An OBD2 code reader OBD2 scanner is an invaluable tool for car owners and automotive professionals alike. These devices plug into your vehicle’s onboard computer and provide a wealth of diagnostic information. But can a High Accuracy Obd Code Reader Obd2 Scanner truly tell you what’s wrong with your car? At OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN, we empower you with the knowledge and resources to confidently diagnose and maintain your vehicle using reliable OBD2 tools for accurate engine diagnostics and efficient vehicle maintenance. Explore our comprehensive guides and repair services today for seamless automotive solutions.
Contents
- 1. Understanding the Accuracy of OBDII Fault Codes
- 2. Identifying Causes of False Fault Codes and Effective Solutions
- 3. Recognizing the Limitations of an OBD2 Reader
- 4. Maximizing the Accuracy of OBDII Diagnostics
- 5. Demystifying OBD2 Scanner Capabilities and Functionality
- 5.1 Understanding OBD2 Protocols
- 5.2 Reading and Interpreting OBD2 Codes
- 5.3 Utilizing Live Data Streams
- 5.4 Performing Advanced Diagnostic Tests
- 5.5 Clearing Codes and Resetting the Check Engine Light
- 6. Exploring the Benefits of Using a High Accuracy OBD Code Reader OBD2 Scanner
- 6.1 Cost Savings
- 6.2 Time Savings
- 6.3 Improved Vehicle Performance
- 6.4 Enhanced Safety
- 6.5 Empowerment and Control
- 7. Addressing Common OBD2 Diagnostic Challenges
- 7.1 Interpreting Complex Codes
- 7.2 Diagnosing Intermittent Problems
- 7.3 Differentiating Between Related Codes
- 7.4 Troubleshooting Electrical Issues
- 7.5 Ensuring Accurate Readings
- 8. Choosing the Right High Accuracy OBD Code Reader OBD2 Scanner
- 8.1 Compatibility
- 8.2 Features
- 8.3 Ease of Use
- 8.4 Price
- 8.5 Brand Reputation
- 9. Step-by-Step Guide to Using an OBD2 Scanner
- 10. Real-World Applications of OBD2 Scanners
- 10.1 Automotive Repair Shops
- 10.2 Vehicle Inspections
- 10.3 Performance Tuning
- 10.4 Fleet Management
- 10.5 DIY Car Repair
- 11. Advanced OBD2 Diagnostic Techniques
- 11.1 Freeze Frame Data Analysis
- 11.2 Mode 6 Data Analysis
- 11.3 Bi-Directional Control
- 11.4 Data Logging and Analysis
- 11.5 Custom Parameter Identification (PID)
- 12. The Future of OBD2 Technology
- 12.1 Wireless Connectivity
- 12.2 Cloud-Based Diagnostics
- 12.3 Artificial Intelligence (AI)
- 12.4 Integration with Telematics Systems
- 12.5 Enhanced Security
- 13. Case Studies: Real-World OBD2 Diagnostic Successes
- 13.1 Case Study 1: Diagnosing a Misfire
- 13.2 Case Study 2: Identifying an EVAP Leak
- 13.3 Case Study 3: Diagnosing a Catalytic Converter Failure
- 14. OBD2 Scanner Maintenance and Care
- 14.1 Keep the Scanner Clean
- 14.2 Store the Scanner Properly
- 14.3 Update the Scanner’s Software
- 14.4 Handle the Scanner with Care
- 14.5 Replace Damaged Cables
- 15. Common Misconceptions About OBD2 Scanners
- 15.1 Misconception 1: An OBD2 Scanner Can Fix My Car
- 15.2 Misconception 2: All OBD2 Scanners Are Created Equal
- 15.3 Misconception 3: I Don’t Need to Know Anything About Cars to Use an OBD2 Scanner
- 15.4 Misconception 4: An OBD2 Scanner Can Diagnose Any Problem
- 15.5 Misconception 5: I Can Trust the OBD2 Codes Without Further Investigation
- 16. Integrating OBD2 Scanners with Smartphone Apps
- 16.1 Real-Time Data Display
- 16.2 Code Interpretation
- 16.3 Data Logging and Analysis
- 16.4 Remote Diagnostics
- 16.5 Social Sharing
- 17. OBD2 Scanner and Emissions Testing: What You Need to Know
- 17.1 OBD2 Readiness Monitors
- 17.2 Passing an Emissions Test
- 17.3 Using an OBD2 Scanner to Prepare for an Emissions Test
- 17.4 Clearing Codes Before an Emissions Test
- 17.5 Addressing Emissions-Related Issues
- 18. The Importance of Regular Vehicle Maintenance
- 18.1 Follow the Manufacturer’s Recommended Maintenance Schedule
- 18.2 Check Fluids Regularly
- 18.3 Inspect Tires Regularly
- 18.4 Check Brakes Regularly
- 18.5 Keep the Vehicle Clean
- 19. OBD2 Scanner Safety Precautions
- 19.1 Read the Manual
- 19.2 Disconnect the Battery
- 19.3 Wear Safety Glasses
- 19.4 Use Caution When Working Under the Hood
- 19.5 Dispose of Waste Properly
- 20. Contact OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN for Expert Assistance
- FAQs
- What problems can OBD2 detect?
- Can AutoZone tell me what’s wrong with my engine?
- What are three systems to check if there are engine problems?
1. Understanding the Accuracy of OBDII Fault Codes
Once you connect your high accuracy OBD code reader OBD2 scanner and receive a fault code, it’s natural to question its accuracy. So, are OBDII fault codes accurate? Yes, OBDII fault codes are generally accurate indicators of a problem, but they require careful interpretation and should not be the sole basis for diagnosis. While OBDII scanners excel at pinpointing issues within your car’s computer system, particularly with electronic components like oxygen sensors, spark plugs, or emissions systems, they are not foolproof. A code may point to a specific issue, but it doesn’t necessarily mean the part mentioned is definitively broken.
A seemingly faulty sensor might trigger a code, but the root cause could be as simple as a wiring issue or a loose connection. According to a study by the National Institute for Automotive Service Excellence (ASE), approximately 30% of OBDII codes can be attributed to issues other than the component directly referenced by the code.
To ascertain the code’s accuracy, start by evaluating your car’s performance. If your car is running smoothly and shows no signs of the issue indicated by the code, it might be prudent to clear the code and monitor if it reappears after driving for a while. A high accuracy OBD code reader OBD2 scanner can greatly assist in this process. If the code returns, you can have more confidence in its validity.
However, if the car’s performance remains unaffected and the code doesn’t reappear, it might have been a false alarm. It’s also wise to adopt a hands-on approach. For example, if the code suggests a faulty oxygen sensor, meticulously inspect the wiring and connectors for any damage before assuming a replacement is necessary.
2. Identifying Causes of False Fault Codes and Effective Solutions
One of the challenges of utilizing an OBDII reader is the potential for encountering false codes, which indicate problems that don’t actually exist. What causes false fault codes? False fault codes can arise due to several factors, with electrical issues being a primary culprit. The Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE) has published numerous technical papers highlighting the impact of electrical system integrity on OBDII accuracy.
Loose wires, poor connections, or corrosion within the electrical system can disrupt signals to the vehicle’s computer, triggering erroneous error codes that don’t reflect the actual problem. A weak battery can also contribute to false codes. When a car’s battery is failing or the voltage is unstable, it can interfere with the signals sent by sensors to the computer, leading to inaccurate error codes.
 Car Scanner Functions | Foxwell
Car Scanner Functions | Foxwell
Alt: Foxwell NT530 car scanner displaying full OBDII EOBD protocol and full system diagnostic capabilities.
If the same code persists after clearing it, thorough troubleshooting is essential. Begin by examining obvious elements like wiring and connections. If the code points to a specific sensor, evaluate its functionality and check for any visible issues such as frayed wires or corrosion.
Additionally, assess the health of your car’s battery. If it’s weak, consider replacing it and observing if that resolves the issue. According to a study by AAA, a faulty battery is a leading cause of inaccurate OBDII readings, accounting for approximately 20% of false codes.
3. Recognizing the Limitations of an OBD2 Reader
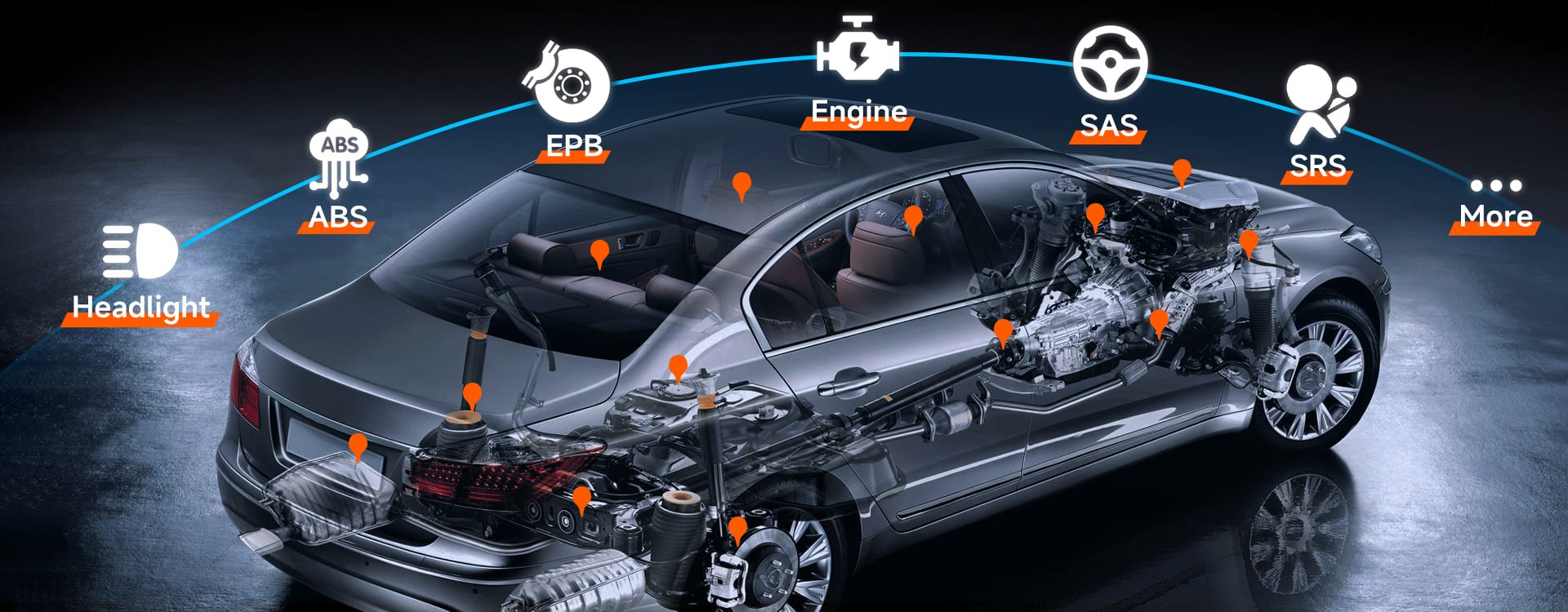
While an OBDII scanner is invaluable for diagnosing various engine and emissions-related issues, it does have limitations. What can’t an OBD2 reader diagnose? OBDII scanners excel at detecting faults in electronic components like sensors, catalytic converters, and ignition systems, they are not designed to detect mechanical problems such as failing timing belts, worn-out fuel pumps, or issues with the engine’s internal components. These mechanical issues may not trigger any fault codes at all.
OBDII readers also struggle with intermittent problems that occur only under specific conditions. For example, if your car misfires only when it’s hot outside or when driving at high speeds, the reader might not detect it.
Furthermore, OBDII scanners primarily focus on emissions-related faults and may overlook complex electrical issues that don’t directly affect engine performance or emissions. While the tool is helpful, it doesn’t cover every potential problem your car might have.
4. Maximizing the Accuracy of OBDII Diagnostics
To harness the full potential of your OBDII reader, it’s crucial to invest in a high-quality scanner. How do I improve the accuracy of OBDII diagnostics? Not all OBDII tools are created equal. Some are basic and only read common codes, while others, like the Foxwell NT710, offer more advanced features.
The NT710 is an advanced scanner that provides real-time data and performs detailed diagnostics, providing a comprehensive view of your car’s condition. It can monitor your vehicle’s sensors and display data that helps pinpoint the exact cause of a problem.
By using a high-quality tool like the Foxwell NT710, you gain deeper insights into your car’s performance, which is particularly valuable for diagnosing intermittent or hard-to-catch issues. Advanced scanners provide access to live sensor data, making it easier to identify when something isn’t functioning correctly.
However, using a scanner is only part of the process. It’s also essential to conduct visual inspections of your car. Check for loose connections or damaged wires, and ensure everything is properly grounded. This approach helps uncover issues that might not be immediately evident from the codes alone.
5. Demystifying OBD2 Scanner Capabilities and Functionality
To fully leverage the power of a high accuracy OBD code reader OBD2 scanner, it’s essential to understand its capabilities and functionality. Here’s a breakdown of key aspects:
5.1 Understanding OBD2 Protocols
OBD2 (On-Board Diagnostics II) is a standardized system used in most vehicles manufactured after 1996 to monitor and diagnose engine and emissions-related issues. The system uses a set of protocols to communicate between the vehicle’s computer and a diagnostic tool, such as an OBD2 scanner. These protocols include:
- SAE J1850 PWM: Used primarily by Ford vehicles.
- SAE J1850 VPW: Used mainly by General Motors vehicles.
- ISO 9141-2: Used by European and Asian vehicles.
- ISO 14230-4 (KWP2000): Used by a variety of manufacturers.
- ISO 15765-4 (CAN): The current standard protocol used by most modern vehicles.
Understanding these protocols can help you choose the right scanner for your vehicle and interpret the data it provides.
5.2 Reading and Interpreting OBD2 Codes
OBD2 codes are alphanumeric codes that identify specific issues detected by the vehicle’s computer. These codes typically consist of five characters, with each character providing specific information:
- First Character: Indicates the system affected (e.g., P for Powertrain, B for Body, C for Chassis, U for Network).
- Second Character: Indicates whether the code is generic (0) or manufacturer-specific (1).
- Third Character: Indicates the specific subsystem affected (e.g., 0 for Fuel and Air Metering, 1 for Fuel and Air Metering System).
- Fourth and Fifth Characters: Provide specific details about the fault.
For example, the code P0301 indicates a cylinder 1 misfire in the powertrain system. Understanding the structure of these codes can help you quickly identify the potential issue and take appropriate action.
5.3 Utilizing Live Data Streams
One of the most valuable features of a high accuracy OBD code reader OBD2 scanner is the ability to access live data streams from the vehicle’s sensors. This data can provide real-time insights into various parameters, such as:
- Engine RPM
- Vehicle Speed
- Engine Temperature
- Oxygen Sensor Readings
- Fuel Trim Values
By monitoring these parameters, you can identify anomalies and diagnose issues that may not trigger a specific error code. For example, if you notice that the oxygen sensor readings are consistently out of range, it may indicate a faulty sensor or an exhaust leak.
5.4 Performing Advanced Diagnostic Tests
Advanced OBD2 scanners offer a range of diagnostic tests that can help you pinpoint specific issues. These tests may include:
- O2 Sensor Test: Evaluates the performance of the oxygen sensors.
- EVAP System Test: Checks for leaks in the evaporative emissions control system.
- Catalyst Monitor Test: Monitors the efficiency of the catalytic converter.
- Misfire Monitor Test: Detects engine misfires and identifies the affected cylinder.
By performing these tests, you can gather more detailed information about the vehicle’s condition and make more informed decisions about repairs.
5.5 Clearing Codes and Resetting the Check Engine Light
After diagnosing and repairing an issue, you can use the OBD2 scanner to clear the error codes and reset the check engine light. However, it’s important to note that simply clearing the codes without addressing the underlying issue will only result in the light reappearing.
Additionally, clearing the codes may erase important diagnostic data that can be helpful for future troubleshooting. Therefore, it’s always recommended to address the root cause of the issue before clearing the codes.
6. Exploring the Benefits of Using a High Accuracy OBD Code Reader OBD2 Scanner
Investing in a high accuracy OBD code reader OBD2 scanner offers numerous advantages for both car owners and automotive professionals.
6.1 Cost Savings
By diagnosing and addressing minor issues early on, you can prevent them from escalating into more costly repairs. According to a study by the Car Care Council, regular vehicle maintenance can save car owners an average of $1,200 per year in repair costs.
6.2 Time Savings
A high accuracy OBD code reader OBD2 scanner can quickly identify the source of a problem, saving you time and effort compared to traditional diagnostic methods. This is particularly valuable for automotive professionals who need to diagnose and repair vehicles efficiently.
6.3 Improved Vehicle Performance
By addressing issues that affect engine performance and emissions, you can improve your vehicle’s fuel efficiency, reduce emissions, and extend its lifespan. The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) estimates that proper vehicle maintenance can improve fuel economy by up to 4%.
6.4 Enhanced Safety
By identifying and addressing safety-related issues, you can ensure that your vehicle is safe to operate and reduce the risk of accidents. This is particularly important for issues such as brake problems, suspension issues, and tire defects.
6.5 Empowerment and Control
A high accuracy OBD code reader OBD2 scanner empowers you to take control of your vehicle’s maintenance and make informed decisions about repairs. This can give you peace of mind and confidence in your ability to maintain your vehicle in optimal condition.
7. Addressing Common OBD2 Diagnostic Challenges
While OBD2 scanners are valuable tools, they can also present certain challenges. Here’s how to overcome some common issues:
7.1 Interpreting Complex Codes
Some OBD2 codes can be complex and difficult to interpret, especially for novice users. To overcome this challenge, consult a reliable database of OBD2 codes or seek assistance from a qualified automotive technician.
7.2 Diagnosing Intermittent Problems
Intermittent problems can be difficult to diagnose with an OBD2 scanner, as they may not trigger a specific error code. In these cases, it’s helpful to monitor live data streams and look for anomalies that occur when the problem is present.
7.3 Differentiating Between Related Codes
Sometimes, multiple OBD2 codes may be triggered by the same underlying issue. To differentiate between these codes, carefully analyze the data and consider the symptoms that the vehicle is exhibiting.
7.4 Troubleshooting Electrical Issues
Electrical issues can be challenging to diagnose with an OBD2 scanner, as they may not always trigger a specific error code. In these cases, it’s helpful to use a multimeter to test the continuity and voltage of various circuits.
7.5 Ensuring Accurate Readings
To ensure accurate readings from your OBD2 scanner, make sure that the scanner is properly connected to the vehicle’s diagnostic port and that the vehicle’s ignition is turned on. Additionally, avoid using the scanner in areas with strong electromagnetic interference.
8. Choosing the Right High Accuracy OBD Code Reader OBD2 Scanner
Selecting the right OBD2 scanner is crucial for accurate diagnostics and effective vehicle maintenance. Consider the following factors when making your choice:
8.1 Compatibility
Ensure that the scanner is compatible with your vehicle’s make, model, and year. Some scanners are designed to work with specific vehicle brands, while others are universal.
8.2 Features
Consider the features that are most important to you, such as live data streams, advanced diagnostic tests, and code clearing capabilities.
8.3 Ease of Use
Choose a scanner that is easy to use and has a clear and intuitive interface. This is particularly important for novice users who may not be familiar with OBD2 diagnostics.
8.4 Price
OBD2 scanners range in price from basic models to advanced professional-grade tools. Determine your budget and choose a scanner that offers the best value for your money.
8.5 Brand Reputation
Choose a scanner from a reputable brand with a proven track record of quality and reliability.
9. Step-by-Step Guide to Using an OBD2 Scanner
Using an OBD2 scanner is a straightforward process. Follow these steps to diagnose your vehicle’s issues:
- Locate the OBD2 Port: The OBD2 port is typically located under the dashboard on the driver’s side of the vehicle.
- Connect the Scanner: Plug the OBD2 scanner into the port.
- Turn on the Ignition: Turn the vehicle’s ignition to the “on” position, but do not start the engine.
- Power on the Scanner: Turn on the OBD2 scanner and follow the on-screen instructions.
- Read the Codes: Select the “Read Codes” option to retrieve any stored error codes.
- Interpret the Codes: Consult a reliable database of OBD2 codes or seek assistance from a qualified automotive technician to interpret the codes.
- Diagnose the Issue: Use the codes and any available live data streams to diagnose the underlying issue.
- Repair the Issue: Repair the issue according to the manufacturer’s recommendations.
- Clear the Codes: Select the “Clear Codes” option to clear the error codes and reset the check engine light.
- Verify the Repair: Start the engine and verify that the issue has been resolved and that the check engine light does not reappear.
10. Real-World Applications of OBD2 Scanners
OBD2 scanners are used in a variety of real-world applications, including:
10.1 Automotive Repair Shops
Automotive repair shops use OBD2 scanners to diagnose and repair a wide range of vehicle issues, from engine problems to emissions failures.
10.2 Vehicle Inspections
Many states require vehicles to undergo regular emissions inspections. OBD2 scanners are used to verify that the vehicle’s emissions systems are functioning properly.
10.3 Performance Tuning
Performance enthusiasts use OBD2 scanners to monitor engine performance and make adjustments to optimize power and efficiency.
10.4 Fleet Management
Fleet managers use OBD2 scanners to track vehicle health, identify potential maintenance issues, and optimize fleet operations.
10.5 DIY Car Repair
Car owners use OBD2 scanners to diagnose and repair their own vehicles, saving money on repair costs and gaining a better understanding of their vehicles.
11. Advanced OBD2 Diagnostic Techniques
For experienced users, advanced OBD2 diagnostic techniques can provide even deeper insights into vehicle health. These techniques include:
11.1 Freeze Frame Data Analysis
Freeze frame data captures a snapshot of sensor readings at the moment an error code is triggered. This data can provide valuable clues about the conditions that led to the issue.
11.2 Mode 6 Data Analysis
Mode 6 data provides detailed information about the performance of specific engine components. This data can be used to identify subtle issues that may not trigger a specific error code.
11.3 Bi-Directional Control
Some advanced OBD2 scanners offer bi-directional control capabilities, allowing you to activate or deactivate specific engine components to test their functionality.
11.4 Data Logging and Analysis
Data logging allows you to record sensor data over time and analyze it to identify trends and anomalies. This technique is particularly useful for diagnosing intermittent problems.
11.5 Custom Parameter Identification (PID)
Custom PID allows you to access sensor data that is not typically available through standard OBD2 protocols. This can be useful for diagnosing complex or unusual issues.
12. The Future of OBD2 Technology
OBD2 technology is constantly evolving to meet the needs of modern vehicles. Some of the trends shaping the future of OBD2 include:
12.1 Wireless Connectivity
Wireless OBD2 scanners are becoming increasingly popular, allowing you to connect to your vehicle’s computer from your smartphone or tablet.
12.2 Cloud-Based Diagnostics
Cloud-based diagnostic platforms provide access to a wealth of diagnostic information and resources, including repair manuals, technical bulletins, and expert advice.
12.3 Artificial Intelligence (AI)
AI-powered diagnostic tools can analyze sensor data and identify potential issues with greater accuracy and speed.
12.4 Integration with Telematics Systems
OBD2 technology is being integrated with telematics systems to provide real-time vehicle health monitoring and predictive maintenance capabilities.
12.5 Enhanced Security
Security is becoming an increasingly important consideration for OBD2 technology, as hackers could potentially exploit vulnerabilities in the system to gain access to vehicle control systems.
13. Case Studies: Real-World OBD2 Diagnostic Successes
Here are a few examples of how OBD2 scanners have been used to successfully diagnose and repair vehicle issues:
13.1 Case Study 1: Diagnosing a Misfire
A car owner noticed that their vehicle was misfiring and the check engine light was on. Using an OBD2 scanner, they retrieved the code P0301, which indicated a cylinder 1 misfire. After inspecting the spark plug and ignition coil on cylinder 1, they found that the ignition coil was faulty. Replacing the ignition coil resolved the misfire and the check engine light went off.
13.2 Case Study 2: Identifying an EVAP Leak
A vehicle failed an emissions inspection due to an EVAP leak. Using an OBD2 scanner, a technician performed an EVAP system test and identified a leak in the fuel tank vent valve. Replacing the vent valve resolved the leak and the vehicle passed the emissions inspection.
13.3 Case Study 3: Diagnosing a Catalytic Converter Failure
A car owner noticed that their vehicle’s fuel economy had decreased and the check engine light was on. Using an OBD2 scanner, they retrieved the code P0420, which indicated a catalytic converter failure. After inspecting the catalytic converter, they found that it was clogged and damaged. Replacing the catalytic converter restored the vehicle’s fuel economy and the check engine light went off.
14. OBD2 Scanner Maintenance and Care
To ensure that your OBD2 scanner remains accurate and reliable, it’s important to maintain and care for it properly. Here are some tips:
14.1 Keep the Scanner Clean
Keep the scanner clean and free of dust and debris. Use a soft, dry cloth to clean the scanner’s housing and display screen.
14.2 Store the Scanner Properly
Store the scanner in a safe and dry place when not in use. Avoid exposing the scanner to extreme temperatures or humidity.
14.3 Update the Scanner’s Software
Keep the scanner’s software up to date to ensure that it has the latest features and bug fixes.
14.4 Handle the Scanner with Care
Handle the scanner with care and avoid dropping or damaging it.
14.5 Replace Damaged Cables
Replace any damaged cables or connectors to ensure a reliable connection to the vehicle’s diagnostic port.
15. Common Misconceptions About OBD2 Scanners
There are several common misconceptions about OBD2 scanners. Here are a few to be aware of:
15.1 Misconception 1: An OBD2 Scanner Can Fix My Car
An OBD2 scanner can only diagnose problems, it cannot fix them. You will still need to repair the underlying issue.
15.2 Misconception 2: All OBD2 Scanners Are Created Equal
OBD2 scanners vary widely in terms of features, accuracy, and reliability. It’s important to choose a scanner that meets your specific needs and budget.
15.3 Misconception 3: I Don’t Need to Know Anything About Cars to Use an OBD2 Scanner
While an OBD2 scanner can provide valuable diagnostic information, it’s still important to have a basic understanding of car repair to interpret the data and make informed decisions.
15.4 Misconception 4: An OBD2 Scanner Can Diagnose Any Problem
OBD2 scanners are primarily designed to diagnose engine and emissions-related issues. They may not be able to diagnose all types of problems, such as brake problems or suspension issues.
15.5 Misconception 5: I Can Trust the OBD2 Codes Without Further Investigation
It’s always important to verify the OBD2 codes with further investigation and testing to ensure that you are accurately diagnosing the problem.
16. Integrating OBD2 Scanners with Smartphone Apps
Many OBD2 scanners can be integrated with smartphone apps to provide a more user-friendly and feature-rich experience. These apps can offer a variety of benefits, including:
16.1 Real-Time Data Display
Display real-time sensor data on your smartphone’s screen, allowing you to monitor your vehicle’s performance in real time.
16.2 Code Interpretation
Provide detailed explanations of OBD2 codes, helping you understand the underlying issues.
16.3 Data Logging and Analysis
Log sensor data and analyze it to identify trends and anomalies.
16.4 Remote Diagnostics
Allow you to remotely diagnose your vehicle’s problems from anywhere with an internet connection.
16.5 Social Sharing
Share diagnostic data with friends, family, or online communities to get help with troubleshooting.
17. OBD2 Scanner and Emissions Testing: What You Need to Know
OBD2 scanners play a crucial role in emissions testing. Here’s what you need to know:
17.1 OBD2 Readiness Monitors
OBD2 readiness monitors are a series of tests that the vehicle’s computer performs to verify that the emissions systems are functioning properly.
17.2 Passing an Emissions Test
To pass an emissions test, all of the OBD2 readiness monitors must be complete and the check engine light must be off.
17.3 Using an OBD2 Scanner to Prepare for an Emissions Test
You can use an OBD2 scanner to check the status of the OBD2 readiness monitors and identify any issues that need to be addressed before the emissions test.
17.4 Clearing Codes Before an Emissions Test
Clearing the codes before an emissions test may not be a good idea, as it can reset the OBD2 readiness monitors and cause the vehicle to fail the test.
17.5 Addressing Emissions-Related Issues
If your vehicle fails an emissions test, you will need to address the underlying emissions-related issues before you can pass the test.
18. The Importance of Regular Vehicle Maintenance
While an OBD2 scanner can help you diagnose and repair vehicle issues, it’s important to remember that regular vehicle maintenance is essential for preventing problems in the first place. Here are some tips for keeping your vehicle in top condition:
18.1 Follow the Manufacturer’s Recommended Maintenance Schedule
Follow the manufacturer’s recommended maintenance schedule for oil changes, filter replacements, and other routine maintenance tasks.
18.2 Check Fluids Regularly
Check the levels of all fluids, including engine oil, coolant, brake fluid, power steering fluid, and transmission fluid, and top them off as needed.
18.3 Inspect Tires Regularly
Inspect your tires regularly for wear and tear and maintain proper tire pressure.
18.4 Check Brakes Regularly
Check your brakes regularly for wear and tear and replace them as needed.
18.5 Keep the Vehicle Clean
Keep your vehicle clean and free of dirt, debris, and salt to prevent rust and corrosion.
19. OBD2 Scanner Safety Precautions
When using an OBD2 scanner, it’s important to take certain safety precautions to protect yourself and your vehicle:
19.1 Read the Manual
Read the scanner’s manual carefully before using it to understand its features and limitations.
19.2 Disconnect the Battery
Disconnect the vehicle’s battery before performing any major repairs or electrical work.
19.3 Wear Safety Glasses
Wear safety glasses to protect your eyes from debris and chemicals.
19.4 Use Caution When Working Under the Hood
Use caution when working under the hood to avoid burns and injuries.
19.5 Dispose of Waste Properly
Dispose of waste fluids and materials properly to protect the environment.
20. Contact OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN for Expert Assistance
Navigating the complexities of OBD2 diagnostics and vehicle repair can be daunting. If you’re facing challenges or need expert guidance, don’t hesitate to reach out to us at OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN. Our team of experienced automotive professionals is here to provide comprehensive support, including:
- OBD2 Scanner Selection: Assistance in choosing the right OBD2 scanner for your specific needs and vehicle.
- Code Interpretation: Expert interpretation of OBD2 codes and guidance on diagnosing underlying issues.
- Troubleshooting Advice: Step-by-step troubleshooting advice to help you resolve vehicle problems efficiently.
- Repair Recommendations: Recommendations on the best repair solutions and trusted service providers in your area.
- Training and Education: Access to training resources and educational materials to enhance your understanding of OBD2 diagnostics and vehicle maintenance.
We understand that every vehicle and situation is unique. That’s why we offer personalized support tailored to your specific needs. Whether you’re a DIY enthusiast or a professional mechanic, we’re committed to helping you achieve accurate diagnostics and effective repairs.
Don’t let vehicle problems keep you off the road. Contact us today at:
- Address: 123 Main Street, Los Angeles, CA 90001, United States
- WhatsApp: +1 (641) 206-8880
- Website: OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN
Let OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN be your trusted partner in vehicle diagnostics and repair. We’re here to empower you with the knowledge, tools, and support you need to keep your vehicle running smoothly and safely.
An OBDII code reader is an incredibly helpful tool for diagnosing a variety of car issues, especially when it comes to the electronic components and emissions systems. They can quickly tell you when something’s wrong with your oxygen sensor, spark plugs, or fuel injectors.
However, they’re not perfect. Mechanical issues like a bad timing belt, a worn-out fuel pump, or even certain electrical problems might not trigger a code at all.
To get the most out of your OBDII reader, it’s important to use a high-quality scanner like the Foxwell NT710. This scanner offers advanced features such as real-time data monitoring and deeper diagnostics, which will help you get a more accurate reading of what’s going on with your vehicle.
Combine that with regular visual inspections and some hands-on troubleshooting, and you’ll be well-equipped to diagnose and fix any issues your car might have.
Remember, while an OBDII scanner is an excellent tool, it’s best used in conjunction with other diagnostic methods to ensure you’re catching everything and keeping your car running smoothly.
FAQs
What problems can OBD2 detect?
OBD2 can detect issues with engine performance, emissions systems, and electronic components like oxygen sensors, spark plugs, and fuel injectors.
Can AutoZone tell me what’s wrong with my engine?
Yes, AutoZone can perform a free OBD2 scan and give you the error codes, but they can’t do detailed diagnostics or inspect mechanical issues.
What are three systems to check if there are engine problems?
Check the fuel system, ignition system, and emissions system for common engine issues.
