The OBD2 spark connector is an essential tool for automotive diagnostics, enabling technicians and car owners to access and interpret vehicle data. At OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN, we provide comprehensive resources and services to help you effectively use OBD2 scanners and perform accurate vehicle repairs. This guide dives into the functionalities, applications, and benefits of using an OBD2 connector, offering clear, step-by-step instructions to ensure optimal vehicle maintenance and performance while also supplying insight into automotive diagnostic tools and repair services.
Contents
- 1. Understanding the OBD2 Spark Connector
- 1.1. What is an OBD2 Spark Connector?
- 1.2. Why is the OBD2 Connector Important?
- 1.3. Key Features of an OBD2 Connector
- 2. Identifying the OBD2 Port in Your Vehicle
- 2.1. Locating the OBD2 Port
- 2.2. Common Locations by Vehicle Type
- 2.3. What to Do if You Can’t Find the Port
- 3. Selecting the Right OBD2 Scanner
- 3.1. Types of OBD2 Scanners
- 3.2. Features to Look for in an OBD2 Scanner
- 3.3. Top OBD2 Scanner Brands
- 4. Connecting and Using the OBD2 Scanner
- 4.1. Step-by-Step Guide to Connecting the Scanner
- 4.2. Reading Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
- 4.3. Understanding Common OBD2 Error Codes
- 4.4. Clearing Codes Safely
- 5. Advanced OBD2 Scanner Functions
- 5.1. Live Data Streaming
- 5.2. Freeze Frame Data
- 5.3. On-Board Monitoring Tests
- 5.4. I/M Readiness Monitors
- 6. OBD2 and Spark Plugs: Diagnosing Ignition Issues
- 6.1. How OBD2 Helps Diagnose Spark Plug Problems
- 6.2. Common Codes Related to Ignition Problems
- 6.3. Steps to Diagnose and Fix Spark Plug Issues
- 7. Utilizing OBD2 for Vehicle Maintenance
- 7.1. Regular OBD2 Checks
- 7.2. Preventative Maintenance Based on OBD2 Data
- 7.3. How OBD2 Can Save You Money
- 8. Common Mistakes to Avoid When Using an OBD2 Scanner
- 8.1. Ignoring Error Codes
- 8.2. Clearing Codes Without Diagnosing the Problem
- 8.3. Using Incompatible Scanners
- 8.4. Not Updating the Scanner Software
- 9. When to Seek Professional Help
- 9.1. Complex Diagnostic Codes
- 9.2. Intermittent Problems
- 9.3. Major Mechanical Issues
- 9.4. Lack of Confidence
- 10. OBD2 Connector and CAN Bus Communication
- 10.1. What is CAN Bus?
- 10.2. How OBD2 Scanners Use CAN Bus
- 10.3. Benefits of CAN Bus in Vehicle Diagnostics
- 11. Future Trends in OBD2 Technology
- 11.1. Wireless OBD2 Scanners
- 11.2. Cloud-Based Diagnostics
- 11.3. Integration with AI and Machine Learning
- 11.4. Enhanced Data Security
- 12. OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN: Your Partner in Automotive Diagnostics
- 12.1. Our Mission
- 12.2. Services We Offer
- 12.3. Why Choose Us?
- 12.4. Contact Us
- FAQ About OBD2 Spark Connectors
- 1. What does OBD2 stand for?
- 2. Where is the OBD2 port located in my car?
- 3. What is a DTC?
- 4. Can I use any OBD2 scanner with my car?
- 5. How do I clear OBD2 error codes?
- 6. Is it safe to drive with an OBD2 error code?
- 7. What is live data streaming?
- 8. What is freeze frame data?
- 9. What are I/M readiness monitors?
- 10. How can OBD2 help with vehicle maintenance?
1. Understanding the OBD2 Spark Connector
1.1. What is an OBD2 Spark Connector?
An OBD2 (On-Board Diagnostics II) spark connector is a standardized interface used to access a vehicle’s computer system. It allows mechanics and vehicle owners to read diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs), monitor vehicle performance, and diagnose issues related to the engine, transmission, and other systems. The “spark” in the context of the connector might refer to its role in diagnosing issues related to the ignition system or spark plugs, which are crucial for engine combustion.
1.2. Why is the OBD2 Connector Important?
The OBD2 connector is crucial because it provides a standardized way to:
- Access Diagnostic Data: Retrieve trouble codes that indicate specific issues.
- Monitor Vehicle Performance: Observe real-time data such as engine RPM, vehicle speed, and sensor readings.
- Ensure Regulatory Compliance: Support emissions testing and compliance with environmental regulations.
This standardization, mandated in the United States in 1996, ensures that any compliant scan tool can interface with any vehicle, simplifying diagnostics and repair.
1.3. Key Features of an OBD2 Connector
The OBD2 connector has several key features:
- Standardized Interface: A 16-pin Data Link Connector (DLC) ensures compatibility across vehicles.
- Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs): Provides access to a standardized set of codes that help identify specific problems.
- Real-Time Data: Allows monitoring of live data streams, providing insights into vehicle operation.
2. Identifying the OBD2 Port in Your Vehicle
2.1. Locating the OBD2 Port
The OBD2 port is typically located inside the passenger compartment of the vehicle. Common locations include:
- Under the dashboard on the driver’s side
- Near the steering column
- Inside the center console
Consulting your vehicle’s owner’s manual can provide the exact location.
2.2. Common Locations by Vehicle Type
- Cars: Typically found under the dashboard, near the steering wheel.
- Trucks: Often located in the same area as cars, but may also be found in the glove compartment or center console.
- SUVs: Usually positioned under the dash, but may be on the passenger side.
2.3. What to Do if You Can’t Find the Port
If you cannot locate the OBD2 port, try the following:
- Check the Owner’s Manual: The manual will provide the exact location.
- Use Online Resources: Search online forums or vehicle-specific websites for guidance.
- Consult a Mechanic: A professional mechanic can quickly locate the port.
3. Selecting the Right OBD2 Scanner
3.1. Types of OBD2 Scanners
There are several types of OBD2 scanners available:
- Basic Code Readers: These scanners read and clear diagnostic trouble codes.
- Enhanced Scanners: They offer additional features like live data streaming and advanced diagnostics.
- Professional Scanners: Used by mechanics, these scanners provide comprehensive diagnostics and repair information.
- Smartphone Adapters: These connect to your smartphone via Bluetooth or Wi-Fi, using an app to display data.
3.2. Features to Look for in an OBD2 Scanner
When selecting an OBD2 scanner, consider the following features:
- Compatibility: Ensure the scanner supports your vehicle’s make and model.
- Ease of Use: Look for a scanner with an intuitive interface and clear display.
- Functionality: Determine if the scanner meets your diagnostic needs, such as reading live data or performing advanced tests.
- Updates: Choose a scanner that offers software updates to support new vehicles and features.
3.3. Top OBD2 Scanner Brands
Some of the top OBD2 scanner brands include:
- Autel: Known for professional-grade scanners with advanced features.
- Launch: Offers a range of scanners suitable for both DIYers and professionals.
- Innova: Provides reliable and user-friendly scanners for basic diagnostics.
- BlueDriver: Specializes in smartphone-based scanners with comprehensive features.
4. Connecting and Using the OBD2 Scanner
4.1. Step-by-Step Guide to Connecting the Scanner
- Turn Off the Ignition: Ensure the vehicle’s ignition is turned off.
- Locate the OBD2 Port: Find the OBD2 port in your vehicle (usually under the dashboard).
- Connect the Scanner: Plug the OBD2 scanner into the port, ensuring it is securely connected.
- Turn On the Ignition: Turn the ignition to the “on” position, but do not start the engine.
- Power On the Scanner: The scanner should power on automatically or may require pressing a power button.
4.2. Reading Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
- Navigate to the DTC Menu: Use the scanner’s menu to select the option to read diagnostic trouble codes.
- Retrieve Codes: The scanner will display any stored DTCs, along with a brief description of each code.
- Record Codes: Note down the codes for further analysis.
4.3. Understanding Common OBD2 Error Codes
Common OBD2 error codes include:
- P0300: Random/Multiple Cylinder Misfire Detected
- P0171: System Too Lean (Bank 1)
- P0420: Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold (Bank 1)
- P0101: Mass Air Flow (MAF) Sensor Circuit Range/Performance
These codes indicate specific issues, such as engine misfires, lean fuel mixtures, or catalytic converter problems.
4.4. Clearing Codes Safely
- Diagnose the Issue: Before clearing codes, diagnose and repair the underlying problem.
- Clear Codes: Use the scanner’s menu to select the option to clear diagnostic trouble codes.
- Verify Repair: After clearing the codes, monitor the vehicle to ensure the issue does not return.
Clearing codes without addressing the underlying problem can lead to recurring issues and potential damage.
 OBD2 Port Location
OBD2 Port Location
OBD2 Port with features labeled.
5. Advanced OBD2 Scanner Functions
5.1. Live Data Streaming
Live data streaming allows you to monitor real-time vehicle parameters, such as:
- Engine RPM: Revolutions per minute of the engine.
- Vehicle Speed: Current speed of the vehicle.
- Coolant Temperature: Temperature of the engine coolant.
- Oxygen Sensor Readings: Data from the oxygen sensors in the exhaust system.
This feature helps diagnose intermittent issues and assess overall engine performance.
5.2. Freeze Frame Data
Freeze frame data captures a snapshot of vehicle conditions when a DTC is stored. This includes:
- Engine Load: Percentage of maximum engine load.
- Fuel Trim: Adjustments made to the fuel mixture.
- Engine Speed: RPM at the time of the fault.
Freeze frame data provides valuable context for diagnosing the cause of the DTC.
5.3. On-Board Monitoring Tests
On-board monitoring tests allow you to run specific tests on vehicle systems, such as:
- Oxygen Sensor Test: Checks the performance of the oxygen sensors.
- Evaporative System Test: Verifies the integrity of the evaporative emissions control system.
- Catalyst Monitor Test: Assesses the efficiency of the catalytic converter.
These tests help ensure that vehicle systems are functioning correctly and meeting emissions standards.
5.4. I/M Readiness Monitors
I/M (Inspection and Maintenance) readiness monitors indicate whether the vehicle’s emissions systems have been tested and are ready for an emissions inspection. These monitors include:
- Catalyst Monitor: Checks the efficiency of the catalytic converter.
- Oxygen Sensor Monitor: Verifies the performance of the oxygen sensors.
- Evaporative System Monitor: Tests the evaporative emissions control system.
- Misfire Monitor: Detects engine misfires.
Ensuring that all I/M monitors are ready is essential for passing an emissions test.
6. OBD2 and Spark Plugs: Diagnosing Ignition Issues
6.1. How OBD2 Helps Diagnose Spark Plug Problems
The OBD2 system can help diagnose spark plug problems by:
- Detecting Misfires: Misfire codes (e.g., P0300, P0301-P0308) indicate that one or more cylinders are not firing correctly, often due to faulty spark plugs.
- Monitoring Oxygen Sensor Readings: Abnormal oxygen sensor readings can indicate incomplete combustion caused by worn or damaged spark plugs.
6.2. Common Codes Related to Ignition Problems
- P0300: Random/Multiple Cylinder Misfire Detected
- P0301-P0308: Cylinder 1-8 Misfire Detected (identifies the specific cylinder with the misfire)
- P0316: Misfire Detected on First 1000 Revolutions at Startup
6.3. Steps to Diagnose and Fix Spark Plug Issues
- Read DTCs: Use an OBD2 scanner to read and record any diagnostic trouble codes.
- Inspect Spark Plugs: Visually inspect the spark plugs for signs of wear, damage, or fouling.
- Test Spark Plugs: Use a spark plug tester to check the spark plugs’ functionality.
- Replace Faulty Plugs: Replace any faulty spark plugs with new ones that meet the vehicle manufacturer’s specifications.
- Clear Codes: After replacing the spark plugs, clear the DTCs using the OBD2 scanner.
- Verify Repair: Monitor the vehicle to ensure the misfire does not return.
7. Utilizing OBD2 for Vehicle Maintenance
7.1. Regular OBD2 Checks
Performing regular OBD2 checks can help:
- Identify Potential Issues Early: Detect minor problems before they escalate into major repairs.
- Maintain Vehicle Performance: Ensure the engine and other systems are operating optimally.
- Improve Fuel Efficiency: Identify issues that can affect fuel economy, such as faulty sensors or misfires.
7.2. Preventative Maintenance Based on OBD2 Data
Based on OBD2 data, you can perform preventative maintenance such as:
- Replacing Sensors: Replace faulty oxygen, MAF, or MAP sensors to maintain proper engine operation.
- Addressing Misfires: Diagnose and repair misfires to prevent engine damage.
- Maintaining Emissions Systems: Ensure that the catalytic converter and other emissions components are functioning correctly.
7.3. How OBD2 Can Save You Money
By using OBD2 for vehicle maintenance, you can:
- Avoid Costly Repairs: Identify and fix minor issues before they cause significant damage.
- Improve Fuel Economy: Maintain optimal engine performance to maximize fuel efficiency.
- Extend Vehicle Life: Ensure that the vehicle is running smoothly, reducing wear and tear on critical components.
8. Common Mistakes to Avoid When Using an OBD2 Scanner
8.1. Ignoring Error Codes
Ignoring error codes can lead to:
- Escalating Problems: Minor issues can become major repairs if left unaddressed.
- Vehicle Damage: Continuing to drive with a known problem can cause further damage to the vehicle.
- Safety Risks: Some issues can compromise vehicle safety.
8.2. Clearing Codes Without Diagnosing the Problem
Clearing codes without diagnosing the underlying problem can:
- Mask the Issue: The problem will likely return, and you may not realize it is still present.
- Delay Necessary Repairs: Delaying repairs can lead to more significant damage and higher costs.
8.3. Using Incompatible Scanners
Using an incompatible scanner can:
- Provide Incorrect Data: The scanner may not be able to read the vehicle’s data correctly.
- Damage the Vehicle’s Computer: In rare cases, an incompatible scanner can damage the vehicle’s computer system.
8.4. Not Updating the Scanner Software
Failing to update the scanner software can:
- Result in Inaccurate Readings: The scanner may not support new vehicles or updated diagnostic codes.
- Miss Out on New Features: Updates often include new features and improvements that can enhance the scanner’s functionality.
9. When to Seek Professional Help
9.1. Complex Diagnostic Codes
If you encounter complex diagnostic codes that you cannot interpret or resolve, seek professional help.
9.2. Intermittent Problems
Intermittent problems can be challenging to diagnose and may require specialized equipment and expertise.
9.3. Major Mechanical Issues
Major mechanical issues, such as engine or transmission problems, should be handled by a qualified mechanic.
9.4. Lack of Confidence
If you are not confident in your ability to diagnose or repair the issue, it is best to seek professional help.
10. OBD2 Connector and CAN Bus Communication
10.1. What is CAN Bus?
CAN (Controller Area Network) bus is a communication protocol used in vehicles to allow different electronic control units (ECUs) to communicate with each other without a host computer. This system ensures efficient data transfer and coordination between various vehicle systems.
10.2. How OBD2 Scanners Use CAN Bus
OBD2 scanners use CAN bus to:
- Access ECU Data: Communicate with the vehicle’s ECUs to retrieve diagnostic data.
- Monitor System Performance: Observe real-time data from various sensors and systems.
- Send Commands: Send commands to the ECUs to perform tests or clear codes.
10.3. Benefits of CAN Bus in Vehicle Diagnostics
The benefits of CAN bus in vehicle diagnostics include:
- Faster Data Transfer: CAN bus provides high-speed data transfer, allowing for quick and efficient diagnostics.
- Improved Reliability: The system is designed to be robust and reliable, ensuring accurate data transmission.
- Standardized Communication: CAN bus provides a standardized communication protocol, ensuring compatibility across vehicles.
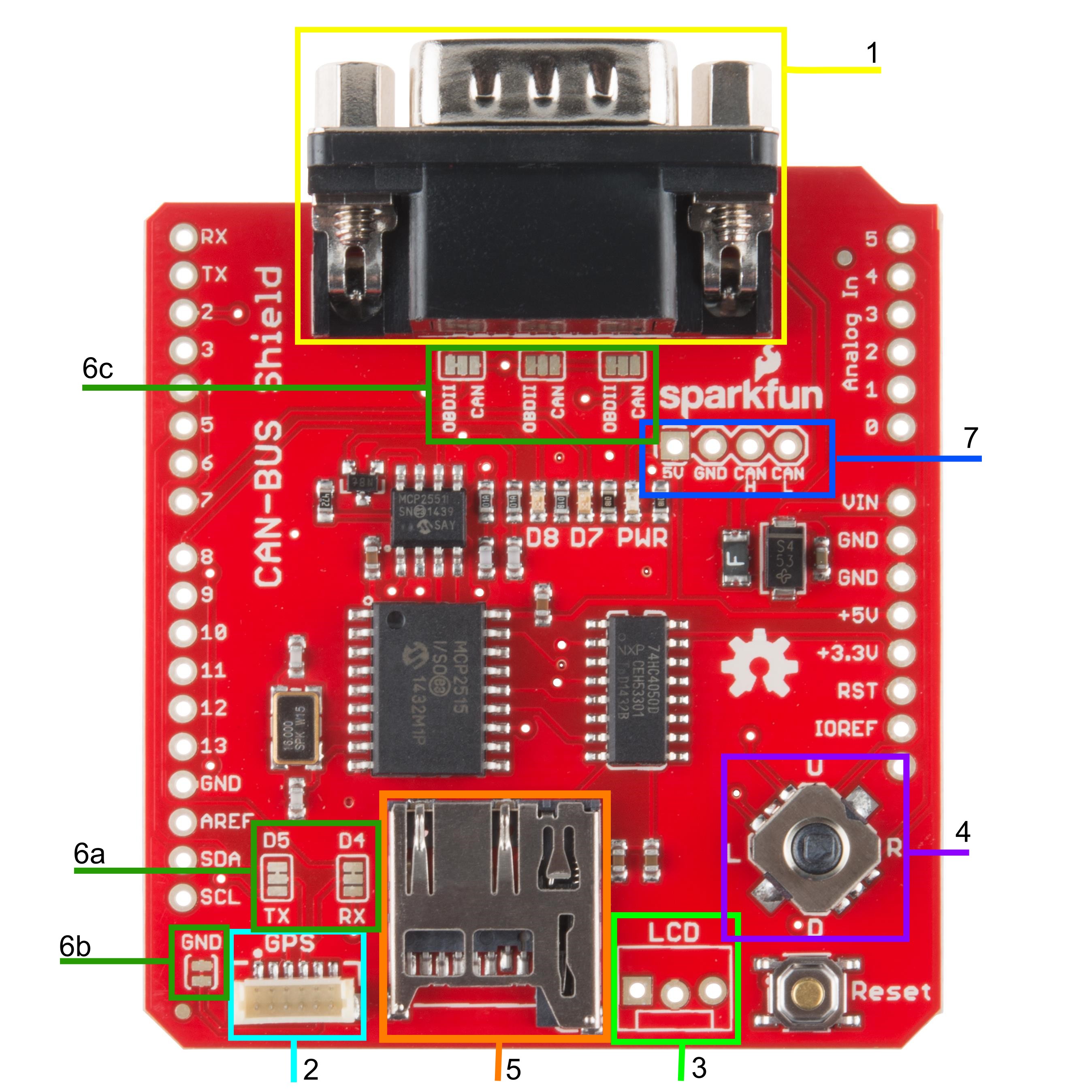
 CAN-Bus Shield connected to a RedBoard
CAN-Bus Shield connected to a RedBoard
CAN-Bus Shield connected to a RedBoard.
11. Future Trends in OBD2 Technology
11.1. Wireless OBD2 Scanners
Wireless OBD2 scanners are becoming increasingly popular, offering the convenience of connecting to your smartphone or tablet via Bluetooth or Wi-Fi.
11.2. Cloud-Based Diagnostics
Cloud-based diagnostics allow you to store and analyze vehicle data in the cloud, providing valuable insights into vehicle performance and maintenance needs.
11.3. Integration with AI and Machine Learning
Integration with AI and machine learning can provide more accurate and efficient diagnostics, helping to identify potential issues before they become major problems.
11.4. Enhanced Data Security
As vehicles become more connected, enhanced data security measures are being implemented to protect against cyber threats and ensure the privacy of vehicle data.
12. OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN: Your Partner in Automotive Diagnostics
12.1. Our Mission
At OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN, our mission is to provide you with the knowledge, tools, and services you need to effectively diagnose and maintain your vehicle.
12.2. Services We Offer
We offer a range of services, including:
- OBD2 Scanner Sales: We provide a variety of OBD2 scanners to meet your diagnostic needs.
- Diagnostic Assistance: Our team of experts can help you interpret diagnostic codes and troubleshoot vehicle problems.
- Repair Services: We offer professional repair services to address any issues identified through OBD2 diagnostics.
- Educational Resources: We provide a wealth of educational resources, including articles, tutorials, and videos, to help you learn about OBD2 technology and vehicle maintenance.
12.3. Why Choose Us?
Choosing OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN means you benefit from:
- Expertise: Our team has extensive knowledge and experience in automotive diagnostics.
- Quality Products: We offer high-quality OBD2 scanners from top brands.
- Exceptional Service: We provide personalized support to ensure you get the help you need.
- Comprehensive Resources: We offer a wide range of resources to help you learn and grow your diagnostic skills.
12.4. Contact Us
For expert advice and assistance with your automotive diagnostic needs, contact us today:
- Address: 123 Main Street, Los Angeles, CA 90001, United States
- WhatsApp: +1 (641) 206-8880
- Website: OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN
FAQ About OBD2 Spark Connectors
1. What does OBD2 stand for?
OBD2 stands for On-Board Diagnostics II, a standardized system for vehicle diagnostics.
2. Where is the OBD2 port located in my car?
The OBD2 port is typically located under the dashboard on the driver’s side, near the steering column, or inside the center console.
3. What is a DTC?
DTC stands for Diagnostic Trouble Code, a code that indicates a specific problem in the vehicle’s systems.
4. Can I use any OBD2 scanner with my car?
Most OBD2 scanners are compatible with all cars manufactured after 1996 in the United States. However, it’s essential to check the scanner’s compatibility with your specific make and model.
5. How do I clear OBD2 error codes?
To clear OBD2 error codes, use the scanner’s menu to select the option to clear diagnostic trouble codes.
6. Is it safe to drive with an OBD2 error code?
It depends on the error code. Some codes indicate minor issues, while others indicate severe problems that could compromise vehicle safety. It is best to diagnose and repair the issue as soon as possible.
7. What is live data streaming?
Live data streaming allows you to monitor real-time vehicle parameters, such as engine RPM, vehicle speed, and sensor readings.
8. What is freeze frame data?
Freeze frame data captures a snapshot of vehicle conditions when a DTC is stored, providing valuable context for diagnosing the cause of the DTC.
9. What are I/M readiness monitors?
I/M (Inspection and Maintenance) readiness monitors indicate whether the vehicle’s emissions systems have been tested and are ready for an emissions inspection.
10. How can OBD2 help with vehicle maintenance?
OBD2 can help identify potential issues early, maintain vehicle performance, improve fuel efficiency, and avoid costly repairs.
The OBD2 spark connector is a powerful tool for vehicle diagnostics and maintenance. By understanding how to use it effectively, you can keep your vehicle running smoothly and avoid costly repairs. At OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN, we are dedicated to providing you with the resources and services you need to make the most of OBD2 technology. Contact us today to learn more and get started.
Ready to take control of your vehicle’s health? Contact OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN now for expert advice, high-quality OBD2 scanners, and professional repair services. Call us at +1 (641) 206-8880 or visit our website at OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN. Let us help you keep your vehicle running at its best!