The 2006 Hyundai Elantra Obd2 Protocol facilitates vehicle diagnostics and repair, and OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN is here to guide you in understanding this crucial aspect of your car’s performance. This knowledge empowers you to troubleshoot issues effectively and maintain your vehicle’s health. Proper understanding of the 2006 Hyundai Elantra OBD2 protocols helps you interpret diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) accurately, select the correct diagnostic tools, and implement effective repair strategies.
Contents
- 1. Understanding OBD2 Protocols for the 2006 Hyundai Elantra
- 1.1. Decoding OBD2: What It Means for Your Car
- 1.2. Key OBD2 Protocols Explained
- 1.3. Why ISO9141-2 Matters for Your 2006 Hyundai Elantra
- 2. Step-by-Step Guide to Accessing OBD2 Data on Your 2006 Hyundai Elantra
- 2.1. Gathering Your Tools
- 2.2. Locating the OBD2 Port
- 2.3. Connecting the OBD2 Scanner
- 2.4. Reading Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
- 2.5. Interpreting the Data
- 2.6. Clearing the Codes (Use with Caution)
- 3. Common OBD2 Codes for the 2006 Hyundai Elantra
- 3.1. Common DTCs and Their Meanings
- 3.2. Diagnosing and Addressing Common Issues
- 3.3. Advanced Diagnostic Tips
- 4. Choosing the Right OBD2 Scanner for Your 2006 Hyundai Elantra
- 4.1. Key Features to Consider
- 4.2. Top OBD2 Scanners for the 2006 Hyundai Elantra
- 4.3. Understanding Scanner Limitations
- 5. Maintaining Your 2006 Hyundai Elantra’s OBD2 System
- 5.1. Regular Check-ups
- 5.2. Proper Maintenance
- 5.3. Environmental Factors
- 6. Advanced Troubleshooting Techniques for the 2006 Hyundai Elantra OBD2 Protocol
- 6.1. Using Live Data
- 6.2. Performing Component Tests
- 6.3. Checking Technical Service Bulletins (TSBs)
- 6.4. Using a Digital Multimeter (DMM)
- 6.5. Smoke Testing for Vacuum Leaks
- 6.6. Professional Diagnostic Tools
- 7. The Role of OBD2 in Emissions Testing for Your 2006 Hyundai Elantra
- 7.1. OBD2 and State Inspections
- 7.2. Understanding Readiness Monitors
- 7.3. Common Reasons for Readiness Monitors Not Setting
- 7.4. Tips for Passing Emissions Tests
- 8. Potential Issues and Solutions Related to the 2006 Hyundai Elantra OBD2 Protocol
- 8.1. Scanner Not Connecting
- 8.2. Inaccurate Readings
- 8.3. Difficulty Clearing Codes
- 8.4. Intermittent Issues
- 9. Upgrading Your 2006 Hyundai Elantra’s Diagnostic Capabilities
- 9.1. Adding Enhanced Diagnostics
- 9.2. Installing Aftermarket Gauges
- 9.3. Utilizing Smartphone Apps
- 9.4. Implementing Performance Tuning
- 10. OBD2 and Beyond: The Future of Vehicle Diagnostics
- 10.1. Advancements in OBD Systems
- 10.2. Integration with Telematics
- 10.3. The Role of Artificial Intelligence (AI)
- 10.4. The Importance of Staying Informed
1. Understanding OBD2 Protocols for the 2006 Hyundai Elantra
What exactly are OBD2 protocols and why are they crucial for your 2006 Hyundai Elantra? OBD2, or On-Board Diagnostics II, is a standardized system that allows you to access the health information of your vehicle. Understanding the specific protocol used by your car enables effective diagnostics and repairs.
The OBD2 protocol for the 2006 Hyundai Elantra is ISO9141-2.
1.1. Decoding OBD2: What It Means for Your Car
OBD2, short for On-Board Diagnostics II, is a standardized system used in vehicles to monitor and report on various aspects of their performance. According to the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), OBD2 was made mandatory for all cars sold in the US after 1996 to standardize emissions testing and provide technicians with a universal diagnostic interface. For your 2006 Hyundai Elantra, understanding OBD2 is essential for:
- Emissions Monitoring: Ensuring your car meets environmental standards.
- Performance Monitoring: Keeping track of engine and transmission health.
- Early Problem Detection: Identifying issues before they become major repairs.
1.2. Key OBD2 Protocols Explained
Different car manufacturers use different OBD2 communication protocols. Here’s a quick rundown:
- J1850 PWM and J1850 VPW: Primarily used by Ford and GM in the past.
- ISO9141-2: Common in European and Asian vehicles, including the 2006 Hyundai Elantra.
- ISO14230-4 (Keyword Protocol 2000): An evolution of ISO9141-2, also used in many vehicles.
- ISO15765-4/SAE J2480 (CAN): The modern standard used in most vehicles since 2008.
1.3. Why ISO9141-2 Matters for Your 2006 Hyundai Elantra
The 2006 Hyundai Elantra uses the ISO9141-2 protocol, which affects:
- Scanner Compatibility: You need a scanner that supports ISO9141-2 to read diagnostic data.
- Data Interpretation: Understanding the protocol helps in accurately interpreting diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs).
- Repair Strategies: Knowing the protocol can guide your repair approach.
2. Step-by-Step Guide to Accessing OBD2 Data on Your 2006 Hyundai Elantra
How can you access and interpret the OBD2 data from your 2006 Hyundai Elantra? By following these steps, you can effectively use an OBD2 scanner to diagnose and address potential issues.
2.1. Gathering Your Tools
To start, you’ll need:
- An OBD2 Scanner: Ensure it supports the ISO9141-2 protocol.
- Your 2006 Hyundai Elantra: Parked in a safe location.
- Vehicle’s Repair Manual (Optional): For looking up specific DTCs.
2.2. Locating the OBD2 Port
The OBD2 port in your 2006 Hyundai Elantra is typically located under the dashboard on the driver’s side. According to SAE J1962, the diagnostic link connector (DLC) should be easily accessible from the driver’s seat. Look for a 16-pin connector.
2.3. Connecting the OBD2 Scanner
- Turn Off the Ignition: Ensure the car is turned off before plugging in the scanner.
- Plug in the Scanner: Connect the OBD2 scanner to the port.
- Turn On the Ignition: Turn the ignition to the “ON” position without starting the engine.
- Follow Scanner Instructions: The scanner will prompt you to follow on-screen instructions.
2.4. Reading Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
- Select “Read Codes”: Choose the option to read diagnostic trouble codes.
- Record the Codes: Write down any DTCs that appear. These codes provide insights into potential issues.
- Understand the Codes: Use your scanner’s manual or a reliable online database to understand what each code means. Websites like OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN provide comprehensive information on DTCs.
2.5. Interpreting the Data
DTCs are typically five-character codes. Here’s how to interpret them:
- First Character: Indicates the system (e.g., P for Powertrain, B for Body, C for Chassis, U for Network).
- Second Character: Specifies whether the code is generic (0) or manufacturer-specific (1).
- Third Character: Identifies the specific subsystem (e.g., fuel system, ignition system).
- Last Two Characters: Indicate the specific fault within that subsystem.
For example, a code like P0300 indicates a random/multiple cylinder misfire in the powertrain system.
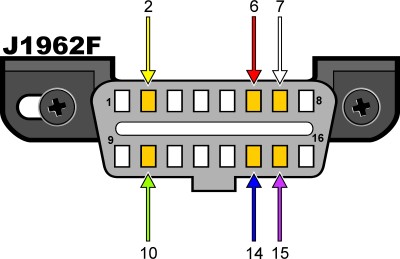 OBDII connector pinout
OBDII connector pinout
Fig. 3 – Understanding OBDII Connector Pinout
2.6. Clearing the Codes (Use with Caution)
- Select “Clear Codes”: If you choose to clear the codes, be aware that this will also reset the car’s computer.
- Verify the Repair: Only clear codes after you have fixed the underlying issue.
- Re-scan: After clearing the codes, drive the car and re-scan to ensure the problem is resolved and the codes do not return.
Caution: Clearing codes without fixing the problem is not recommended. The codes will likely reappear, and you may mask underlying issues.
3. Common OBD2 Codes for the 2006 Hyundai Elantra
What are some common OBD2 codes you might encounter with your 2006 Hyundai Elantra, and what do they signify? Recognizing these common codes can help you prioritize and address issues efficiently.
3.1. Common DTCs and Their Meanings
Here are some common DTCs you might find:
| Code | Description | Possible Causes |
|---|---|---|
| P0171 | System Too Lean (Bank 1) | Vacuum leak, faulty O2 sensor, MAF sensor issue, fuel pump problem |
| P0300 | Random/Multiple Cylinder Misfire Detected | Faulty spark plugs, ignition coils, fuel injectors, vacuum leaks, low compression |
| P0420 | Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold (Bank 1) | Faulty catalytic converter, O2 sensor issues, exhaust leaks |
| P0138 | O2 Sensor Circuit High Voltage (Bank 1, Sensor 2) | Faulty O2 sensor, wiring issue, exhaust leak |
| P0505 | Idle Air Control System Malfunction | Faulty IAC valve, vacuum leak, throttle body issue |
| P0715 | Transmission Turbine/Input Shaft Speed Sensor A Circuit | Faulty input shaft speed sensor, wiring issue, transmission problem |
| C1102 | ABS Sensor Malfunction | Faulty ABS sensor, wiring issue, wheel bearing problem |
| B1620 | Horn Circuit Malfunction | Shorted or open circuit in the horn system, defective horn relay, faulty horn switch, wiring issue, defective horn |
3.2. Diagnosing and Addressing Common Issues
- P0171 (System Too Lean):
- Check for Vacuum Leaks: Inspect hoses and intake manifold for leaks.
- Inspect O2 Sensor: Ensure the O2 sensor is functioning correctly.
- Clean MAF Sensor: Clean the Mass Airflow (MAF) sensor to ensure accurate readings.
- P0300 (Random/Multiple Cylinder Misfire):
- Check Spark Plugs: Replace worn or damaged spark plugs.
- Inspect Ignition Coils: Test ignition coils and replace any faulty ones.
- Check Fuel Injectors: Ensure fuel injectors are delivering the correct amount of fuel.
- P0420 (Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold):
- Inspect Catalytic Converter: A failing catalytic converter often triggers this code.
- Check O2 Sensors: Ensure O2 sensors are functioning correctly.
- Check for Exhaust Leaks: Repair any exhaust leaks that could affect the catalytic converter’s performance.
- P0138 (O2 Sensor Circuit High Voltage):
- Inspect O2 Sensor: Check for damage or contamination and replace if necessary.
- Check Wiring: Inspect the wiring and connectors leading to the O2 sensor for any signs of damage or corrosion.
- Look for Exhaust Leaks: Check for exhaust leaks near the O2 sensor that could affect its readings.
3.3. Advanced Diagnostic Tips
- Use Live Data: Many OBD2 scanners can display live data from sensors. This can help you see real-time readings and identify anomalies.
- Consult Technical Service Bulletins (TSBs): Check for TSBs related to your car model. These bulletins often provide specific diagnostic and repair procedures for common issues.
- Professional Assistance: If you are unsure about any diagnostic or repair procedure, seek help from a qualified mechanic.
4. Choosing the Right OBD2 Scanner for Your 2006 Hyundai Elantra
How do you select the best OBD2 scanner to use with your 2006 Hyundai Elantra? Selecting the right scanner is crucial for accurate and efficient diagnostics.
4.1. Key Features to Consider
- Protocol Support: Ensure the scanner supports ISO9141-2.
- Ease of Use: Look for a scanner with an intuitive interface and clear display.
- Data Display: Real-time data, freeze frame data, and graphing capabilities are valuable.
- Code Definitions: Built-in code definitions save time and effort.
- Update Capability: Choose a scanner that can be updated with the latest DTCs and vehicle information.
4.2. Top OBD2 Scanners for the 2006 Hyundai Elantra
Here are some recommended OBD2 scanners:
| Scanner Name | Key Features | Price Range |
|---|---|---|
| Autel MaxiCOM MK808 | Supports all OBD2 protocols, advanced diagnostics, service functions, live data streaming, and bi-directional control. | $500-600 |
| BlueDriver Bluetooth Pro | Wireless connectivity, comprehensive diagnostics, code definitions, repair reports generated from a vast database of known fixes, and freeze frame data. | $120-130 |
| Innova 3100i | Reads and clears OBD2 codes, ABS codes, live data, freeze frame data, battery and charging system test, and oil reset. | $80-100 |
| FOXWELL NT301 | Comprehensive OBD2 functions, DTC lookup, live data, freeze frame data, I/M readiness test, and supports all OBD2 protocols. | $60-80 |
| Launch CRP129E | Full OBD2 functions, enhanced diagnostics for engine, transmission, ABS, and SRS systems, auto VIN detect, and one-click software updates. | $230-250 |
4.3. Understanding Scanner Limitations
- Basic Scanners: These typically only read and clear OBD2 codes.
- Advanced Scanners: These offer more features like live data, bidirectional control, and advanced diagnostics, but come at a higher cost.
- Software Updates: Keep your scanner updated to ensure it has the latest code definitions and vehicle coverage.
5. Maintaining Your 2006 Hyundai Elantra’s OBD2 System
How can you ensure that your 2006 Hyundai Elantra’s OBD2 system remains in optimal condition? Regular maintenance and care can prevent issues and ensure accurate diagnostics.
5.1. Regular Check-ups
- Scan Regularly: Scan your car every few months to check for pending codes, even if the check engine light is not on.
- Monitor Performance: Keep an eye on your car’s performance, including fuel economy, engine smoothness, and any unusual noises or vibrations.
- Address Issues Promptly: Address any detected issues as soon as possible to prevent further damage.
5.2. Proper Maintenance
- Follow Maintenance Schedule: Adhere to the manufacturer’s recommended maintenance schedule.
- Use Quality Parts: Use high-quality replacement parts to ensure compatibility and reliability.
- Check Wiring and Connectors: Regularly inspect wiring and connectors for corrosion, damage, or loose connections.
5.3. Environmental Factors
- Avoid Extreme Conditions: Protect your car from extreme temperatures and moisture, which can damage electronic components.
- Keep It Clean: Keep the OBD2 port and surrounding area clean and free of debris.
- Professional Inspections: Periodically have your car inspected by a professional mechanic to identify potential issues early.
6. Advanced Troubleshooting Techniques for the 2006 Hyundai Elantra OBD2 Protocol
What advanced techniques can you use to troubleshoot complex OBD2 issues on your 2006 Hyundai Elantra? These techniques can help you diagnose and resolve even the most challenging problems.
6.1. Using Live Data
Live data allows you to monitor real-time sensor readings. Key parameters to monitor include:
- O2 Sensor Readings: Monitor O2 sensor voltages to detect lean or rich conditions.
- MAF Sensor Readings: Check MAF sensor readings to ensure proper airflow.
- Fuel Trims: Monitor short-term and long-term fuel trims to identify fuel delivery issues.
- Engine Temperature: Ensure the engine reaches and maintains the correct operating temperature.
By comparing these readings to the manufacturer’s specifications, you can pinpoint faulty components or systems.
6.2. Performing Component Tests
Many advanced OBD2 scanners can perform component tests, such as:
- Fuel Injector Test: Activate and deactivate fuel injectors to check their functionality.
- EGR Valve Test: Control the EGR valve to ensure it opens and closes properly.
- Throttle Actuator Control: Adjust the throttle position to verify the throttle body’s operation.
These tests can help isolate issues to specific components.
6.3. Checking Technical Service Bulletins (TSBs)
TSBs are issued by manufacturers to address common issues. Check for TSBs related to your 2006 Hyundai Elantra to see if there are any known fixes for your specific problem. Websites like the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) offer free access to TSBs.
6.4. Using a Digital Multimeter (DMM)
A DMM can be used to check:
- Voltage: Verify proper voltage levels at sensors and actuators.
- Continuity: Check wiring for breaks or shorts.
- Resistance: Measure the resistance of sensors and components to ensure they are within specification.
6.5. Smoke Testing for Vacuum Leaks
A smoke tester can help locate vacuum leaks by introducing smoke into the intake system and identifying where it escapes. This is particularly useful for diagnosing lean conditions (P0171, P0174).
6.6. Professional Diagnostic Tools
For complex issues, consider using professional diagnostic tools, such as:
- Oscilloscope: Allows you to visualize electrical signals and identify intermittent problems.
- Fuel Pressure Tester: Measures fuel pressure to diagnose fuel delivery issues.
- Compression Tester: Checks cylinder compression to identify engine mechanical problems.
7. The Role of OBD2 in Emissions Testing for Your 2006 Hyundai Elantra
How does OBD2 affect emissions testing for your 2006 Hyundai Elantra? Understanding this role is vital for ensuring your vehicle meets regulatory standards.
7.1. OBD2 and State Inspections
Many states use OBD2 data as part of their emissions testing process. The test involves:
- Checking for DTCs: Ensuring there are no active DTCs related to emissions.
- Verifying Readiness Monitors: Confirming that all readiness monitors have been set.
7.2. Understanding Readiness Monitors
Readiness monitors are self-tests performed by the car’s computer to verify the functionality of emissions-related systems. Common monitors include:
- Catalyst Monitor: Checks the efficiency of the catalytic converter.
- Oxygen Sensor Monitor: Verifies the performance of the O2 sensors.
- Evaporative System Monitor: Tests the evaporative emissions control system.
- EGR System Monitor: Checks the functionality of the EGR system.
If any of these monitors are not set, your car may fail the emissions test.
7.3. Common Reasons for Readiness Monitors Not Setting
- Recent Code Clearing: Clearing DTCs resets the monitors, and they need to be driven to completion.
- Faulty Components: A malfunctioning sensor or component can prevent a monitor from setting.
- Driving Conditions: Specific driving conditions may be required to set certain monitors.
7.4. Tips for Passing Emissions Tests
- Address DTCs: Fix any issues causing DTCs before the test.
- Complete Drive Cycle: Perform a complete drive cycle to set all readiness monitors.
- Check for TSBs: Check for any TSBs related to emissions issues on your car.
8. Potential Issues and Solutions Related to the 2006 Hyundai Elantra OBD2 Protocol
What common problems might you face when working with the OBD2 protocol on your 2006 Hyundai Elantra, and how can you resolve them?
8.1. Scanner Not Connecting
- Problem: The OBD2 scanner fails to connect to the car’s computer.
- Possible Causes:
- Faulty Scanner: The scanner itself may be defective.
- Damaged OBD2 Port: The OBD2 port in the car may be damaged or have corroded pins.
- Blown Fuse: A blown fuse may be preventing power from reaching the OBD2 port.
- Communication Protocol Issue: The scanner may not support the ISO9141-2 protocol used by the 2006 Hyundai Elantra.
- Solutions:
- Test the Scanner: Try the scanner on another car to verify it works.
- Inspect the OBD2 Port: Check the OBD2 port for damage or corrosion.
- Check Fuses: Locate and check the fuse for the OBD2 port. Replace if blown.
- Verify Protocol Support: Ensure the scanner supports the ISO9141-2 protocol.
8.2. Inaccurate Readings
- Problem: The OBD2 scanner provides inaccurate or inconsistent readings.
- Possible Causes:
- Faulty Sensors: A malfunctioning sensor may be providing incorrect data.
- Wiring Issues: Damaged or corroded wiring can affect sensor readings.
- Software Glitches: The scanner’s software may have glitches or bugs.
- Solutions:
- Check Sensor Connections: Inspect sensor wiring and connectors for damage or corrosion.
- Replace Faulty Sensors: Replace any sensors that are known to be faulty.
- Update Scanner Software: Ensure the scanner has the latest software updates.
8.3. Difficulty Clearing Codes
- Problem: The OBD2 scanner is unable to clear DTCs.
- Possible Causes:
- Underlying Issue: The DTC will reappear if the underlying issue has not been resolved.
- Scanner Limitation: Some scanners may not be able to clear certain codes.
- Software Glitch: The scanner’s software may have a glitch preventing code clearing.
- Solutions:
- Resolve the Underlying Issue: Fix the problem causing the DTC before attempting to clear it.
- Try a Different Scanner: Try using a different scanner to clear the code.
- Disconnect the Battery: As a last resort, disconnect the car battery for a few minutes to reset the computer.
8.4. Intermittent Issues
- Problem: The check engine light comes on and off intermittently.
- Possible Causes:
- Loose Connections: Loose wiring connections can cause intermittent issues.
- Faulty Sensors: Sensors that are beginning to fail may cause intermittent problems.
- Environmental Factors: Temperature and humidity can affect sensor performance.
- Solutions:
- Check Wiring Connections: Inspect all wiring connections for looseness or corrosion.
- Monitor Sensor Data: Use live data to monitor sensor readings and identify any anomalies.
- Replace Suspect Sensors: Replace any sensors that are suspected of causing intermittent issues.
9. Upgrading Your 2006 Hyundai Elantra’s Diagnostic Capabilities
Are there ways to enhance the diagnostic capabilities of your 2006 Hyundai Elantra beyond the standard OBD2 system?
9.1. Adding Enhanced Diagnostics
- Professional Scanners: Invest in a professional-grade scanner that offers enhanced diagnostics beyond basic OBD2 functions.
- Manufacturer-Specific Software: Use software designed specifically for Hyundai vehicles to access more detailed diagnostic information.
- Data Logging: Use a data logger to record sensor data over time for in-depth analysis.
9.2. Installing Aftermarket Gauges
- Monitor Key Parameters: Install aftermarket gauges to monitor key parameters like boost pressure, air/fuel ratio, and oil pressure.
- Early Warning System: Gauges can provide an early warning of potential problems before they trigger a DTC.
- Customization: Gauges can be customized to display the information that is most important to you.
9.3. Utilizing Smartphone Apps
- OBD2 App: There are many OBD2 apps available for smartphones that can read and display diagnostic data.
- Real-Time Data: Some apps can display real-time data and allow you to monitor your car’s performance.
- Custom Dashboards: Create custom dashboards to display the information that is most relevant to you.
9.4. Implementing Performance Tuning
- ECU Remapping: Remapping the car’s ECU can improve performance and fuel economy.
- Custom Tuning: Custom tuning allows you to optimize the car’s performance for specific modifications.
- Dyno Tuning: Dyno tuning involves testing and tuning the car on a dynamometer to achieve maximum performance.
10. OBD2 and Beyond: The Future of Vehicle Diagnostics
What does the future hold for vehicle diagnostics, and how will systems like OBD2 evolve?
10.1. Advancements in OBD Systems
- OBD-III: The next generation of OBD systems is expected to provide even more detailed diagnostic information and real-time monitoring.
- Wireless Connectivity: Future OBD systems may rely more on wireless connectivity for data transmission and remote diagnostics.
- Cloud-Based Diagnostics: Cloud-based diagnostic platforms will allow technicians to access vehicle data and diagnostic tools from anywhere.
10.2. Integration with Telematics
- Real-Time Monitoring: Telematics systems can provide real-time monitoring of vehicle health and performance.
- Predictive Maintenance: Telematics data can be used to predict when maintenance will be needed.
- Remote Diagnostics: Telematics systems can allow technicians to perform remote diagnostics and troubleshoot issues.
10.3. The Role of Artificial Intelligence (AI)
- AI-Powered Diagnostics: AI algorithms can analyze vehicle data and identify potential problems more accurately.
- Automated Troubleshooting: AI can automate the troubleshooting process and provide step-by-step repair instructions.
- Personalized Recommendations: AI can provide personalized recommendations for maintenance and repairs based on your driving habits and vehicle condition.
10.4. The Importance of Staying Informed
- Continued Education: Stay informed about the latest advancements in vehicle diagnostics and repair techniques.
- Professional Training: Attend professional training courses to enhance your skills and knowledge.
- Online Resources: Utilize online resources like OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN to stay up-to-date on the latest diagnostic tools and techniques.
Understanding the 2006 Hyundai Elantra OBD2 protocol ensures that you can maintain your vehicle effectively and diagnose issues promptly. At OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN, we’re dedicated to providing you with the knowledge and resources you need for successful car maintenance and repairs.
For expert guidance on using OBD2 scanners and comprehensive car repair services, contact us at:
- Address: 123 Main Street, Los Angeles, CA 90001, United States
- WhatsApp: +1 (641) 206-8880
- Website: OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN
Let OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN be your trusted partner in automotive diagnostics and repair.

