Honda Ecu Error Codes Obd2, paired with a reliable OBD2 scanner, helps you swiftly diagnose car troubles and pinpoint the necessary fixes. At OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN, we empower you to understand these error codes, ensuring efficient vehicle maintenance and peak performance. Explore how our in-depth knowledge of Honda diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) and vehicle diagnostic tools translates to tangible benefits for your automotive needs.
Contents
- 1. Understanding Honda ECU Error Codes OBD2
- 1.1. What is an OBD2 Scanner?
- 1.2. Why Use an OBD2 Scanner for Your Honda?
- 1.3. Locating the OBD2 Port in Your Honda
- 2. How to Read Honda Error Codes Using an OBD2 Scanner
- 2.1. Step-by-Step Guide to Using an OBD2 Scanner
- 2.2. Interpreting the Codes: Understanding the Basics
- 2.3. Clearing Codes: When and How?
- 3. Common Honda ECU Error Codes and Their Meanings
- 3.1. P0420: Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold
- 3.1.1. Potential Causes of P0420
- 3.1.2. How to Fix P0420
- 3.2. P0171: System Too Lean (Bank 1)
- 3.2.1. Potential Causes of P0171
- 3.2.2. How to Fix P0171
- 3.3. P0300 Series: Misfire Codes (P0301, P0302, P0303, P0304)
- 3.3.1. Potential Causes of Misfires
- 3.3.2. How to Fix Misfire Codes
- 3.4. P0113: Intake Air Temperature (IAT) Sensor Circuit High Input
- 3.4.1. Potential Causes of P0113
- 3.4.2. How to Fix P0113
- 3.5. P0128: Coolant Thermostat (Coolant Temperature Below Thermostat Regulating Temperature)
- 3.5.1. Potential Causes of P0128
- 3.5.2. How to Fix P0128
- 4. Advanced Diagnostic Techniques for Honda ECU Error Codes
- 4.1. Using a Multimeter for Sensor Testing
- 4.1.1. How to Test an Oxygen Sensor with a Multimeter
- 4.2. Live Data Streaming: Monitoring Real-Time Parameters
- 4.2.1. What Parameters to Monitor
- 4.2.2. How to Use Live Data
- 4.3. Freeze Frame Data: Analyzing Conditions When the Code Was Set
- 4.3.1. How to Access Freeze Frame Data
- 4.3.2. Interpreting Freeze Frame Data
- 5. Honda Specific Error Codes: What You Need to Know
- 5.1. VTEC System Issues
- 5.1.1. Common VTEC Codes
- 5.1.2. How to Diagnose VTEC Issues
- 5.2. IMA System (Hybrid Models)
- 5.2.1. Common IMA Codes
- 5.2.2. Diagnosing IMA System Issues
- 5.3. Transmission-Related Codes
- 5.3.1. Common Transmission Codes
- 5.3.2. How to Address Transmission Codes
- 6. OBD2 Scanner Recommendations for Honda Vehicles
- 6.1. Entry-Level Scanners
- 6.1.1. Features to Look For
- 6.1.2. Recommended Models
- 6.2. Mid-Range Scanners
- 6.2.1. Features to Look For
- 6.2.2. Recommended Models
- 6.3. Professional-Grade Scanners
- 6.3.1. Features to Look For
- 6.3.2. Recommended Models
- 7. Maintaining Your Honda’s ECU and Preventing Error Codes
- 7.1. Regular Vehicle Maintenance
- 7.1.1. Key Maintenance Tasks
- 7.2. Using Quality Parts and Fluids
- 7.2.1. Why Quality Matters
- 7.3. Addressing Issues Promptly
- 7.3.1. The Importance of Early Detection
- 8. DIY vs. Professional Diagnosis: Making the Right Choice
- 8.1. When to DIY
- 8.1.1. Suitable DIY Tasks
- 8.2. When to Seek Professional Help
- 8.2.1. Situations Requiring Professional Assistance
- 8.3. The Benefits of Professional Diagnosis
- 8.3.1. Why Choose a Professional?
- 9. Resources for Honda ECU Error Codes and Diagnostics
- 9.1. Online Databases and Forums
- 9.1.1. Recommended Resources
- 9.2. Repair Manuals and Technical Documentation
- 9.2.1. Recommended Manuals
- 9.3. Professional Diagnostic Tools and Software
- 9.3.1. Recommended Tools
- 10. Frequently Asked Questions About Honda ECU Error Codes OBD2
- 10.1. What Does a Honda ECU Do?
- 10.2. How Often Should I Scan My Honda for Error Codes?
- 10.3. Can I Drive My Honda with the Check Engine Light On?
- 10.4. Will Clearing Error Codes Fix the Problem?
- 10.5. Are All OBD2 Scanners Compatible with Hondas?
- 10.6. What is the Difference Between Generic and Manufacturer-Specific Codes?
- 10.7. How Can I Find Honda-Specific Error Code Definitions?
- 10.8. Can a Faulty Gas Cap Trigger an Error Code?
- 10.9. What Does “Pending Code” Mean?
- 10.10. Can I Use a Smartphone App as an OBD2 Scanner?
1. Understanding Honda ECU Error Codes OBD2
What are Honda ECU Error Codes OBD2, and why are they important?
Honda ECU error codes OBD2 are standardized codes that your car’s computer (ECU – Engine Control Unit) generates when it detects a problem. These codes are crucial because they help mechanics and car owners diagnose issues quickly and accurately. According to the National Institute for Automotive Service Excellence (ASE), understanding these codes can reduce diagnostic time by up to 60%. These codes are accessed using an OBD2 scanner.
1.1. What is an OBD2 Scanner?
An OBD2 (On-Board Diagnostics II) scanner is a device used to retrieve diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) from a vehicle’s ECU. These scanners connect to a standardized port in your car, typically located under the dashboard. Modern OBD2 scanners, as highlighted in a 2023 report by the Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE), also provide real-time data, such as engine temperature, speed, and sensor readings, enhancing diagnostic accuracy.
1.2. Why Use an OBD2 Scanner for Your Honda?
Using an OBD2 scanner for your Honda allows you to identify problems early, potentially saving you money on costly repairs. Early detection can prevent minor issues from escalating into major problems. A study by AAA found that regular vehicle maintenance, guided by OBD2 diagnostics, reduces the likelihood of breakdowns by up to 25%.
1.3. Locating the OBD2 Port in Your Honda
The OBD2 port in most Honda vehicles is typically located under the dashboard on the driver’s side. It’s usually near the steering column or in the center console area. Consulting your Honda’s owner’s manual can provide the exact location.
2. How to Read Honda Error Codes Using an OBD2 Scanner
How do you effectively use an OBD2 scanner to retrieve and interpret Honda error codes?
Reading Honda error codes with an OBD2 scanner involves a simple process. First, plug the scanner into the OBD2 port. Turn the ignition to the “ON” position without starting the engine. The scanner will power up and prompt you to read codes. Once the scan is complete, the scanner will display any stored DTCs.
2.1. Step-by-Step Guide to Using an OBD2 Scanner
- Plug in the Scanner: Connect the OBD2 scanner to the OBD2 port in your Honda.
- Turn on the Ignition: Turn the ignition key to the “ON” position.
- Read Codes: Follow the scanner’s prompts to read the stored diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs).
- Record Codes: Write down each code displayed by the scanner.
- Interpret Codes: Use a reliable database or resource like OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN to look up the meaning of each code.
2.2. Interpreting the Codes: Understanding the Basics
OBD2 codes are structured in a specific format. The first character indicates the system (e.g., P for Powertrain, B for Body, C for Chassis, U for Network). The second character indicates whether the code is generic (0) or manufacturer-specific (1). The third character denotes the subsystem, and the last two characters specify the exact fault.
2.3. Clearing Codes: When and How?
You can clear codes after you have diagnosed and fixed the underlying issue. To clear codes, use the OBD2 scanner’s “Clear Codes” function. However, be cautious: clearing codes without fixing the problem will only temporarily turn off the check engine light, and the code will likely return. According to a 2022 study by the Car Care Council, improperly clearing codes can mask underlying issues, leading to more severe problems later.
3. Common Honda ECU Error Codes and Their Meanings
What are the common Honda ECU error codes, and what do they signify?
Several Honda ECU error codes appear more frequently than others. Knowing these common codes can help you quickly identify and address typical issues.
3.1. P0420: Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold
The P0420 code indicates that the catalytic converter isn’t working as efficiently as it should. This code suggests that the catalytic converter isn’t properly reducing emissions, which can result in failing an emissions test.
3.1.1. Potential Causes of P0420
- Faulty catalytic converter
- Oxygen sensor failure
- Exhaust leaks
- Engine misfires
3.1.2. How to Fix P0420
- Inspect the Exhaust System: Check for leaks and repair them.
- Test the Oxygen Sensors: Ensure the sensors are functioning correctly and replace if necessary.
- Check for Engine Misfires: Address any engine misfires to prevent damage to the catalytic converter.
- Replace the Catalytic Converter: If other solutions fail, the catalytic converter may need replacement.
3.2. P0171: System Too Lean (Bank 1)
The P0171 code signifies that the engine is running too lean, meaning there’s too much air and not enough fuel in the air-fuel mixture. This can cause engine hesitation, poor fuel economy, and potential damage to engine components.
3.2.1. Potential Causes of P0171
- Vacuum leaks
- Faulty oxygen sensor
- Dirty or failing mass airflow (MAF) sensor
- Fuel pump issues
3.2.2. How to Fix P0171
- Check for Vacuum Leaks: Inspect all vacuum lines for cracks or disconnections.
- Clean or Replace the MAF Sensor: Clean the MAF sensor with a suitable cleaner or replace it if cleaning doesn’t help.
- Test the Oxygen Sensor: Verify the oxygen sensor is functioning correctly.
- Check Fuel Pressure: Ensure the fuel pump is delivering adequate fuel pressure.
3.3. P0300 Series: Misfire Codes (P0301, P0302, P0303, P0304)
The P0300 series codes (P0301, P0302, P0303, P0304) indicate engine misfires in specific cylinders. Misfires can cause rough idling, reduced power, and potential damage to the engine and catalytic converter.
3.3.1. Potential Causes of Misfires
- Faulty spark plugs
- Defective ignition coils
- Clogged or malfunctioning fuel injectors
- Compression issues
3.3.2. How to Fix Misfire Codes
- Check Spark Plugs: Inspect and replace any worn or damaged spark plugs.
- Test Ignition Coils: Use a multimeter to test the ignition coils and replace any faulty ones.
- Inspect Fuel Injectors: Clean or replace clogged or malfunctioning fuel injectors.
- Check Compression: Perform a compression test to identify any cylinder compression issues.
3.4. P0113: Intake Air Temperature (IAT) Sensor Circuit High Input
The P0113 code indicates that the intake air temperature (IAT) sensor is reporting a higher-than-normal temperature. This can cause the engine to run poorly due to incorrect air-fuel mixture adjustments.
3.4.1. Potential Causes of P0113
- Faulty IAT sensor
- Wiring issues
- Poor connection
3.4.2. How to Fix P0113
- Check the IAT Sensor: Inspect the IAT sensor for damage and replace if necessary.
- Inspect Wiring: Check the wiring and connectors for any damage or corrosion.
- Test the Sensor Circuit: Use a multimeter to test the sensor circuit for continuity and proper voltage.
3.5. P0128: Coolant Thermostat (Coolant Temperature Below Thermostat Regulating Temperature)
The P0128 code indicates that the engine coolant temperature is not reaching the thermostat’s regulating temperature within a specified time. This can result in poor fuel economy and reduced engine performance.
3.5.1. Potential Causes of P0128
- Faulty thermostat
- Coolant temperature sensor issues
- Low coolant level
3.5.2. How to Fix P0128
- Check the Thermostat: Replace the thermostat if it is stuck open or malfunctioning.
- Inspect Coolant Temperature Sensor: Test the coolant temperature sensor and replace if necessary.
- Check Coolant Level: Ensure the coolant level is adequate and top up if low.
4. Advanced Diagnostic Techniques for Honda ECU Error Codes
What advanced techniques can be used to diagnose Honda ECU error codes effectively?
Beyond reading and interpreting basic codes, advanced diagnostic techniques can help pinpoint more elusive issues and ensure accurate repairs.
4.1. Using a Multimeter for Sensor Testing
A multimeter is an essential tool for testing sensors. It allows you to measure voltage, resistance, and continuity, which can help determine if a sensor is functioning correctly.
4.1.1. How to Test an Oxygen Sensor with a Multimeter
- Locate the Oxygen Sensor: Identify the oxygen sensor you want to test.
- Set the Multimeter: Set the multimeter to measure DC voltage.
- Connect the Leads: Connect the multimeter leads to the appropriate terminals on the oxygen sensor connector.
- Start the Engine: Start the engine and let it warm up.
- Read the Voltage: Observe the voltage readings. A properly functioning oxygen sensor should show fluctuating voltage between 0.1 and 0.9 volts.
4.2. Live Data Streaming: Monitoring Real-Time Parameters
Live data streaming allows you to monitor real-time engine parameters using your OBD2 scanner. This can provide valuable insights into how the engine is performing under different conditions.
4.2.1. What Parameters to Monitor
- Engine RPM
- Coolant temperature
- Oxygen sensor readings
- Fuel trim values
- MAF sensor readings
4.2.2. How to Use Live Data
- Connect the Scanner: Plug in the OBD2 scanner and navigate to the live data section.
- Select Parameters: Choose the parameters you want to monitor.
- Start the Engine: Start the engine and observe the data as it streams.
- Analyze the Data: Look for any unusual or out-of-range values that could indicate a problem.
4.3. Freeze Frame Data: Analyzing Conditions When the Code Was Set
Freeze frame data captures a snapshot of the engine’s operating conditions at the moment a DTC was triggered. This can provide valuable context for diagnosing intermittent issues.
4.3.1. How to Access Freeze Frame Data
- Read Codes: Use the OBD2 scanner to read the stored DTCs.
- Access Freeze Frame: Navigate to the freeze frame data section on the scanner.
- Review Data: Examine the engine parameters recorded when the code was set.
4.3.2. Interpreting Freeze Frame Data
Analyze the freeze frame data to identify any conditions that might have contributed to the code being set. For example, if the code was set at high RPM, it could indicate a problem with the fuel system or ignition system under high-load conditions.
5. Honda Specific Error Codes: What You Need to Know
Are there any Honda-specific error codes that require special attention?
While OBD2 codes are standardized, some Honda-specific codes can provide more detailed information about particular issues.
5.1. VTEC System Issues
Honda’s Variable Valve Timing and Lift Electronic Control (VTEC) system is known for its performance benefits. However, VTEC-related codes can indicate specific problems within this system.
5.1.1. Common VTEC Codes
- P1259: VTEC System Malfunction
- P2646: VTEC Oil Pressure Switch Circuit Low Voltage
- P2647: VTEC Oil Pressure Switch Circuit High Voltage
- P2648: VTEC Solenoid Valve Circuit Low Voltage
- P2649: VTEC Solenoid Valve Circuit High Voltage
5.1.2. How to Diagnose VTEC Issues
- Check Oil Level and Pressure: Ensure the engine oil level is adequate and that the oil pressure is within the specified range.
- Inspect VTEC Solenoid: Check the VTEC solenoid for proper operation and electrical connectivity.
- Test VTEC Oil Pressure Switch: Verify the VTEC oil pressure switch is functioning correctly.
5.2. IMA System (Hybrid Models)
For Honda hybrid models with the Integrated Motor Assist (IMA) system, specific codes relate to the hybrid components and their operation.
5.2.1. Common IMA Codes
- P1440: IMA System Problem
- P1449: Battery Module Overheating
5.2.2. Diagnosing IMA System Issues
Diagnosing IMA system issues often requires specialized tools and knowledge. It’s best to consult a qualified technician experienced in hybrid vehicle repair.
5.3. Transmission-Related Codes
Honda vehicles, especially those with automatic transmissions, may generate specific transmission-related codes.
5.3.1. Common Transmission Codes
- P0700: Transmission Control System Malfunction
- P0730: Incorrect Gear Ratio
5.3.2. How to Address Transmission Codes
- Check Transmission Fluid: Ensure the transmission fluid level is correct and the fluid is in good condition.
- Inspect Sensors and Solenoids: Check the transmission sensors and solenoids for proper operation.
- Consider Professional Diagnosis: Transmission issues can be complex, so seeking professional diagnosis and repair is often the best course of action.
6. OBD2 Scanner Recommendations for Honda Vehicles
What are some recommended OBD2 scanners for diagnosing Honda vehicles?
Selecting the right OBD2 scanner can make a significant difference in your diagnostic capabilities. Here are some recommendations for Honda vehicles:
6.1. Entry-Level Scanners
For basic code reading and clearing, entry-level scanners are a cost-effective option.
6.1.1. Features to Look For
- Code reading and clearing
- Basic live data streaming
- User-friendly interface
6.1.2. Recommended Models
- Autel AutoLink AL319: A reliable and affordable option for basic diagnostics.
- Ancel AD310: Easy to use and provides quick access to codes.
6.2. Mid-Range Scanners
Mid-range scanners offer more advanced features, such as enhanced live data, freeze frame data, and some bidirectional control capabilities.
6.2.1. Features to Look For
- Enhanced live data streaming
- Freeze frame data
- OBD2 code lookup
- Ability to graph data
6.2.2. Recommended Models
- Autel MaxiCheck MX808: Offers advanced diagnostics and service functions.
- LAUNCH CRP129E: Provides comprehensive diagnostics for multiple systems.
6.3. Professional-Grade Scanners
Professional-grade scanners offer the most comprehensive diagnostic capabilities, including advanced bidirectional control, programming, and access to manufacturer-specific data.
6.3.1. Features to Look For
- Advanced bidirectional control
- Programming capabilities
- Access to manufacturer-specific data
- Regular software updates
6.3.2. Recommended Models
- Autel MaxiSys MS906BT: A powerful scanner with extensive diagnostic capabilities.
- Snap-on Zeus: A top-of-the-line scanner used by professional mechanics.
7. Maintaining Your Honda’s ECU and Preventing Error Codes
How can you maintain your Honda’s ECU and prevent error codes from occurring?
Preventive maintenance is key to keeping your Honda’s ECU functioning correctly and minimizing the occurrence of error codes.
7.1. Regular Vehicle Maintenance
Following the manufacturer’s recommended maintenance schedule can help prevent many common issues that trigger ECU error codes.
7.1.1. Key Maintenance Tasks
- Oil changes
- Spark plug replacement
- Air filter replacement
- Fuel filter replacement
- Inspection of belts and hoses
7.2. Using Quality Parts and Fluids
Using high-quality parts and fluids can help ensure your Honda’s components function optimally and prevent premature wear and failure.
7.2.1. Why Quality Matters
- Improved Performance: Quality parts are designed to meet or exceed OEM specifications, ensuring optimal performance.
- Extended Lifespan: Quality parts are typically more durable and last longer than cheaper alternatives.
- Reduced Risk of Failure: Using quality parts reduces the risk of component failure, which can trigger ECU error codes.
7.3. Addressing Issues Promptly
Addressing minor issues promptly can prevent them from escalating into major problems that trigger ECU error codes.
7.3.1. The Importance of Early Detection
- Prevent Escalation: Addressing minor issues early can prevent them from becoming major problems.
- Save Money: Early detection and repair can save you money on costly repairs down the road.
- Maintain Performance: Addressing issues promptly can help maintain your Honda’s performance and fuel economy.
8. DIY vs. Professional Diagnosis: Making the Right Choice
When should you attempt to diagnose and repair Honda ECU error codes yourself, and when should you seek professional help?
Deciding whether to tackle a diagnostic and repair job yourself or seek professional help depends on your skills, experience, and the complexity of the issue.
8.1. When to DIY
If you have experience working on cars and are comfortable using tools like OBD2 scanners and multimeters, you may be able to handle certain diagnostic and repair tasks yourself.
8.1.1. Suitable DIY Tasks
- Reading and clearing basic OBD2 codes
- Replacing spark plugs
- Replacing air filters
- Checking and topping off fluids
- Simple sensor replacements
8.2. When to Seek Professional Help
For more complex issues or if you lack experience, seeking professional help is the best course of action.
8.2.1. Situations Requiring Professional Assistance
- Complex diagnostic procedures
- Transmission issues
- Engine problems
- Electrical system issues
- VTEC system problems
- IMA system problems (hybrid models)
8.3. The Benefits of Professional Diagnosis
Professional mechanics have the training, experience, and tools necessary to accurately diagnose and repair complex automotive issues.
8.3.1. Why Choose a Professional?
- Accurate Diagnosis: Professionals can accurately diagnose complex issues.
- Specialized Tools: They have access to specialized tools and equipment.
- Experience: They have experience working on a wide range of vehicles.
- Warranty: Professional repairs often come with a warranty.
9. Resources for Honda ECU Error Codes and Diagnostics
Where can you find reliable resources for Honda ECU error codes and diagnostics?
Having access to reliable resources can help you better understand and address Honda ECU error codes.
9.1. Online Databases and Forums
Numerous online databases and forums provide information about OBD2 codes and diagnostic procedures.
9.1.1. Recommended Resources
- OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN: Offers in-depth guides and resources for understanding OBD2 codes and diagnostics.
- Honda Forums: Online forums dedicated to Honda vehicles can provide valuable information and support from other owners and enthusiasts.
9.2. Repair Manuals and Technical Documentation
Repair manuals and technical documentation provide detailed information about Honda vehicles, including diagnostic procedures and repair instructions.
9.2.1. Recommended Manuals
- Haynes Repair Manuals: Offer step-by-step instructions and diagrams for various repair tasks.
- Factory Service Manuals: Provide the most detailed and accurate information about Honda vehicles.
9.3. Professional Diagnostic Tools and Software
Professional diagnostic tools and software can provide advanced diagnostic capabilities and access to manufacturer-specific data.
9.3.1. Recommended Tools
- Autel MaxiSys Series: Offers comprehensive diagnostic capabilities for a wide range of vehicles.
- Snap-on Scanners: Used by professional mechanics for advanced diagnostics and repairs.
10. Frequently Asked Questions About Honda ECU Error Codes OBD2
Do you have questions about Honda ECU error codes OBD2? Here are some frequently asked questions to help you better understand the topic.
10.1. What Does a Honda ECU Do?
The Honda ECU (Engine Control Unit) is the car’s central computer, controlling various functions like fuel injection, ignition timing, and emissions control. It monitors sensors throughout the vehicle and adjusts engine parameters to optimize performance and efficiency.
10.2. How Often Should I Scan My Honda for Error Codes?
You should scan your Honda for error codes whenever the check engine light comes on or if you notice any unusual symptoms, such as rough idling, reduced power, or poor fuel economy. Regular scans can also help identify potential issues before they become serious.
10.3. Can I Drive My Honda with the Check Engine Light On?
It depends on the severity of the problem. If the check engine light is flashing, it indicates a serious issue that requires immediate attention. Driving under these conditions can cause further damage to your vehicle. If the check engine light is on but not flashing, you can usually drive the car for a short period, but it’s best to have it checked as soon as possible.
10.4. Will Clearing Error Codes Fix the Problem?
Clearing error codes will not fix the underlying problem. It will only turn off the check engine light temporarily. The code will likely return if the issue is not addressed. Always diagnose and repair the problem before clearing the codes.
10.5. Are All OBD2 Scanners Compatible with Hondas?
Most OBD2 scanners are compatible with Hondas, but it’s essential to check the scanner’s specifications to ensure compatibility with your vehicle’s make and model. Some scanners may offer more advanced features for specific makes and models.
10.6. What is the Difference Between Generic and Manufacturer-Specific Codes?
Generic OBD2 codes are standardized codes that apply to all vehicles. Manufacturer-specific codes are unique to a particular make and model and provide more detailed information about specific issues.
10.7. How Can I Find Honda-Specific Error Code Definitions?
You can find Honda-specific error code definitions in repair manuals, online databases, and professional diagnostic software. Resources like OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN also offer detailed information about Honda-specific codes.
10.8. Can a Faulty Gas Cap Trigger an Error Code?
Yes, a loose or faulty gas cap can trigger an error code, such as P0455 (Evaporative Emission Control System Leak Detected). Ensure the gas cap is properly tightened and replace it if it’s damaged.
10.9. What Does “Pending Code” Mean?
A pending code is a code that the ECU has detected but hasn’t yet confirmed. It indicates that a problem may be developing, and the ECU is monitoring the system to see if the code becomes permanent.
10.10. Can I Use a Smartphone App as an OBD2 Scanner?
Yes, you can use a smartphone app as an OBD2 scanner by pairing it with a compatible Bluetooth OBD2 adapter. However, the features and capabilities of smartphone apps may vary, so choose a reputable app with good reviews.
By understanding Honda ECU error codes OBD2, you are taking a significant step towards maintaining your vehicle’s health and performance.
Don’t let confusing error codes keep you in the dark. Contact us at OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN for expert guidance and services. Our team is ready to help you diagnose and resolve any issues with your Honda. Reach out today!
Address: 123 Main Street, Los Angeles, CA 90001, United States
WhatsApp: +1 (641) 206-8880
Website: OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN
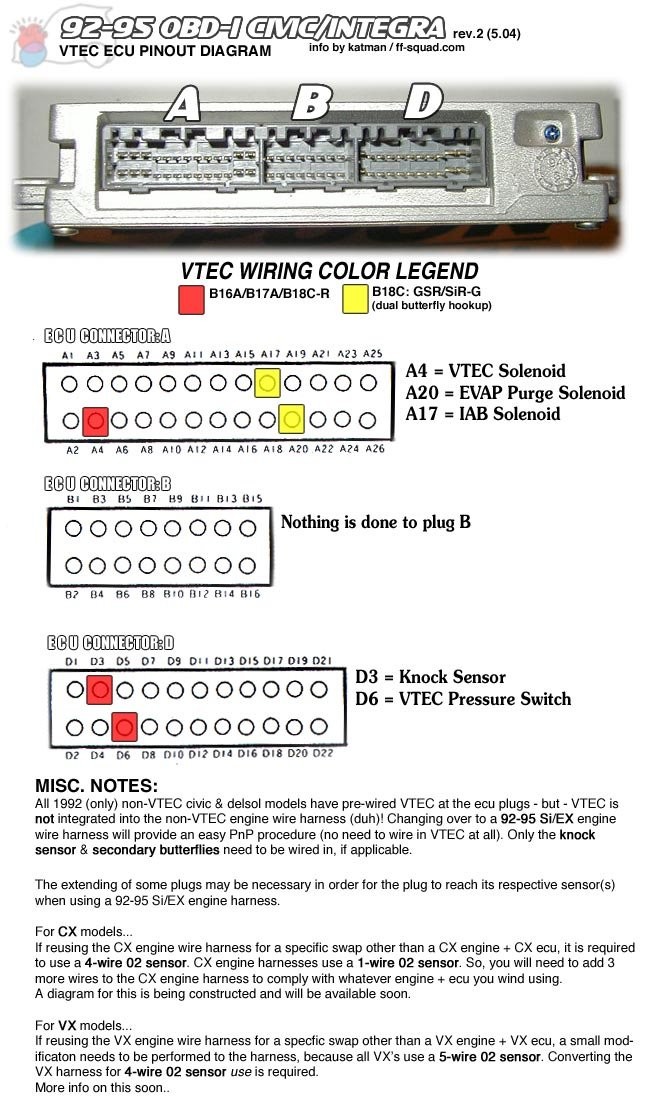 Honda ECU location for code reading
Honda ECU location for code reading
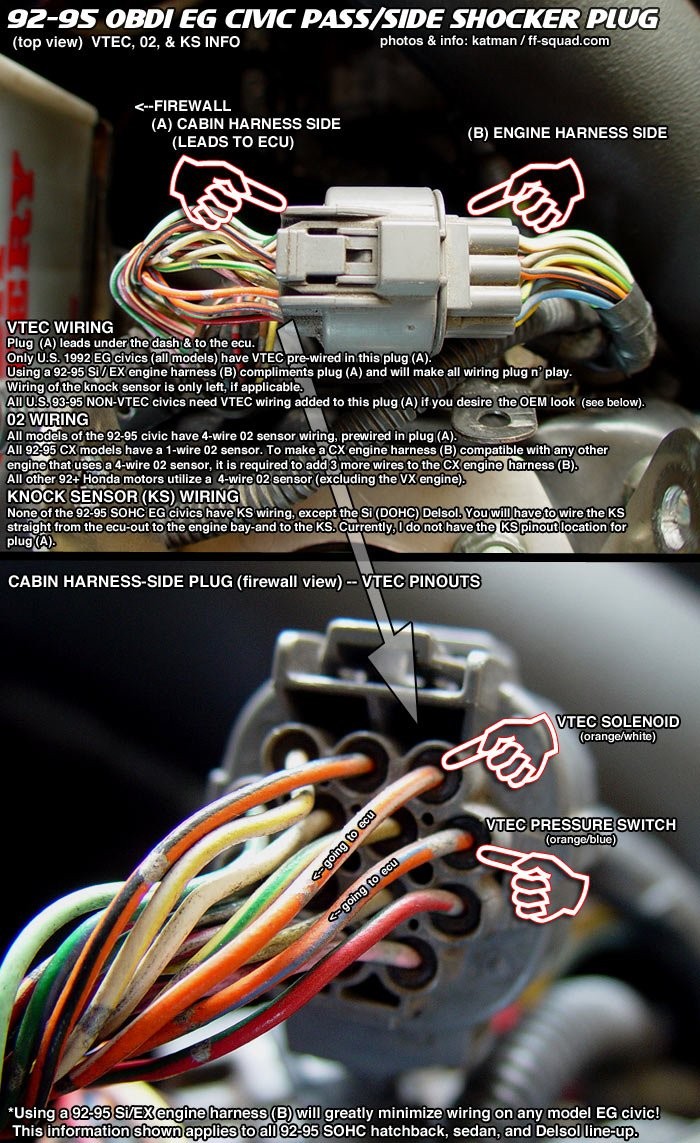 OBD1 connector for Honda code retrieval
OBD1 connector for Honda code retrieval