The 409.1 Obd2 Cable is a specific type of interface used for diagnosing and accessing data from older vehicles, primarily those using the ISO9141-2 and ISO14230-4 (KWP2000) protocols. If you’re aiming to unlock deeper diagnostic insights and streamline your automotive repair tasks, OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN offers expert guidance and resources to help you effectively utilize the 409.1 OBD2 cable. With our support, you can improve vehicle diagnostics, reduce downtime, and ensure precise, cost-effective repairs, enhancing both your expertise and customer satisfaction, and we offer comprehensive guides and support for mastering automotive diagnostics.
1. What is a 409.1 OBD2 Cable?
A 409.1 OBD2 cable is an interface that connects a computer to a vehicle’s On-Board Diagnostics II (OBD2) system, used to read diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs), access live data, and perform basic diagnostics on older vehicles. This cable primarily supports the ISO9141-2 and ISO14230-4 (KWP2000) communication protocols, commonly found in vehicles manufactured before the widespread adoption of CAN bus systems.
- Function: The primary function is to facilitate communication between a diagnostic tool (usually a laptop running diagnostic software) and the vehicle’s ECU (Engine Control Unit).
- Protocols: Supports ISO9141-2 and ISO14230-4 (KWP2000) protocols.
- Use Cases: Ideal for older Volkswagen, Audi, Skoda, and SEAT models, as well as other vehicles using these specific protocols.
- Alternatives: Modern vehicles require OBD2 scanners that support CAN bus and other newer protocols.
2. What Vehicles Are Compatible with the 409.1 OBD2 Cable?
The 409.1 OBD2 cable is primarily compatible with older vehicles that use the ISO9141-2 and KWP2000 communication protocols, commonly found in models from the late 1990s to mid-2000s. These vehicles often include brands like Volkswagen, Audi, Skoda, and SEAT.
- Volkswagen: Many VW models from the late 1990s and early 2000s, such as the Golf Mk4, Passat B5, and Jetta A4.
- Audi: Audi A3, A4, and A6 models produced during the same period.
- Skoda: Skoda Octavia and other models from the late 1990s to mid-2000s.
- SEAT: SEAT León and Ibiza models within the specified years.
Note: Compatibility depends on the vehicle’s manufacturing year and the specific communication protocols it uses. Always verify compatibility before use.
3. How Do I Install the 409.1 OBD2 Cable Drivers?
Installing the drivers for a 409.1 OBD2 cable involves a series of steps to ensure your computer can properly communicate with the cable. Usually, you need to download the drivers from the manufacturer’s website or from a reliable source, then install them through the Device Manager on your computer.
- Download Drivers: Obtain the correct drivers from the manufacturer’s website or a trusted source.
- Connect Cable: Plug the 409.1 OBD2 cable into your computer’s USB port.
- Open Device Manager: Access Device Manager via the Control Panel.
- Locate the Device: Look for the cable under “Ports (COM & LPT)” or “Other devices” with a yellow exclamation mark.
- Update Driver: Right-click the device and select “Update driver.”
- Browse Manually: Choose “Browse my computer for drivers” and navigate to the folder where you saved the downloaded drivers.
- Install Driver: Follow the on-screen prompts to complete the installation.
- Verify Installation: Check Device Manager to ensure the cable is recognized without errors.
4. What Software is Compatible with the 409.1 OBD2 Cable?
Several software programs are compatible with the 409.1 OBD2 cable, designed to read diagnostic data, perform tests, and allow you to make adjustments to your vehicle. VCDS Lite, ScanMaster-ELM, and others offer different features and interfaces, catering to a range of diagnostic needs.
- VCDS Lite: A popular choice for Volkswagen, Audi, Skoda, and SEAT vehicles, offering comprehensive diagnostic capabilities.
- ScanMaster-ELM: Compatible with various vehicles, supporting generic OBD2 functions and some advanced features.
- OpenDiag: A free diagnostic software that supports many functions for various car brands.
- FiatECUScan/MultiECUScan: (Now known as AlfaOBD) Primarily used for Fiat, Alfa Romeo, and Lancia vehicles, but also supports generic OBD2 functions.
5. How Do I Use the 409.1 OBD2 Cable for Vehicle Diagnostics?
Using the 409.1 OBD2 cable for vehicle diagnostics involves connecting the cable to your vehicle, launching compatible software on your computer, and then reading and interpreting the data displayed by the software. Proper usage allows you to identify issues, clear diagnostic trouble codes, and monitor live sensor data.
- Connect the Cable: Plug the OBD2 end of the 409.1 cable into the OBD2 port of your vehicle. This port is typically located under the dashboard.
- Connect to Computer: Plug the USB end of the cable into your computer.
- Launch Diagnostic Software: Open the diagnostic software compatible with the 409.1 cable (e.g., VCDS Lite, ScanMaster-ELM).
- Select the Correct COM Port: In the software settings, select the correct COM port assigned to the cable. You can find this in the Device Manager under “Ports (COM & LPT).”
- Test the Connection: Most software will have an option to test the connection to ensure the cable is communicating with the vehicle.
- Read Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs): Use the software to read any stored DTCs. These codes indicate specific problems within the vehicle.
- Interpret DTCs: Research the meaning of each DTC to understand the underlying issue. Online databases and repair manuals can be valuable resources.
- View Live Data: Monitor live sensor data to assess the performance of various components in real-time.
- Clear DTCs (If Necessary): After addressing the issues, you can use the software to clear the DTCs.
- Verify the Repair: After clearing the codes, take the vehicle for a test drive and re-scan to ensure the problem is resolved and no new codes appear.
6. What Are the Common Issues When Using a 409.1 OBD2 Cable?
Common issues when using a 409.1 OBD2 cable include driver installation problems, software incompatibility, connection errors, and inaccurate data. Troubleshooting these issues typically involves verifying driver installation, ensuring software compatibility, checking cable connections, and consulting reliable resources for accurate diagnostic information.
-
Driver Installation Issues:
- Problem: Incorrect or corrupted drivers can prevent the cable from functioning correctly.
- Solution: Reinstall the drivers from a trusted source. Ensure the drivers are compatible with your operating system.
-
Software Incompatibility:
- Problem: Using software that is not compatible with the 409.1 cable or the vehicle can lead to errors.
- Solution: Verify that the software supports the 409.1 cable and is suitable for your vehicle’s make and model.
-
Connection Errors:
- Problem: Loose or faulty connections between the cable, the vehicle’s OBD2 port, or the computer can disrupt communication.
- Solution: Check all connections to ensure they are secure. Try using a different USB port on your computer.
-
Inaccurate Data:
- Problem: The diagnostic data may be inaccurate due to faulty sensors or issues within the vehicle’s ECU.
- Solution: Cross-reference the data with other sources, such as repair manuals or online databases, to verify its accuracy.
-
Cable Malfunction:
- Problem: The 409.1 cable itself may be defective.
- Solution: Test the cable with another vehicle or computer to determine if the cable is the source of the problem.
7. What Does a 409.1 OBD2 Cable Cost?
The cost of a 409.1 OBD2 cable can vary widely depending on the brand, quality, and source. Genuine, high-quality cables from reputable manufacturers are generally more expensive than generic or clone versions.
- Generic/Clone Cables: These can range from $10 to $30, often available on online marketplaces like eBay or AliExpress.
- Reputable Brands: Cables from known brands may cost between $30 and $70, offering better reliability and support.
- Professional Versions: High-end cables designed for professional use can cost upwards of $100, providing advanced features and durability.
8. Where Can I Buy a Genuine 409.1 OBD2 Cable?
Purchasing a genuine 409.1 OBD2 cable is crucial for reliability and accurate diagnostics. You can find genuine cables from reputable suppliers, diagnostic tool manufacturers, and specialized automotive parts retailers.
- Ross-Tech: While Ross-Tech is known for their high-end VCDS systems, it’s worth checking their website or contacting them directly to inquire about genuine 409.1 cables or suitable alternatives.
- Specialized Automotive Parts Retailers: Look for retailers that specialize in automotive diagnostic tools and equipment.
- Online Marketplaces: Exercise caution when buying from online marketplaces like Amazon or eBay. Check seller reviews and product descriptions carefully to ensure you are purchasing a genuine product.
- Direct from Manufacturers: Some diagnostic tool manufacturers may offer genuine 409.1 cables or recommend reliable sources.
9. How Does the 409.1 OBD2 Cable Compare to Modern OBD2 Scanners?
The 409.1 OBD2 cable is designed for older vehicles using specific communication protocols, whereas modern OBD2 scanners support a wider range of protocols, including CAN bus, and offer advanced features like Bluetooth connectivity and comprehensive diagnostic functions. The 409.1 cable is limited to older vehicles, while modern scanners provide broader compatibility and enhanced capabilities.
-
Protocols:
- 409.1 OBD2 Cable: Supports ISO9141-2 and ISO14230-4 (KWP2000) protocols.
- Modern OBD2 Scanners: Supports CAN bus, J1850 PWM, J1850 VPW, ISO9141-2, ISO14230-4, and more.
-
Vehicle Compatibility:
- 409.1 OBD2 Cable: Limited to older vehicles (late 1990s to mid-2000s) that use the ISO9141-2 and KWP2000 protocols.
- Modern OBD2 Scanners: Compatible with a wide range of vehicles, including newer models with CAN bus systems.
-
Features:
- 409.1 OBD2 Cable: Basic diagnostics, reading and clearing DTCs, viewing live data.
- Modern OBD2 Scanners: Advanced diagnostics, bidirectional control, component testing, Bluetooth connectivity, smartphone integration, and more.
-
Connectivity:
- 409.1 OBD2 Cable: Typically connects to a computer via USB.
- Modern OBD2 Scanners: May offer USB, Bluetooth, or Wi-Fi connectivity.
-
Software:
- 409.1 OBD2 Cable: Requires specific software like VCDS Lite or ScanMaster-ELM.
- Modern OBD2 Scanners: Often come with proprietary software or apps, with support for third-party applications.
10. Can I Use a 409.1 OBD2 Cable on a CAN Bus Vehicle?
No, you cannot use a 409.1 OBD2 cable on a vehicle that uses a CAN (Controller Area Network) bus system. The 409.1 cable is designed for older protocols like ISO9141-2 and KWP2000, which are incompatible with CAN bus. Attempting to use it on a CAN bus vehicle will result in a failure to communicate, and could potentially damage the vehicle’s electronic systems.
11. What is VCDS Lite and How Does It Relate to the 409.1 OBD2 Cable?
VCDS Lite is a diagnostic software specifically designed to work with the 409.1 OBD2 cable, primarily used for Volkswagen, Audi, Skoda, and SEAT vehicles. It allows users to perform basic diagnostics, read and clear diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs), view live data, and perform some adaptations on older vehicles.
- Functionality: VCDS Lite provides a user-friendly interface for accessing and interpreting diagnostic information from compatible vehicles.
- Compatibility: It is specifically designed to work with the 409.1 OBD2 cable and older vehicles using the ISO9141-2 and KWP2000 protocols.
- Limitations: VCDS Lite has limited functionality compared to the full version of VCDS, and it does not support newer vehicles with CAN bus systems.
12. What Are Some Alternatives to the 409.1 OBD2 Cable for Modern Vehicles?
For modern vehicles, alternatives to the 409.1 OBD2 cable include advanced OBD2 scanners that support CAN bus and other current protocols, Bluetooth OBD2 adapters for smartphone connectivity, and professional diagnostic tools with comprehensive capabilities. These options provide broader compatibility and enhanced features for diagnosing and servicing modern vehicles.
-
Advanced OBD2 Scanners:
- Description: These scanners support multiple protocols, including CAN bus, and offer advanced features like bidirectional control, component testing, and live data streaming.
- Examples: Autel MaxiCOM MK808, Launch X431 V+, Snap-on Solus Edge.
-
Bluetooth OBD2 Adapters:
- Description: These adapters connect to your smartphone or tablet via Bluetooth and work with various OBD2 apps for basic diagnostics and monitoring.
- Examples: OBDLink MX+, Veepeak OBDCheck BLE, BlueDriver Bluetooth Professional OBDII Scan Tool.
-
Professional Diagnostic Tools:
- Description: These tools are designed for professional mechanics and offer comprehensive diagnostic capabilities, including advanced coding, programming, and module flashing.
- Examples: Ross-Tech VCDS (for VW/Audi/Skoda/SEAT), BMW ISTA, Mercedes XENTRY.
13. How Do I Troubleshoot a “No Communication” Error with the 409.1 OBD2 Cable?
Troubleshooting a “No Communication” error with the 409.1 OBD2 cable involves checking the cable connections, verifying driver installation, ensuring software compatibility, and testing the cable on a known-good vehicle. These steps help identify and resolve the issue, allowing you to establish a connection with the vehicle’s ECU.
-
Check Cable Connections:
- Ensure the OBD2 connector is securely plugged into the vehicle’s OBD2 port.
- Verify the USB connector is properly connected to your computer.
- Inspect the cable for any visible damage.
-
Verify Driver Installation:
- Open Device Manager and check for any errors related to the cable.
- Reinstall the drivers from a trusted source, ensuring they are compatible with your operating system.
-
Ensure Software Compatibility:
- Make sure you are using software that is compatible with the 409.1 cable and your vehicle’s make and model.
- Check the software settings to ensure the correct COM port is selected for the cable.
-
Test the Cable on a Known-Good Vehicle:
- If possible, try using the cable on another vehicle that is known to be compatible with the 409.1 cable.
- This can help determine if the issue is with the cable itself or with the original vehicle.
-
Check Vehicle’s OBD2 Port:
- Inspect the vehicle’s OBD2 port for any damage or corrosion.
- Ensure the port is receiving power. You can use a multimeter to check for voltage.
-
Restart Computer and Software:
- Sometimes, simply restarting your computer and the diagnostic software can resolve communication issues.
-
Disable Other USB Devices:
- Disconnect any unnecessary USB devices from your computer to avoid potential conflicts.
-
Check for Software Conflicts:
- Ensure there are no conflicting software programs running in the background that may be interfering with the diagnostic software.
14. What Are the Limitations of Using a 409.1 OBD2 Cable?
Limitations of using a 409.1 OBD2 cable include its incompatibility with modern CAN bus vehicles, limited diagnostic capabilities compared to advanced scanners, and reliance on older software. These constraints make it less suitable for diagnosing and servicing newer vehicles with advanced electronic systems.
-
Incompatibility with CAN Bus Vehicles:
- The 409.1 OBD2 cable is not compatible with vehicles that use the CAN (Controller Area Network) bus system, which is common in modern vehicles.
-
Limited Diagnostic Capabilities:
- Compared to advanced OBD2 scanners, the 409.1 cable offers limited diagnostic capabilities. It primarily supports basic functions like reading and clearing DTCs and viewing live data.
-
Reliance on Older Software:
- The 409.1 cable relies on older software like VCDS Lite and ScanMaster-ELM, which may not be as user-friendly or feature-rich as modern diagnostic software.
-
Lack of Advanced Features:
- The 409.1 cable does not support advanced features like bidirectional control, component testing, and module programming, which are available in more advanced scanners.
-
Limited Vehicle Coverage:
- The cable is primarily designed for older Volkswagen, Audi, Skoda, and SEAT vehicles, and may not work well with other makes and models.
-
USB Connectivity:
- The 409.1 cable typically connects to a computer via USB, which can be less convenient than wireless options like Bluetooth or Wi-Fi.
15. Can I Update the Firmware on a 409.1 OBD2 Cable?
Generally, you cannot update the firmware on a 409.1 OBD2 cable, as these cables are typically basic interfaces without firmware update capabilities. Firmware updates are more common in advanced OBD2 scanners and professional diagnostic tools that require periodic updates to support new features and vehicle models.
16. What is the Difference Between a Genuine and a Clone 409.1 OBD2 Cable?
The primary differences between a genuine and a clone 409.1 OBD2 cable lie in their reliability, build quality, software compatibility, and level of support. Genuine cables offer better performance, compatibility, and support, while clone cables may be cheaper but often come with risks and limitations.
-
Reliability:
- Genuine: Genuine cables are typically more reliable and less prone to errors or malfunctions.
- Clone: Clone cables may be unreliable and prone to communication errors or damage.
-
Build Quality:
- Genuine: Genuine cables are made with high-quality components and better construction.
- Clone: Clone cables often use cheaper components and may have poor build quality.
-
Software Compatibility:
- Genuine: Genuine cables are designed to work seamlessly with compatible diagnostic software.
- Clone: Clone cables may have compatibility issues with diagnostic software, leading to limited functionality or errors.
-
Support:
- Genuine: Genuine cables come with support from the manufacturer, including driver updates and technical assistance.
- Clone: Clone cables typically lack support, making it difficult to troubleshoot issues or obtain assistance.
-
Performance:
- Genuine: Genuine cables offer better performance and faster communication speeds.
- Clone: Clone cables may have slower communication speeds and may not accurately transmit data.
-
Risk of Damage:
- Genuine: Genuine cables are designed to protect both the vehicle and the diagnostic equipment from damage.
- Clone: Clone cables may pose a risk of damage to the vehicle’s ECU or the diagnostic equipment due to poor design or faulty components.
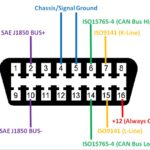
17. How to Identify Pinout of 409.1 OBD2 Cable?
Identifying the pinout of a 409.1 OBD2 cable involves understanding the standard OBD2 pin assignments and verifying the connections with a multimeter. This process helps ensure correct connections and prevents potential damage when using the cable for diagnostics.
-
Understand Standard OBD2 Pin Assignments:
- OBD2 connectors have a standard pinout defined by the SAE J1962 specification. Key pins include:
- Pin 4: Chassis Ground
- Pin 5: Signal Ground
- Pin 7: K-Line (ISO 9141-2 and ISO 14230-4)
- Pin 15: L-Line (ISO 9141-2 and ISO 14230-4)
- Pin 16: Battery Voltage (12V)
- OBD2 connectors have a standard pinout defined by the SAE J1962 specification. Key pins include:
-
Visual Inspection:
- Examine the OBD2 connector on the 409.1 cable.
- Note the presence and arrangement of the pins.
- Compare the pin arrangement with the standard OBD2 pinout diagram.
-
Use a Multimeter:
- Set the multimeter to the continuity testing mode.
- Identify Pin 4 (Chassis Ground) and Pin 5 (Signal Ground) on the OBD2 connector.
- Use the multimeter to confirm continuity between these pins and the ground wire in the cable.
- Identify Pin 7 (K-Line) and Pin 15 (L-Line).
- Use the multimeter to trace these pins to their corresponding connections on the cable’s circuit board or connector.
- Identify Pin 16 (Battery Voltage).
- Use the multimeter to confirm that this pin is connected to the 12V power supply in the cable.
-
Refer to Documentation:
- Check the documentation or specifications that came with the 409.1 OBD2 cable.
- The documentation may provide a detailed pinout diagram or wiring schematic.
-
Online Resources:
- Search online for pinout diagrams or wiring schematics specific to the 409.1 OBD2 cable.
- Look for reliable sources, such as automotive forums or diagnostic tool websites.
18. What Should I Do If My 409.1 OBD2 Cable is Not Working?
If your 409.1 OBD2 cable is not working, start by checking the physical connections, ensuring the drivers are correctly installed, verifying software compatibility, and testing the cable on another compatible vehicle. By systematically addressing these potential issues, you can identify the root cause and restore the cable’s functionality.
-
Check Physical Connections:
- Ensure the OBD2 connector is securely plugged into the vehicle’s OBD2 port.
- Verify that the USB connector is properly connected to your computer.
- Inspect the cable for any visible damage, such as frayed wires or broken connectors.
-
Verify Driver Installation:
- Open Device Manager on your computer.
- Look for the 409.1 OBD2 cable under “Ports (COM & LPT)” or “Other devices.”
- If the cable is listed with a yellow exclamation mark or is not recognized, reinstall the drivers.
- Download the latest drivers from a trusted source, such as the manufacturer’s website.
- Follow the installation instructions provided with the drivers.
-
Ensure Software Compatibility:
- Make sure you are using diagnostic software that is compatible with the 409.1 OBD2 cable and your vehicle’s make and model.
- Check the software requirements and ensure your computer meets the minimum specifications.
- Verify that the software is properly configured to use the correct COM port for the cable.
-
Test the Cable on Another Vehicle:
- If possible, try using the 409.1 OBD2 cable on another vehicle that is known to be compatible with the cable.
- This can help determine if the issue is with the cable itself or with the original vehicle.
-
Check the Vehicle’s OBD2 Port:
- Inspect the vehicle’s OBD2 port for any damage, corrosion, or bent pins.
- Ensure that the OBD2 port is receiving power. You can use a multimeter to check for voltage between pins 4 and 16 (should be approximately 12V).
-
Restart Your Computer and Software:
- Sometimes, simply restarting your computer and the diagnostic software can resolve communication issues.
- Close all other applications that may be using the COM port.
-
Disable Antivirus Software:
- Temporarily disable your antivirus software, as it may be interfering with the communication between the cable and the software.
-
Try a Different USB Port:
- Try using a different USB port on your computer, as some ports may not provide enough power or may have compatibility issues.
-
Check for Conflicting Devices:
- Ensure that there are no other devices connected to your computer that may be conflicting with the 409.1 OBD2 cable.
19. What Security Precautions Should I Take When Using a 409.1 OBD2 Cable?
When using a 409.1 OBD2 cable, it’s important to use reputable software, protect your computer from malware, avoid making unauthorized changes to vehicle settings, and ensure the cable is securely connected. Taking these precautions can help prevent security breaches and protect your vehicle’s electronic systems.
-
Use Reputable Software:
- Only use diagnostic software from trusted sources.
- Avoid downloading software from unofficial websites or peer-to-peer networks.
- Ensure that the software is up-to-date with the latest security patches.
-
Protect Your Computer from Malware:
- Install and maintain a reputable antivirus program on your computer.
- Scan your computer regularly for malware and other security threats.
- Be cautious when opening email attachments or clicking on links from unknown sources.
-
Avoid Making Unauthorized Changes:
- Only make changes to vehicle settings that you fully understand.
- Consult a qualified mechanic or technician before making any modifications to the vehicle’s ECU or other electronic systems.
- Be aware that making unauthorized changes can void your vehicle’s warranty and may have unintended consequences.
-
Ensure Secure Connection:
- Make sure the 409.1 OBD2 cable is securely connected to both your computer and the vehicle’s OBD2 port.
- Avoid using the cable in public places where unauthorized individuals may be able to access your vehicle’s data.
-
Monitor Data Access:
- Be aware of the data that the diagnostic software is accessing and transmitting.
- Avoid sharing sensitive vehicle data with untrusted parties.
-
Use a Firewall:
- Enable a firewall on your computer to prevent unauthorized access to your vehicle’s data.
-
Disconnect When Not in Use:
- When you are finished using the 409.1 OBD2 cable, disconnect it from both your computer and the vehicle’s OBD2 port.
20. What are the Ethical Considerations of Using a 409.1 OBD2 Cable?
The ethical considerations of using a 409.1 OBD2 cable include respecting vehicle owners’ privacy, obtaining consent before accessing vehicle data, using the cable for legal and legitimate purposes, and responsibly handling diagnostic information. Adhering to these principles ensures ethical and responsible use of diagnostic tools.
-
Respect Vehicle Owners’ Privacy:
- Vehicle data can contain sensitive information about the owner’s driving habits, location, and personal information.
- Always respect the privacy of vehicle owners and avoid accessing or sharing their data without their consent.
-
Obtain Consent:
- Before accessing a vehicle’s data using a 409.1 OBD2 cable, obtain the owner’s consent.
- Explain the purpose of the diagnostic procedure and the type of data that will be accessed.
- Provide the owner with the option to decline the diagnostic procedure if they are not comfortable with it.
-
Use for Legal and Legitimate Purposes:
- Only use the 409.1 OBD2 cable for legal and legitimate purposes, such as diagnosing and repairing vehicle problems.
- Avoid using the cable for illegal activities, such as tampering with vehicle odometers or disabling safety features.
-
Handle Diagnostic Information Responsibly:
- Handle diagnostic information responsibly and avoid misinterpreting or misusing it.
- Provide accurate and honest diagnostic reports to vehicle owners.
- Avoid making false or misleading claims about vehicle problems.
-
Protect Data Security:
- Take steps to protect the security of vehicle data and prevent unauthorized access.
- Use strong passwords and encryption to protect your computer and diagnostic software.
- Avoid storing sensitive vehicle data on unsecured devices or networks.
-
Comply with Regulations:
- Comply with all applicable laws and regulations regarding the use of diagnostic tools and access to vehicle data.
- Be aware of data privacy laws and regulations, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR).
-
Maintain Professionalism:
- Maintain professionalism and ethical conduct when using a 409.1 OBD2 cable.
- Avoid engaging in unethical practices, such as charging excessive fees or performing unnecessary repairs.
By understanding the capabilities and limitations of the 409.1 OBD2 cable, you can effectively diagnose and address issues in older vehicles. At OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN, we’re dedicated to providing you with the knowledge and resources needed to master automotive diagnostics.
Navigating the complexities of vehicle diagnostics can be challenging, but you don’t have to do it alone. Contact us at 123 Main Street, Los Angeles, CA 90001, United States, or reach out via WhatsApp at +1 (641) 206-8880. Visit our website at OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN for more information and expert assistance.