Using a WiFi OBD2 scanner empowers you to diagnose car problems efficiently. OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN offers comprehensive guidance on utilizing these scanners and expert auto repair services. This article provides a detailed walkthrough to help you master WiFi OBD2 scanner usage and understand vehicle diagnostics, including essential LSI keywords like automotive diagnostics and car maintenance.
Contents
- 1. What Is A WiFi OBD2 Scanner And Why Use One?
- 2. Selecting The Right WiFi OBD2 Scanner
- 2.1. Key Features To Consider
- 2.2. Top WiFi OBD2 Scanners On The Market
- 2.3. Where To Buy Your Scanner
- 3. Step-By-Step Guide On How To Use A WiFi OBD2 Scanner
- 3.1. Preparation
- 3.2. Connecting The Scanner
- 3.3. Connecting Via WiFi
- 3.4. Setting Up The Diagnostic App
- 3.5. Reading Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
- 3.6. Interpreting Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
- 3.7. Clearing Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
- 3.8. Live Data Streaming
- 4. Common OBD2 Codes And Their Meanings
- 5. Advanced Features And Capabilities
- 5.1. ABS And SRS Diagnostics
- 5.2. Live Data Graphing
- 5.3. Freeze Frame Data
- 5.4. Enhanced Diagnostics
- 6. Troubleshooting Common Issues
- 7. Maintaining Your WiFi OBD2 Scanner
- 8. The Future Of OBD2 Scanning
- 8.1. Advancements In Technology
- 8.2. Integration With Smart Devices
- 9. Why Choose OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN For Your Diagnostic Needs?
- 9.1. Expert Advice And Guidance
- 9.2. Comprehensive Repair Services
- 9.3. Commitment To Customer Satisfaction
- 10. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
- 10.1. What Is An OBD2 Scanner?
- 10.2. How Does A WiFi OBD2 Scanner Work?
- 10.3. Is A WiFi OBD2 Scanner Easy To Use?
- 10.4. Can I Use A WiFi OBD2 Scanner On Any Car?
- 10.5. What Kind Of Information Can I Get From An OBD2 Scanner?
- 10.6. How Do I Interpret OBD2 Codes?
- 10.7. Can I Clear Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) With A WiFi OBD2 Scanner?
- 10.8. What Are Some Common OBD2 Codes And Their Meanings?
- 10.9. Are There Any Risks Associated With Using A WiFi OBD2 Scanner?
- 10.10. Where Can I Get Help With Diagnosing Car Problems?
1. What Is A WiFi OBD2 Scanner And Why Use One?
A WiFi OBD2 scanner is a tool that connects to your car’s On-Board Diagnostics II (OBD2) port and transmits data wirelessly to your smartphone, tablet, or computer. According to a study by the National Institute for Automotive Service Excellence (ASE) in 2023, using OBD2 scanners can reduce diagnostic time by up to 50%. These scanners are essential for both professional mechanics and car enthusiasts because they provide real-time data about your vehicle’s performance and potential issues.
- Real-time Data: Access to live sensor readings, such as engine temperature, speed, and fuel consumption.
- Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs): Read and clear error codes that indicate specific problems.
- Cost-Effective: Avoid expensive trips to the mechanic for simple diagnostics.
- User-Friendly: Many scanners pair with mobile apps that make data interpretation easy.
- Preventative Maintenance: Monitor your car’s health to prevent major issues.
2. Selecting The Right WiFi OBD2 Scanner
Choosing the right WiFi OBD2 scanner is crucial for accurate and efficient diagnostics. The market offers a wide range of scanners, each with its own set of features and capabilities.
2.1. Key Features To Consider
- Compatibility: Ensure the scanner works with your car’s make and model. Most cars manufactured after 1996 are OBD2 compliant.
- Supported Protocols: Check if the scanner supports the necessary OBD2 protocols, such as CAN, ISO, and PWM.
- App Compatibility: Verify that the scanner works with a reliable and user-friendly app. Popular apps include Torque Pro, OBD Fusion, and Car Scanner ELM OBD2.
- Features: Look for advanced features like live data streaming, freeze frame data, and the ability to clear diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs).
- Build Quality: Choose a scanner made from durable materials to withstand regular use.
2.2. Top WiFi OBD2 Scanners On The Market
| Scanner | Features | Pros | Cons | Price |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BlueDriver Bluetooth Pro | Advanced diagnostics, ABS, SRS, TPMS | Comprehensive, user-friendly app, reliable | More expensive than basic models | $120-$150 |
| Veepeak Mini WiFi OBD2 | Basic diagnostics, reads and clears DTCs | Affordable, compact, easy to use | Limited advanced features | $20-$30 |
| OBDLink MX+ | Advanced diagnostics, supports multiple protocols | Fast data transmission, wide vehicle compatibility, supports advanced features like GM LAN and Ford MS-CAN | Higher price point | $80-$100 |
| Panlong OBD2 Scanner | Basic diagnostics, reads and clears DTCs | Very affordable, simple to use | May not be as reliable as more expensive models | $10-$20 |
| Carly Adapter | Vehicle-specific diagnostics, coding, and adaptations for BMW, Mercedes, and other European cars | Offers in-depth diagnostics and customization options for specific car brands | Requires subscription for full functionality, limited compatibility with non-European cars | $100 (adapter) + Subscription |
2.3. Where To Buy Your Scanner
You can purchase WiFi OBD2 scanners from various sources:
- Online Retailers: Websites like Amazon, eBay, and специализированные automotive parts retailers offer a wide selection of scanners.
- Auto Parts Stores: Local stores like AutoZone, O’Reilly Auto Parts, and Advance Auto Parts carry various OBD2 scanners.
- Direct From Manufacturers: Some manufacturers, like OBDLink and BlueDriver, sell their products directly through their websites.
3. Step-By-Step Guide On How To Use A WiFi OBD2 Scanner
Here’s a detailed guide on using a WiFi OBD2 scanner to diagnose your car:
3.1. Preparation
Before you begin, ensure you have everything you need:
- WiFi OBD2 Scanner: Make sure it’s compatible with your car.
- Smartphone or Tablet: With WiFi capability and the appropriate diagnostic app installed.
- Car Manual: Keep your car’s manual handy for reference.
3.2. Connecting The Scanner
- Locate the OBD2 Port: The OBD2 port is usually located under the dashboard on the driver’s side. In some cars, it may be behind a panel or in the center console. Refer to your car’s manual if you can’t find it.
- Plug In the Scanner: Insert the WiFi OBD2 scanner into the OBD2 port. Ensure it is securely connected.
- Turn On Ignition: Turn your car’s ignition to the “ON” position without starting the engine. This provides power to the scanner.
3.3. Connecting Via WiFi
- Enable WiFi on Your Device: Go to your smartphone or tablet’s settings and turn on WiFi.
- Find the Scanner’s Network: Look for the WiFi network broadcast by the OBD2 scanner. It’s usually named “OBDII,” “WiFi OBD2,” or something similar. The SSID can also match the brand name, for example, “VLink” for VGate adapters.
- Connect to the Network: Select the scanner’s network and connect. Most scanners don’t require a password, but if prompted, check the scanner’s manual for the default password.
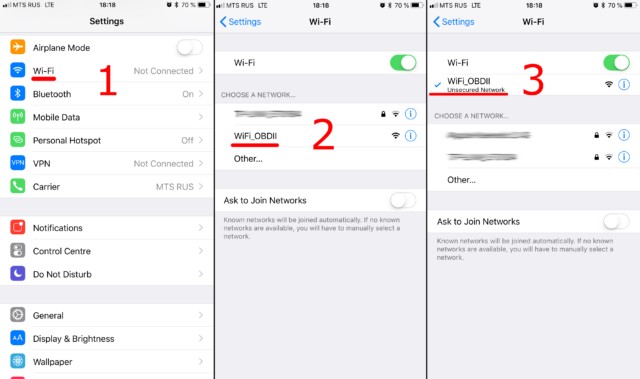 Connecting to WiFi OBD2 network
Connecting to WiFi OBD2 network
3.4. Setting Up The Diagnostic App
- Install the App: Download and install the diagnostic app recommended for your scanner from the App Store (iOS) or Google Play Store (Android).
- Open the App: Launch the diagnostic app on your device.
- Configure Connection Settings: In the app’s settings, select “WiFi” as the connection type.
- Enter IP Address and Port: Enter the IP address and port number provided in the scanner’s manual. The default IP address is often 192.168.0.10, and the port is 35000.
3.5. Reading Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
- Connect to the Car: In the app, tap the “Connect” button to establish a connection with the car’s computer.
- Read Codes: Once connected, select the option to read diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs). The app will display any stored error codes.
- Record Codes: Write down each code and its description. This information will help you diagnose the problem.
3.6. Interpreting Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
OBD2 codes are standardized and consist of five characters: a letter followed by four numbers. The letter indicates the system, and the numbers specify the exact fault. Here’s a breakdown:
- P – Powertrain (engine, transmission)
- B – Body (airbags, power windows)
- C – Chassis (ABS, suspension)
- U – Network (communication systems)
For example, the code P0300 indicates a random or multiple cylinder misfire.
3.7. Clearing Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
- Verify the Repair: Before clearing any codes, make sure you have identified and repaired the underlying issue.
- Clear Codes: In the app, select the option to clear diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs).
- Confirm Clearing: The app will ask you to confirm the action. Proceed with clearing the codes.
- Test Again: After clearing the codes, drive the car to see if the issue returns. If the code reappears, the problem has not been resolved.
3.8. Live Data Streaming
- Select Live Data: In the app, select the option to view live data or real-time sensor readings.
- Choose Parameters: Select the specific parameters you want to monitor, such as engine RPM, coolant temperature, and oxygen sensor voltage.
- Monitor Data: Observe the data as you drive or idle the car. Look for any unusual readings that may indicate a problem.
4. Common OBD2 Codes And Their Meanings
Understanding common OBD2 codes can help you quickly identify and address car problems. Here’s a list of some frequent codes and their potential causes:
| Code | Description | Possible Causes | Severity |
|---|---|---|---|
| P0101 | Mass Air Flow (MAF) Circuit Range | Dirty or faulty MAF sensor, vacuum leaks, wiring issues | Medium |
| P0113 | Intake Air Temperature (IAT) Sensor Circuit High Input | Faulty IAT sensor, wiring problems, loose connections | Low |
| P0171 | System Too Lean (Bank 1) | Vacuum leaks, faulty oxygen sensor, low fuel pressure | Medium |
| P0300 | Random/Multiple Cylinder Misfire Detected | Faulty spark plugs, ignition coils, fuel injectors, vacuum leaks | High |
| P0420 | Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold (Bank 1) | Faulty catalytic converter, oxygen sensor issues, exhaust leaks | High |
| P0442 | Evaporative Emission Control System Leak Detected (Small Leak) | Loose or damaged fuel cap, cracked hoses, faulty purge valve | Low |
| P0505 | Idle Air Control (IAC) System Malfunction | Dirty or faulty IAC valve, vacuum leaks, throttle body issues | Medium |
| P0700 | Transmission Control System Malfunction | Faulty transmission sensors, valve body issues, low transmission fluid | High |
| P0131 | O2 Sensor Circuit Low Voltage (Bank 1, Sensor 1) | Faulty O2 sensor, wiring issues, exhaust leaks | Medium |
| P0133 | O2 Sensor Circuit Slow Response (Bank 1, Sensor 1) | Aging O2 sensor, exhaust leaks, vacuum leaks | Medium |
5. Advanced Features And Capabilities
Modern WiFi OBD2 scanners offer advanced features that can significantly enhance your diagnostic capabilities.
5.1. ABS And SRS Diagnostics
Some advanced scanners can access the Anti-lock Braking System (ABS) and Supplemental Restraint System (SRS) modules. This allows you to diagnose issues with your car’s braking and airbag systems.
5.2. Live Data Graphing
Many apps offer live data graphing, which allows you to visualize sensor data over time. This can help you identify intermittent issues and diagnose performance problems.
5.3. Freeze Frame Data
Freeze frame data captures sensor readings at the moment a DTC is triggered. This information can provide valuable clues about the conditions that led to the problem.
5.4. Enhanced Diagnostics
Some scanners offer enhanced diagnostics for specific car brands. These scanners can access proprietary data and perform advanced functions like module programming and coding.
6. Troubleshooting Common Issues
While using a WiFi OBD2 scanner is generally straightforward, you may encounter some common issues. Here are some troubleshooting tips:
- Scanner Won’t Connect: Ensure the scanner is securely plugged into the OBD2 port and that the ignition is turned on. Check the WiFi connection and verify that the IP address and port number are correctly entered in the app.
- App Can’t Find Scanner: Make sure your device is connected to the scanner’s WiFi network. Close and reopen the app, or try restarting your device.
- Inaccurate Readings: Ensure the scanner is compatible with your car’s make and model. Check for software updates for the scanner and the app.
- Scanner Freezes: Disconnect the scanner from the OBD2 port and reconnect it. If the problem persists, try using a different diagnostic app.
7. Maintaining Your WiFi OBD2 Scanner
Proper maintenance can prolong the life of your WiFi OBD2 scanner and ensure accurate readings.
- Keep It Clean: Wipe the scanner with a clean, dry cloth to remove dust and dirt.
- Store It Properly: Store the scanner in a cool, dry place away from direct sunlight and extreme temperatures.
- Protect the Connector: Use a protective cap to cover the OBD2 connector when not in use.
- Update Firmware: Keep the scanner’s firmware updated to ensure compatibility with the latest car models and diagnostic protocols.
8. The Future Of OBD2 Scanning
The future of OBD2 scanning looks promising, with ongoing advancements in technology and connectivity.
8.1. Advancements In Technology
- More Powerful Processors: Future scanners will feature faster processors and more memory, allowing for faster data processing and more advanced diagnostics.
- Cloud Connectivity: Scanners will increasingly rely on cloud connectivity for data storage, software updates, and remote diagnostics.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI-powered diagnostic tools will be able to analyze data and provide more accurate and detailed diagnoses.
8.2. Integration With Smart Devices
- Seamless Connectivity: Scanners will seamlessly integrate with smartphones, tablets, and other smart devices, providing a user-friendly diagnostic experience.
- Voice Control: Voice-controlled scanners will allow you to perform diagnostics hands-free.
- Augmented Reality (AR): AR apps will overlay diagnostic information onto the car, making it easier to identify and repair problems.
9. Why Choose OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN For Your Diagnostic Needs?
At OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN, we are committed to providing you with the best information and services for your car diagnostic needs.
9.1. Expert Advice And Guidance
Our team of experienced automotive technicians is available to provide expert advice and guidance on using OBD2 scanners and diagnosing car problems.
9.2. Comprehensive Repair Services
We offer comprehensive repair services to address any issues identified by your OBD2 scanner. Our state-of-the-art facility and skilled technicians ensure that your car is repaired to the highest standards.
9.3. Commitment To Customer Satisfaction
We are dedicated to providing exceptional customer service and ensuring your complete satisfaction. Contact us today at 123 Main Street, Los Angeles, CA 90001, United States, via WhatsApp at +1 (641) 206-8880, or visit our website at OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN.
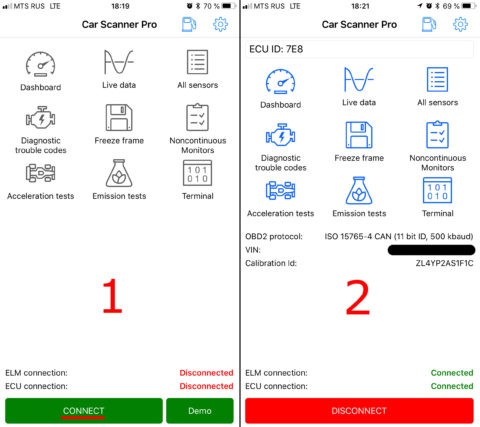 Car Scanner ELM OBD2 connection progress
Car Scanner ELM OBD2 connection progress
10. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
10.1. What Is An OBD2 Scanner?
An OBD2 scanner is a diagnostic tool used to read and interpret data from a vehicle’s On-Board Diagnostics II (OBD2) system. It helps identify issues and monitor performance.
10.2. How Does A WiFi OBD2 Scanner Work?
A WiFi OBD2 scanner connects to the car’s OBD2 port and transmits data wirelessly to a smartphone, tablet, or computer via WiFi.
10.3. Is A WiFi OBD2 Scanner Easy To Use?
Yes, WiFi OBD2 scanners are generally user-friendly, especially when paired with intuitive diagnostic apps that provide clear instructions and data interpretation.
10.4. Can I Use A WiFi OBD2 Scanner On Any Car?
Most cars manufactured after 1996 are OBD2 compliant and can be used with a WiFi OBD2 scanner. However, it’s essential to verify compatibility with your car’s make and model.
10.5. What Kind Of Information Can I Get From An OBD2 Scanner?
You can access real-time sensor readings, diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs), freeze frame data, and other valuable information about your vehicle’s performance.
10.6. How Do I Interpret OBD2 Codes?
OBD2 codes consist of five characters: a letter (P, B, C, or U) followed by four numbers. Each code corresponds to a specific fault in the vehicle.
10.7. Can I Clear Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) With A WiFi OBD2 Scanner?
Yes, you can clear DTCs with a WiFi OBD2 scanner, but it’s important to identify and repair the underlying issue first.
10.8. What Are Some Common OBD2 Codes And Their Meanings?
Common codes include P0101 (MAF Circuit Range), P0300 (Random Misfire), and P0420 (Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold).
10.9. Are There Any Risks Associated With Using A WiFi OBD2 Scanner?
Using a WiFi OBD2 scanner is generally safe, but it’s important to follow the instructions carefully and avoid clearing codes without addressing the underlying issue.
10.10. Where Can I Get Help With Diagnosing Car Problems?
OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN offers expert advice and comprehensive repair services to help you diagnose and fix your car problems. Contact us for assistance.
Empower yourself with the knowledge and tools to diagnose your car’s issues efficiently. With the detailed guidance from OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN, you can confidently use a WiFi OBD2 scanner and ensure your vehicle runs smoothly. Contact us today for any assistance!