The Elm327 Car Obd2 Can Bus Scanner is a powerful tool for diagnosing vehicle issues, providing valuable insights into your car’s health, and saving you money on repairs. At OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN, we empower you with the knowledge and resources to effectively use this technology, understand car diagnostics, and maintain your vehicle efficiently. This guide also highlights how you can consult our professionals to enhance your understanding of OBD2 functionalities and receive immediate solutions for your vehicle-related questions.
Contents
- 1. Understanding the ELM327 Car OBD2 CAN Bus Scanner
- 1.1. Key Features and Functionality
- 1.2. OBD2 and CAN Bus Explained
- 1.3. Why Use an ELM327 Scanner?
- 2. Selecting the Right ELM327 Scanner
- 2.1. Types of ELM327 Scanners
- 2.2. Key Considerations When Choosing a Scanner
- 2.3. Recommended ELM327 Scanners
- 3. Setting Up Your ELM327 Scanner
- 3.1. Installing OBD2 Software/App
- 3.2. Connecting the Scanner to Your Vehicle
- 3.3. Pairing with Your Device (Smartphone/Laptop)
- 4. Reading and Interpreting Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
- 4.1. How to Read DTCs
- 4.2. Understanding DTC Structure
- 4.3. Common DTCs and Their Meanings
- 4.4. Where to Find More Information About DTCs
- 5. Monitoring Live Data with Your ELM327 Scanner
- 5.1. What is Live Data?
- 5.2. How to Access Live Data
- 5.3. Interpreting Live Data
- 5.4. Using Live Data for Diagnostics
- 6. Clearing Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
- 6.1. How to Clear DTCs
- 6.2. Important Considerations Before Clearing Codes
- 6.3. Readiness Monitors
- 7. Advanced Features and Functions
- 7.1. Enhanced OEM Diagnostics
- 7.2. Bi-Directional Control
- 7.3. Data Logging
- 8. Troubleshooting Common Issues
- 8.1. Scanner Won’t Connect
- 8.2. App Can’t Read Codes
- 8.3. Inaccurate Data
- 9. Safety Precautions
- 10. Maximizing the Benefits with OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN
- 10.1. How OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN Can Help
- 10.2. Contact Us for Expert Advice
- 11. The Future of ELM327 Scanners and OBD2 Technology
- 11.1. Advancements in Technology
- 11.2. Impact on Automotive Repair
- 12. ELM327 Car OBD2 CAN Bus Scanner: FAQ
- 12.1. What is an OBD2 scanner?
- 12.2. What is the CAN bus?
- 12.3. Is an ELM327 scanner compatible with my car?
- 12.4. Can I use an ELM327 scanner to diagnose ABS or airbag issues?
- 12.5. Do I need to be a mechanic to use an ELM327 scanner?
- 12.6. Can an ELM327 scanner reset the check engine light?
- 12.7. What is live data monitoring?
- 12.8. What are readiness monitors?
- 12.9. How do I update the firmware on my ELM327 scanner?
- 12.10. Where can I find more information about OBD2 technology?
- 13. ELM327 Car OBD2 CAN Bus Scanner: Conclusion
1. Understanding the ELM327 Car OBD2 CAN Bus Scanner
What exactly is an ELM327 car OBD2 CAN bus scanner, and why is it essential for modern car owners and automotive technicians?
The ELM327 car OBD2 CAN bus scanner is a compact electronic device that interfaces with your vehicle’s On-Board Diagnostics (OBD) system. According to a study by the University of California, Berkeley’s Transportation Sustainability Research Center in 2022, OBD systems have become standardized across most vehicles manufactured since 1996, providing a wealth of diagnostic information. It uses the Controller Area Network (CAN) bus protocol to communicate with the car’s Engine Control Unit (ECU) and other modules, allowing you to read diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs), monitor sensor data, and even perform basic vehicle diagnostics right from your smartphone or laptop.
1.1. Key Features and Functionality
Here’s a breakdown of the key features and functionalities of an ELM327 scanner:
- Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) Reading: Identifies the source of engine problems by reading standardized DTCs.
- Live Data Monitoring: Displays real-time data from various sensors like engine temperature, O2 sensor readings, and vehicle speed.
- Freeze Frame Data: Captures sensor data at the moment a DTC is triggered, providing a snapshot of the conditions leading to the issue.
- Vehicle Information Retrieval: Obtains vehicle identification number (VIN), calibration identification, and other vehicle-specific information.
- Code Clearing: Resets the check engine light after repairs are made.
1.2. OBD2 and CAN Bus Explained
- OBD2 (On-Board Diagnostics II): A standardized system used in vehicles to monitor engine performance and emissions. The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) mandated OBD2 for all cars sold in the United States starting in 1996 to ensure emissions compliance.
- CAN Bus (Controller Area Network): A robust communication protocol used within the vehicle to allow various electronic control units (ECUs) to communicate with each other without a host computer. CAN bus systems reduce wiring complexity and improve data transmission reliability, as noted in a 2020 report by the Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE).
1.3. Why Use an ELM327 Scanner?
- Cost Savings: Diagnose and potentially fix minor issues yourself, saving on expensive mechanic fees.
- Informed Decision-Making: Gain a better understanding of your vehicle’s condition before taking it to a mechanic, preventing unnecessary repairs.
- Preventative Maintenance: Monitor your vehicle’s performance and identify potential problems early on, preventing major breakdowns.
- Vehicle Health Monitoring: Keep track of vital engine parameters and ensure optimal performance.
2. Selecting the Right ELM327 Scanner
Choosing the right ELM327 scanner is crucial to ensure compatibility and functionality. With a wide range of options available, it’s essential to consider your specific needs and budget.
2.1. Types of ELM327 Scanners
- Bluetooth ELM327 Scanners: Connect wirelessly to your smartphone or tablet, offering convenience and portability.
- Wi-Fi ELM327 Scanners: Similar to Bluetooth scanners but connect via Wi-Fi, potentially offering faster data transfer rates.
- USB ELM327 Scanners: Connect directly to your laptop via USB, providing a stable and reliable connection.
2.2. Key Considerations When Choosing a Scanner
- Compatibility: Ensure the scanner supports the OBD2 protocols used by your vehicle. Most scanners support the standard protocols (ISO 9141-2, ISO 14230-4, SAE J1850 VPW, SAE J1850 PWM, and ISO 15765-4 CAN), but it’s always best to double-check.
- Software Support: Choose a scanner that works with your preferred OBD2 software or app. Popular options include Torque Pro, OBD Fusion, and Car Scanner ELM OBD2.
- Features: Consider the features you need, such as live data monitoring, freeze frame data, and advanced diagnostics.
- Build Quality: Opt for a scanner made from durable materials to ensure longevity.
- User Reviews: Read reviews from other users to get an idea of the scanner’s performance and reliability.
- Price: ELM327 scanners range in price from around $10 to $100 or more. Set a budget and choose a scanner that offers the best value for your money.
2.3. Recommended ELM327 Scanners
| Scanner | Connection Type | Key Features | Price Range |
|---|---|---|---|
| Veepeak Mini Bluetooth OBD2 Scanner | Bluetooth | Compact size, easy to use, compatible with Android and Windows, reads and clears DTCs, live data monitoring. | $15-25 |
| OBDLink MX+ | Bluetooth | Advanced diagnostics, supports proprietary vehicle protocols, enhanced OEM support, security features. | $100+ |
| BAFX Products OBD2 Reader | Bluetooth | Reliable performance, compatible with Android, reads and clears DTCs, live data monitoring, freeze frame data. | $20-30 |
| ScanTool OBDLink SX USB | USB | Fast data transfer, reliable connection, compatible with Windows, reads and clears DTCs, live data monitoring, supports all OBD2 protocols. | $50-70 |
| Wireless Car Adapter OBDII | Wi-Fi | Compatible with iOS and Android, reads and clears DTCs, live data monitoring, easy to set up. | $20-30 |
These recommendations are based on a combination of features, reliability, user reviews, and value for money. Always verify compatibility with your specific vehicle before purchasing.
3. Setting Up Your ELM327 Scanner
Once you’ve chosen your ELM327 scanner, setting it up is a straightforward process. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
3.1. Installing OBD2 Software/App
- Choose an App: Select an OBD2 software application or app that suits your needs and is compatible with your smartphone or laptop. Consider popular options like Torque Pro, OBD Fusion, Car Scanner ELM OBD2, or the manufacturer’s recommended software.
- Download and Install: Download the software or app from the appropriate app store (Google Play Store for Android, Apple App Store for iOS) or the manufacturer’s website. Follow the installation instructions.
- Configure Settings: Once installed, open the app and configure any necessary settings, such as vehicle profile, units of measurement, and communication protocols.
3.2. Connecting the Scanner to Your Vehicle
- Locate the OBD2 Port: Find the OBD2 port in your vehicle. It’s typically located under the dashboard on the driver’s side. Refer to your vehicle’s owner’s manual if you’re unsure of its location.
- Plug in the Scanner: Plug the ELM327 scanner into the OBD2 port. Ensure it’s securely connected.
- Turn on the Ignition: Turn the vehicle’s ignition to the “on” position, but do not start the engine. This provides power to the OBD2 system.
3.3. Pairing with Your Device (Smartphone/Laptop)
- Bluetooth Scanners:
- Enable Bluetooth on your smartphone or laptop.
- In your device’s Bluetooth settings, search for available devices.
- Select the ELM327 scanner from the list of available devices. You may be prompted to enter a pairing code (usually “1234” or “0000”).
- Once paired, open the OBD2 app and select the ELM327 scanner as the connected device.
- Wi-Fi Scanners:
- On your smartphone or laptop, connect to the Wi-Fi network broadcast by the ELM327 scanner. The network name and password are usually found in the scanner’s documentation.
- Open the OBD2 app and enter the scanner’s IP address (usually 192.168.0.10) and port number (usually 35000).
- USB Scanners:
- Connect the USB ELM327 scanner to your laptop using a USB cable.
- Install any necessary drivers if prompted.
- Open the OBD2 software on your laptop and select the correct COM port for the scanner.
4. Reading and Interpreting Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
One of the primary functions of an ELM327 scanner is to read and interpret Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs). These codes provide valuable information about potential issues with your vehicle’s engine and other systems.
4.1. How to Read DTCs
- Connect the Scanner: Ensure your ELM327 scanner is properly connected to your vehicle and paired with your device.
- Open the OBD2 App: Launch the OBD2 app on your smartphone or laptop.
- Select “Read Codes”: Navigate to the diagnostic section of the app and select the option to “Read Codes” or “Retrieve DTCs.”
- View the Codes: The app will display a list of DTCs, if any are present. Each code consists of five characters: one letter followed by four numbers (e.g., P0301).
4.2. Understanding DTC Structure
The five characters in a DTC provide information about the system and nature of the fault:
- First Character:
- P: Powertrain (engine, transmission)
- B: Body (airbags, power windows)
- C: Chassis (ABS, suspension)
- U: Network (communication)
- Second Character:
- 0: Generic (SAE defined)
- 1, 2, 3: Manufacturer-specific
- Third Character: Indicates the subsystem:
- 1: Fuel and air metering
- 2: Fuel and air metering (injector circuit)
- 3: Ignition system or misfire
- 4: Auxiliary emission controls
- 5: Vehicle speed control, idle control system
- 6: Computer output circuit
- 7: Transmission
- 8: Transmission
- Fourth and Fifth Characters: Specify the particular fault within the subsystem.
4.3. Common DTCs and Their Meanings
| DTC | Description | Possible Causes |
|---|---|---|
| P0300 | Random/Multiple Cylinder Misfire Detected | Faulty spark plugs, ignition coils, fuel injectors, vacuum leaks, low compression. |
| P0301 | Cylinder 1 Misfire Detected | Faulty spark plug, ignition coil, fuel injector, low compression in cylinder 1. |
| P0171 | System Too Lean (Bank 1) | Vacuum leak, faulty MAF sensor, faulty O2 sensor, low fuel pressure. |
| P0174 | System Too Lean (Bank 2) | Vacuum leak, faulty MAF sensor, faulty O2 sensor, low fuel pressure. |
| P0420 | Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold | Faulty catalytic converter, faulty O2 sensors, exhaust leaks. |
| P0401 | Insufficient EGR Flow | Blocked EGR valve, faulty EGR valve, faulty EGR pressure sensor. |
| P0101 | Mass Air Flow (MAF) Sensor Range/Performance | Dirty or faulty MAF sensor, intake leaks. |
| P0113 | Intake Air Temperature (IAT) Sensor Circuit High Input | Faulty IAT sensor, wiring issues. |
| P0505 | Idle Air Control (IAC) System Malfunction | Dirty or faulty IAC valve, vacuum leaks. |
This table provides a starting point for diagnosing common issues. Always consult your vehicle’s service manual for more specific information.
4.4. Where to Find More Information About DTCs
- OBD2 Software/App: Many OBD2 apps include a built-in DTC lookup feature that provides detailed information about each code.
- Online Databases: Websites like OBD-Codes.com and the National Institute for Automotive Service Excellence (ASE) offer comprehensive DTC databases.
- Vehicle Service Manual: Your vehicle’s service manual contains detailed information about DTCs and troubleshooting procedures.
5. Monitoring Live Data with Your ELM327 Scanner
In addition to reading DTCs, ELM327 scanners can also display live data from various sensors in your vehicle. This real-time information can be invaluable for diagnosing performance issues and monitoring your vehicle’s health.
5.1. What is Live Data?
Live data, also known as real-time data or sensor data, refers to the continuous stream of information transmitted by your vehicle’s sensors to the ECU. This data includes parameters such as engine temperature, RPM, vehicle speed, O2 sensor readings, fuel trim, and more.
5.2. How to Access Live Data
- Connect the Scanner: Ensure your ELM327 scanner is properly connected to your vehicle and paired with your device.
- Open the OBD2 App: Launch the OBD2 app on your smartphone or laptop.
- Select “Live Data”: Navigate to the diagnostic section of the app and select the option to “Live Data,” “Real-Time Data,” or a similar term.
- Choose Parameters: Select the specific parameters you want to monitor from the list of available sensors.
- View the Data: The app will display the selected parameters in real-time, often in the form of graphs, gauges, or numerical values.
5.3. Interpreting Live Data
Interpreting live data requires some knowledge of how your vehicle’s systems operate. Here are some key parameters to monitor and their typical values:
| Parameter | Description | Typical Values | Potential Issues |
|---|---|---|---|
| Engine Coolant Temperature | Temperature of the engine coolant, indicating engine operating temperature. | 195-220°F (90-104°C) | Overheating, thermostat issues, coolant leaks. |
| RPM | Revolutions Per Minute, indicating engine speed. | Idle: 600-1000 RPM, Cruising: 1500-3000 RPM | Idle issues, misfires, transmission problems. |
| Vehicle Speed | Speed of the vehicle. | Varies depending on driving conditions. | Speed sensor issues, transmission problems. |
| O2 Sensor Readings | Voltage output of the oxygen sensors, indicating the air-fuel mixture. | Varies depending on sensor type and operating conditions. | Lean or rich conditions, faulty O2 sensors, exhaust leaks. |
| Fuel Trim | Adjustments made by the ECU to compensate for deviations in the air-fuel mixture. | Short Term Fuel Trim (STFT): +/- 10%, Long Term Fuel Trim (LTFT): +/- 10% | Vacuum leaks, faulty MAF sensor, fuel injector issues. |
| Mass Air Flow (MAF) | Amount of air entering the engine. | Varies depending on engine size and RPM. | Dirty or faulty MAF sensor, intake leaks. |
| Throttle Position | Position of the throttle plate, indicating how much air is entering the engine. | Idle: 0-5%, Wide Open Throttle (WOT): 80-100% | Throttle position sensor issues, throttle body issues. |
Monitoring these parameters over time can help you identify trends and potential problems before they become major issues.
5.4. Using Live Data for Diagnostics
Live data can be used to diagnose a wide range of issues, such as:
- Misfires: Monitor RPM and misfire counters to identify misfiring cylinders.
- Vacuum Leaks: Monitor fuel trim values to detect lean conditions caused by vacuum leaks.
- O2 Sensor Issues: Monitor O2 sensor readings to identify faulty or sluggish sensors.
- Overheating: Monitor engine coolant temperature to detect overheating conditions.
- Performance Issues: Monitor various parameters to identify performance issues such as low power, poor fuel economy, or rough idling.
6. Clearing Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
After diagnosing and repairing the issue that triggered a DTC, you’ll need to clear the code to turn off the check engine light.
6.1. How to Clear DTCs
- Connect the Scanner: Ensure your ELM327 scanner is properly connected to your vehicle and paired with your device.
- Open the OBD2 App: Launch the OBD2 app on your smartphone or laptop.
- Select “Clear Codes”: Navigate to the diagnostic section of the app and select the option to “Clear Codes,” “Erase DTCs,” or a similar term.
- Confirm the Action: The app may ask you to confirm that you want to clear the codes.
- Verify the Result: After clearing the codes, start the engine and check if the check engine light has turned off.
6.2. Important Considerations Before Clearing Codes
- Diagnose the Issue First: Clearing codes without addressing the underlying issue will only result in the check engine light turning back on.
- Record the Codes: Before clearing the codes, record them for future reference. This can be helpful if the issue returns.
- Check for Readiness Monitors: After clearing the codes, the ECU will need to run readiness monitors to ensure that all systems are functioning properly. This process can take several drive cycles.
6.3. Readiness Monitors
Readiness monitors are diagnostic tests that the ECU performs to verify the proper operation of various systems, such as the oxygen sensors, catalytic converter, and evaporative emissions system. Before a vehicle can pass an emissions test, all applicable readiness monitors must be complete.
7. Advanced Features and Functions
Some ELM327 scanners offer advanced features and functions that can provide even more insight into your vehicle’s operation.
7.1. Enhanced OEM Diagnostics
Some scanners support enhanced OEM diagnostics, which allow you to access manufacturer-specific diagnostic codes and data. This can be particularly useful for diagnosing issues that are not covered by the standard OBD2 protocols.
7.2. Bi-Directional Control
Bi-directional control allows you to send commands to the ECU to activate or deactivate certain components, such as fuel injectors, solenoids, and relays. This can be helpful for testing components and diagnosing electrical issues.
7.3. Data Logging
Data logging allows you to record live data over time and analyze it later. This can be useful for identifying intermittent issues and tracking your vehicle’s performance.
8. Troubleshooting Common Issues
While ELM327 scanners are generally reliable, you may encounter some issues during setup or operation.
8.1. Scanner Won’t Connect
- Check Compatibility: Ensure the scanner is compatible with your vehicle’s OBD2 protocols.
- Verify Connection: Make sure the scanner is securely plugged into the OBD2 port.
- Check Bluetooth/Wi-Fi: Ensure Bluetooth or Wi-Fi is enabled on your device and that you’ve properly paired with the scanner.
- Restart Devices: Try restarting your smartphone or laptop and the scanner.
- Update Firmware: Check for firmware updates for the scanner and install them if available.
8.2. App Can’t Read Codes
- Select Correct Protocol: Ensure the OBD2 app is configured to use the correct communication protocol for your vehicle.
- Check Ignition: Make sure the vehicle’s ignition is turned to the “on” position, but do not start the engine.
- Try a Different App: Try using a different OBD2 app to see if the issue is with the software.
8.3. Inaccurate Data
- Check Sensor Connections: Ensure the sensors are properly connected and functioning correctly.
- Calibrate Sensors: Some OBD2 apps allow you to calibrate sensors for more accurate readings.
- Consult Service Manual: Refer to your vehicle’s service manual for accurate sensor specifications and troubleshooting procedures.
9. Safety Precautions
When using an ELM327 scanner, it’s important to follow these safety precautions:
- Do Not Use While Driving: Avoid using the scanner while driving, as it can be distracting.
- Park in a Safe Location: When performing diagnostics, park your vehicle in a safe location away from traffic.
- Disconnect Scanner After Use: Disconnect the scanner from the OBD2 port after use to prevent battery drain.
- Consult a Professional: If you’re unsure about any diagnostic or repair procedure, consult a qualified mechanic.
10. Maximizing the Benefits with OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN
OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN is committed to providing you with the resources and expertise you need to effectively use your ELM327 scanner and maintain your vehicle.
10.1. How OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN Can Help
- Expert Guidance: We offer expert guidance and support to help you understand and interpret diagnostic data.
- Troubleshooting Assistance: Our team can assist you with troubleshooting complex issues and finding the right solutions.
- Repair Recommendations: We can provide repair recommendations based on your vehicle’s diagnostic data.
- Educational Resources: We offer a wealth of educational resources, including articles, videos, and tutorials, to help you learn more about OBD2 technology and vehicle diagnostics.
10.2. Contact Us for Expert Advice
Do you feel overwhelmed by the technical data from your OBD2 scanner? Are you unsure how to interpret the results and take appropriate action? OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN is here to assist.
Address: 123 Main Street, Los Angeles, CA 90001, United States
WhatsApp: +1 (641) 206-8880
Website: OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN
Contact us today for expert advice on using your ELM327 scanner and understanding your vehicle’s diagnostic data. Our experienced technicians are ready to provide personalized assistance and help you make informed decisions about your vehicle’s maintenance and repair.
11. The Future of ELM327 Scanners and OBD2 Technology
The ELM327 scanner and OBD2 technology are constantly evolving, with new features and capabilities being added all the time.
11.1. Advancements in Technology
- Wireless Connectivity: More scanners are adopting wireless connectivity options like Bluetooth and Wi-Fi.
- Cloud-Based Diagnostics: Cloud-based diagnostics are becoming increasingly popular, allowing you to store and access diagnostic data from anywhere.
- Artificial Intelligence: AI-powered diagnostic tools are emerging, offering more accurate and efficient diagnostics.
11.2. Impact on Automotive Repair
As OBD2 technology becomes more advanced, it will have a significant impact on the automotive repair industry:
- Increased Efficiency: Mechanics will be able to diagnose issues more quickly and accurately.
- Reduced Costs: Diagnostic costs will likely decrease as technology becomes more accessible.
- Improved Customer Service: Mechanics will be able to provide better customer service by offering more transparent and data-driven diagnoses.
12. ELM327 Car OBD2 CAN Bus Scanner: FAQ
Here are some frequently asked questions about ELM327 car OBD2 CAN bus scanners:
12.1. What is an OBD2 scanner?
An OBD2 scanner is a diagnostic tool used to read data from a vehicle’s On-Board Diagnostics (OBD) system. It helps identify issues by reading diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) and monitoring live sensor data.
12.2. What is the CAN bus?
The CAN (Controller Area Network) bus is a communication protocol that allows various electronic control units (ECUs) in a vehicle to communicate with each other.
12.3. Is an ELM327 scanner compatible with my car?
Most vehicles manufactured after 1996 are OBD2 compliant, making them compatible with ELM327 scanners. However, it’s essential to verify that the scanner supports the specific OBD2 protocols used by your vehicle.
12.4. Can I use an ELM327 scanner to diagnose ABS or airbag issues?
Some ELM327 scanners can diagnose ABS and airbag issues, but this depends on the scanner’s capabilities and the OBD2 software you’re using. Look for scanners that support enhanced OEM diagnostics for more comprehensive coverage.
12.5. Do I need to be a mechanic to use an ELM327 scanner?
No, you don’t need to be a mechanic to use an ELM327 scanner. However, some technical knowledge is helpful for interpreting the data and performing repairs.
12.6. Can an ELM327 scanner reset the check engine light?
Yes, an ELM327 scanner can reset the check engine light after you’ve diagnosed and repaired the underlying issue.
12.7. What is live data monitoring?
Live data monitoring is the process of viewing real-time data from your vehicle’s sensors, such as engine temperature, RPM, and O2 sensor readings.
12.8. What are readiness monitors?
Readiness monitors are diagnostic tests that the ECU performs to verify the proper operation of various systems. These monitors must be complete before a vehicle can pass an emissions test.
12.9. How do I update the firmware on my ELM327 scanner?
The process for updating the firmware on your ELM327 scanner varies depending on the manufacturer. Refer to the scanner’s documentation for specific instructions.
12.10. Where can I find more information about OBD2 technology?
You can find more information about OBD2 technology on websites like OBD2-Codes.com, the National Institute for Automotive Service Excellence (ASE), and OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN.
13. ELM327 Car OBD2 CAN Bus Scanner: Conclusion
The ELM327 car OBD2 CAN bus scanner is a valuable tool for any car owner or automotive technician, empowering you to diagnose vehicle issues, monitor performance, and save money on repairs. By understanding the features and functions of these scanners, you can take control of your vehicle’s health and ensure its longevity. With the support and resources available at OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN, you can confidently use this technology to keep your vehicle running smoothly. Don’t hesitate to contact us for expert advice and personalized assistance. Your vehicle will thank you for it.
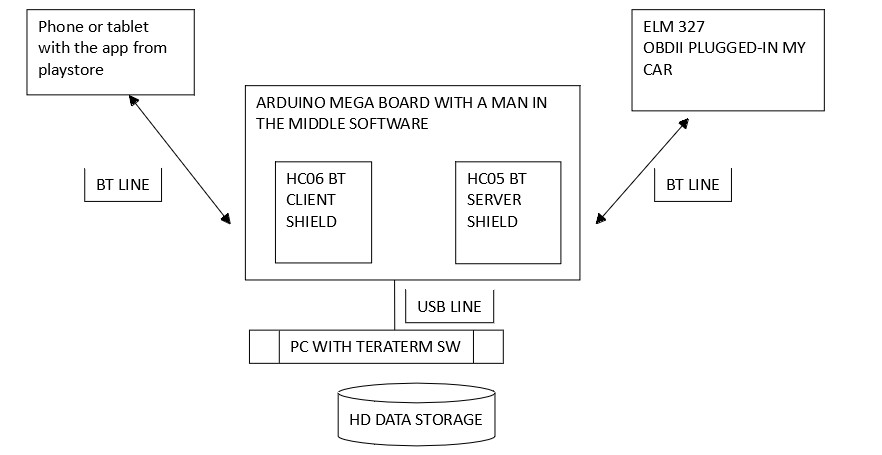 Man in the Middle
Man in the Middle
Alt: Man in the Middle diagram showing communication between a smartphone app, ELM327 scanner, car ECU, Arduino sniffer, and PC for CAN bus analysis.
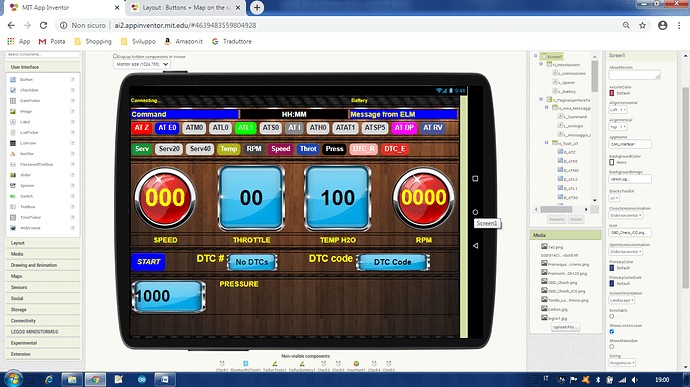 Screen
Screen
Alt: Screenshot of an App Inventor interface displaying real-time car diagnostic data, including throttle, temperature, and pressure readings via ELM327 scanner.
 blocks
blocks
Alt: Visual representation of App Inventor blocks used to code a car diagnostic app interacting with an ELM327 OBD2 scanner.
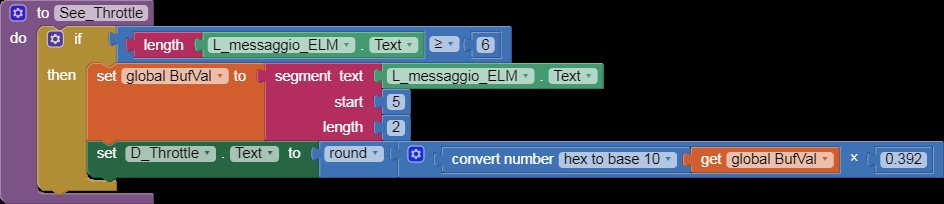 See_Throttle
See_Throttle
Alt: App Inventor code block for displaying throttle data received from an ELM327 OBD2 scanner.
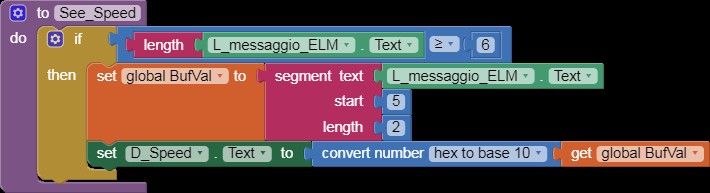 See_Speed
See_Speed
Alt: Code block showcasing the retrieval and display of vehicle speed data via an ELM327 OBD2 interface in App Inventor.
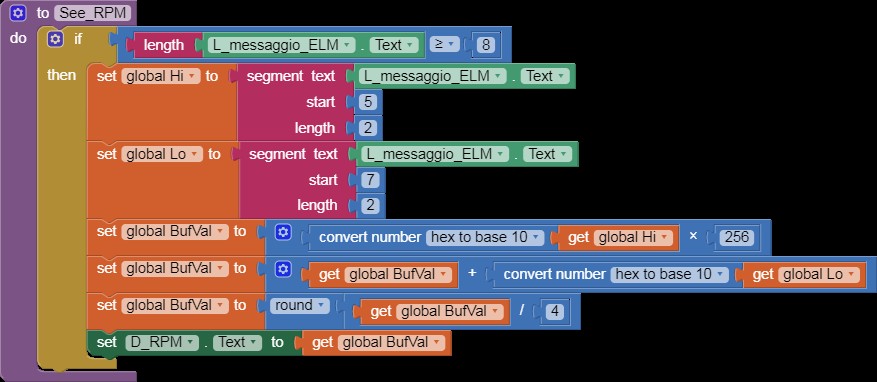 See_RPM
See_RPM
Alt: App Inventor code displaying RPM data extracted from a car’s ECU via an ELM327 OBD2 scanner.
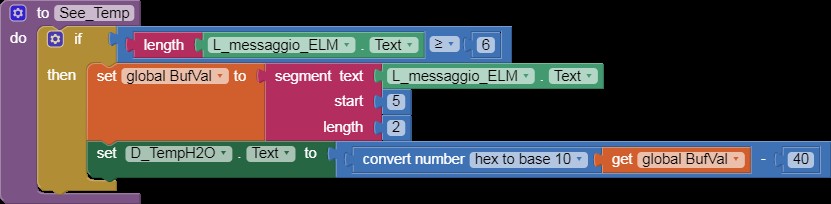 See_Temp
See_Temp
Alt: Code snippet in App Inventor used to read and show temperature readings from a car using an ELM327 OBD2 device.
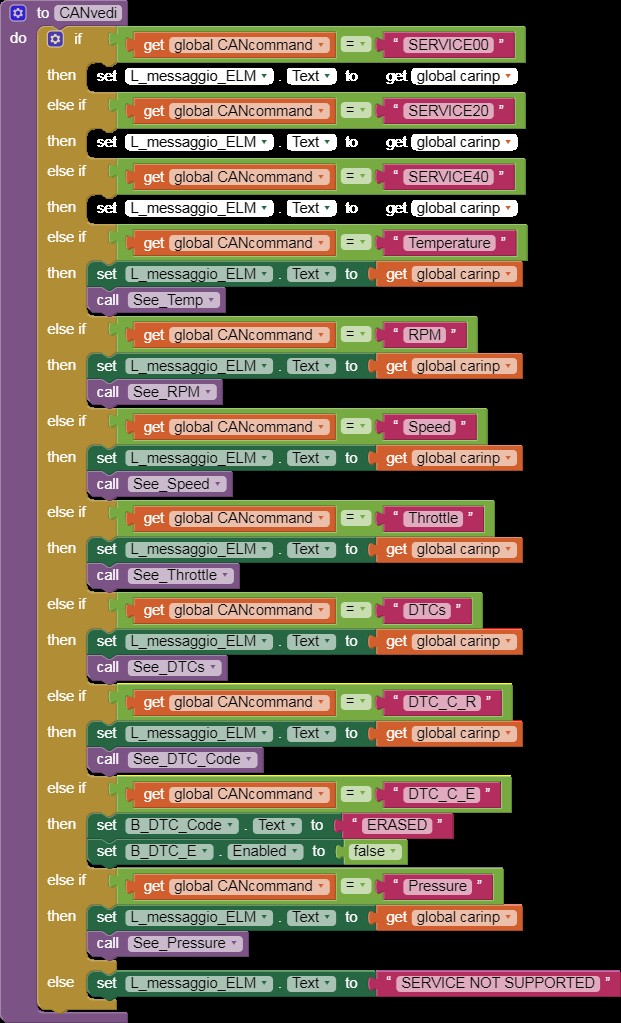 CANvedi
CANvedi
Alt: An image showcasing CAN bus data processing in an App Inventor-based OBD2 scanner application.
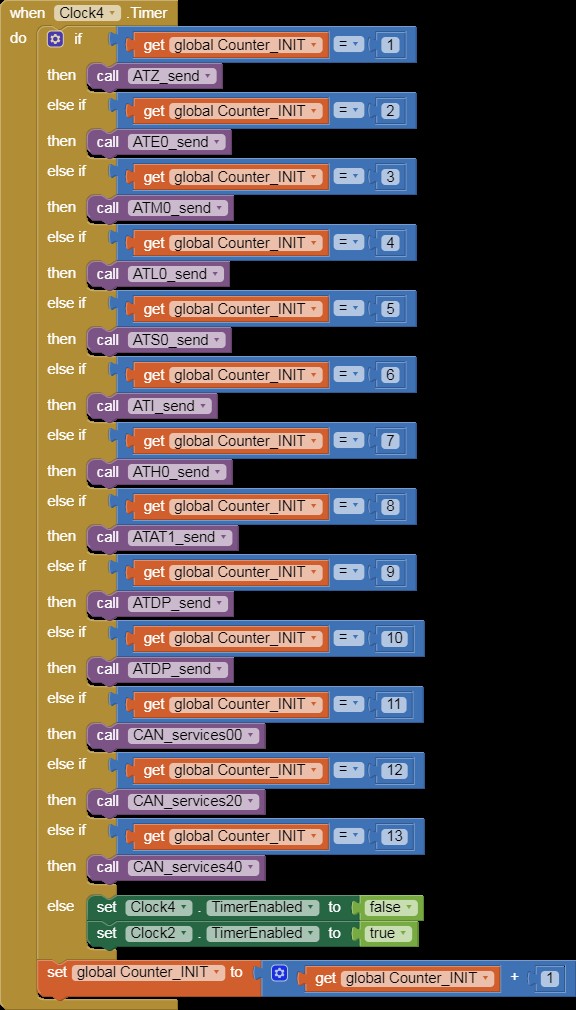 when Clock4 Timer
when Clock4 Timer
Alt: Code for a timer in App Inventor used to periodically send AT initialization commands to an ELM327 OBD2 scanner for CAN bus communication.
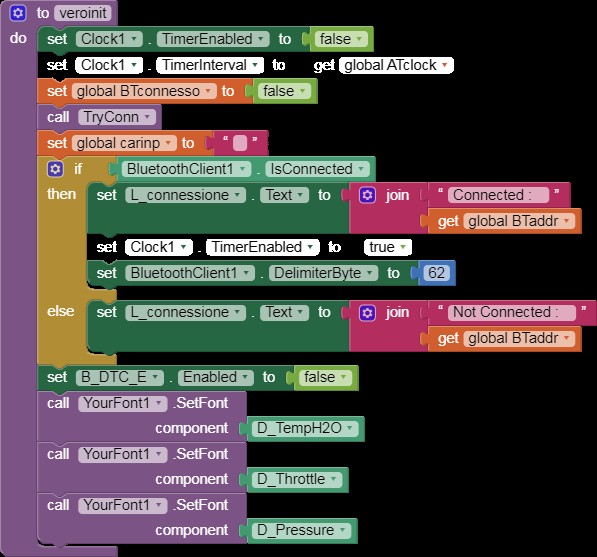 veroinit
veroinit
Alt: Implementation of a true initialization block in App Inventor for setting up the ELM327 scanner for CAN bus communication.
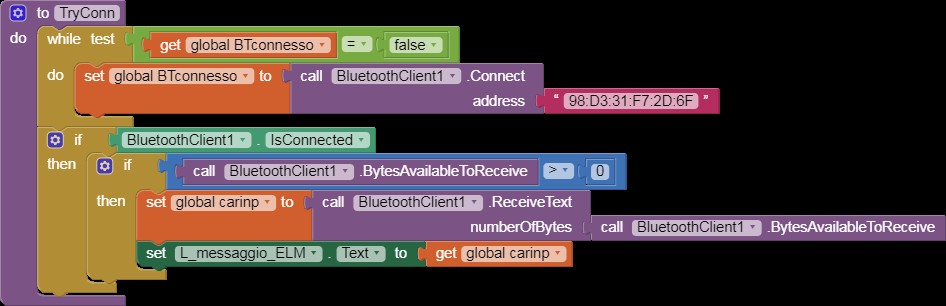 TryConn
TryConn
Alt: App Inventor code snippet for attempting a connection to the ELM327 OBD2 scanner.
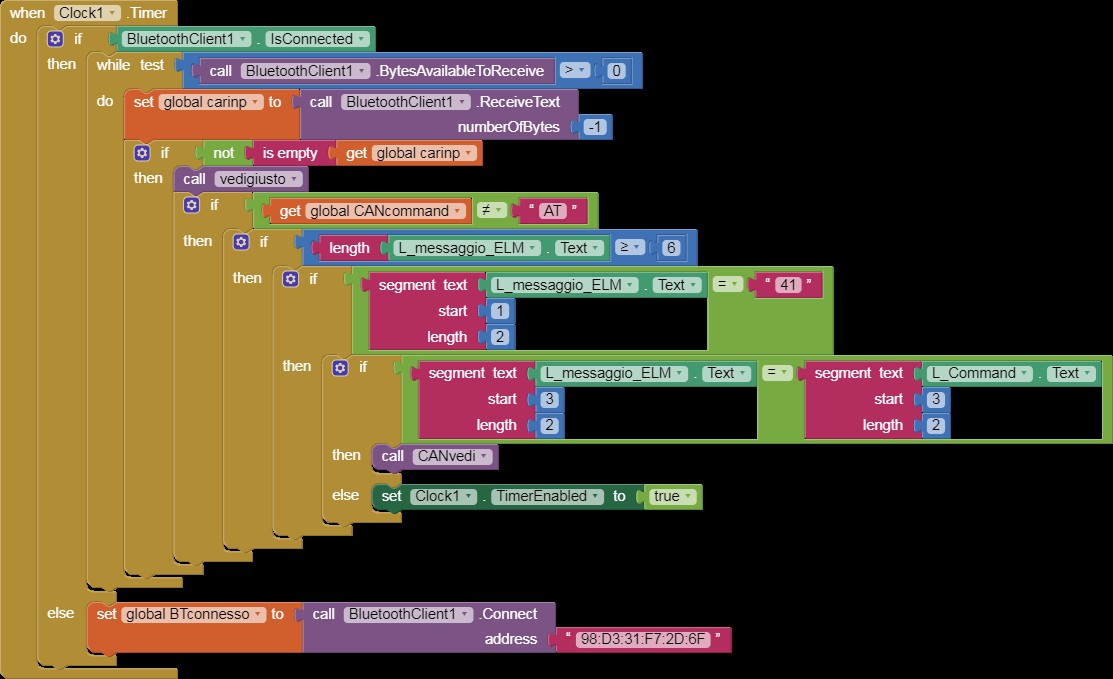 when Clock1 Timer
when Clock1 Timer
Alt: Code to receive and process data from the ELM327 OBD2 scanner inside the App Inventor clock timer.
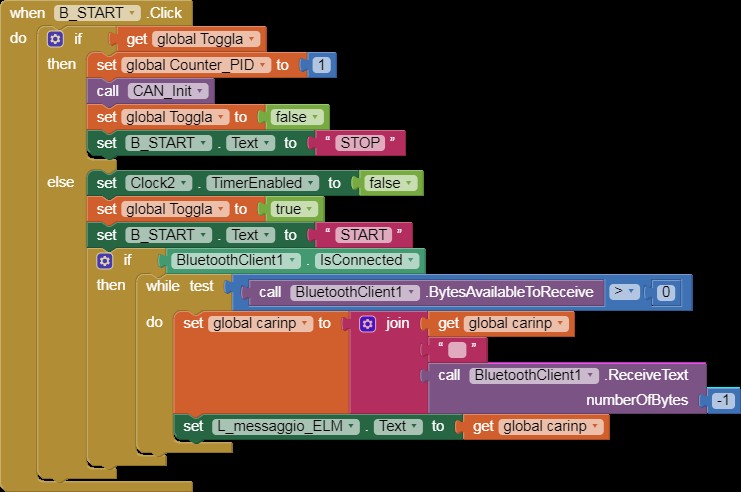 when B_START Click
when B_START Click
Alt: App Inventor code block triggered by a start button click, used to initiate the communication with the car’s ECU via the ELM327 scanner.