The 2002 F150 Obd2 Fuse is crucial for your vehicle’s diagnostic system to function correctly, and knowing its location is essential for troubleshooting. At OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN, we provide comprehensive guides and services to help you identify and resolve automotive issues efficiently. Understanding the location and function of this fuse can save you time and money on repairs.
Contents
- 1. What is the Purpose of the 2002 F150 OBD2 Fuse?
- 2. Where is the OBD2 Fuse Located on a 2002 F150?
- 3. Step-by-Step Guide to Locating the OBD2 Fuse
- 4. Why is the OBD2 Port Not Working Even After Replacing the Fuse?
- 5. How to Diagnose a Blown OBD2 Fuse
- 6. Common Issues That Can Cause the OBD2 Fuse to Blow
- 7. How to Prevent the OBD2 Fuse from Blowing
- 8. How to Replace a Blown OBD2 Fuse in Your 2002 F150
- 9. What to Do If the New Fuse Keeps Blowing
- 10. Understanding OBD2 Scanner Functionality
- 11. Using an OBD2 Scanner to Diagnose Electrical Issues
- 12. How to Properly Maintain Your 2002 F150’s Electrical System
- 13. Where to Find Reliable OBD2 Fuse and Electrical System Information
- 14. The Importance of Using the Correct Fuse for the OBD2 System
- 15. What are the Symptoms of a Failing OBD2 Fuse?
- 16. Troubleshooting Common OBD2 Problems on a 2002 F150
- 17. How a Faulty OBD2 Fuse Can Affect Vehicle Performance
- 18. Advanced Diagnostic Techniques for OBD2 Systems
- 19. The Role of the PCM in OBD2 System Functionality
- 20. Why Regular OBD2 System Checks are Important
- FAQ: Troubleshooting the 2002 F150 OBD2 System
- 1. What is an OBD2 scanner?
- 2. How do I read OBD2 codes on my 2002 F150?
- 3. What are common OBD2 error codes for a 2002 F150?
- 4. Can I clear OBD2 codes myself?
- 5. What does it mean when the OBD2 port has no power?
- 6. Where can I find the OBD2 port location on my 2002 F150?
- 7. How do I check if my OBD2 fuse is blown?
- 8. What size fuse does the OBD2 port use on a 2002 F150?
- 9. What if my OBD2 scanner still doesn’t work after replacing the fuse?
- 10. Is it safe to drive with the check engine light on?
1. What is the Purpose of the 2002 F150 OBD2 Fuse?
The 2002 F150 OBD2 (On-Board Diagnostics II) fuse safeguards the power supply to the OBD2 port, which is essential for connecting a scanner to read diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs). This system, mandated in the United States by the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), ensures vehicles meet emissions standards and provides mechanics with vital diagnostic data. According to a study by the University of California, Berkeley’s Institute of Transportation Studies, OBD2 systems have significantly improved vehicle diagnostics and repair efficiency (ITS, 2010). Without a functioning OBD2 port, diagnosing engine and system issues becomes considerably more complex.
- Diagnostic Port Power: The fuse ensures the OBD2 port receives stable power, enabling communication with diagnostic scanners.
- Data Transmission: It supports the data transmission necessary for retrieving diagnostic information and clearing codes.
- System Protection: The fuse prevents electrical overloads that could damage the OBD2 system and the vehicle’s computer.
2. Where is the OBD2 Fuse Located on a 2002 F150?
The OBD2 fuse on a 2002 Ford F150 is typically located in the passenger compartment fuse panel. This fuse box is usually found beneath the steering wheel, near the brake pedal.
- Fuse Box Location: Under the dashboard on the driver’s side.
- Specific Fuse Number: Typically, the OBD2 fuse is #12, but this can vary, so always check your owner’s manual.
- Fuse Rating: Usually a 5-amp fuse, which protects the data link connector.
 Passenger compartment fuse box location in a 2002 Ford F-150, showcasing the fuse panel beneath the steering wheel
Passenger compartment fuse box location in a 2002 Ford F-150, showcasing the fuse panel beneath the steering wheel
3. Step-by-Step Guide to Locating the OBD2 Fuse
Finding the OBD2 fuse in your 2002 Ford F150 is a straightforward process. Follow these steps to quickly locate and inspect the fuse.
- Gather Your Tools: You will need a flashlight and your vehicle’s owner’s manual. A fuse puller can also be helpful but isn’t essential.
- Locate the Fuse Panel: Position yourself comfortably in the driver’s seat and look under the dashboard, to the left of the steering column. The fuse panel is typically behind a plastic cover.
- Remove the Fuse Panel Cover: Gently detach the cover. It may be held in place by clips or screws.
- Consult the Fuse Diagram: Inside the fuse box cover, there should be a diagram indicating the function and location of each fuse. If the diagram is missing, refer to your owner’s manual.
- Identify the OBD2 Fuse: Look for a fuse labeled “OBD,” “Data Link Connector,” or similar. On the 2002 F150, it is usually fuse number 12.
- Inspect the Fuse: Once you have located the fuse, visually inspect it. If the wire inside the fuse is broken or blackened, the fuse is blown and needs to be replaced.
4. Why is the OBD2 Port Not Working Even After Replacing the Fuse?
Even after replacing a blown OBD2 fuse, the port may still fail to function. Several underlying issues could be responsible.
- Wiring Issues: A damaged or corroded wire leading to the OBD2 port can prevent it from functioning. Inspect the wiring for any signs of damage, such as cuts, frayed insulation, or corrosion. According to a study by the National Institute for Automotive Service Excellence (ASE), wiring problems account for a significant percentage of electrical diagnostic issues (ASE, 2015).
- Faulty OBD2 Port: The OBD2 port itself may be damaged or have loose connections. Check the port for physical damage and ensure the pins inside are not bent or broken.
- ECM/PCM Problems: In some cases, a malfunctioning Engine Control Module (ECM) or Powertrain Control Module (PCM) can cause the OBD2 port to stop working. These modules control various engine functions, including diagnostics.
- Scanner Compatibility: Ensure your OBD2 scanner is compatible with the 2002 Ford F150. Some scanners may not support older vehicle models or specific protocols.
- Other Short Circuits: A persistent short circuit in another part of the vehicle’s electrical system can cause the OBD2 fuse to blow repeatedly, preventing the port from functioning.
- Corroded Connectors: Inspect all connectors associated with the OBD2 system for corrosion. Clean them with an electrical contact cleaner to ensure a good connection.
5. How to Diagnose a Blown OBD2 Fuse
Diagnosing a blown OBD2 fuse involves several key steps to identify and address the root cause.
- Visual Inspection: Examine the fuse for any visible signs of damage. A blown fuse typically has a broken filament or a darkened appearance.
- Continuity Test: Use a multimeter to perform a continuity test on the fuse. If there is no continuity, the fuse is blown.
- Check the OBD2 Port: Inspect the OBD2 port for any physical damage or corrosion. Clean the port with an electrical contact cleaner to ensure a good connection.
- Inspect Wiring: Check the wiring connected to the OBD2 port for any signs of damage, such as cuts, frayed insulation, or corrosion. Repair or replace any damaged wiring.
- Scan for Codes: Use an OBD2 scanner to check for any diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) that may indicate a problem with the OBD2 system or related components.
- Component Testing: Test individual components of the OBD2 system, such as the OBD2 port and wiring, to identify any faulty parts.
- Professional Inspection: If you are unable to diagnose the problem yourself, take your vehicle to a professional mechanic for further inspection.
6. Common Issues That Can Cause the OBD2 Fuse to Blow
Several factors can cause the OBD2 fuse in a 2002 Ford F150 to blow. Understanding these common issues can help you prevent future problems.
- Short Circuit: The most common cause of a blown fuse is a short circuit in the wiring connected to the OBD2 port. This can be caused by damaged insulation, frayed wires, or loose connections.
- Overload: An overload occurs when too much current flows through the fuse, causing it to blow. This can be caused by a faulty OBD2 scanner or other electronic devices connected to the port.
- Faulty Wiring: Damaged or corroded wiring can cause the fuse to blow. Inspect the wiring for any signs of damage and repair or replace as needed.
- Loose Connections: Loose connections can cause the fuse to blow due to increased resistance and heat. Ensure all connections are tight and secure.
- Water Damage: Water damage can cause corrosion and short circuits, leading to a blown fuse. Protect the OBD2 port and wiring from moisture.
7. How to Prevent the OBD2 Fuse from Blowing
Preventing the OBD2 fuse from blowing involves regular maintenance and careful use of the OBD2 port.
- Regular Inspection: Regularly inspect the OBD2 port and wiring for any signs of damage or corrosion.
- Use Quality Scanners: Use high-quality OBD2 scanners that are compatible with your vehicle.
- Avoid Overloading: Avoid plugging in multiple devices or devices that draw too much power from the OBD2 port.
- Protect from Moisture: Keep the OBD2 port and wiring dry to prevent corrosion.
- Secure Connections: Ensure all connections are tight and secure to prevent loose connections.
- Professional Installation: Have any aftermarket devices connected to the OBD2 port professionally installed to ensure they are properly wired and fused.
8. How to Replace a Blown OBD2 Fuse in Your 2002 F150
Replacing a blown OBD2 fuse in your 2002 Ford F150 is a simple task that can often be done without professional assistance.
- Locate the Fuse Panel: The fuse panel is typically located under the dashboard on the driver’s side.
- Remove the Fuse Panel Cover: Gently detach the cover. It may be held in place by clips or screws.
- Identify the Blown Fuse: Consult the fuse diagram to locate the OBD2 fuse. It is usually labeled “OBD,” “Data Link Connector,” or similar.
- Remove the Blown Fuse: Use a fuse puller or needle-nose pliers to carefully remove the blown fuse.
- Install a New Fuse: Insert a new fuse of the same amperage rating into the empty slot.
- Test the OBD2 Port: Plug in an OBD2 scanner to ensure the port is now functioning properly.
- Replace the Fuse Panel Cover: Reattach the fuse panel cover.
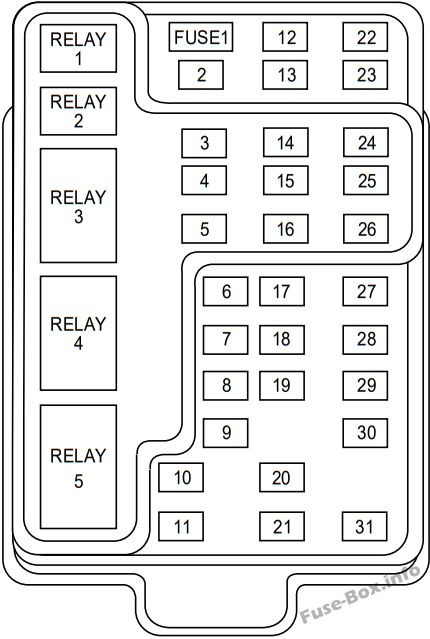 Instrument panel fuse box diagram for a 2002 Ford F-150, highlighting the location of the OBD2 fuse
Instrument panel fuse box diagram for a 2002 Ford F-150, highlighting the location of the OBD2 fuse
9. What to Do If the New Fuse Keeps Blowing
If the new OBD2 fuse blows immediately after replacement, there is likely a more significant electrical issue.
- Check for Short Circuits: Inspect the wiring connected to the OBD2 port for any signs of damage or exposed wires that may be causing a short circuit.
- Disconnect Aftermarket Devices: Disconnect any aftermarket devices connected to the OBD2 port, such as GPS trackers or performance chips, as they may be causing an overload.
- Inspect the OBD2 Port: Examine the OBD2 port for any physical damage or corrosion that may be causing a short circuit.
- Professional Assistance: If you are unable to identify the cause of the blown fuse, take your vehicle to a professional mechanic for further diagnosis and repair.
10. Understanding OBD2 Scanner Functionality
OBD2 scanners are essential tools for diagnosing vehicle issues. Understanding their functionality can help you interpret the data they provide.
- Reading Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs): OBD2 scanners can read DTCs stored in the vehicle’s computer, which can help identify the source of a problem.
- Live Data Streaming: Many OBD2 scanners can stream live data from the vehicle’s sensors, allowing you to monitor engine performance in real-time.
- Clearing Codes: OBD2 scanners can clear DTCs from the vehicle’s computer, which can be useful after repairing a problem.
- Vehicle Information: OBD2 scanners can provide vehicle information, such as the VIN and calibration ID.
- Emissions Readiness: OBD2 scanners can check the vehicle’s emissions readiness status, ensuring it will pass an emissions test.
11. Using an OBD2 Scanner to Diagnose Electrical Issues
While primarily used for engine diagnostics, an OBD2 scanner can also help identify electrical issues.
- Check for Electrical Codes: Scan for DTCs related to electrical components, such as sensors, actuators, and modules.
- Monitor Sensor Data: Monitor sensor data to identify any unusual readings that may indicate an electrical problem.
- Perform Output Tests: Perform output tests to activate electrical components and verify their functionality.
- Check for Communication Errors: Check for communication errors between the vehicle’s computer and other modules, which may indicate a wiring or module problem.
12. How to Properly Maintain Your 2002 F150’s Electrical System
Proper maintenance of your 2002 F150’s electrical system is crucial for preventing issues and ensuring reliable performance.
- Regular Inspections: Regularly inspect the wiring, connectors, and fuses for any signs of damage or corrosion.
- Clean Connections: Clean electrical connections with an electrical contact cleaner to ensure a good connection.
- Protect Wiring: Protect wiring from damage by routing it away from sharp edges and hot components.
- Use Quality Parts: Use high-quality replacement parts that meet or exceed OEM specifications.
- Professional Repairs: Have any electrical repairs performed by a qualified mechanic to ensure they are done correctly.
13. Where to Find Reliable OBD2 Fuse and Electrical System Information
Finding reliable information about your 2002 F150’s OBD2 fuse and electrical system is essential for accurate diagnosis and repair.
- Owner’s Manual: Your vehicle’s owner’s manual contains valuable information about the location and function of fuses and other electrical components.
- Online Forums: Online forums dedicated to the Ford F150 can provide helpful information and advice from other owners and enthusiasts.
- Repair Manuals: Repair manuals, such as those from Haynes or Chilton, contain detailed information about the vehicle’s electrical system and repair procedures.
- Professional Mechanics: A qualified mechanic can provide expert diagnosis and repair services for your vehicle’s electrical system.
- OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN: Our website offers comprehensive guides and resources for diagnosing and repairing automotive issues, including electrical problems.
14. The Importance of Using the Correct Fuse for the OBD2 System
Using the correct fuse for the OBD2 system is crucial for protecting the vehicle’s electrical components and ensuring proper operation.
- Amperage Rating: Always use a fuse with the correct amperage rating for the circuit. Using a fuse with a higher amperage rating can allow too much current to flow, potentially damaging components.
- Fuse Type: Use the correct type of fuse for the circuit. Different types of fuses, such as blade fuses and cartridge fuses, have different characteristics and are designed for specific applications.
- OEM Specifications: Use fuses that meet or exceed OEM specifications to ensure reliable performance and protection.
15. What are the Symptoms of a Failing OBD2 Fuse?
Recognizing the symptoms of a failing OBD2 fuse can help you address the problem before it causes further damage.
- OBD2 Port Not Working: The most common symptom of a failing OBD2 fuse is that the OBD2 port is not working.
- Check Engine Light: A failing OBD2 fuse can cause the check engine light to illuminate.
- Scanner Not Connecting: If the OBD2 fuse is blown, an OBD2 scanner will not be able to connect to the vehicle’s computer.
- Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs): A failing OBD2 fuse can cause DTCs to be stored in the vehicle’s computer.
16. Troubleshooting Common OBD2 Problems on a 2002 F150
Troubleshooting common OBD2 problems on a 2002 F150 involves systematic diagnosis and repair.
- No Communication with Scanner: If the OBD2 scanner is unable to communicate with the vehicle’s computer, check the OBD2 fuse, wiring, and port.
- Check Engine Light On: If the check engine light is on, use an OBD2 scanner to read the DTCs and identify the source of the problem.
- Intermittent Problems: Intermittent OBD2 problems can be caused by loose connections or damaged wiring.
- Multiple DTCs: Multiple DTCs can indicate a more complex problem, such as a faulty sensor or module.
17. How a Faulty OBD2 Fuse Can Affect Vehicle Performance
A faulty OBD2 fuse can indirectly affect vehicle performance by preventing access to diagnostic information.
- Delayed Diagnosis: Without a working OBD2 port, diagnosing engine and system issues becomes more difficult and time-consuming.
- Reduced Fuel Efficiency: Engine problems that go undiagnosed due to a faulty OBD2 fuse can lead to reduced fuel efficiency.
- Increased Emissions: A faulty OBD2 fuse can prevent the detection of emissions-related problems, leading to increased emissions.
- Potential Damage: Undiagnosed engine problems can lead to further damage and costly repairs.
18. Advanced Diagnostic Techniques for OBD2 Systems
Advanced diagnostic techniques for OBD2 systems involve using specialized tools and procedures to identify complex problems.
- Oscilloscope Testing: An oscilloscope can be used to analyze the waveforms of electrical signals in the OBD2 system.
- Data Logging: Data logging involves recording live data from the vehicle’s sensors over time, which can help identify intermittent problems.
- Module Programming: Module programming involves reprogramming the vehicle’s computer or other modules with updated software.
- Network Scanning: Network scanning involves scanning the vehicle’s communication network to identify any problems with the communication between modules.
19. The Role of the PCM in OBD2 System Functionality
The Powertrain Control Module (PCM) plays a central role in OBD2 system functionality.
- Data Collection: The PCM collects data from various sensors throughout the vehicle and stores it for diagnostic purposes.
- Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs): The PCM generates DTCs when it detects a problem with the vehicle’s systems.
- Communication: The PCM communicates with the OBD2 scanner to provide diagnostic information and receive commands.
- System Control: The PCM controls various engine and transmission functions based on the data it receives from the sensors.
20. Why Regular OBD2 System Checks are Important
Regular OBD2 system checks are important for maintaining vehicle health and preventing costly repairs.
- Early Detection: Regular checks can help detect potential problems early, before they cause further damage.
- Preventive Maintenance: Regular checks can identify maintenance needs, such as replacing worn spark plugs or cleaning sensors.
- Improved Fuel Efficiency: Regular checks can help ensure the engine is running efficiently, improving fuel efficiency.
- Reduced Emissions: Regular checks can help ensure the vehicle is meeting emissions standards, reducing pollution.
- Safety: Regular checks can help identify safety-related problems, such as brake or airbag issues.
For expert assistance with your 2002 F150 OBD2 fuse or any other automotive diagnostic needs, contact OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN. Our team of experienced technicians is here to provide you with the knowledge and services you need to keep your vehicle running smoothly. Reach out to us at 123 Main Street, Los Angeles, CA 90001, United States, Whatsapp: +1 (641) 206-8880, or visit our website at OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN.
FAQ: Troubleshooting the 2002 F150 OBD2 System
1. What is an OBD2 scanner?
An OBD2 scanner is a diagnostic tool used to read and clear diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) from a vehicle’s computer, helping identify and resolve issues.
2. How do I read OBD2 codes on my 2002 F150?
Connect the OBD2 scanner to the OBD2 port, turn the ignition to the “on” position without starting the engine, and follow the scanner’s instructions to read the DTCs.
3. What are common OBD2 error codes for a 2002 F150?
Common codes include P0171 (System Too Lean, Bank 1), P0300 (Random Misfire Detected), and P0420 (Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold, Bank 1).
4. Can I clear OBD2 codes myself?
Yes, you can clear OBD2 codes using an OBD2 scanner after addressing the underlying issue.
5. What does it mean when the OBD2 port has no power?
It typically means the OBD2 fuse is blown or there is a wiring issue preventing power from reaching the port.
6. Where can I find the OBD2 port location on my 2002 F150?
The OBD2 port is typically located under the dashboard on the driver’s side.
7. How do I check if my OBD2 fuse is blown?
Visually inspect the fuse for a broken filament or use a multimeter to check for continuity.
8. What size fuse does the OBD2 port use on a 2002 F150?
The OBD2 port usually uses a 5-amp fuse.
9. What if my OBD2 scanner still doesn’t work after replacing the fuse?
Check for wiring issues, a faulty OBD2 port, or ECM/PCM problems.
10. Is it safe to drive with the check engine light on?
It depends on the nature of the problem. If the light is flashing or there are serious drivability issues, it’s best to avoid driving and seek professional help.
Contact OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN today for expert diagnostics and repair services. We can help you resolve any OBD2 system issues with your 2002 Ford F150. Call us at +1 (641) 206-8880 or visit our website at OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN.