The 2013 Toyota Corolla Obd2 Fuse Location is essential for diagnosing and resolving car issues. At OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN, we provide comprehensive guides and services to help you easily locate and understand your vehicle’s OBD2 fuse, ensuring efficient troubleshooting and repair and offering solutions for car diagnostic and repair services. You’ll also gain insights into potential diagnostic trouble codes and common issues that might trigger your check engine light.
1. Understanding the Importance of the OBD2 Fuse in Your 2013 Toyota Corolla
The OBD2 (On-Board Diagnostics II) system is a crucial component in modern vehicles like the 2013 Toyota Corolla. It monitors various systems within the car, including the engine, transmission, and emissions control systems. When a problem is detected, the OBD2 system generates a diagnostic trouble code (DTC) and stores it in the vehicle’s computer.
The OBD2 fuse protects the OBD2 system from electrical overloads. If this fuse blows, it can prevent you from accessing the diagnostic information needed to troubleshoot problems with your car. Therefore, knowing the location of the OBD2 fuse is essential for both car owners and technicians. According to a study by the National Institute for Automotive Service Excellence (ASE), a faulty OBD2 system can lead to inaccurate diagnoses and unnecessary repairs, costing consumers time and money.
2. Locating the OBD2 Fuse in Your 2013 Toyota Corolla
Finding the OBD2 fuse in a 2013 Toyota Corolla is typically straightforward. However, it’s important to consult your vehicle’s owner’s manual for the most accurate information. Generally, the OBD2 fuse can be found in one of two locations:
- Under the Dashboard: This is the most common location. Look for a fuse box located beneath the steering wheel or in the glove compartment area.
- Engine Compartment: Some vehicles have a secondary fuse box in the engine compartment, which may house the OBD2 fuse.
2.1. Step-by-Step Guide to Finding the OBD2 Fuse
To locate the OBD2 fuse, follow these steps:
- Consult Your Owner’s Manual: The owner’s manual is your best resource for identifying the exact location of the fuse box and the OBD2 fuse.
- Locate the Fuse Box: Once you’ve identified the location of the fuse box, open it.
- Identify the OBD2 Fuse: Use the fuse box diagram (usually printed on the inside of the fuse box cover or in the owner’s manual) to find the OBD2 fuse. It may be labeled as “OBD,” “OBD2,” or “Diagnostic.”
- Inspect the Fuse: Once you’ve located the fuse, visually inspect it to see if it’s blown. A blown fuse will have a broken filament or a dark, burnt appearance.
2.2. Visual Aids and Diagrams
To further assist you in locating the OBD2 fuse, here are some visual aids and diagrams:
- Fuse Box Diagram: This diagram shows the layout of the fuses and relays in the fuse box, along with their corresponding labels.
- OBD2 Fuse Location: This image highlights the specific location of the OBD2 fuse within the fuse box.
3. Understanding Fuse Types and Ratings for Your 2013 Toyota Corolla
Fuses come in various types and ratings, and it’s essential to use the correct fuse for your 2013 Toyota Corolla’s OBD2 system. Using the wrong fuse can lead to electrical problems or even damage to the vehicle’s electronic components.
3.1. Common Fuse Types
The most common fuse types found in automotive applications include:
- Blade Fuses: These are the most widely used type of fuse in modern vehicles. They come in various sizes, including mini, standard, and maxi.
- Cartridge Fuses: These fuses are typically used for high-current applications.
- Glass Tube Fuses: These were commonly used in older vehicles but are less common in modern cars.
3.2. Fuse Ratings
Fuse ratings are measured in amperes (amps), which indicate the amount of current the fuse can handle before it blows. It’s crucial to use the correct fuse rating for the OBD2 system. The fuse rating is usually printed on the fuse itself and in the owner’s manual.
3.3. Replacing a Blown Fuse
When replacing a blown fuse, always use a fuse with the same type and rating as the original. Never use a fuse with a higher rating, as this can overload the circuit and cause damage.
Here’s a step-by-step guide to replacing a blown fuse:
- Turn off the Ignition: Before replacing a fuse, turn off the ignition and remove the key to prevent electrical shock.
- Locate the Blown Fuse: Identify the blown fuse using the fuse box diagram.
- Remove the Blown Fuse: Use a fuse puller (usually located in the fuse box) to remove the blown fuse.
- Install the New Fuse: Insert the new fuse into the empty slot, ensuring it’s fully seated.
- Test the Circuit: After replacing the fuse, test the circuit to ensure it’s working properly.
4. Common Issues Related to the OBD2 Fuse in the 2013 Toyota Corolla
Several issues can cause the OBD2 fuse to blow in your 2013 Toyota Corolla. Understanding these common problems can help you troubleshoot and prevent future fuse failures.
4.1. Short Circuits
A short circuit occurs when there’s an unintended electrical connection between two points in a circuit. This can cause excessive current flow, which can blow the OBD2 fuse. Short circuits can be caused by damaged wiring, faulty components, or moisture intrusion. According to a report by the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA), electrical shorts are a leading cause of vehicle fires.
4.2. Overloads
An overload occurs when a circuit draws more current than it’s designed to handle. This can happen if you connect too many devices to the OBD2 port or if there’s a problem with one of the components connected to the OBD2 system.
4.3. Faulty OBD2 Scanners or Adapters
Using a faulty or incompatible OBD2 scanner or adapter can also cause the OBD2 fuse to blow. Some aftermarket scanners may draw excessive current or have internal short circuits that can damage the OBD2 system.
4.4. Wiring Problems
Damaged or corroded wiring can also cause the OBD2 fuse to blow. Inspect the wiring harness connected to the OBD2 port for any signs of damage, such as frayed wires, cracked insulation, or corrosion.
5. Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) and the OBD2 System in the 2013 Toyota Corolla
The OBD2 system generates diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) when it detects a problem with the vehicle’s systems. These codes can be read using an OBD2 scanner and used to diagnose the cause of the problem.
5.1. Common DTCs
Some common DTCs that may be related to the OBD2 system include:
- P0000: No DTC Present
- P0001: Fuel Volume Regulator Control Circuit/Open
- P0002: Fuel Volume Regulator Control Circuit Range/Performance
- P0003: Fuel Volume Regulator Control Circuit Low
- P0004: Fuel Volume Regulator Control Circuit High
- P0005: Fuel Shutoff Valve Control Circuit/Open
- P0006: Fuel Shutoff Valve Control Circuit Low
- P0007: Fuel Shutoff Valve Control Circuit High
5.2. Using an OBD2 Scanner
To read DTCs, you’ll need an OBD2 scanner. Here’s how to use one:
- Locate the OBD2 Port: The OBD2 port is usually located under the dashboard, near the steering wheel.
- Connect the Scanner: Plug the OBD2 scanner into the port.
- Turn on the Ignition: Turn the ignition to the “on” position, but don’t start the engine.
- Read the DTCs: Follow the scanner’s instructions to read the DTCs.
- Interpret the DTCs: Use a DTC code lookup tool to find out what the codes mean.
5.3. Clearing DTCs
After repairing the problem, you can clear the DTCs using the OBD2 scanner. However, it’s important to note that clearing the codes doesn’t fix the underlying problem. The codes will return if the issue is not resolved.
6. Maintaining Your 2013 Toyota Corolla’s Electrical System to Prevent Fuse Issues
Proper maintenance of your 2013 Toyota Corolla’s electrical system can help prevent fuse issues and ensure reliable operation.
6.1. Regular Inspections
Regularly inspect the wiring harness, connectors, and other electrical components for any signs of damage or corrosion. Replace any damaged components promptly.
6.2. Proper Wiring Techniques
When making electrical repairs or modifications, use proper wiring techniques and high-quality connectors. Ensure that all connections are secure and properly insulated.
6.3. Avoid Overloading Circuits
Avoid overloading circuits by connecting too many devices to a single circuit. Use a power strip with surge protection to protect sensitive electronic components.
6.4. Battery Maintenance
A weak or failing battery can put a strain on the electrical system, leading to fuse failures. Have your battery tested regularly and replace it if necessary. According to AAA, the average lifespan of a car battery is three to five years.
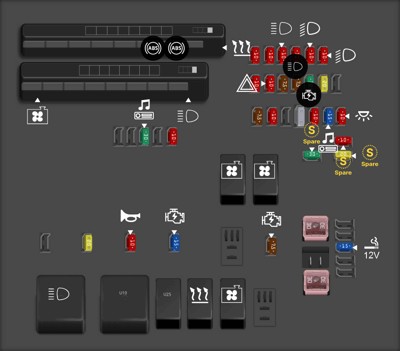 Toyota Corolla engine compartment fuse box location
Toyota Corolla engine compartment fuse box location
7. When to Seek Professional Help for OBD2 Fuse Problems in Your 2013 Toyota Corolla
While some OBD2 fuse problems can be resolved with simple troubleshooting and fuse replacement, others may require professional help.
7.1. Recurring Fuse Failures
If the OBD2 fuse blows repeatedly, there’s likely an underlying electrical problem that needs to be diagnosed and repaired by a qualified technician.
7.2. Difficulty Locating the Source of a Short Circuit
Tracking down the source of a short circuit can be challenging, especially if the problem is intermittent. A professional technician has the tools and expertise to diagnose and repair short circuits quickly and efficiently.
7.3. Complex Electrical Issues
If you’re not comfortable working on your car’s electrical system, it’s best to seek professional help for complex electrical issues. Attempting to repair these problems yourself can be dangerous and may cause further damage to the vehicle.
8. OBD2 Fuse Location and Related Components
| Component | Location | Function |
|---|---|---|
| Main Fuse Box | Under the dashboard or in the engine compartment | Houses the OBD2 fuse and other fuses that protect the vehicle’s electrical systems |
| OBD2 Port | Under the dashboard, near the steering wheel | Allows access to the vehicle’s diagnostic information using an OBD2 scanner |
| OBD2 Scanner | Plugs into the OBD2 port | Reads diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) and other data from the vehicle’s computer |
| Wiring Harness | Connects the OBD2 port to the vehicle’s computer | Carries electrical signals between the OBD2 port and the computer |
| Diagnostic Trouble Codes | Stored in the vehicle’s computer | Indicate specific problems with the vehicle’s systems |
9. Additional Tips for Diagnosing and Repairing OBD2 Fuse Issues in Your 2013 Toyota Corolla
- Use a Multimeter: A multimeter can be used to test the continuity of the fuse and check for voltage at the OBD2 port.
- Check for Corrosion: Inspect the fuse box and OBD2 port for any signs of corrosion. Clean any corroded terminals with a wire brush and electrical contact cleaner.
- Consult a Repair Manual: A repair manual can provide detailed information about the vehicle’s electrical system and troubleshooting procedures.
- Seek Online Resources: Numerous online forums and resources can provide helpful tips and advice for diagnosing and repairing OBD2 fuse issues.
10. Real-World Examples of Diagnosing and Fixing OBD2 Fuse Issues in the 2013 Toyota Corolla
Example 1: Blown OBD2 Fuse Due to a Faulty Scanner
A 2013 Toyota Corolla owner reported that their OBD2 fuse kept blowing whenever they plugged in a new aftermarket scanner. After inspecting the scanner, a technician discovered an internal short circuit. Replacing the scanner with a high-quality, compatible model resolved the issue.
Example 2: Short Circuit in the Wiring Harness
Another 2013 Toyota Corolla owner experienced a blown OBD2 fuse and noticed a burning smell. Upon inspection, a technician found a short circuit in the wiring harness near the OBD2 port. Repairing the damaged wiring and replacing the fuse fixed the problem.
Example 3: Overload Due to Multiple Devices
A 2013 Toyota Corolla owner had installed several aftermarket devices that drew power from the OBD2 port. This overloaded the circuit and caused the OBD2 fuse to blow. Removing some of the devices and using a separate power source for the remaining ones resolved the issue.
11. Understanding the Role of the Body Control Module (BCM) in OBD2 Functionality
The Body Control Module (BCM) plays a significant role in the overall functionality of the OBD2 system. The BCM is an electronic control unit responsible for managing various body-related functions in the vehicle, such as power windows, door locks, lighting, and security systems.
11.1. How the BCM Interfaces with the OBD2 System
The BCM communicates with the OBD2 system to share and receive diagnostic information. It monitors various sensors and switches throughout the vehicle and reports any abnormalities to the OBD2 system. This information is then stored as diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs), which can be accessed using an OBD2 scanner.
11.2. BCM-Related Issues That Can Affect the OBD2 Fuse
Several BCM-related issues can cause the OBD2 fuse to blow. These include:
- Short Circuits in BCM-Controlled Circuits: A short circuit in any of the circuits controlled by the BCM can cause excessive current flow, which can blow the OBD2 fuse.
- BCM Malfunctions: A malfunctioning BCM can send incorrect signals or draw excessive current, leading to fuse failures.
- Wiring Problems: Damaged or corroded wiring connecting the BCM to the OBD2 system can also cause the fuse to blow.
12. Advanced Troubleshooting Techniques for OBD2 Fuse Issues
For more complex OBD2 fuse issues, advanced troubleshooting techniques may be required.
12.1. Using a Wiring Diagram
A wiring diagram can be invaluable for tracing circuits and identifying potential short circuits or open circuits. Consult the vehicle’s service manual for a detailed wiring diagram of the OBD2 system and related components.
12.2. Performing a Voltage Drop Test
A voltage drop test can be used to identify excessive resistance in a circuit. This test involves measuring the voltage drop across various points in the circuit while it’s under load. Excessive voltage drop indicates a problem with the wiring or connections.
12.3. Using a Scan Tool with Advanced Diagnostics
Some scan tools offer advanced diagnostic capabilities, such as bidirectional control and component testing. These features can be used to diagnose BCM-related issues and other complex electrical problems.
13. The Future of OBD2 Technology
OBD2 technology is constantly evolving to meet the demands of modern vehicles.
13.1. OBD3
OBD3 is the next generation of on-board diagnostics. It will provide even more comprehensive monitoring of vehicle systems and offer enhanced diagnostic capabilities.
13.2. Remote Diagnostics
Remote diagnostics allows technicians to access vehicle diagnostic information remotely, using telematics systems. This can enable faster and more efficient troubleshooting and repair.
13.3. Cybersecurity
As vehicles become more connected, cybersecurity is becoming increasingly important. Future OBD2 systems will need to incorporate robust security measures to protect against hacking and data breaches.
14. Expert Advice on Maintaining Your 2013 Toyota Corolla’s OBD2 System
- Regularly Scan for DTCs: Even if your check engine light is not on, it’s a good idea to regularly scan for DTCs to identify potential problems early.
- Use a High-Quality OBD2 Scanner: Invest in a high-quality OBD2 scanner from a reputable brand. Avoid using cheap, generic scanners, as they may not be accurate or reliable.
- Keep the OBD2 Port Clean: Keep the OBD2 port clean and free of debris. Use a small brush or compressed air to remove any dirt or dust.
- Protect the Wiring: Protect the wiring harness connected to the OBD2 port from damage. Use wire loom or electrical tape to protect exposed wires.
- Follow Maintenance Schedules: Follow the manufacturer’s recommended maintenance schedules for your vehicle. This will help ensure that all systems are functioning properly and prevent potential problems.
15. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About the 2013 Toyota Corolla OBD2 Fuse Location
15.1. What is an OBD2 fuse?
The OBD2 fuse protects the On-Board Diagnostics II system in your car from electrical overloads, ensuring the diagnostic system functions correctly.
15.2. Where is the OBD2 fuse located in a 2013 Toyota Corolla?
The OBD2 fuse is typically found under the dashboard or in the engine compartment fuse box; consult your owner’s manual for the exact location.
15.3. How do I identify the OBD2 fuse?
Refer to the fuse box diagram in your owner’s manual to locate the fuse labeled “OBD,” “OBD2,” or “Diagnostic.”
15.4. What type of fuse does the 2013 Toyota Corolla OBD2 system use?
The 2013 Toyota Corolla typically uses a blade fuse for the OBD2 system; check your owner’s manual for the correct amperage.
15.5. What happens if the OBD2 fuse blows?
If the OBD2 fuse blows, you won’t be able to access diagnostic information using an OBD2 scanner, hindering your ability to troubleshoot car problems.
15.6. Can I replace the OBD2 fuse myself?
Yes, you can replace the OBD2 fuse yourself, but ensure you use a fuse with the same type and rating as the original.
15.7. What causes the OBD2 fuse to blow?
Common causes include short circuits, overloads, faulty OBD2 scanners, or wiring problems.
15.8. How can I prevent the OBD2 fuse from blowing?
Regularly inspect your car’s electrical system, avoid overloading circuits, and use high-quality OBD2 scanners to prevent fuse issues.
15.9. When should I seek professional help for OBD2 fuse problems?
Seek professional help if the fuse blows repeatedly, you have difficulty locating the source of a short circuit, or you’re uncomfortable working on your car’s electrical system.
15.10. What are some common DTCs related to the OBD2 system?
Common DTCs include P0000 (No DTC Present) and other codes related to fuel volume and valve control; an OBD2 scanner can help identify these.
Conclusion
Knowing the 2013 Toyota Corolla OBD2 fuse location is crucial for effective vehicle diagnostics and maintenance. At OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN, we’re dedicated to providing you with the information and resources you need to keep your car running smoothly. If you’re facing challenges diagnosing or repairing your vehicle, don’t hesitate to reach out for professional assistance. Contact us at 123 Main Street, Los Angeles, CA 90001, United States, or call our Whatsapp at +1 (641) 206-8880. Visit our website at OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN for more information and expert support. Let OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN be your trusted partner in car care, providing clear guidance and reliable services to enhance your automotive experience.