Changing car settings with OBD2 scanners offers a powerful way to customize your vehicle’s performance and features. OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN provides comprehensive guidance and tools to help you unlock your car’s full potential. This article explores how to effectively use OBD2 scanners to modify various car settings, enhance your driving experience, and maintain optimal vehicle health.
Contents
- 1. What is an OBD2 Scanner and How Does it Work?
- 1.1. Key Components of an OBD2 Scanner
- 1.2. How OBD2 Scanners Communicate with Your Car
- 2. Identifying Your Vehicle’s Compatibility with OBD2 Settings Modifications
- 2.1. Checking Your Vehicle’s Manual
- 2.2. Using Online Compatibility Checkers
- 2.3. Consulting with Automotive Professionals
- 3. Essential OBD2 Scanner Features for Car Settings Modifications
- 3.1. Bi-Directional Control
- 3.2. Live Data Streaming
- 3.3. Coding and Programming Capabilities
- 3.4. Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) Reading and Clearing
- 4. Step-by-Step Guide to Changing Car Settings with OBD2
- 4.1. Connecting the OBD2 Scanner
- 4.2. Navigating the Scanner’s Interface
- 4.3. Backing Up Existing Settings
- 4.4. Modifying Desired Settings
- 4.5. Testing and Monitoring the Changes
- 5. Common Car Settings You Can Change With OBD2
- 5.1. Fuel Injection Parameters
- 5.2. Ignition Timing
- 5.3. Idle Speed
- 5.4. Speed Limiter
- 5.5. Electronic Stability Control (ESC)
- 5.6. Transmission Shift Points
- 5.7. Lighting Configurations
- 6. Safety Precautions and Best Practices
- 6.1. Understanding the Risks
- 6.2. Using Reliable Equipment
- 6.3. Following Instructions Carefully
- 6.4. Monitoring Vehicle Performance
- 6.5. Seeking Professional Assistance
- 7. Advanced Techniques for Optimizing Car Settings
- 7.1. Custom Tuning
- 7.2. Data Logging and Analysis
- 7.3. Dyno Testing
- 7.4. Using Performance Monitoring Tools
- 8. Troubleshooting Common Issues
- 8.1. Scanner Not Connecting
- 8.2. Incorrect Data Displayed
- 8.3. Error Messages
- 8.4. Vehicle Not Starting
- 9. Maintaining Optimal Vehicle Performance After Settings Modifications
- 9.1. Regular Inspections
- 9.2. Monitoring Fuel Efficiency
- 9.3. Checking Engine Performance
- 9.4. Staying Updated on Software and Firmware
- 9.5. Keeping Records of Changes
- 10. The Future of OBD2 Settings Modifications
- 10.1. Enhanced Connectivity
- 10.2. Artificial Intelligence (AI) Integration
- 10.3. Increased Customization Options
- 10.4. Improved Security Measures
- 10.5. Greater Accessibility
- FAQ: Change Car Settings With OBD2
- 1. What is an OBD2 scanner?
- 2. Can I really change car settings with OBD2?
- 3. Is it safe to change car settings with OBD2?
- 4. What kind of OBD2 scanner do I need to change car settings?
- 5. How do I know if my vehicle is compatible with OBD2 settings modifications?
- 6. What are some common car settings I can change with OBD2?
- 7. What should I do before modifying any car settings with an OBD2 scanner?
- 8. How can I troubleshoot issues if something goes wrong during settings modifications?
- 9. What are the risks of changing car settings with OBD2?
- 10. Where can I get help with changing car settings with OBD2?
1. What is an OBD2 Scanner and How Does it Work?
An OBD2 scanner is a diagnostic tool that allows you to access and modify various car settings. This tool connects to your vehicle’s On-Board Diagnostics II (OBD2) port, enabling you to read diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs), monitor real-time data, and adjust certain parameters to optimize performance.
The OBD2 port is a standardized interface found in most vehicles manufactured after 1996. It provides access to the car’s engine control unit (ECU) and other electronic systems. According to the Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE), the OBD2 standard ensures that all vehicles can be diagnosed using a common set of codes and protocols, facilitating easier and more consistent vehicle maintenance.
1.1. Key Components of an OBD2 Scanner
- Connector: Plugs into the vehicle’s OBD2 port.
- Microprocessor: Processes data received from the vehicle.
- Display Screen: Shows diagnostic information and settings.
- Software Interface: Allows users to navigate and modify settings.
1.2. How OBD2 Scanners Communicate with Your Car
OBD2 scanners use various communication protocols, such as CAN (Controller Area Network), ISO 9141-2, and SAE J1850, to interact with your vehicle’s ECU. These protocols enable the scanner to request and receive data, as well as send commands to adjust settings.
 OBD2 scanner connecting to a car's OBD2 port, showing the connector and cable
OBD2 scanner connecting to a car's OBD2 port, showing the connector and cable
2. Identifying Your Vehicle’s Compatibility with OBD2 Settings Modifications
Before attempting to change car settings with an OBD2 scanner, it’s essential to verify your vehicle’s compatibility. Not all vehicles support advanced settings modifications through the OBD2 port.
2.1. Checking Your Vehicle’s Manual
Your vehicle’s owner’s manual is a valuable resource for determining what settings can be adjusted via OBD2. Look for sections discussing diagnostics, electronic control systems, or customizable features.
2.2. Using Online Compatibility Checkers
Several online tools and databases can help you determine whether your vehicle supports specific OBD2 settings modifications. These resources typically require you to enter your vehicle’s make, model, and year.
2.3. Consulting with Automotive Professionals
If you’re unsure about your vehicle’s compatibility, consult with a qualified automotive technician. Professionals at OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN can provide expert guidance and ensure that any modifications are safe and effective. You can reach us at +1 (641) 206-8880 for immediate assistance.
3. Essential OBD2 Scanner Features for Car Settings Modifications
To effectively change car settings with an OBD2 scanner, certain features are essential. These features provide the necessary control and precision for making accurate adjustments.
3.1. Bi-Directional Control
Bi-directional control allows the OBD2 scanner to send commands to the vehicle’s ECU, enabling you to activate or deactivate specific functions, run diagnostic tests, and adjust parameters.
3.2. Live Data Streaming
Live data streaming provides real-time information about your vehicle’s performance, including sensor readings, engine parameters, and system status. This feature is crucial for monitoring the effects of any settings modifications.
3.3. Coding and Programming Capabilities
Advanced OBD2 scanners offer coding and programming capabilities, allowing you to reprogram the ECU and customize various settings, such as lighting configurations, driver assistance features, and performance parameters.
3.4. Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) Reading and Clearing
The ability to read and clear DTCs is essential for identifying and resolving any issues that may arise during or after settings modifications. This feature helps you maintain optimal vehicle health and performance.
4. Step-by-Step Guide to Changing Car Settings with OBD2
Changing car settings with an OBD2 scanner involves a systematic process to ensure accuracy and safety. Follow these steps for a successful modification.
4.1. Connecting the OBD2 Scanner
- Locate the OBD2 port in your vehicle, typically found under the dashboard on the driver’s side.
- Plug the OBD2 scanner into the port, ensuring a secure connection.
- Turn on your vehicle’s ignition but do not start the engine.
4.2. Navigating the Scanner’s Interface
- Power on the OBD2 scanner and wait for it to establish a connection with the vehicle’s ECU.
- Use the scanner’s navigation menu to access the settings modification features.
- Refer to the scanner’s user manual for specific instructions on navigating the interface.
4.3. Backing Up Existing Settings
Before making any changes, it’s crucial to back up your vehicle’s existing settings. This allows you to revert to the original configuration if needed.
- Use the OBD2 scanner to save a copy of the current ECU settings.
- Store the backup file in a safe location, such as a USB drive or computer.
4.4. Modifying Desired Settings
- Identify the specific settings you want to modify, such as fuel injection parameters, ignition timing, or electronic stability control.
- Use the OBD2 scanner to access the relevant settings menu.
- Carefully adjust the parameters according to your desired specifications.
- Double-check all modifications before saving the changes.
4.5. Testing and Monitoring the Changes
After modifying the settings, it’s essential to test and monitor the changes to ensure they are functioning correctly.
- Start your vehicle’s engine and allow it to run for a few minutes.
- Use the OBD2 scanner’s live data streaming feature to monitor key performance parameters.
- Take the vehicle for a test drive to evaluate the effects of the modifications under various driving conditions.
- Check for any DTCs or warning lights that may indicate issues with the new settings.
5. Common Car Settings You Can Change With OBD2
OBD2 scanners offer the ability to modify a wide range of car settings, enhancing performance, convenience, and personalization.
5.1. Fuel Injection Parameters
Adjusting fuel injection parameters can improve fuel efficiency, increase horsepower, and optimize engine performance. According to a study by the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), fine-tuning fuel injection settings can result in fuel savings of up to 10%.
5.2. Ignition Timing
Modifying ignition timing can enhance engine responsiveness and power output. Advancing the ignition timing can lead to improved acceleration, while retarding the timing can reduce engine knocking and improve fuel economy.
5.3. Idle Speed
Adjusting the idle speed can prevent stalling, improve engine smoothness, and reduce emissions. A properly set idle speed ensures that the engine runs efficiently when the vehicle is stationary.
5.4. Speed Limiter
Disabling or modifying the speed limiter can allow the vehicle to reach its maximum potential speed. However, it’s important to note that exceeding posted speed limits can be dangerous and illegal.
5.5. Electronic Stability Control (ESC)
Adjusting the ESC settings can affect the vehicle’s handling and stability. Disabling ESC can allow for more aggressive driving maneuvers, while increasing its sensitivity can enhance safety in adverse conditions.
5.6. Transmission Shift Points
Modifying transmission shift points can improve acceleration, fuel economy, and overall driving experience. Optimizing shift points ensures that the engine operates within its most efficient range.
5.7. Lighting Configurations
Customizing lighting configurations can enhance the vehicle’s appearance and improve visibility. This may include adjusting daytime running lights, fog lights, and interior lighting settings.
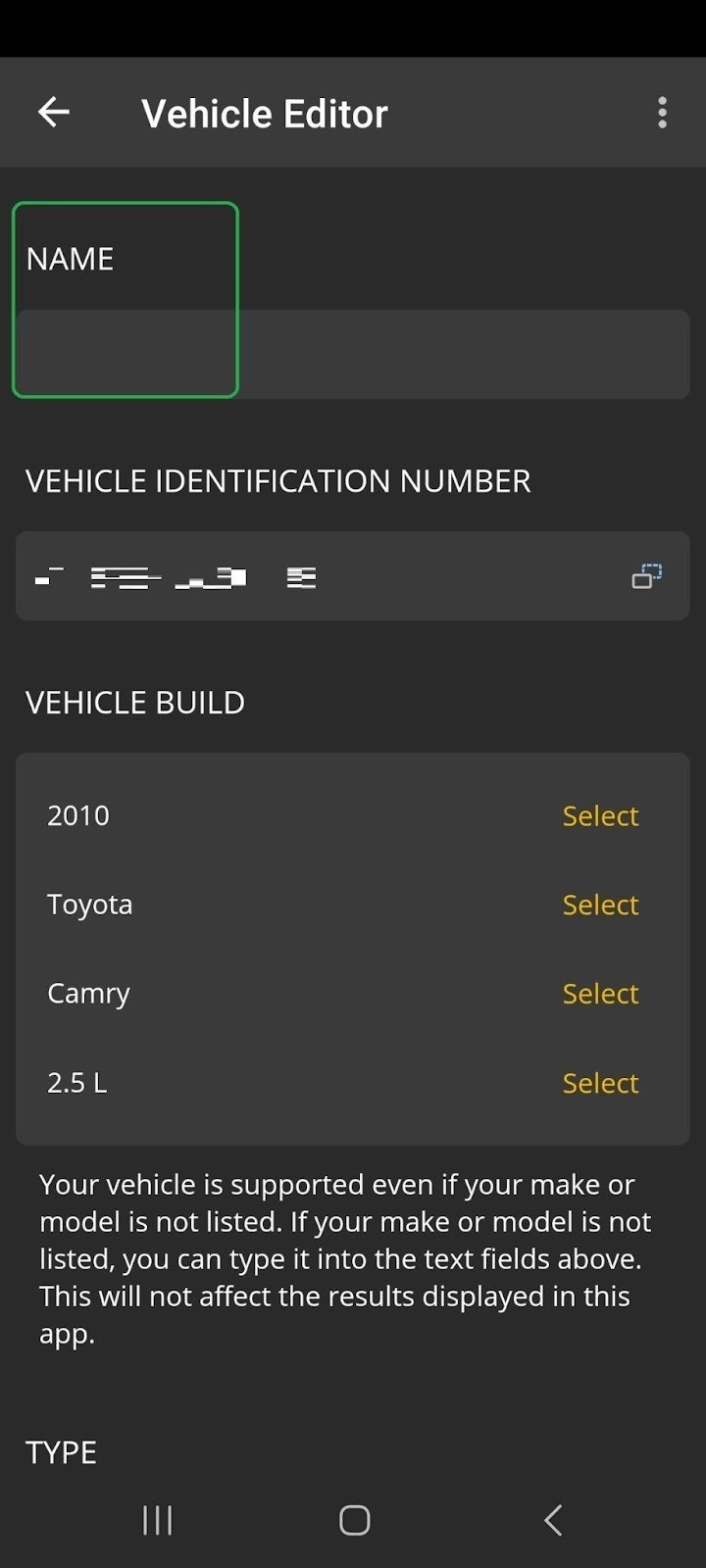 Android screen showing the Vehicle Editor options, highlighting the customized vehicle name
Android screen showing the Vehicle Editor options, highlighting the customized vehicle name
6. Safety Precautions and Best Practices
When changing car settings with an OBD2 scanner, it’s crucial to follow safety precautions and best practices to prevent damage to your vehicle and ensure your personal safety.
6.1. Understanding the Risks
Modifying car settings can have unintended consequences, such as engine damage, reduced fuel efficiency, or compromised safety systems. It’s essential to understand these risks before making any changes.
6.2. Using Reliable Equipment
Use a high-quality OBD2 scanner from a reputable manufacturer. Avoid using cheap or unreliable equipment, as it may provide inaccurate data or cause damage to your vehicle’s ECU.
6.3. Following Instructions Carefully
Always follow the instructions in the OBD2 scanner’s user manual and any relevant service documentation. Incorrect settings modifications can lead to serious problems.
6.4. Monitoring Vehicle Performance
After making any changes, closely monitor your vehicle’s performance for any signs of issues, such as unusual noises, vibrations, or warning lights.
6.5. Seeking Professional Assistance
If you’re unsure about any aspect of the settings modification process, seek assistance from a qualified automotive technician. The experts at OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN are available to provide guidance and support. Contact us at our Los Angeles location at 123 Main Street, Los Angeles, CA 90001, United States.
7. Advanced Techniques for Optimizing Car Settings
For experienced users, advanced techniques can further optimize car settings for maximum performance and efficiency.
7.1. Custom Tuning
Custom tuning involves creating a personalized ECU program tailored to your specific vehicle and driving style. This can result in significant improvements in horsepower, torque, and fuel economy.
7.2. Data Logging and Analysis
Data logging involves recording various vehicle parameters during driving conditions. Analyzing this data can help you identify areas for improvement and fine-tune settings for optimal performance.
7.3. Dyno Testing
Dyno testing involves measuring your vehicle’s horsepower and torque output on a dynamometer. This provides accurate data for evaluating the effects of settings modifications and optimizing performance.
7.4. Using Performance Monitoring Tools
Performance monitoring tools, such as gauges and displays, can provide real-time feedback on your vehicle’s performance. This allows you to monitor the effects of settings modifications and make further adjustments as needed.
8. Troubleshooting Common Issues
When changing car settings with an OBD2 scanner, you may encounter some common issues. Here are some troubleshooting tips to help you resolve them.
8.1. Scanner Not Connecting
- Ensure the OBD2 scanner is properly plugged into the vehicle’s OBD2 port.
- Check the scanner’s power supply and connection cables.
- Verify that the vehicle’s ignition is turned on.
- Consult the scanner’s user manual for troubleshooting steps.
8.2. Incorrect Data Displayed
- Ensure the OBD2 scanner is compatible with your vehicle’s make, model, and year.
- Check the scanner’s software version and update if necessary.
- Verify that the correct units of measurement are selected.
- Consult the scanner’s user manual for calibration instructions.
8.3. Error Messages
- Read the error message carefully and follow any instructions provided.
- Consult the scanner’s user manual for troubleshooting steps.
- Search online forums and databases for solutions to common error messages.
- Contact the scanner manufacturer’s support team for assistance.
8.4. Vehicle Not Starting
- Ensure all settings modifications were made correctly and are compatible with your vehicle.
- Check the vehicle’s battery and charging system.
- Consult a qualified automotive technician for assistance.
- Revert to the original settings if necessary.
9. Maintaining Optimal Vehicle Performance After Settings Modifications
After changing car settings with an OBD2 scanner, it’s essential to maintain optimal vehicle performance through regular maintenance and monitoring.
9.1. Regular Inspections
Schedule regular inspections with a qualified automotive technician to check for any issues related to the settings modifications.
9.2. Monitoring Fuel Efficiency
Track your vehicle’s fuel efficiency to ensure that the settings modifications are not negatively impacting fuel economy.
9.3. Checking Engine Performance
Monitor your engine’s performance for any signs of issues, such as reduced power, increased emissions, or unusual noises.
9.4. Staying Updated on Software and Firmware
Keep your OBD2 scanner’s software and firmware updated to ensure compatibility with your vehicle and access to the latest features and improvements.
9.5. Keeping Records of Changes
Maintain detailed records of all settings modifications, including the date, time, and specific parameters adjusted. This will help you track the effects of the changes and revert to previous settings if needed.
10. The Future of OBD2 Settings Modifications
The future of OBD2 settings modifications is promising, with ongoing advancements in technology and increasing opportunities for customization and optimization.
10.1. Enhanced Connectivity
Future OBD2 scanners will feature enhanced connectivity options, such as Wi-Fi and cloud integration, allowing for remote diagnostics, data sharing, and software updates.
10.2. Artificial Intelligence (AI) Integration
AI-powered OBD2 scanners will be able to analyze vehicle data, predict potential issues, and provide personalized recommendations for settings modifications.
10.3. Increased Customization Options
Future OBD2 scanners will offer even greater customization options, allowing users to fine-tune a wider range of settings and personalize their driving experience.
10.4. Improved Security Measures
Security measures will be enhanced to protect against unauthorized access and prevent malicious modifications to vehicle settings.
10.5. Greater Accessibility
OBD2 settings modifications will become more accessible to a wider audience, with user-friendly interfaces and comprehensive documentation.
By understanding how to Change Car Settings With Obd2 scanners, you can unlock your vehicle’s full potential and enjoy a more personalized and optimized driving experience. OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN is committed to providing the tools and resources you need to succeed in this exciting field.
FAQ: Change Car Settings With OBD2
1. What is an OBD2 scanner?
An OBD2 scanner is a diagnostic tool used to read and clear diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs), monitor real-time data, and modify certain vehicle settings. It connects to the vehicle’s OBD2 port, providing access to the engine control unit (ECU).
2. Can I really change car settings with OBD2?
Yes, you can change certain car settings with an OBD2 scanner, but the extent of modifications depends on the vehicle’s make, model, and year. Common settings include fuel injection parameters, ignition timing, idle speed, and electronic stability control.
3. Is it safe to change car settings with OBD2?
It can be safe if done correctly. Always back up existing settings before making changes, follow instructions carefully, and use reliable equipment. If unsure, seek assistance from a qualified automotive technician.
4. What kind of OBD2 scanner do I need to change car settings?
You need an OBD2 scanner with bi-directional control, live data streaming, and coding/programming capabilities. Ensure the scanner is compatible with your vehicle.
5. How do I know if my vehicle is compatible with OBD2 settings modifications?
Check your vehicle’s owner’s manual, use online compatibility checkers, or consult with automotive professionals at OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN for expert guidance.
6. What are some common car settings I can change with OBD2?
Common settings include fuel injection parameters, ignition timing, idle speed, speed limiter, electronic stability control, transmission shift points, and lighting configurations.
7. What should I do before modifying any car settings with an OBD2 scanner?
Back up your vehicle’s existing settings. This allows you to revert to the original configuration if needed.
8. How can I troubleshoot issues if something goes wrong during settings modifications?
Ensure the scanner is properly connected, check for error messages, and consult the scanner’s user manual. If issues persist, seek assistance from a qualified automotive technician.
9. What are the risks of changing car settings with OBD2?
Risks include engine damage, reduced fuel efficiency, compromised safety systems, and potential legal issues if modifying certain settings like speed limiters.
10. Where can I get help with changing car settings with OBD2?
You can get help from qualified automotive technicians, online forums, and the support team at OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN. Contact us at +1 (641) 206-8880 for immediate assistance.
Unlock your vehicle’s full potential and enjoy a more personalized and optimized driving experience with OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN. Contact us today to learn more about our services and how we can help you achieve your automotive goals. Visit our website or call us at +1 (641) 206-8880. Our location is 123 Main Street, Los Angeles, CA 90001, United States.
