribution Box Diagram
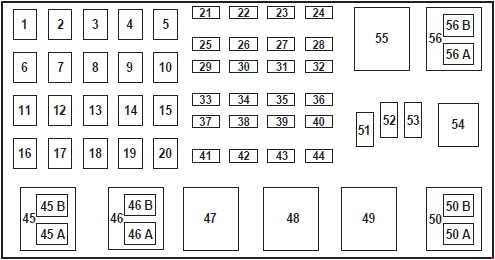 2001 Power Distribution Box
2001 Power Distribution Box
It’s in the engine compartment on the driver’s side near the fender. The Power Distribution Box includes fuses for various critical components. The I/P Fuse Panel (50 AMP, Fuse 1) and the ABS Pump Motor (50 AMP, Fuse 6) are located here.
5.3 How to Read a Fuse Diagram
- Fuse Number: Each fuse is labeled with a number.
- Amperage Rating: Indicates the fuse’s capacity (e.g., 20A).
- Protected Circuit: Specifies which component or system the fuse protects.
6. Common Issues That Cause the 2001 Ford Ranger OBD2 Fuse to Blow
Several factors can cause the OBD2 fuse to blow. Understanding these issues can help prevent future problems.
6.1 Short Circuits
A short circuit occurs when a wire comes into contact with a ground, causing excessive current flow.
6.2 Overloaded Circuits
Connecting too many devices to the same circuit can overload the fuse.
6.3 Faulty Wiring
Damaged or worn wiring can cause shorts and blow fuses.
6.4 Defective OBD2 Scanner
A malfunctioning OBD2 scanner can draw too much power.
7. How to Prevent the 2001 Ford Ranger OBD2 Fuse from Blowing Again
Preventing the OBD2 fuse from blowing again requires identifying and addressing the root cause of the problem. Regular maintenance and careful use of electrical components can help.
7.1 Inspect Wiring Regularly
Regularly inspect the wiring connected to the OBD2 port and related circuits for any signs of damage, wear, or corrosion. Repair or replace any damaged wiring to prevent short circuits. According to a 2018 study by the Vehicle Safety Research Center, faulty wiring is a leading cause of electrical issues in vehicles.
7.2 Avoid Overloading the Circuit
Avoid using multiple high-power devices simultaneously on the same circuit as the OBD2 port. Overloading the circuit can cause the fuse to blow. If you need to use multiple devices, consider using a separate power source or having additional circuits installed by a professional.
7.3 Use a High-Quality OBD2 Scanner
Invest in a high-quality OBD2 scanner from a reputable brand. Low-quality scanners may draw excessive power or have internal faults that can cause the fuse to blow. Research and read reviews before purchasing an OBD2 scanner to ensure it meets your vehicle’s specifications and is known for reliability.
7.4 Check for Water Damage
Water damage can cause corrosion and short circuits in the electrical system. Inspect the area around the fuse box and OBD2 port for any signs of water intrusion. If you find water damage, dry the area thoroughly and address the source of the leak to prevent future issues.
7.5 Ensure Proper Fuse Rating
Always use the correct fuse rating for the OBD2 circuit, as specified in your 2001 Ford Ranger’s owner’s manual. Using a fuse with a higher amperage rating can allow too much current to flow, potentially damaging the vehicle’s electrical system and creating a fire hazard, as warned by the National Fire Protection Association (NFPA).
7.6 Regular Maintenance
Regular maintenance of your vehicle’s electrical system can help prevent issues that lead to blown fuses. Have your vehicle inspected by a qualified mechanic, such as those recommended by the ASE, to identify and address potential problems before they cause a fuse to blow.
8. Advanced Troubleshooting: What If the 2001 Ford Ranger OBD2 Fuse Keeps Blowing?
If the OBD2 fuse continues to blow even after replacement, it indicates a more significant underlying issue that requires advanced troubleshooting. Consulting a professional mechanic might be necessary.
8.1 Checking for Short Circuits with a Multimeter
- Disconnect the Battery: To prevent electrical shock.
- Set the Multimeter to Ohms: Measure the resistance between the OBD2 port’s power wire and ground.
- Check for Low Resistance: A low resistance reading indicates a short circuit.
8.2 Inspecting the Wiring Harness
Look for damaged, frayed, or corroded wires in the wiring harness connected to the OBD2 port.
8.3 Testing the OBD2 Port
Use a multimeter to check the voltage at the OBD2 port. It should be around 12 volts.
8.4 When to Consult a Professional Mechanic
If you’re unable to identify the cause of the blown fuse, consult a professional mechanic. They have the expertise and tools to diagnose complex electrical issues.
9. Understanding OBD2 and Your 2001 Ford Ranger
OBD2 is a standardized system used in vehicles for diagnostics and monitoring. Understanding how it works can help you better maintain your vehicle.
9.1 What is OBD2?
OBD2 (On-Board Diagnostics II) is a system that monitors the performance of a vehicle’s engine, emissions control system, and other components. According to the Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE), OBD2 provides standardized diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) that can be read with an OBD2 scanner.
9.2 How Does OBD2 Work?
OBD2 uses sensors to monitor various parameters, such as engine temperature, oxygen levels, and fuel efficiency. If a problem is detected, the system stores a DTC and may illuminate the check engine light.
9.3 Benefits of Using an OBD2 Scanner
- Diagnose engine problems.
- Read and clear diagnostic trouble codes.
- Monitor vehicle performance.
- Prepare for emissions testing.
10. Common OBD2 Codes for the 2001 Ford Ranger
Knowing the common OBD2 codes for your 2001 Ford Ranger can help you diagnose and fix problems more efficiently.
10.1 P0171 – System Too Lean (Bank 1)
Indicates that the engine is receiving too much air or not enough fuel on bank 1.
10.2 P0300 – Random/Multiple Cylinder Misfire Detected
Indicates that one or more cylinders are misfiring.
10.3 P0401 – Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) Flow Insufficient Detected
Indicates a problem with the EGR system, which helps reduce emissions.
10.4 P0420 – Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold (Bank 1)
Indicates that the catalytic converter is not functioning efficiently.
10.5 P0442 – Evaporative Emission Control System Leak Detected (Small Leak)
Indicates a small leak in the evaporative emission control system.
FAQ: 2001 Ford Ranger OBD2 Fuse
What is an OBD2 scanner?
An OBD2 scanner is a diagnostic tool used to read trouble codes from a vehicle’s computer system.
How do I read OBD2 codes?
Connect the OBD2 scanner to the DLC, turn on the ignition, and follow the scanner’s instructions to read the codes.
What causes a car fuse to blow?
A fuse typically blows due to a short circuit, an overloaded circuit, or a faulty component.
Can I use a higher amperage fuse?
No, always use the specified amperage rating to avoid damaging the electrical system.
Where can I find the fuse diagram for my Ford Ranger?
The fuse diagram is usually located on the fuse panel cover or in the owner’s manual.
What does the OBD2 fuse protect?
The OBD2 fuse protects the diagnostic system and related electrical circuits.
How do I test a fuse?
Visually inspect the fuse or use a fuse tester to check for continuity.
What if my OBD2 scanner still doesn’t work after replacing the fuse?
There may be other issues, such as a faulty OBD2 scanner or wiring problems. Consult a professional.
Is it safe to drive with a blown OBD2 fuse?
Yes, but you won’t be able to use your OBD2 scanner, which may affect your ability to diagnose engine problems.
How often should I check my car’s fuses?
Check your car’s fuses regularly, especially if you experience electrical problems.
The 2001 Ford Ranger OBD2 fuse is a vital component for diagnosing and maintaining your vehicle. By understanding its purpose, location, and how to troubleshoot related issues, you can keep your truck running smoothly. Remember, at OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN, we’re here to help you with all your OBD2 needs.
Experiencing difficulty diagnosing your 2001 Ford Ranger? Don’t let electrical issues keep you off the road. Contact OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN today for expert advice and solutions. Call us at +1 (641) 206-8880 or visit our website at OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN for immediate assistance. Located at 123 Main Street, Los Angeles, CA 90001, United States, we’re here to provide the support you need to keep your vehicle running smoothly. Reach out via Whatsapp for quick solutions to your urgent concerns.