The Best Pc Obd2 Software empowers you with in-depth vehicle diagnostics, allowing you to identify and address car issues efficiently. OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN offers expert insights into selecting the optimal software for your needs. This article delves into the top PC-based OBD2 solutions, focusing on their features, benefits, and suitability for various users, ensuring you make an informed decision for your automotive diagnostic needs.
Contents
- 1. What is OBD2 and Why Do You Need Software for Your PC?
- 1.1 Understanding the OBD2 System
- 1.1.1 Key Components of the OBD2 System
- 1.1.2 How OBD2 Works
- 1.2 Why Use PC-Based OBD2 Software?
- 1.2.1 Advantages of PC-Based OBD2 Software
- 1.2.2 Who Benefits from PC-Based OBD2 Software?
- 2. Key Features to Look for in the Best PC OBD2 Software
- 2.1 Comprehensive Code Reading and Interpretation
- 2.1.1 Standard vs. Manufacturer-Specific Codes
- 2.1.2 Importance of a Comprehensive DTC Database
- 2.2 Live Data Monitoring and Graphing
- 2.2.1 Essential Data Parameters to Monitor
- 2.2.2 Benefits of Real-Time Data Visualization
- 2.3 Bi-Directional Control and Active Testing
- 2.3.1 Examples of Bi-Directional Control Functions
- 2.3.2 Why Bi-Directional Control is Important for Diagnostics
- 2.4 Data Logging and Reporting Capabilities
- 2.4.1 Benefits of Data Logging
- 2.4.2 Key Elements of a Comprehensive Report
- 2.5 Ease of Use and User Interface
- 2.5.1 Importance of Intuitive Navigation
- 2.5.2 Customization Options for a Personalized Experience
- 3. Top PC OBD2 Software Options in 2024
- 3.1 TOAD Pro: Comprehensive Diagnostics and ECU Remapping
- 3.1.1 Key Features of TOAD Pro
- 3.1.2 Pros and Cons of TOAD Pro
- 3.2 AutoEnginuity ScanTool: Brand-Specific Diagnostics
- 3.2.1 Key Features of AutoEnginuity ScanTool
- 3.2.2 Pros and Cons of AutoEnginuity ScanTool
- 3.3 PCMScan: Customizable Dashboards and Data Logging
- 3.3.1 Key Features of PCMScan
- 3.3.2 Pros and Cons of PCMScan
- 3.4 ProScan: User-Friendly Interface and Performance Testing
- 3.4.1 Key Features of ProScan
- 3.4.2 Pros and Cons of ProScan
- 3.5 OBD Auto Doctor: Mac OS X Compatibility and DTC Database
- 3.5.1 Key Features of OBD Auto Doctor
- 3.5.2 Pros and Cons of OBD Auto Doctor
- 4. Step-by-Step Guide to Using PC OBD2 Software
- 4.1 Connecting Your PC to the Vehicle
- 4.1.1 Choosing the Right OBD2 Adapter
- 4.1.2 Step-by-Step Connection Instructions
- 4.2 Installing and Configuring the Software
- 4.2.1 Software Installation Process
- 4.2.2 Configuring Software Settings for Optimal Performance
- 4.3 Reading and Interpreting Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
- 4.3.1 How to Read DTCs
- 4.3.2 Understanding the Meaning of Different DTCs
- 4.4 Monitoring Live Data and Performing Active Tests
- 4.4.1 How to Monitor Live Data
- 4.4.2 Performing Active Tests for Diagnostic Purposes
- 4.5 Clearing Codes and Resetting the ECU
- 4.5.1 When and How to Clear Codes
- 4.5.2 Potential Risks of Resetting the ECU Without Addressing the Underlying Issue
- 5. OBD2 Software for Specific Needs and Budgets
- 5.1 Best OBD2 Software for DIY Enthusiasts
- 5.1.1 Recommended Software Options
- 5.1.2 Key Features for DIYers
- 5.2 Best OBD2 Software for Professional Mechanics
- 5.2.1 Recommended Software Options
- 5.2.2 Key Features for Professionals
- 5.3 Best OBD2 Software for Mac Users
- 5.3.1 Recommended Software Options
- 5.3.2 Key Features for Mac Users
- 5.4 Free vs. Paid OBD2 Software: What You Need to Know
- 5.4.1 Limitations of Free OBD2 Software
- 5.4.2 Benefits of Investing in Paid Software
- 6. Common OBD2 Error Codes and How to Troubleshoot Them
- 6.1 P0171 and P0174: System Too Lean
- 6.1.1 Potential Causes
- 6.1.2 Troubleshooting Steps
- 6.2 P0300: Random/Multiple Cylinder Misfire Detected
- 6.2.1 Potential Causes
- 6.2.2 Troubleshooting Steps
- 6.3 P0420: Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold
- 6.3.1 Potential Causes
- 6.3.2 Troubleshooting Steps
- 6.4 P0101: Mass Air Flow (MAF) Sensor Range/Performance Problem
- 6.4.1 Potential Causes
- 6.4.2 Troubleshooting Steps
- 6.5 P0113: Intake Air Temperature Sensor Circuit High Input
- 6.5.1 Potential Causes
- 6.5.2 Troubleshooting Steps
- 7. Tips for Optimizing Your Use of PC OBD2 Software
- 7.1 Keeping Your Software Up to Date
- 7.1.1 Benefits of Regular Software Updates
- 7.1.2 How to Check for and Install Updates
- 7.2 Properly Maintaining Your OBD2 Adapter
- 7.2.1 Cleaning and Storage Tips
- 7.2.2 Troubleshooting Connection Issues
- 7.3 Understanding Vehicle-Specific Diagnostic Procedures
- 7.3.1 Consulting Vehicle Repair Manuals
- 7.3.2 Utilizing Online Resources and Forums
- 8. The Future of OBD2 Technology
- 8.1 Enhanced Diagnostics and Data Analysis
- 8.1.1 Integration with Cloud-Based Services
- 8.1.2 Predictive Maintenance Capabilities
- 8.2 Wireless Connectivity and Remote Diagnostics
- 8.2.1 Advancements in Bluetooth and Wi-Fi Technology
- 8.2.2 Implications for Vehicle Maintenance and Repair
- 9. FAQ About PC OBD2 Software
- What is an OBD2 scanner?
- How do I read OBD2 fault codes?
- What are common car problems and how to fix them?
- What is the best OBD2 software for a PC?
- Can I use OBD2 software on my Mac?
- Is free OBD2 software reliable?
- How often should I update my OBD2 software?
- What are the benefits of monitoring live data?
- What is bi-directional control and why is it important?
- How can OBD2 software save me money on car repairs?
- 10. Take Action: Get Started with PC OBD2 Software Today
1. What is OBD2 and Why Do You Need Software for Your PC?
On-Board Diagnostics version 2 (OBD2) is a standardized system that provides access to vehicle health information, and you need software for your PC to interpret this data. According to the EPA, OBD2 was standardized in 1996 to monitor emissions-related components. Using PC-based OBD2 software allows for in-depth analysis beyond basic code reading, offering live data, advanced diagnostics, and customization options.
1.1 Understanding the OBD2 System
The OBD2 system is a vital component of modern vehicles, offering a standardized interface for accessing a wealth of data about your car’s performance and health. It’s essentially a window into your vehicle’s inner workings, providing insights that can help you diagnose problems, monitor performance, and maintain your car in optimal condition.
1.1.1 Key Components of the OBD2 System
- Sensors: These devices monitor various parameters throughout the vehicle, such as engine temperature, oxygen levels, and throttle position.
- Engine Control Unit (ECU): Often referred to as the “brain” of the car, the ECU collects data from sensors, interprets it, and adjusts various systems to optimize performance.
- OBD2 Port: A standardized connector, usually located under the dashboard, that allows you to connect a scan tool or PC interface to access the data collected by the ECU.
- Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs): Standardized codes that the ECU generates when it detects a problem. These codes help identify the source of the issue.
 OBD2 Port Location
OBD2 Port Location
1.1.2 How OBD2 Works
The OBD2 system constantly monitors the performance of various vehicle systems. When a problem is detected, the ECU stores a corresponding DTC and may illuminate the “check engine” light on the dashboard. By connecting an OBD2 scanner or PC interface, you can retrieve these DTCs and other data, providing valuable insights into the nature of the problem.
1.2 Why Use PC-Based OBD2 Software?
While handheld OBD2 scanners are convenient, PC-based software offers several advantages, especially for those seeking in-depth diagnostics and analysis. According to a study by the University of California, Berkeley, PC-based software often provides more detailed data and advanced features compared to handheld devices.
1.2.1 Advantages of PC-Based OBD2 Software
- Larger Display: PC screens provide a more comprehensive view of data, making it easier to analyze complex information.
- Advanced Features: PC software often includes features like data logging, graphing, and customizable dashboards, which are not typically found on handheld scanners.
- Software Updates: PC-based software can be easily updated with the latest diagnostic information and features.
- Report Generation: PC software allows you to generate detailed reports that can be shared with mechanics or used for record-keeping.
1.2.2 Who Benefits from PC-Based OBD2 Software?
- DIY Mechanics: Home mechanics can use PC software to diagnose and repair their own vehicles, saving money on labor costs.
- Car Enthusiasts: Enthusiasts can use the software to monitor their vehicle’s performance and make informed modifications.
- Small Repair Shops: Smaller shops can use PC-based software as a cost-effective alternative to expensive professional scan tools.
2. Key Features to Look for in the Best PC OBD2 Software
When selecting the best PC OBD2 software, several key features can significantly impact its effectiveness and usability. According to a report by the National Institute for Automotive Service Excellence (ASE), the most valuable features include comprehensive code reading, live data monitoring, and bi-directional control capabilities.
2.1 Comprehensive Code Reading and Interpretation
The primary function of OBD2 software is to read and interpret Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs). The best software should provide detailed descriptions of the codes, potential causes, and recommended solutions.
2.1.1 Standard vs. Manufacturer-Specific Codes
- Standard Codes: These codes are defined by the Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE) and are common across all vehicles.
- Manufacturer-Specific Codes: These codes are unique to specific vehicle manufacturers and provide more detailed information about problems within those vehicles.
The software should be able to read both standard and manufacturer-specific codes to provide a comprehensive diagnosis.
2.1.2 Importance of a Comprehensive DTC Database
A comprehensive DTC database is essential for accurate code interpretation. The software should include a database with detailed information about thousands of codes, including potential causes, symptoms, and repair instructions.
2.2 Live Data Monitoring and Graphing
Live data monitoring allows you to view real-time data from your vehicle’s sensors, providing valuable insights into its performance. Graphing capabilities enable you to visualize this data, making it easier to identify trends and anomalies.
2.2.1 Essential Data Parameters to Monitor
- Engine RPM: Revolutions per minute, indicating engine speed.
- Coolant Temperature: Monitors the engine’s cooling system.
- Oxygen Sensor Readings: Indicates the efficiency of the combustion process.
- Fuel Trim: Adjustments made by the ECU to optimize fuel delivery.
- Vehicle Speed: Real-time speed of the vehicle.
2.2.2 Benefits of Real-Time Data Visualization
Real-time data visualization helps you identify intermittent problems and monitor the effects of repairs. By graphing data over time, you can see how different parameters interact and identify potential issues before they trigger a DTC.
2.3 Bi-Directional Control and Active Testing
Bi-directional control allows you to send commands to the vehicle’s ECU to activate certain functions or components. Active testing enables you to diagnose problems by testing specific systems, such as the fuel pump or cooling fan.
2.3.1 Examples of Bi-Directional Control Functions
- Fuel Injector Activation: Test individual fuel injectors to check for proper operation.
- Cooling Fan Control: Activate the cooling fan to check its functionality.
- EGR Valve Control: Test the Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) valve to ensure it is opening and closing properly.
2.3.2 Why Bi-Directional Control is Important for Diagnostics
Bi-directional control is essential for diagnosing complex problems that may not trigger DTCs. By actively testing components, you can isolate problems and verify repairs.
2.4 Data Logging and Reporting Capabilities
Data logging allows you to record live data for later analysis. Reporting capabilities enable you to generate detailed reports that can be shared with mechanics or used for record-keeping.
2.4.1 Benefits of Data Logging
- Identify Intermittent Problems: Capture data during specific driving conditions to identify problems that only occur sporadically.
- Analyze Vehicle Performance: Review data to assess the vehicle’s overall performance and identify areas for improvement.
- Compare Data Over Time: Track changes in vehicle performance over time to identify potential problems early.
2.4.2 Key Elements of a Comprehensive Report
- DTC Information: Detailed descriptions of any stored DTCs.
- Live Data: A summary of the live data collected during the test.
- Graphs: Visual representations of the data to highlight trends and anomalies.
- Recommendations: Suggested repairs or maintenance based on the diagnostic results.
2.5 Ease of Use and User Interface
The best PC OBD2 software should be easy to use, with a clear and intuitive user interface. A well-designed interface will save you time and frustration, allowing you to focus on diagnosing and repairing your vehicle.
2.5.1 Importance of Intuitive Navigation
The software should be easy to navigate, with clear menus and logical organization. You should be able to quickly access the features you need without having to search through complicated menus.
2.5.2 Customization Options for a Personalized Experience
Customization options allow you to tailor the software to your specific needs and preferences. This may include customizable dashboards, configurable data displays, and adjustable settings.
 OBD2 Software Dashboard
OBD2 Software Dashboard
3. Top PC OBD2 Software Options in 2024
Selecting the right PC OBD2 software can greatly improve your ability to diagnose and maintain your vehicle. Here are some of the top options available in 2024, each offering a unique set of features and capabilities.
3.1 TOAD Pro: Comprehensive Diagnostics and ECU Remapping
TOAD (Total OBD & ECU Auto Diagnostics) Pro is a comprehensive OBD2 software package designed for both home users and professional mechanics. According to user reviews on automotive forums, TOAD Pro is praised for its extensive vehicle compatibility and advanced features.
3.1.1 Key Features of TOAD Pro
- Extensive Vehicle Compatibility: Supports a wide range of vehicles, including cars, trucks, and SUVs.
- Comprehensive Code Reading: Reads and interprets standard and manufacturer-specific DTCs.
- Live Data Monitoring: Provides real-time data from various vehicle sensors.
- ECU Remapping: Allows you to modify your vehicle’s ECU settings to optimize performance and fuel economy.
- User-Friendly Interface: Easy-to-use interface with customizable dashboards and data displays.
3.1.2 Pros and Cons of TOAD Pro
Pros:
- Comprehensive feature set
- Extensive vehicle compatibility
- ECU remapping capabilities
- User-friendly interface
Cons:
- Higher price point compared to other options
- ECU remapping requires advanced knowledge
3.2 AutoEnginuity ScanTool: Brand-Specific Diagnostics
AutoEnginuity’s ScanTool is a brand-specific diagnostic tool that offers in-depth diagnostics for a wide range of vehicles. According to the company’s website, ScanTool supports brands like BMW, Ford, GM, Chrysler, Nissan, Hyundai, Kia, Land Rover, Jaguar, and Honda.
3.2.1 Key Features of AutoEnginuity ScanTool
- Brand-Specific Diagnostics: Provides in-depth diagnostics for specific vehicle brands.
- ABS, Airbag, and Transmission Access: Accesses ABS, airbag, and transmission controllers.
- Live Data Monitoring: Monitors real-time data from various vehicle sensors.
- Bi-Directional Controls: Offers bi-directional control for active testing and component activation.
- Data Logging and Reporting: Logs data for later analysis and generates detailed reports.
3.2.2 Pros and Cons of AutoEnginuity ScanTool
Pros:
- In-depth diagnostics for specific brands
- Access to ABS, airbag, and transmission controllers
- Bi-directional control capabilities
- Data logging and reporting features
Cons:
- High price point
- May require additional modules for full functionality
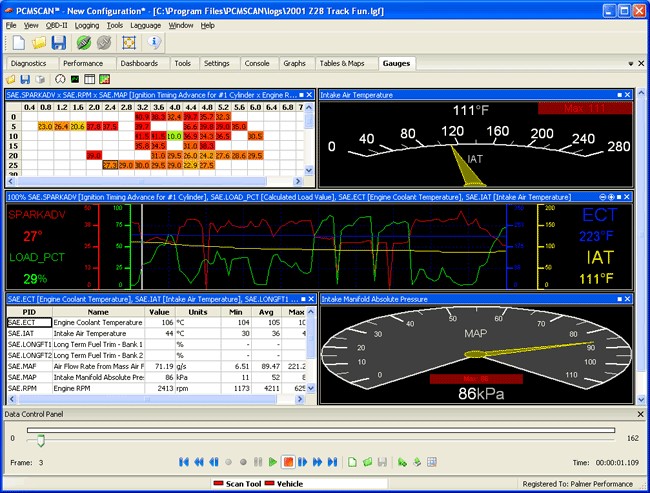
3.3 PCMScan: Customizable Dashboards and Data Logging
PCMScan is a fully featured OBD2 diagnostic software that supports a wide variety of OBD hardware interfaces. According to user reviews on automotive forums, PCMScan is praised for its customizable dashboards and data logging capabilities.
3.3.1 Key Features of PCMScan
- Customizable Dashboards: Allows you to create personalized dashboards with the data parameters you want to monitor.
- Data Logging: Logs data for later analysis.
- DTC Reading and Interpretation: Reads and interprets standard DTCs.
- Freeze Frame Data: Captures data when a DTC is triggered.
- OBD-II Terminal: Provides an OBD-II terminal for sending custom commands to the vehicle.
3.3.2 Pros and Cons of PCMScan
Pros:
- Customizable dashboards
- Data logging capabilities
- OBD-II terminal for advanced users
- Affordable price point
Cons:
- Outdated interface
- Limited manufacturer-specific code support
- No recent updates
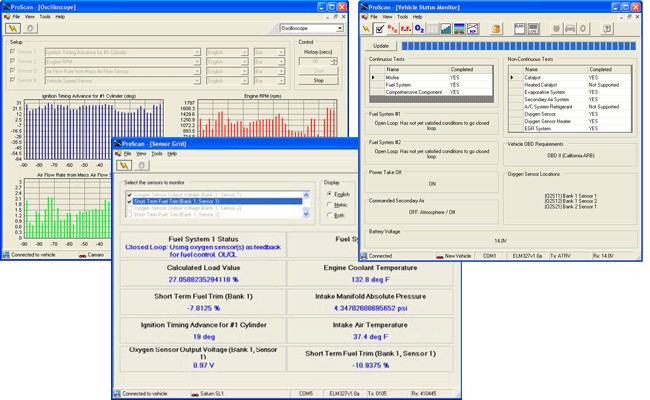
3.4 ProScan: User-Friendly Interface and Performance Testing
ProScan is an OBD2 software package that offers a user-friendly interface and performance testing capabilities. According to the software’s website, ProScan allows you to read and clear DTCs, monitor live data, and test your vehicle’s performance.
3.4.1 Key Features of ProScan
- User-Friendly Interface: Easy-to-use interface for beginners.
- DTC Reading and Clearing: Reads and clears standard DTCs.
- Live Data Monitoring: Monitors real-time data from various vehicle sensors.
- Performance Testing: Tests your vehicle’s 0-60 mph time, horsepower, and torque.
- Fuel Economy Adjustment: Adjusts fuel economy settings.
3.4.2 Pros and Cons of ProScan
Pros:
- User-friendly interface
- Performance testing capabilities
- Fuel economy adjustment settings
- Affordable price point
Cons:
- Limited manufacturer-specific code support
- Basic feature set
3.5 OBD Auto Doctor: Mac OS X Compatibility and DTC Database
OBD Auto Doctor is a sophisticated OBD2 car diagnostic tool that is compatible with Mac OS X. According to the software’s website, OBD Auto Doctor allows you to check and reset codes and communicate directly with your car’s OBD2 system.
3.5.1 Key Features of OBD Auto Doctor
- Mac OS X Compatibility: Compatible with Mac OS X.
- DTC Reading and Clearing: Reads and clears standard DTCs.
- Live Data Monitoring: Monitors real-time data from various vehicle sensors.
- DTC Database: Includes a DTC database with over 14,000 alarm codes.
- Fuel Emission and Consumption Monitoring: Monitors fuel emission and consumption.
3.5.2 Pros and Cons of OBD Auto Doctor
Pros:
- Mac OS X compatibility
- Comprehensive DTC database
- Fuel emission and consumption monitoring
- User-friendly interface
Cons:
- Limited manufacturer-specific code support
- Higher price point compared to other options
4. Step-by-Step Guide to Using PC OBD2 Software
Using PC OBD2 software can seem daunting, but with a step-by-step guide, you can easily diagnose and maintain your vehicle. Here’s a comprehensive guide to get you started.
4.1 Connecting Your PC to the Vehicle
The first step is to connect your PC to the vehicle using an OBD2 adapter. This adapter serves as the interface between your PC and the vehicle’s OBD2 port.
4.1.1 Choosing the Right OBD2 Adapter
There are several types of OBD2 adapters available, including:
- USB Adapters: These adapters connect directly to your PC via a USB cable.
- Bluetooth Adapters: These adapters connect wirelessly to your PC via Bluetooth.
- Wi-Fi Adapters: These adapters connect wirelessly to your PC via Wi-Fi.
Choose an adapter that is compatible with your PC and the OBD2 software you plan to use.
4.1.2 Step-by-Step Connection Instructions
- Locate the OBD2 port in your vehicle (typically under the dashboard).
- Plug the OBD2 adapter into the port.
- If using a USB adapter, connect the USB cable to your PC.
- If using a Bluetooth or Wi-Fi adapter, pair the adapter with your PC.
4.2 Installing and Configuring the Software
Once you have connected the adapter, the next step is to install and configure the OBD2 software on your PC.
4.2.1 Software Installation Process
- Download the OBD2 software from the manufacturer’s website.
- Run the installation program and follow the on-screen instructions.
- Activate the software using the provided license key.
4.2.2 Configuring Software Settings for Optimal Performance
- Open the OBD2 software and go to the settings menu.
- Select the correct OBD2 adapter type.
- Configure the communication settings (e.g., COM port, baud rate).
- Test the connection to ensure the software can communicate with the vehicle.
4.3 Reading and Interpreting Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
After connecting the adapter and configuring the software, you can start reading and interpreting DTCs.
4.3.1 How to Read DTCs
- Select the “Read Codes” or “Diagnostic Codes” option in the software.
- The software will scan the vehicle’s ECU and display any stored DTCs.
4.3.2 Understanding the Meaning of Different DTCs
DTCs are typically five-character codes that follow a specific format:
- First Character: Indicates the system (e.g., P for Powertrain, B for Body, C for Chassis, U for Network).
- Second Character: Indicates whether the code is generic (0) or manufacturer-specific (1).
- Third Character: Indicates the specific subsystem (e.g., Fuel System, Ignition System, Emission Control System).
- Fourth and Fifth Characters: Provide further information about the specific fault.
Use the software’s DTC database or online resources to look up the meaning of each code.
4.4 Monitoring Live Data and Performing Active Tests
In addition to reading DTCs, you can also monitor live data and perform active tests using the OBD2 software.
4.4.1 How to Monitor Live Data
- Select the “Live Data” or “Real-Time Data” option in the software.
- Choose the data parameters you want to monitor (e.g., Engine RPM, Coolant Temperature, Oxygen Sensor Readings).
- The software will display the real-time values of the selected parameters.
4.4.2 Performing Active Tests for Diagnostic Purposes
- Select the “Active Tests” or “Bi-Directional Controls” option in the software.
- Choose the test you want to perform (e.g., Fuel Injector Activation, Cooling Fan Control).
- Follow the on-screen instructions to perform the test.
4.5 Clearing Codes and Resetting the ECU
After diagnosing and repairing the problem, you can clear the codes and reset the ECU using the OBD2 software.
4.5.1 When and How to Clear Codes
- Clear codes after you have fixed the underlying problem to turn off the “check engine” light.
- Select the “Clear Codes” or “Reset ECU” option in the software.
- Confirm that you want to clear the codes.
4.5.2 Potential Risks of Resetting the ECU Without Addressing the Underlying Issue
- The “check engine” light may come back on if the underlying problem is not fixed.
- You may mask a more serious problem by clearing the codes without addressing the root cause.
 Performing Active Tests
Performing Active Tests
5. OBD2 Software for Specific Needs and Budgets
Choosing the right OBD2 software often depends on your specific needs and budget. Here’s a breakdown of software options tailored to different user profiles.
5.1 Best OBD2 Software for DIY Enthusiasts
DIY enthusiasts need software that is easy to use, affordable, and provides enough functionality to diagnose and repair their own vehicles.
5.1.1 Recommended Software Options
- ProScan: Offers a user-friendly interface and performance testing capabilities at an affordable price.
- PCMScan: Provides customizable dashboards and data logging capabilities for in-depth analysis.
5.1.2 Key Features for DIYers
- User-friendly interface
- DTC reading and clearing
- Live data monitoring
- Affordable price point
5.2 Best OBD2 Software for Professional Mechanics
Professional mechanics need software that is comprehensive, reliable, and provides advanced features for diagnosing and repairing a wide range of vehicles.
5.2.1 Recommended Software Options
- TOAD Pro: Offers comprehensive diagnostics, ECU remapping, and extensive vehicle compatibility.
- AutoEnginuity ScanTool: Provides brand-specific diagnostics, bi-directional controls, and data logging capabilities.
5.2.2 Key Features for Professionals
- Comprehensive code reading and interpretation
- Live data monitoring and graphing
- Bi-directional control and active testing
- Data logging and reporting capabilities
5.3 Best OBD2 Software for Mac Users
Mac users need software that is compatible with their operating system and provides the necessary functionality for diagnosing and repairing their vehicles.
5.3.1 Recommended Software Options
- OBD Auto Doctor: Compatible with Mac OS X and offers a comprehensive DTC database.
- EOBD Facile: Simple and easy to set up on Mac computers.
- Movi/ Movi Pro: Simplistic design that will pull car faults with precise-live PID parameter reports.
5.3.2 Key Features for Mac Users
- Mac OS X compatibility
- DTC reading and clearing
- Live data monitoring
- User-friendly interface
5.4 Free vs. Paid OBD2 Software: What You Need to Know
There are both free and paid OBD2 software options available. Here’s what you need to know about the differences between them.
5.4.1 Limitations of Free OBD2 Software
- Limited functionality
- Basic code reading and clearing
- Limited vehicle compatibility
- No support for manufacturer-specific codes
- No advanced features like bi-directional control or data logging
5.4.2 Benefits of Investing in Paid Software
- Comprehensive code reading and interpretation
- Live data monitoring and graphing
- Bi-directional control and active testing
- Data logging and reporting capabilities
- Extensive vehicle compatibility
- Regular software updates and support
6. Common OBD2 Error Codes and How to Troubleshoot Them
Understanding common OBD2 error codes can help you diagnose and repair your vehicle more efficiently. Here’s a guide to some of the most common codes and how to troubleshoot them.
6.1 P0171 and P0174: System Too Lean
These codes indicate that the engine is running too lean, meaning there is too much air and not enough fuel in the air-fuel mixture.
6.1.1 Potential Causes
- Vacuum leak
- Faulty oxygen sensor
- Dirty mass airflow (MAF) sensor
- Low fuel pressure
6.1.2 Troubleshooting Steps
- Check for vacuum leaks by listening for hissing sounds around the engine.
- Inspect the oxygen sensor for damage or contamination.
- Clean the MAF sensor with a MAF sensor cleaner.
- Check the fuel pressure with a fuel pressure gauge.
6.2 P0300: Random/Multiple Cylinder Misfire Detected
This code indicates that the engine is experiencing a misfire in one or more cylinders.
6.2.1 Potential Causes
- Faulty spark plugs
- Faulty ignition coils
- Vacuum leak
- Low compression
- Clogged fuel injectors
6.2.2 Troubleshooting Steps
- Inspect the spark plugs for damage or wear.
- Test the ignition coils with a multimeter.
- Check for vacuum leaks by listening for hissing sounds around the engine.
- Perform a compression test to check for low compression.
- Clean or replace the fuel injectors.
6.3 P0420: Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold
This code indicates that the catalytic converter is not functioning efficiently.
6.3.1 Potential Causes
- Faulty catalytic converter
- Faulty oxygen sensors
- Exhaust leak
- Engine misfire
6.3.2 Troubleshooting Steps
- Inspect the catalytic converter for damage or corrosion.
- Test the oxygen sensors with a multimeter.
- Check for exhaust leaks by listening for hissing sounds around the exhaust system.
- Address any engine misfires.
6.4 P0101: Mass Air Flow (MAF) Sensor Range/Performance Problem
This code indicates that the MAF sensor is not functioning properly.
6.4.1 Potential Causes
- Dirty or damaged MAF sensor
- Vacuum leak
- Faulty wiring
6.4.2 Troubleshooting Steps
- Clean the MAF sensor with a MAF sensor cleaner.
- Check for vacuum leaks by listening for hissing sounds around the engine.
- Inspect the wiring and connectors for damage or corrosion.
6.5 P0113: Intake Air Temperature Sensor Circuit High Input
This code indicates that the intake air temperature (IAT) sensor is reporting a high temperature reading.
6.5.1 Potential Causes
- Faulty IAT sensor
- Faulty wiring
6.5.2 Troubleshooting Steps
- Test the IAT sensor with a multimeter.
- Inspect the wiring and connectors for damage or corrosion.
7. Tips for Optimizing Your Use of PC OBD2 Software
To get the most out of your PC OBD2 software, consider these optimization tips.
7.1 Keeping Your Software Up to Date
Regularly updating your OBD2 software ensures you have the latest diagnostic information and features.
7.1.1 Benefits of Regular Software Updates
- Access to the latest DTC definitions
- Improved vehicle compatibility
- Bug fixes and performance improvements
- New features and functionality
7.1.2 How to Check for and Install Updates
- Open the OBD2 software and go to the settings menu.
- Select the “Check for Updates” option.
- Follow the on-screen instructions to download and install any available updates.
7.2 Properly Maintaining Your OBD2 Adapter
Maintaining your OBD2 adapter ensures it functions properly and provides accurate data.
7.2.1 Cleaning and Storage Tips
- Clean the adapter with a soft, dry cloth to remove any dirt or debris.
- Store the adapter in a safe place to prevent damage.
- Avoid exposing the adapter to extreme temperatures or moisture.
7.2.2 Troubleshooting Connection Issues
- Check the connection between the adapter and your PC.
- Ensure the adapter is properly plugged into the OBD2 port.
- Restart your PC and the OBD2 software.
- Try a different USB port or Bluetooth connection.
7.3 Understanding Vehicle-Specific Diagnostic Procedures
Different vehicles may require different diagnostic procedures. Understanding these procedures can help you diagnose and repair your vehicle more effectively.
7.3.1 Consulting Vehicle Repair Manuals
- Consult your vehicle’s repair manual for specific diagnostic procedures.
- The repair manual will provide detailed information about the vehicle’s systems and components.
- Follow the instructions in the repair manual carefully to avoid damaging the vehicle.
7.3.2 Utilizing Online Resources and Forums
- Utilize online resources and forums for additional diagnostic information.
- Online forums can provide valuable insights from other vehicle owners and mechanics.
- Be sure to verify the accuracy of any information you find online.
8. The Future of OBD2 Technology
OBD2 technology is constantly evolving to meet the changing needs of the automotive industry. Here’s a look at the future of OBD2 technology.
8.1 Enhanced Diagnostics and Data Analysis
Future OBD2 systems will provide enhanced diagnostics and data analysis capabilities.
8.1.1 Integration with Cloud-Based Services
- OBD2 systems will be integrated with cloud-based services to provide real-time data analysis.
- Cloud-based services will provide access to a vast amount of diagnostic information.
- Data can be shared with mechanics and other professionals for remote diagnostics.
8.1.2 Predictive Maintenance Capabilities
- OBD2 systems will use predictive maintenance algorithms to identify potential problems before they occur.
- Predictive maintenance will help vehicle owners avoid costly repairs.
- Vehicle owners will receive alerts and recommendations for preventative maintenance.
8.2 Wireless Connectivity and Remote Diagnostics
Wireless connectivity and remote diagnostics will become more prevalent in future OBD2 systems.
8.2.1 Advancements in Bluetooth and Wi-Fi Technology
- Bluetooth and Wi-Fi technology will continue to improve, providing faster and more reliable connections.
- Vehicle owners will be able to monitor their vehicle’s health from anywhere.
- Remote diagnostics will allow mechanics to diagnose problems without physically inspecting the vehicle.
8.2.2 Implications for Vehicle Maintenance and Repair
- Vehicle maintenance and repair will become more efficient and convenient.
- Vehicle owners will be able to schedule maintenance and repairs based on real-time data.
- Remote diagnostics will reduce the need for costly and time-consuming inspections.
9. FAQ About PC OBD2 Software
Here are some frequently asked questions about PC OBD2 software.
What is an OBD2 scanner?
An OBD2 scanner is a tool used to read and interpret data from a vehicle’s On-Board Diagnostics (OBD2) system, helping diagnose issues and monitor performance.
How do I read OBD2 fault codes?
Connect an OBD2 scanner or PC-based software to your vehicle’s OBD2 port, then use the software to read and interpret the Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs).
What are common car problems and how to fix them?
Common car problems include engine misfires, vacuum leaks, and faulty oxygen sensors, which can be addressed by replacing spark plugs, repairing leaks, or replacing sensors.
What is the best OBD2 software for a PC?
The best OBD2 software for a PC includes TOAD Pro, AutoEnginuity ScanTool, PCMScan, and ProScan, depending on your specific needs and budget.
Can I use OBD2 software on my Mac?
Yes, OBD Auto Doctor, EOBD Facile, and Movi/Movi Pro are compatible with Mac OS X and offer diagnostic features.
Is free OBD2 software reliable?
Free OBD2 software has limitations in functionality and vehicle compatibility compared to paid software, which offers comprehensive code reading and advanced features.
How often should I update my OBD2 software?
Regularly update your OBD2 software to ensure access to the latest DTC definitions, improved vehicle compatibility, and new features.
What are the benefits of monitoring live data?
Monitoring live data allows you to view real-time data from your vehicle’s sensors, helping identify intermittent problems and monitor the effects of repairs.
What is bi-directional control and why is it important?
Bi-directional control allows you to send commands to the vehicle’s ECU to activate certain functions or components, essential for diagnosing complex problems.
How can OBD2 software save me money on car repairs?
OBD2 software helps you diagnose issues early, allowing you to address problems before they become costly repairs, and enabling you to perform some repairs yourself.
10. Take Action: Get Started with PC OBD2 Software Today
Choosing the right PC OBD2 software can transform how you maintain and repair your vehicle. With the detailed insights and recommendations provided by OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN, you’re well-equipped to make an informed decision. Whether you’re a DIY enthusiast, a professional mechanic, or a Mac user, there’s an OBD2 software solution tailored to your needs.
Don’t wait until your “check engine” light illuminates to start diagnosing your vehicle. By investing in the best PC OBD2 software, you can proactively monitor your vehicle’s health, identify potential problems early, and save money on costly repairs.
Ready to take control of your vehicle’s diagnostics?
Contact OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN today for expert guidance on selecting the right PC OBD2 software and OBD2 adapter for your specific needs. Our team of experienced technicians is here to help you get started with comprehensive vehicle diagnostics and maintenance.
- Address: 123 Main Street, Los Angeles, CA 90001, United States
- WhatsApp: +1 (641) 206-8880
- Website: OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN
Let OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN empower you with the knowledge and tools you need to keep your vehicle running smoothly and efficiently. Act now and experience the peace of mind that comes with proactive vehicle maintenance.