Clearing a code on an OBD2 scanner is a straightforward process that empowers you to diagnose and potentially resolve minor car issues yourself. OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN provides you with the knowledge and tools to confidently tackle these tasks. By understanding how to clear trouble codes, you gain control over your vehicle’s diagnostics and maintenance. Delve into the world of automotive diagnostics and learn how to clear error codes, understand diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs), and perform essential vehicle maintenance with confidence.
Contents
- 1. Understanding the OBD2 System and Its Importance
- 2. Identifying the Need to Clear a Code
- 3. Essential Tools for Clearing OBD2 Codes
- 4. Step-by-Step Guide: How to Clear a Code on an OBD2 Scanner
- Step 1: Prepare Your Vehicle
- Step 2: Locate the OBD2 Port
- Step 3: Connect the OBD2 Scanner
- Step 4: Turn On the Ignition
- Step 5: Power On the OBD2 Scanner
- Step 6: Read the Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
- Step 7: Record and Research the Codes
- Step 8: Fix the Underlying Issue
- Step 9: Clear the Codes
- Step 10: Verify the Clear
- Step 11: Disconnect the Scanner
- Step 12: Start the Engine and Check
- 5. Common OBD2 Codes and Their Solutions
- 6. Common Mistakes to Avoid When Clearing Codes
- 7. The Role of OBD2 Scanners in Vehicle Maintenance
- 8. Understanding OBD2 Readiness Monitors
- 9. Advanced Diagnostic Techniques Using OBD2 Scanners
- 10. Choosing the Right OBD2 Scanner for Your Needs
- 11. The Future of OBD2 Technology
- 12. Troubleshooting Common OBD2 Scanner Issues
- FAQ: Clearing Codes on an OBD2 Scanner
- Conclusion: Taking Control of Your Vehicle’s Diagnostics
1. Understanding the OBD2 System and Its Importance
What is the significance of the OBD2 system in modern vehicles?
The On-Board Diagnostics II (OBD2) system is a standardized system used in most vehicles manufactured after 1996 to monitor the performance of the engine, emissions system, and other critical components. According to the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), OBD2 was implemented to ensure vehicles meet stringent emission standards. The OBD2 system’s primary function is to detect malfunctions and alert the driver via the check engine light (CEL) on the dashboard. When a problem is detected, the OBD2 system stores a diagnostic trouble code (DTC) that provides information about the nature and location of the fault.
- Emission Control: The OBD2 system is critical for monitoring and maintaining vehicle emissions within the regulatory limits set by environmental agencies.
- Performance Monitoring: It helps in identifying issues that could affect the vehicle’s performance, such as misfires, fuel delivery problems, and sensor failures.
- Standardization: The OBD2 system provides a standardized interface, allowing any compatible scan tool to access diagnostic information, regardless of vehicle make or model.
- Early Detection: By detecting problems early, the OBD2 system can help prevent more significant and costly repairs.
2. Identifying the Need to Clear a Code
When is it appropriate to clear a code on an OBD2 scanner?
Clearing a code on an OBD2 scanner is appropriate in specific situations, primarily after you’ve addressed the underlying issue that triggered the diagnostic trouble code (DTC). According to the National Institute for Automotive Service Excellence (ASE), simply clearing the code without fixing the problem will only result in the check engine light (CEL) coming back on. Clearing a code is appropriate when:
- The Issue Has Been Repaired: Once you have fixed the problem causing the DTC, clearing the code confirms that the repair was successful.
- False Alarm: Sometimes, a temporary glitch or sensor malfunction can trigger a code. If the vehicle runs normally after inspection, clearing the code might be reasonable.
- Verification of Repair: After a repair, clearing the code and performing a drive cycle helps confirm that the system is functioning correctly.
- During Diagnostic Process: Clearing codes can be part of the diagnostic process to see if a particular code recurs, indicating an ongoing issue.
It is crucial to understand the reason for the DTC before clearing it. Randomly clearing codes without addressing the problem can mask underlying issues and lead to more severe damage.
3. Essential Tools for Clearing OBD2 Codes
What tools are necessary to clear OBD2 codes effectively?
To effectively clear OBD2 codes, you need specific tools that can read, interpret, and clear diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs). The most essential tools include:
- OBD2 Scanner: This is the primary tool used to interface with your vehicle’s OBD2 system. Basic scanners can read and clear codes, while advanced models offer features like live data streaming, freeze frame data, and bidirectional control.
- Smartphone or Tablet with OBD2 App: Many OBD2 adapters connect to smartphones or tablets via Bluetooth or Wi-Fi. These apps can read and clear codes and often provide additional diagnostic information.
- Repair Manual or Online Database: A repair manual specific to your vehicle or a reliable online database (like those from OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN) is essential for interpreting DTCs and understanding the underlying issues.
- Basic Hand Tools: Depending on the identified problem, you may need basic hand tools such as wrenches, screwdrivers, and pliers to perform necessary repairs.
- Multimeter: A multimeter can be used to test electrical components, such as sensors and circuits, to diagnose issues accurately.
Using the right tools ensures you can accurately diagnose and resolve issues, making the process of clearing OBD2 codes more effective and preventing future problems.
4. Step-by-Step Guide: How to Clear a Code on an OBD2 Scanner
How do you properly clear a code using an OBD2 scanner?
Clearing a code on an OBD2 scanner involves a series of steps to ensure you properly address any underlying issues and confirm that the code does not immediately return. Here is a detailed guide:
Step 1: Prepare Your Vehicle
Ensure your vehicle is parked in a safe location. Turn off the engine and remove the keys from the ignition. This prevents any accidental electrical issues during the process.
Step 2: Locate the OBD2 Port
The OBD2 port is typically located under the dashboard on the driver’s side. It is a 16-pin connector, trapezoidal in shape. Refer to your vehicle’s manual if you have trouble finding it.
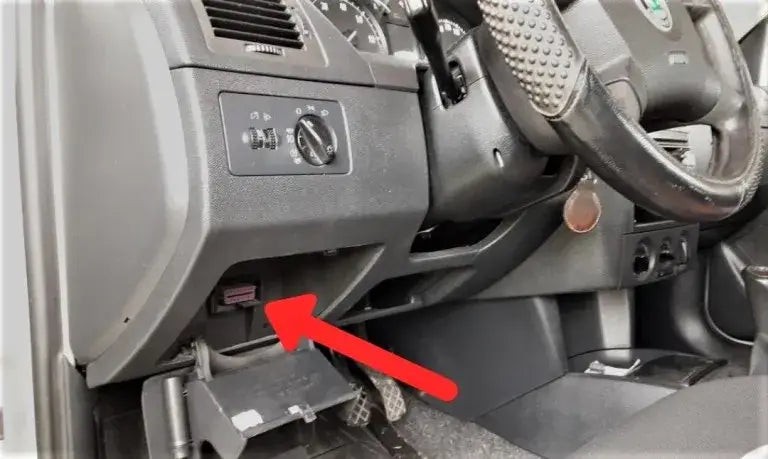 Locating the OBDII port under the dashboard
Locating the OBDII port under the dashboard
Alt text: Locating the OBD2 port under the dashboard of a car, showing the standard 16-pin connector.
Step 3: Connect the OBD2 Scanner
Plug the OBD2 scanner into the port. Ensure it is securely connected. You may hear a click or feel it snap into place.
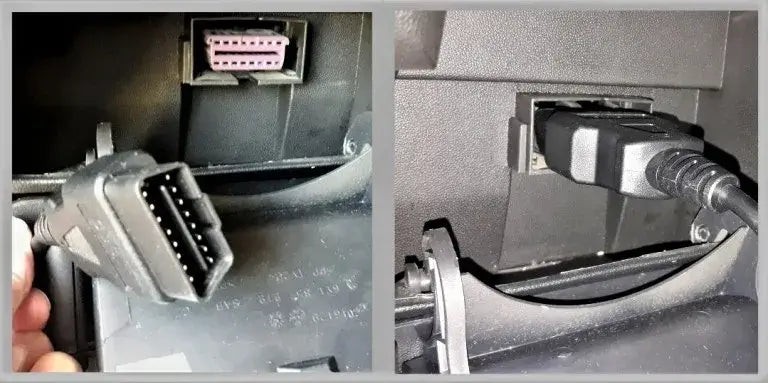 Connecting an OBD2 scanner to the OBD2 port
Connecting an OBD2 scanner to the OBD2 port
Alt text: Connecting an OBD2 scanner to the OBD2 port, ensuring a secure connection for accurate data retrieval.
Step 4: Turn On the Ignition
Turn the ignition to the “ON” position without starting the engine. This provides power to the OBD2 system and allows the scanner to communicate with the vehicle’s computer.
 Turning the ignition to the ON position
Turning the ignition to the ON position
Alt text: Turning the car ignition to the “ON” position to power the OBD2 system for scanning.
Step 5: Power On the OBD2 Scanner
Turn on the OBD2 scanner. It should power up automatically or have a power button. Follow the scanner’s instructions to connect to the vehicle’s computer.
Step 6: Read the Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
Select the option to read codes from the scanner menu. The scanner will retrieve any stored DTCs from the vehicle’s computer.
 OBD2 scanner displaying error codes
OBD2 scanner displaying error codes
Alt text: An OBD2 scanner displaying a list of diagnostic trouble codes retrieved from the vehicle’s computer.
Step 7: Record and Research the Codes
Write down each DTC and research its meaning. Use a repair manual or a reliable online database like OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN to understand the potential causes and solutions.
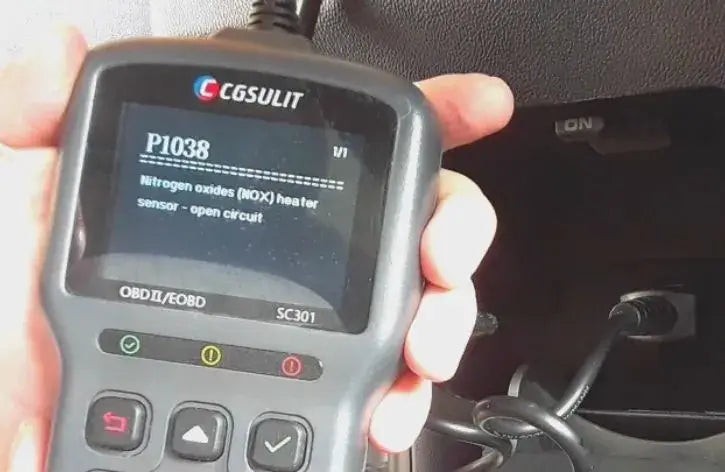 OBD2 code reader displaying diagnostic trouble codes
OBD2 code reader displaying diagnostic trouble codes
Alt text: Close-up of an OBD2 code reader screen displaying specific diagnostic trouble codes and their descriptions.
Step 8: Fix the Underlying Issue
Address the problem indicated by the DTC. This might involve replacing a faulty sensor, repairing a vacuum leak, or performing other necessary repairs.
Step 9: Clear the Codes
After fixing the issue, navigate to the “Clear Codes” or “Erase Codes” option in the scanner menu. Confirm your selection to clear the codes.
 Selecting the clear codes option on an OBD2 scanner
Selecting the clear codes option on an OBD2 scanner
Alt text: Selecting the “Clear Codes” option on an OBD2 scanner to erase stored diagnostic trouble codes.
Step 10: Verify the Clear
Turn off the ignition for a few minutes, then turn it back on and re-scan the vehicle. Ensure that the DTCs have been cleared and do not reappear.
Step 11: Disconnect the Scanner
Turn off the ignition and disconnect the OBD2 scanner from the port.
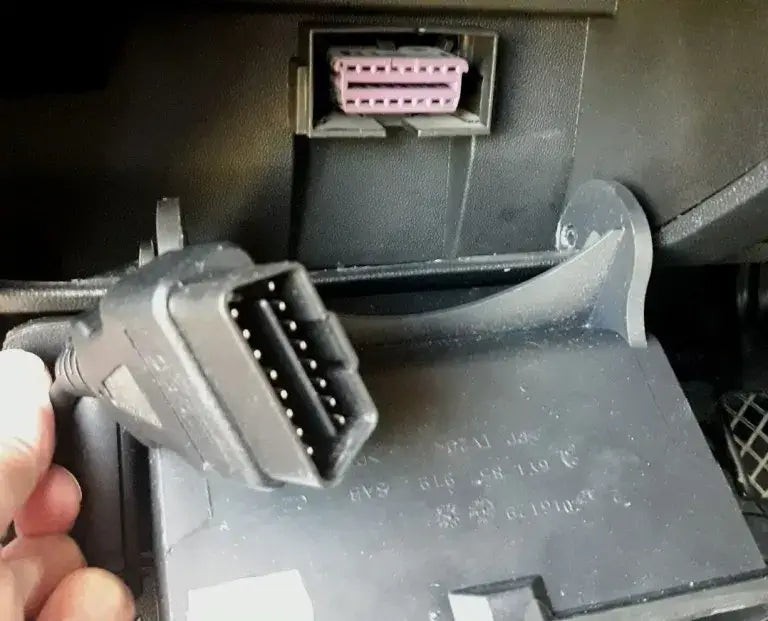 Disconnecting the OBD2 scanner from the OBD2 port
Disconnecting the OBD2 scanner from the OBD2 port
Alt text: Disconnecting an OBD2 scanner from the OBD2 port after clearing the diagnostic trouble codes.
Step 12: Start the Engine and Check
Start the engine and observe the check engine light. It should remain off. If the light comes back on, it indicates that the issue was not fully resolved or that another problem exists.
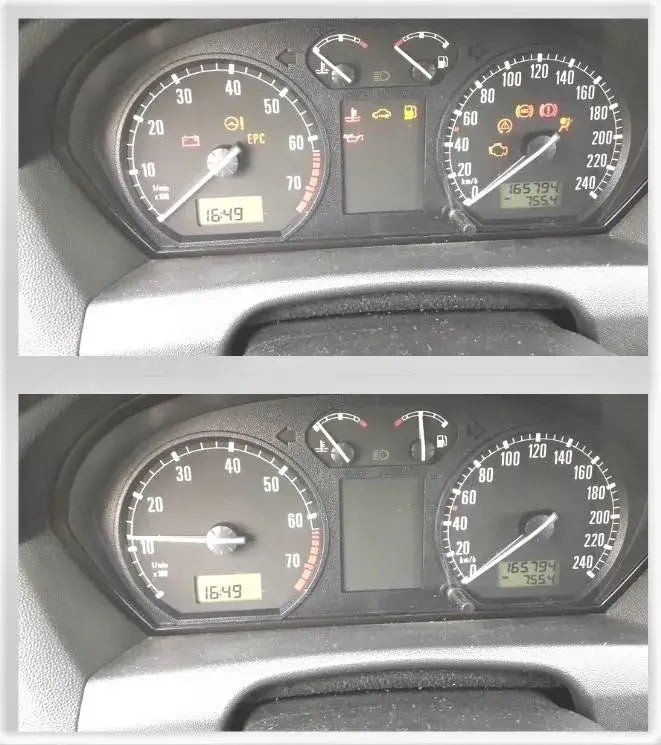 Check engine light off after clearing codes
Check engine light off after clearing codes
Alt text: Dashboard showing the check engine light is off after successfully clearing the codes with an OBD2 scanner.
Following these steps ensures you can effectively clear codes on an OBD2 scanner and verify that the underlying issues have been properly addressed.
5. Common OBD2 Codes and Their Solutions
What are some typical OBD2 codes and how can they be resolved?
Understanding common OBD2 codes and their solutions can help you address vehicle issues efficiently. Here are some of the most frequently encountered codes and their common fixes:
| Code | Description | Common Causes | Solutions |
|---|---|---|---|
| P0171 | System Too Lean (Bank 1) | Vacuum leaks, faulty MAF sensor, fuel pump issue | Check for vacuum leaks, replace MAF sensor, inspect fuel pump |
| P0300 | Random/Multiple Misfire Detected | Faulty spark plugs, ignition coils, vacuum leaks | Replace spark plugs, replace ignition coils, check for vacuum leaks |
| P0420 | Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold (Bank 1) | Failing catalytic converter, exhaust leaks, faulty O2 sensors | Replace catalytic converter, repair exhaust leaks, replace O2 sensors |
| P0442 | Evaporative Emission Control System Leak Detected (Small Leak) | Loose fuel cap, damaged EVAP hoses, faulty purge valve | Tighten fuel cap, replace EVAP hoses, replace purge valve |
| P0505 | Idle Control System Malfunction | Dirty throttle body, faulty IAC valve, vacuum leaks | Clean throttle body, replace IAC valve, check for vacuum leaks |
| P0113 | Intake Air Temperature Sensor Circuit High Input | Faulty IAT sensor, wiring issues | Replace IAT sensor, check wiring connections and repair any damages |
| P0301 | Cylinder 1 Misfire Detected | Faulty spark plug, ignition coil, fuel injector | Replace spark plug, ignition coil, or fuel injector in cylinder 1 |
| P0011 | “A” Camshaft Position Timing – Over-Advanced or System Performance (Bank 1) | Faulty camshaft position sensor, oil flow issues | Replace camshaft position sensor, check oil levels and oil flow to engine |
This table provides a quick reference for diagnosing and resolving common OBD2 codes, helping you keep your vehicle running smoothly. Always consult a repair manual or a trusted source like OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN for detailed instructions and safety precautions.
6. Common Mistakes to Avoid When Clearing Codes
What are the common pitfalls to avoid when clearing OBD2 codes?
Clearing OBD2 codes can seem straightforward, but several common mistakes can lead to further complications. Avoiding these pitfalls ensures a more effective and accurate diagnostic process.
- Not Diagnosing the Underlying Issue: The most significant mistake is clearing a code without identifying and fixing the root cause. According to ASE, clearing a code without addressing the problem will only result in the check engine light (CEL) returning.
- Ignoring Freeze Frame Data: Many OBD2 scanners provide freeze frame data, which captures the engine conditions when the code was triggered. Ignoring this information can make it difficult to diagnose intermittent issues.
- Assuming the Code is Always Accurate: While OBD2 codes provide valuable information, they don’t always pinpoint the exact problem. Further investigation and testing are often necessary to confirm the diagnosis.
- Using a Low-Quality Scanner: Inexpensive or unreliable scanners may not provide accurate information, leading to misdiagnosis and wasted time.
- Not Following Proper Procedures: Failing to follow the correct steps for clearing codes, such as ensuring the ignition is in the correct position, can result in the code not being cleared or causing other issues.
- Clearing Codes Before an Emissions Test: Clearing codes shortly before an emissions test can cause the vehicle to fail, as the OBD2 system requires time to complete its readiness monitors.
Avoiding these common mistakes can help you more effectively diagnose and resolve vehicle issues, ensuring your repairs are successful and long-lasting.
7. The Role of OBD2 Scanners in Vehicle Maintenance
How do OBD2 scanners contribute to overall vehicle maintenance?
OBD2 scanners play a crucial role in modern vehicle maintenance by providing valuable diagnostic information that helps identify and address potential issues early. According to a study by the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA), regular use of OBD2 scanners can significantly reduce vehicle breakdowns and improve overall safety.
- Early Detection of Problems: OBD2 scanners allow you to identify potential problems before they escalate into major repairs. This can save you money on costly repairs and prevent unexpected breakdowns.
- Accurate Diagnostics: By providing specific diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs), OBD2 scanners help pinpoint the source of the problem, reducing the need for guesswork and trial-and-error repairs.
- Monitoring Vehicle Performance: Advanced OBD2 scanners can monitor live data, such as engine temperature, RPM, and sensor readings, providing insights into the vehicle’s performance and helping you identify any anomalies.
- Ensuring Emissions Compliance: OBD2 scanners help ensure your vehicle complies with emissions standards by identifying issues that could lead to excessive pollution.
- DIY Repairs: With an OBD2 scanner, you can perform many basic repairs yourself, saving money on labor costs and gaining a better understanding of your vehicle.
Integrating OBD2 scanners into your regular vehicle maintenance routine can lead to improved reliability, safety, and cost savings.
8. Understanding OBD2 Readiness Monitors
What are OBD2 readiness monitors and why are they important?
OBD2 readiness monitors are diagnostic tests that the vehicle’s computer performs to ensure that all emission control systems are functioning correctly. These monitors run periodically during normal driving conditions. According to the EPA, readiness monitors are essential for verifying that a vehicle is environmentally compliant.
- Purpose of Readiness Monitors: Readiness monitors confirm that critical emission control systems, such as the oxygen sensors, catalytic converter, evaporative emission control system, and EGR system, are operating within specified parameters.
- Importance for Emissions Testing: Before an emissions test, a vehicle must have all or most of its readiness monitors set to “ready” or “complete.” If the monitors are not ready, the vehicle will fail the test.
- Impact of Clearing Codes: Clearing OBD2 codes resets all readiness monitors, meaning the vehicle will need to be driven under specific conditions to allow the monitors to run and complete their tests.
- Driving Cycle: A driving cycle involves a series of driving conditions (e.g., highway driving, city driving, idling) that help the readiness monitors run and complete.
- Common Readiness Monitors:
- Oxygen Sensor Monitor: Tests the functionality of the oxygen sensors.
- Catalyst Monitor: Checks the efficiency of the catalytic converter.
- Evaporative System Monitor: Verifies the integrity of the evaporative emission control system.
- EGR System Monitor: Tests the functionality of the exhaust gas recirculation system.
Understanding and monitoring OBD2 readiness monitors is crucial for ensuring your vehicle passes emissions tests and operates efficiently.
9. Advanced Diagnostic Techniques Using OBD2 Scanners
What advanced diagnostic techniques can be performed using OBD2 scanners?
Beyond reading and clearing codes, OBD2 scanners offer advanced diagnostic capabilities that can help you troubleshoot complex vehicle issues. These techniques provide more in-depth insights into your vehicle’s performance and can save time and money on repairs.
- Live Data Streaming: This feature allows you to monitor real-time data from various sensors and components, such as engine temperature, RPM, oxygen sensor readings, and fuel trim values. Analyzing live data can help identify anomalies and pinpoint the source of a problem.
- Freeze Frame Data: When a diagnostic trouble code (DTC) is triggered, the OBD2 system captures a snapshot of the engine conditions at that moment. This “freeze frame” data can provide valuable clues about the circumstances that led to the code.
- Bidirectional Control: Advanced OBD2 scanners offer bidirectional control, which allows you to send commands to specific vehicle components to test their functionality. For example, you can activate the fuel pump, EGR valve, or cooling fan to see if they are working correctly.
- O2 Sensor Testing: Oxygen sensor testing involves monitoring the voltage output of the O2 sensors to determine if they are responding correctly to changes in the exhaust gas composition. This can help identify faulty sensors or exhaust leaks.
- Fuel Trim Analysis: Fuel trim values indicate how much the engine’s computer is adjusting the fuel mixture to maintain optimal performance. Analyzing fuel trim data can help diagnose issues such as vacuum leaks, faulty MAF sensors, or fuel injector problems.
- EVAP System Testing: Advanced scanners can perform tests on the evaporative emission control system to check for leaks or malfunctions. This can help identify issues with the fuel cap, purge valve, or EVAP hoses.
By mastering these advanced diagnostic techniques, you can use OBD2 scanners to effectively troubleshoot a wide range of vehicle problems and ensure your car runs smoothly.
10. Choosing the Right OBD2 Scanner for Your Needs
How do you select an OBD2 scanner that fits your specific requirements?
Selecting the right OBD2 scanner depends on your specific needs and the types of vehicles you work with. Here are some factors to consider when choosing an OBD2 scanner:
- Basic vs. Advanced Features: Basic scanners can read and clear codes, while advanced models offer features like live data streaming, freeze frame data, bidirectional control, and access to manufacturer-specific codes.
- Compatibility: Ensure the scanner is compatible with your vehicle’s make and model. Some scanners are designed to work with specific vehicle brands, while others offer broader compatibility.
- Ease of Use: Look for a scanner with a user-friendly interface and clear instructions. A scanner with a large display and intuitive menu navigation can make the diagnostic process easier.
- Portability: Consider the size and weight of the scanner, especially if you plan to use it in multiple locations. Compact, handheld scanners are convenient for on-the-go diagnostics.
- Connectivity: Some scanners connect to smartphones or tablets via Bluetooth or Wi-Fi, allowing you to view data on a larger screen and access additional features through mobile apps.
- Update Capability: Choose a scanner that can be easily updated with the latest software and diagnostic information. Regular updates ensure the scanner remains compatible with new vehicle models and diagnostic protocols.
- Price: OBD2 scanners range in price from basic models under $50 to advanced professional-grade tools costing several hundred dollars. Determine your budget and choose a scanner that offers the best value for your needs.
Consider these factors to choose an OBD2 scanner that meets your diagnostic needs and helps you keep your vehicle running smoothly.
11. The Future of OBD2 Technology
What advancements are expected in OBD2 technology in the coming years?
The future of OBD2 technology is expected to bring numerous advancements aimed at improving vehicle diagnostics, enhancing data accessibility, and integrating with emerging automotive technologies. According to a report by McKinsey & Company, the automotive industry is undergoing a significant transformation driven by connectivity, autonomous driving, and electrification, and OBD2 technology will play a crucial role in this evolution.
- Enhanced Data Accessibility: Future OBD2 systems will provide more comprehensive and detailed data, including access to manufacturer-specific parameters and advanced sensor data.
- Wireless Connectivity: Wireless OBD2 adapters will become more prevalent, allowing seamless integration with smartphones, tablets, and cloud-based diagnostic platforms.
- Remote Diagnostics: Remote diagnostics capabilities will enable technicians to diagnose and troubleshoot vehicle issues from a distance, reducing the need for physical inspections and improving service efficiency.
- Integration with ADAS: OBD2 systems will increasingly integrate with Advanced Driver Assistance Systems (ADAS), providing valuable data for monitoring and maintaining these safety-critical technologies.
- Cybersecurity Enhancements: As vehicles become more connected, cybersecurity will be a major focus. Future OBD2 systems will incorporate advanced security measures to protect against hacking and unauthorized access.
- Predictive Maintenance: Predictive maintenance capabilities will use OBD2 data to forecast potential vehicle failures, allowing for proactive repairs and reducing the risk of breakdowns.
- Standardization of Data Formats: Efforts will be made to standardize data formats across different vehicle makes and models, simplifying the diagnostic process and improving data compatibility.
These advancements in OBD2 technology will revolutionize vehicle diagnostics and maintenance, leading to safer, more efficient, and more reliable vehicles.
12. Troubleshooting Common OBD2 Scanner Issues
What steps can you take to troubleshoot common issues encountered with OBD2 scanners?
Encountering issues with your OBD2 scanner can be frustrating, but many problems can be resolved with simple troubleshooting steps. Here are some common issues and their solutions:
- Scanner Won’t Connect:
- Check the Connection: Ensure the scanner is securely plugged into the OBD2 port.
- Verify Power: Make sure the ignition is in the “ON” position without starting the engine.
- Check Compatibility: Confirm the scanner is compatible with your vehicle’s make and model.
- Scanner Won’t Power On:
- Check the Power Source: Ensure the scanner has power, either through the vehicle’s battery or its own battery.
- Inspect the Connector: Check the OBD2 port for any damage or debris that could prevent a good connection.
- Inaccurate Codes:
- Update the Scanner: Ensure the scanner has the latest software updates to access the most accurate diagnostic information.
- Verify the Code: Double-check the code against a reliable database, such as OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN, to ensure accuracy.
- Scanner Freezes or Crashes:
- Restart the Scanner: Try turning the scanner off and back on to reset it.
- Check for Updates: Ensure the scanner has the latest software updates, which often include bug fixes and performance improvements.
- Bluetooth Connectivity Issues:
- Pair the Devices: Make sure the scanner is properly paired with your smartphone or tablet via Bluetooth.
- Check Compatibility: Confirm the scanner and your device are compatible with each other.
- Cannot Clear Codes:
- Fix the Underlying Issue: Ensure you have addressed the problem that triggered the code before attempting to clear it.
- Follow the Procedure: Make sure you are following the correct steps for clearing codes, including turning the ignition to the correct position.
By following these troubleshooting steps, you can resolve common issues with your OBD2 scanner and ensure it functions properly.
FAQ: Clearing Codes on an OBD2 Scanner
Here are some frequently asked questions about clearing codes on an OBD2 scanner:
-
What is an OBD2 scanner?
An OBD2 scanner is a diagnostic tool used to read and clear diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) from a vehicle’s computer, helping identify and resolve issues.
-
How do I read OBD2 codes?
Connect the scanner to the OBD2 port, turn the ignition to the “ON” position, and follow the scanner’s instructions to read the stored DTCs.
-
Can I clear a code without fixing the problem?
Yes, but the check engine light will likely return if the underlying issue is not addressed. It’s crucial to diagnose and fix the problem before clearing the code.
-
Will clearing codes affect my car’s performance?
Clearing codes itself won’t affect performance, but addressing the issues identified by the codes can improve your car’s performance and efficiency.
-
How often should I scan my car with an OBD2 scanner?
You should scan your car whenever the check engine light comes on or if you notice any unusual symptoms. Regular scans can also help identify potential issues early.
-
What does the check engine light indicate?
The check engine light indicates that the vehicle’s computer has detected a problem. The OBD2 scanner can help you identify the specific issue.
-
Are all OBD2 scanners compatible with every car?
Most OBD2 scanners are compatible with vehicles manufactured after 1996, but it’s essential to check the scanner’s compatibility with your specific make and model.
-
Can I use my smartphone as an OBD2 scanner?
Yes, you can use a Bluetooth or Wi-Fi OBD2 adapter that connects to your smartphone and use a compatible app to read and clear codes.
-
What are readiness monitors?
Readiness monitors are diagnostic tests that the vehicle’s computer performs to ensure that all emission control systems are functioning correctly. They must be ready for the vehicle to pass an emissions test.
-
What is a driving cycle?
A driving cycle involves a series of driving conditions that help the readiness monitors run and complete their tests after clearing OBD2 codes.
Conclusion: Taking Control of Your Vehicle’s Diagnostics
Learning how to clear a code on an OBD2 scanner is a valuable skill that puts you in control of your vehicle’s diagnostics. By understanding the OBD2 system, using the right tools, and following the correct procedures, you can effectively identify and resolve many common vehicle issues.
At OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN, we are dedicated to providing you with the knowledge and resources you need to confidently maintain and repair your vehicle. Don’t let the check engine light cause unnecessary stress. With the right information and tools, you can diagnose and address issues quickly and efficiently.
Are you ready to take control of your vehicle’s diagnostics? Contact us today at 123 Main Street, Los Angeles, CA 90001, United States, or call us on WhatsApp at +1 (641) 206-8880. Visit our website at OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN to explore our range of OBD2 scanners, diagnostic resources, and expert support. Let OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN empower you to keep your vehicle running smoothly and efficiently.