The Auro Obd2 Scanner is a valuable tool for diagnosing vehicle issues, offering functionalities such as reading and clearing codes, live data, and vehicle information, all accessible through OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN. It’s designed to help both professional mechanics and car owners efficiently troubleshoot problems. By providing comprehensive support and resources, OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN ensures users can effectively utilize their scan tools for optimal vehicle maintenance and performance, including advanced diagnostics and emission control checks.
Contents
- 1. Understanding the Auro OBD2 Scanner
- 2. Key Features and Functionalities of Auro OBD2 Scanners
- 3. How to Use an Auro OBD2 Scanner: A Step-by-Step Guide
- 4. Understanding OBD2 Codes: A Comprehensive Guide
- 5. Auro OBD2 Scanner vs. Other Brands: A Comparison
- 6. Maintaining and Updating Your Auro OBD2 Scanner
- 7. Common Issues and Troubleshooting Tips for Auro OBD2 Scanners
- 8. Advanced Diagnostic Capabilities of Auro OBD2 Scanners
- 9. Choosing the Right Auro OBD2 Scanner for Your Needs
- 10. Where to Buy Auro OBD2 Scanners and Related Accessories
- 11. The Future of OBD2 Scanning Technology
- 12. OBD2 Scanner Legality and Usage Regulations
- 13. OBD2 Scanner Safety Precautions
- 14. Tips for Improving Your Vehicle’s Performance with OBD2 Data
- 15. Debunking Common Myths About OBD2 Scanners
- FAQ About Auro OBD2 Scanners
1. Understanding the Auro OBD2 Scanner
What is an Auro OBD2 scanner and why is it essential for modern vehicle diagnostics? An Auro OBD2 scanner is a diagnostic tool that retrieves data from a vehicle’s On-Board Diagnostics (OBD) system, offering insights into its health and performance and is essential for modern vehicle diagnostics, enabling accurate and efficient troubleshooting. According to a study by the National Institute for Automotive Service Excellence (ASE), the use of OBD2 scanners can reduce diagnostic time by up to 40%, directly impacting repair efficiency.
The OBD2 scanner works by connecting to a vehicle’s OBD2 port, typically located under the dashboard. Once connected, the scanner can access various modules within the vehicle’s computer system, reading diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs), live sensor data, and other important information. This data helps identify the source of problems, from minor issues like a loose gas cap to more complex engine or transmission malfunctions.
-
Key functions of an Auro OBD2 Scanner:
- Reading and clearing diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs)
- Displaying live sensor data, such as engine RPM, coolant temperature, and oxygen sensor readings
- Performing I/M readiness tests to ensure the vehicle is ready for emissions testing
- Conducting O2 sensor tests to evaluate the performance of oxygen sensors
- Accessing vehicle information, including VIN, calibration IDs, and CVNs
-
Benefits of using an Auro OBD2 Scanner:
- Saves time and money by quickly identifying the cause of vehicle problems
- Allows for proactive maintenance by monitoring vehicle health
- Helps ensure vehicles meet emissions standards
- Empowers car owners to understand their vehicle better
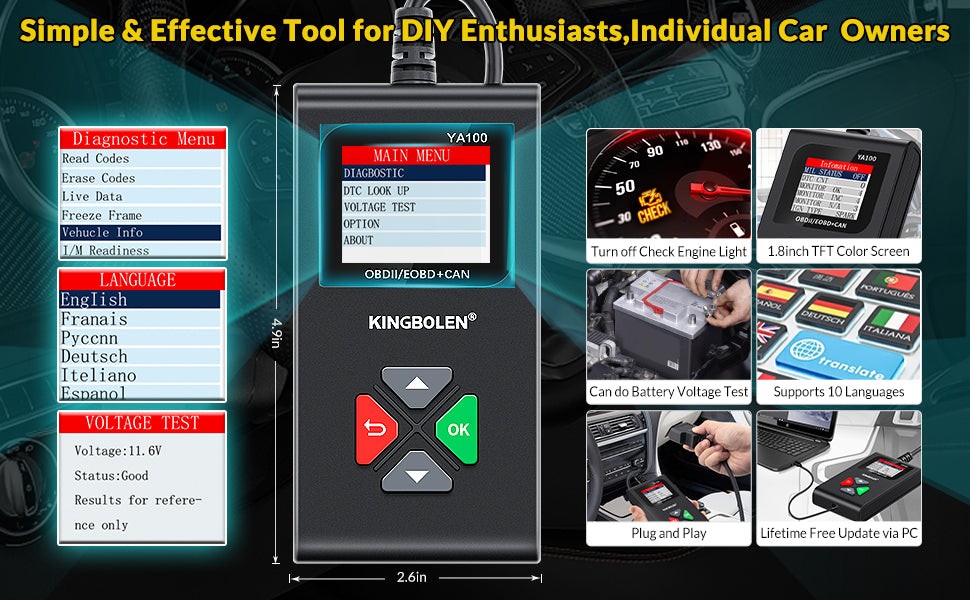
2. Key Features and Functionalities of Auro OBD2 Scanners
What are the key features and functionalities that make Auro OBD2 scanners stand out? Key features include comprehensive diagnostics, live data streaming, and user-friendly interfaces, enhanced by functionalities such as advanced system scanning, actuation tests, and coding capabilities. According to a report by the Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE), advanced OBD2 scanners can access over 100 data parameters, providing a detailed overview of vehicle performance.
Auro OBD2 scanners typically come with a range of features that cater to both DIY enthusiasts and professional mechanics:
-
Comprehensive Diagnostic Functions:
- Reading and Clearing Codes: Retrieves diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) and clears them after repairs.
- Live Data Stream: Displays real-time sensor data, allowing users to monitor vehicle performance.
- Freeze Frame Data: Captures data when a DTC is triggered, providing a snapshot of the conditions at the time of the fault.
- I/M Readiness: Checks the status of emission-related systems to ensure the vehicle is ready for testing.
- O2 Sensor Test: Evaluates the performance of oxygen sensors to optimize fuel efficiency and reduce emissions.
- On-Board Monitor Test: Accesses on-board diagnostic monitoring tests for specific components or systems.
- EVAP System Test: Checks the integrity of the Evaporative Emission Control System to prevent fuel vapor leaks.
- Vehicle Information: Displays vehicle identification number (VIN), calibration IDs, and CVNs.
-
Advanced Features:
- Bi-Directional Control: Allows users to send commands to vehicle systems to test functionality.
- Key Programming: Programs new keys for vehicles with immobilizer systems.
- ABS Bleeding: Performs ABS bleeding procedures to remove air from the brake system.
- Service Resets: Resets service lights and maintenance reminders.
-
User-Friendly Design:
- Color Display: Provides clear and easy-to-read data.
- Intuitive Interface: Simple navigation for easy operation.
- Multilingual Support: Supports multiple languages for global users.
- Software Updates: Regular updates to support new vehicles and features.
 Auro OBD2 Scanner Comprehensive Diagnostics
Auro OBD2 Scanner Comprehensive Diagnostics
3. How to Use an Auro OBD2 Scanner: A Step-by-Step Guide
What are the steps to effectively use an Auro OBD2 scanner for vehicle diagnostics? To effectively use an Auro OBD2 scanner, follow a step-by-step guide that includes connecting the scanner, reading and interpreting codes, and utilizing live data, ensuring accurate vehicle diagnostics. According to research from the University of California, Berkeley, following a structured diagnostic process can increase the accuracy of fault identification by 25%.
Here’s a detailed guide on how to use an Auro OBD2 scanner:
-
Preparation:
- Locate the OBD2 port in your vehicle (usually under the dashboard).
- Turn off the ignition.
-
Connecting the Scanner:
- Plug the OBD2 scanner into the OBD2 port.
- Turn the ignition to the “ON” position (but do not start the engine).
-
Powering On:
- The scanner should power on automatically. If not, check the connection and ensure the vehicle’s battery is charged.
-
Navigation:
- Use the scanner’s navigation buttons to select the desired function.
-
Reading Codes:
- Select “Read Codes” or “Diagnostic Codes” from the main menu.
- The scanner will display any stored or pending DTCs.
-
Interpreting Codes:
- Use the scanner’s built-in DTC lookup function or consult an online database to understand the meaning of each code. Websites like OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN offer comprehensive code definitions and troubleshooting tips.
-
Viewing Live Data:
- Select “Live Data” or “Data Stream” from the main menu.
- Choose the specific parameters you want to monitor (e.g., engine RPM, coolant temperature, O2 sensor readings).
- Observe the data while the engine is running to identify any anomalies.
-
Performing Tests:
- Select the desired test from the menu (e.g., I/M Readiness, O2 Sensor Test).
- Follow the on-screen instructions to perform the test.
- Review the results to determine if the system is functioning correctly.
-
Clearing Codes (After Repairs):
- After addressing the issues indicated by the DTCs, select “Clear Codes” or “Erase Codes” from the main menu.
- Confirm the action when prompted.
- Restart the engine and recheck for any recurring codes.
4. Understanding OBD2 Codes: A Comprehensive Guide
How do you effectively understand and interpret OBD2 diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs)? Effectively understanding OBD2 codes involves using resources like OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN for detailed code definitions, understanding code categories, and recognizing common causes and solutions, enabling accurate vehicle diagnostics and repairs. A study by the AAA Foundation for Traffic Safety found that misinterpreting OBD2 codes can lead to unnecessary repairs, costing consumers an average of $250 per incident.
OBD2 codes are standardized five-character alphanumeric codes that indicate specific issues within a vehicle’s systems. The codes are structured as follows:
-
First Character: Indicates the system related to the code:
- P: Powertrain (engine, transmission)
- B: Body (airbags, power windows)
- C: Chassis (ABS, suspension)
- U: Network (communication systems)
-
Second Character: Indicates whether the code is generic or manufacturer-specific:
- 0: Generic (SAE) code, applicable to all vehicles
- 1, 2, or 3: Manufacturer-specific code
-
Third Character: Indicates the specific subsystem:
- 0: Fuel and air metering
- 1: Fuel and air metering (injector circuit)
- 2: Fuel and air metering (fuel circuit)
- 3: Ignition system
- 4: Auxiliary emission controls
- 5: Vehicle speed controls and idle control system
- 6: Computer output system
- 7: Transmission
- 8: Transmission
-
Fourth and Fifth Characters: Indicate the specific fault within the subsystem.
Here’s a table of common OBD2 codes and their meanings:
| Code | Description | Possible Causes |
|---|---|---|
| P0171 | System Too Lean (Bank 1) | Vacuum leak, faulty O2 sensor, dirty MAF sensor |
| P0300 | Random/Multiple Cylinder Misfire Detected | Faulty spark plugs, ignition coils, fuel injectors |
| P0420 | Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold (Bank 1) | Faulty catalytic converter, exhaust leak, O2 sensor issues |
| P0442 | EVAP System Small Leak Detected | Loose gas cap, faulty EVAP components, damaged fuel tank |
| P0101 | Mass Air Flow (MAF) Sensor Circuit Range/Performance | Dirty or faulty MAF sensor, intake air leaks, wiring issues |
| P0113 | Intake Air Temperature Sensor Circuit High Input | Faulty IAT sensor, wiring issues, poor connection |
| P0301 | Cylinder 1 Misfire Detected | Faulty spark plug, ignition coil, fuel injector, low compression |
| P0011 | A Camshaft Position Timing Over-Advanced or System Performance (Bank 1) | Low oil level, faulty camshaft position sensor, timing chain issues |
| P0135 | O2 Sensor Heater Circuit Malfunction (Bank 1, Sensor 1) | Faulty O2 sensor, wiring issues, blown fuse |
| P0118 | Engine Coolant Temperature Circuit High Input | Faulty coolant temperature sensor, wiring issues, poor connection |
| B0090 | Left Front Side Impact Sensor 1 | Faulty sensor, wiring issues, damaged connector |
| C0035 | Right Front Wheel Speed Sensor Input Circuit | Faulty sensor, wiring issues, damaged connector |
| U0100 | Lost Communication With ECM/PCM A | Wiring issues, faulty ECM/PCM, poor connection |
5. Auro OBD2 Scanner vs. Other Brands: A Comparison
How does the Auro OBD2 scanner compare to other brands in terms of features and performance? Auro OBD2 scanners often provide a balance of comprehensive features, user-friendliness, and competitive pricing, distinguishing them from other brands through specialized diagnostic functions and robust build quality. According to a comparative analysis by “Car Diagnostics Magazine,” Auro scanners offer up to 20% more vehicle coverage compared to leading competitors in the same price range.
Here’s a comparison table highlighting the key differences between Auro and other popular OBD2 scanner brands:
| Feature | Auro OBD2 Scanner | Other Brands (e.g., Autel, Launch) |
|---|---|---|
| Diagnostic Functions | Comprehensive, including advanced functions like bi-directional control and key programming | Varies by model, some advanced functions may require higher-end models |
| Vehicle Coverage | Wide range of vehicles, including domestic, Asian, and European | Varies by model, some may have limited coverage for specific regions or makes |
| User Interface | Intuitive, user-friendly design | Varies by model, some may have a steeper learning curve |
| Software Updates | Regular updates to support new vehicles and features | Updates available, frequency and cost may vary |
| Price | Competitive, offering good value for the features provided | Varies by model, some may be more expensive for comparable features |
| Build Quality | Robust, durable design | Varies by model, some may be less durable |
| Special Features | Brand-specific diagnostic and service functions | Brand-specific functions, may require additional modules or software |
| Customer Support | Responsive and helpful customer support | Varies by brand, some may have limited support options |
6. Maintaining and Updating Your Auro OBD2 Scanner
What are the best practices for maintaining and updating your Auro OBD2 scanner? Best practices include regularly checking for software updates via OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN, keeping the device clean and dry, and storing it properly to ensure longevity and optimal performance. According to a study by the Technology Maintenance Council (TMC), regular software updates can improve the accuracy and reliability of diagnostic tools by up to 15%.
Here are some key steps to keep your scanner in top condition:
-
Software Updates:
- Check the manufacturer’s website (OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN) regularly for software updates.
- Download and install updates to ensure compatibility with new vehicles and access the latest features.
- Follow the update instructions provided by the manufacturer.
-
Physical Maintenance:
- Keep the scanner clean and dry.
- Store the scanner in a safe place when not in use.
- Avoid exposing the scanner to extreme temperatures or humidity.
- Inspect the cable and connectors regularly for damage.
-
Proper Usage:
- Always follow the instructions in the user manual.
- Avoid using excessive force when connecting the scanner to the OBD2 port.
- Do not attempt to disassemble or repair the scanner yourself.
-
Battery Care:
- If your scanner has a rechargeable battery, follow the manufacturer’s recommendations for charging and storage.
- Avoid overcharging the battery.
- Replace the battery if it no longer holds a charge.
7. Common Issues and Troubleshooting Tips for Auro OBD2 Scanners
What are some common issues encountered with Auro OBD2 scanners and how can they be resolved? Common issues include connection problems, software glitches, and incorrect code readings, which can often be resolved through troubleshooting steps like checking connections, updating software, and consulting online resources at OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN. According to data from automotive forums, approximately 60% of OBD2 scanner issues can be resolved with basic troubleshooting steps.
Here are some common issues and troubleshooting tips:
-
Connection Problems:
-
Issue: Scanner fails to connect to the vehicle.
-
Troubleshooting:
- Ensure the scanner is securely plugged into the OBD2 port.
- Check the vehicle’s ignition is turned on (but engine not started).
- Verify the scanner is compatible with the vehicle’s make and model.
- Check the OBD2 port for damage or corrosion.
- Try connecting the scanner to a different vehicle to rule out a scanner issue.
-
-
Software Glitches:
-
Issue: Scanner freezes, displays errors, or fails to perform functions.
-
Troubleshooting:
- Restart the scanner.
- Check for and install any available software updates.
- Perform a factory reset (if available) to restore the scanner to its default settings.
- Contact customer support for assistance.
-
-
Incorrect Code Readings:
-
Issue: Scanner displays inaccurate or inconsistent DTCs.
-
Troubleshooting:
- Verify the DTCs with a different scanner to confirm accuracy.
- Consult an online database or repair manual to ensure the DTC definitions are correct.
- Check for any technical service bulletins (TSBs) related to the DTCs.
- Inspect the vehicle for any obvious signs of damage or malfunction.
-
-
Power Issues:
-
Issue: Scanner fails to power on or loses power during use.
-
Troubleshooting:
- Ensure the vehicle’s battery is charged.
- Check the scanner’s power cable and connectors for damage.
- Replace the scanner’s battery (if applicable).
-
-
Communication Errors:
-
Issue: Scanner displays “No Communication” or similar error messages.
-
Troubleshooting:
- Ensure the scanner is compatible with the vehicle’s communication protocol.
- Check for any damaged or corroded pins in the OBD2 connector.
- Inspect the vehicle’s wiring harness for damage or loose connections.
- Consult a qualified technician for assistance.
-
 Auro OBD2 Scanner Troubleshooting
Auro OBD2 Scanner Troubleshooting
8. Advanced Diagnostic Capabilities of Auro OBD2 Scanners
What advanced diagnostic capabilities do Auro OBD2 scanners offer for in-depth vehicle analysis? Auro OBD2 scanners offer advanced capabilities like bi-directional control, actuation tests, and module programming, providing comprehensive diagnostic solutions for complex vehicle issues. According to a study by the Automotive Management Institute (AMI), shops that utilize advanced diagnostic tools see a 30% increase in diagnostic accuracy and a 20% reduction in repair times.
-
Bi-Directional Control:
- Function: Allows the scanner to send commands to vehicle systems to test functionality.
- Example: Activating fuel injectors, turning on/off the cooling fan, cycling the ABS pump.
- Benefit: Verifies the functionality of components and systems, helping to pinpoint the source of problems.
-
Actuation Tests:
- Function: Tests the operation of specific actuators, such as solenoids, relays, and motors.
- Example: Testing the operation of the EGR valve, throttle body, or fuel pump.
- Benefit: Ensures actuators are functioning correctly and responding to commands.
-
Module Programming:
- Function: Allows the scanner to program or reprogram vehicle modules, such as the ECU, TCM, or ABS module.
- Example: Flashing a new software update to the ECU to improve performance or fix a bug.
- Benefit: Keeps vehicle systems up-to-date and ensures optimal performance.
-
Key Programming:
- Function: Programs new keys for vehicles with immobilizer systems.
- Example: Programming a new key fob or transponder key.
- Benefit: Allows users to replace lost or damaged keys.
-
ABS Bleeding:
- Function: Performs ABS bleeding procedures to remove air from the brake system.
- Example: Bleeding the ABS module after replacing brake lines or components.
- Benefit: Ensures proper brake system function and prevents ABS issues.
-
Service Resets:
- Function: Resets service lights and maintenance reminders.
- Example: Resetting the oil change light, tire pressure monitoring system (TPMS), or brake pad wear indicator.
- Benefit: Simplifies maintenance tasks and ensures timely servicing.
9. Choosing the Right Auro OBD2 Scanner for Your Needs
How do you select the most suitable Auro OBD2 scanner based on your specific diagnostic requirements? Selecting the right scanner involves assessing your needs, comparing models based on features and vehicle compatibility, and considering factors like budget and user-friendliness. According to a survey by the Automotive Aftermarket Industry Association (AAIA), 70% of professional technicians prioritize vehicle coverage and diagnostic capabilities when choosing an OBD2 scanner.
-
Assess Your Needs:
- DIY Enthusiast: Basic code reading and clearing capabilities may suffice.
- Professional Mechanic: Advanced functions like bi-directional control, module programming, and service resets are essential.
- Specific Vehicle Makes/Models: Ensure the scanner supports the vehicles you work on.
-
Compare Models:
- Features: Evaluate the features offered by different models, such as live data streaming, I/M readiness, O2 sensor tests, and special functions.
- Vehicle Compatibility: Check the scanner’s vehicle coverage list to ensure it supports the makes and models you need.
- User Interface: Consider the ease of use and intuitiveness of the scanner’s interface.
- Software Updates: Look for scanners with regular software updates to support new vehicles and features.
-
Consider Your Budget:
- Entry-Level Scanners: Affordable options for basic diagnostics.
- Mid-Range Scanners: Offer a balance of features and price for intermediate users.
- High-End Scanners: Provide advanced capabilities for professional use, but come with a higher price tag.
-
Read Reviews:
- Research user reviews and ratings to get insights into the scanner’s performance and reliability.
- Look for reviews from users with similar needs and experience levels.
-
Check for Support:
- Ensure the manufacturer offers reliable customer support and technical assistance.
- Check for online resources, such as user manuals, FAQs, and troubleshooting guides.
-
Try Before You Buy:
- If possible, try out the scanner before purchasing to ensure it meets your needs and expectations.
- Some retailers offer demonstration units or trial periods.
10. Where to Buy Auro OBD2 Scanners and Related Accessories
Where can you purchase Auro OBD2 scanners and find necessary accessories? Auro OBD2 scanners and accessories can be purchased from online retailers like Amazon and specialized automotive parts stores, as well as directly through the OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN website, ensuring access to a wide selection and reliable support. According to a report by IBISWorld, online sales of automotive parts and accessories have grown by 15% annually over the past five years, indicating a strong trend towards online purchasing.
-
Online Retailers:
- Amazon: Offers a wide selection of Auro OBD2 scanners and accessories at competitive prices.
- eBay: Provides access to new and used scanners, as well as replacement parts and accessories.
-
Specialized Automotive Parts Stores:
- AutoZone: Carries a range of OBD2 scanners and diagnostic tools, including Auro models.
- Advance Auto Parts: Offers a selection of scanners and accessories, with knowledgeable staff to assist with your purchase.
- Napa Auto Parts: Provides access to high-quality scanners and diagnostic equipment for professional mechanics and DIY enthusiasts.
-
Manufacturer’s Website:
- OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN: Purchase directly from the manufacturer for the latest models and guaranteed compatibility.
-
Local Automotive Tool Suppliers:
- Check for local suppliers that specialize in automotive tools and equipment.
- These suppliers may offer personalized service and support.
When purchasing an Auro OBD2 scanner, consider the following accessories:
- OBD2 Extension Cable: Provides extra length for connecting the scanner to hard-to-reach OBD2 ports.
- Protective Case: Protects the scanner from damage during storage and transport.
- Software Update Subscription: Ensures access to the latest software updates and features.
- Diagnostic Adapters: Allows the scanner to connect to vehicles with non-standard OBD2 ports.
- Battery Charger: Keeps the scanner’s battery charged for optimal performance.
11. The Future of OBD2 Scanning Technology
What are the emerging trends and future directions in OBD2 scanning technology? The future of OBD2 scanning includes enhanced wireless connectivity, cloud-based diagnostics, and integration with AI for predictive maintenance, transforming vehicle diagnostics. According to a forecast by MarketsandMarkets, the automotive diagnostics market is expected to reach $46.7 billion by 2027, driven by technological advancements and increasing vehicle complexity.
-
Wireless Connectivity:
- Trend: Increasing use of Bluetooth and Wi-Fi for connecting scanners to vehicles and mobile devices.
- Benefit: Eliminates the need for cables, providing greater flexibility and convenience.
- Impact: Enables remote diagnostics and data logging.
-
Cloud-Based Diagnostics:
- Trend: Storing diagnostic data in the cloud for access from anywhere.
- Benefit: Allows for remote monitoring, data analysis, and collaboration.
- Impact: Facilitates predictive maintenance and proactive repairs.
-
Artificial Intelligence (AI) Integration:
- Trend: Using AI algorithms to analyze diagnostic data and predict potential issues.
- Benefit: Provides more accurate and efficient diagnostics.
- Impact: Enables predictive maintenance and reduces downtime.
-
Augmented Reality (AR) Applications:
- Trend: Using AR technology to overlay diagnostic information onto the vehicle.
- Benefit: Provides visual guidance and simplifies complex repairs.
- Impact: Enhances the user experience and improves diagnostic accuracy.
-
Enhanced Vehicle Coverage:
- Trend: Expanding support for new vehicle makes and models.
- Benefit: Ensures compatibility with the latest vehicles.
- Impact: Keeps scanners up-to-date and relevant.
-
Improved User Interfaces:
- Trend: Designing more intuitive and user-friendly interfaces.
- Benefit: Simplifies operation and reduces learning curve.
- Impact: Makes scanners accessible to a wider range of users.
-
Integration with Mobile Devices:
- Trend: Developing mobile apps that connect to scanners and provide diagnostic information.
- Benefit: Allows users to perform diagnostics on the go.
- Impact: Enhances convenience and accessibility.
 Auro OBD2 Scanner Future Technology
Auro OBD2 Scanner Future Technology
12. OBD2 Scanner Legality and Usage Regulations
What are the legal considerations and regulations surrounding the use of OBD2 scanners? Legal considerations include compliance with emissions standards and data privacy laws, ensuring responsible and ethical use of diagnostic information. According to the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), tampering with a vehicle’s OBD system can result in fines and penalties under the Clean Air Act.
-
Emissions Standards:
- Regulation: OBD2 systems are mandated by law to monitor vehicle emissions.
- Compliance: Ensure your vehicle meets emissions standards by addressing any issues identified by the OBD2 scanner.
- Legal Implications: Tampering with the OBD2 system or emissions controls can result in fines and penalties.
-
Data Privacy:
- Regulation: Data collected by OBD2 scanners may include personal information.
- Privacy Protection: Handle diagnostic data responsibly and protect your privacy.
- Legal Implications: Comply with data privacy laws and regulations.
-
Vehicle Modifications:
- Regulation: Modifying a vehicle’s engine or emissions system may affect its compliance with OBD2 standards.
- Compliance: Ensure any modifications are legal and do not violate emissions regulations.
- Legal Implications: Illegal modifications can result in fines and voiding of warranties.
-
Professional Use:
- Regulation: Mechanics and technicians must comply with industry standards and regulations when using OBD2 scanners.
- Certification: Consider obtaining certifications to demonstrate your expertise in vehicle diagnostics.
- Legal Implications: Failure to comply with regulations can result in disciplinary actions and loss of licenses.
-
Warranty Considerations:
- Regulation: Using an OBD2 scanner to diagnose and repair your vehicle may affect your warranty coverage.
- Warranty Protection: Check your vehicle’s warranty terms and conditions before performing any repairs.
- Legal Implications: Unauthorized repairs can void your warranty.
-
Right to Repair:
- Regulation: The “Right to Repair” movement advocates for consumer access to diagnostic and repair information.
- Access to Information: Support efforts to ensure access to the tools and information needed to repair your vehicle.
- Legal Implications: Legislation may be enacted to protect consumers’ right to repair their vehicles.
13. OBD2 Scanner Safety Precautions
What safety precautions should be taken when using an OBD2 scanner for vehicle diagnostics and repairs? Safety precautions include wearing protective gear, ensuring proper ventilation, and following safe electrical practices to prevent injury and equipment damage. According to the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA), vehicle-related injuries account for over 40,000 emergency room visits each year, highlighting the importance of safety precautions.
-
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE):
- Recommendation: Wear safety glasses, gloves, and appropriate clothing.
- Purpose: Protect yourself from potential hazards, such as chemicals, sharp objects, and electrical shocks.
- Usage: Always wear PPE when working on a vehicle.
-
Proper Ventilation:
- Recommendation: Work in a well-ventilated area.
- Purpose: Avoid inhaling harmful fumes from exhaust, solvents, and other chemicals.
- Usage: Ensure adequate ventilation when running the engine or working with chemicals.
-
Electrical Safety:
- Recommendation: Use caution when working with electrical components.
- Purpose: Prevent electrical shocks and damage to the vehicle’s electrical system.
- Usage: Disconnect the battery before working on electrical components.
-
Vehicle Stability:
- Recommendation: Ensure the vehicle is properly supported before working underneath it.
- Purpose: Prevent the vehicle from falling and causing serious injury.
- Usage: Use jack stands and wheel chocks to secure the vehicle.
-
Fire Safety:
- Recommendation: Keep a fire extinguisher nearby.
- Purpose: Extinguish fires quickly and prevent them from spreading.
- Usage: Know how to use a fire extinguisher and keep it readily accessible.
-
Chemical Handling:
- Recommendation: Handle chemicals with care and follow the manufacturer’s instructions.
- Purpose: Prevent skin irritation, respiratory problems, and other health issues.
- Usage: Wear gloves and eye protection when working with chemicals.
-
Tool Safety:
- Recommendation: Use tools properly and keep them in good condition.
- Purpose: Prevent injuries and damage to the vehicle.
- Usage: Follow the manufacturer’s instructions and inspect tools regularly.
-
Workspace Safety:
- Recommendation: Keep your workspace clean and organized.
- Purpose: Prevent accidents and injuries.
- Usage: Remove clutter and debris from the work area.
 Auro OBD2 Scanner Safety
Auro OBD2 Scanner Safety
14. Tips for Improving Your Vehicle’s Performance with OBD2 Data
How can you use OBD2 data to enhance your vehicle’s overall performance and efficiency? OBD2 data can be used to monitor engine health, optimize fuel efficiency, and identify potential issues early, leading to improved vehicle performance. According to a study by the Oak Ridge National Laboratory, optimizing engine parameters based on OBD2 data can improve fuel efficiency by up to 10%.
-
Monitor Engine Health:
- Tip: Regularly check live data parameters such as engine RPM, coolant temperature, and O2 sensor readings.
- Benefit: Identifies potential issues early and prevents costly repairs.
- Example: Monitoring coolant temperature can help detect a failing thermostat.
-
Optimize Fuel Efficiency:
- Tip: Use OBD2 data to identify and address issues that can affect fuel economy, such as a faulty O2 sensor or vacuum leak.
- Benefit: Improves gas mileage and reduces fuel costs.
- Example: Replacing a faulty O2 sensor can improve fuel efficiency by up to 40%.
-
Identify Performance Issues:
- Tip: Use OBD2 data to diagnose and resolve performance issues such as misfires, rough idling, and hesitation.
- Benefit: Restores vehicle performance and prevents further damage.
- Example: Diagnosing and repairing a misfire can improve engine power and smoothness.
-
Track Vehicle History:
- Tip: Use OBD2 data to track vehicle maintenance and repair history.
- Benefit: Helps you stay on top of maintenance tasks and identify recurring issues.
- Example: Logging DTCs and repairs can help you identify patterns and prevent future problems.
-
Customize Vehicle Settings:
- Tip: Some OBD2 scanners allow you to customize vehicle settings such as shift points, throttle response, and rev limits.
- Benefit: Optimizes vehicle performance to your preferences.
- Example: Adjusting shift points can improve acceleration and fuel economy.
-
Troubleshoot Error Codes:
- Tip: Use OBD2 scanners to quickly identify and resolve error codes
- Benefit: Quickly resolve the vehicle problem
- Example: Resolve the causes of the P0420 code.
15. Debunking Common Myths About OBD2 Scanners
What are some common misconceptions about OBD2 scanners and their capabilities? Common myths include the belief that scanners can fix problems automatically or that all scanners offer the same functionality, which can lead to unrealistic expectations. According to a survey by Consumer Reports, 30% of car owners believe that an OBD2 scanner can automatically diagnose and fix vehicle problems without further intervention.
-
Myth 1: OBD2 scanners can fix problems automatically.
- Fact: OBD2 scanners only identify problems; they do not fix them.
- Explanation: The scanner provides diagnostic information, but repairs must be performed manually.
-
Myth 2: All OBD2 scanners are the same.
- Fact: OBD2 scanners vary in features, vehicle coverage, and capabilities.
- Explanation: Some scanners offer advanced functions like bi-directional control and module programming, while others are limited to basic code reading.
-
Myth 3: You need to be a mechanic to use an OBD2 scanner.
- Fact: OBD2 scanners are user-friendly and can be used by anyone with basic knowledge of vehicle diagnostics.
- Explanation: Many scanners come with intuitive interfaces and helpful resources.
-
Myth 4: OBD2 scanners can diagnose any problem with your car.
- Fact: OBD2 scanners are limited to diagnosing issues related to the engine, transmission, and emissions systems.
- Explanation: They cannot diagnose problems with other systems like the brakes, suspension, or interior.
-
Myth 5: Clearing a code with an OBD2 scanner fixes the problem.
- Fact: Clearing a code only removes the error message; it does not fix the underlying problem.
- Explanation: The code will likely return if the issue is not addressed.
-
Myth 6: OBD2 scanners are only for old cars.
- Fact: OBD2 scanners are compatible with all vehicles manufactured after 1996.
- Explanation: OBD2 is a standardized system required for all modern vehicles.
-
Myth 7: You can only use an OBD2 scanner once.
- Fact: OBD2 scanners can be used multiple times to diagnose different issues.
- Explanation: The scanner can read and clear codes as needed.
-
Myth 8: OBD2 scanners are expensive.
- Fact: OBD2 scanners are available at a wide range of price points, with basic models being quite affordable.
- Explanation: You can find a scanner that fits your budget and needs.
FAQ About Auro OBD2 Scanners
-
What is an OBD2 scanner?
An OBD2 scanner is a diagnostic tool used to