Using an OBD2 scanner with your laptop allows you to diagnose car problems efficiently, saving time and money. OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN offers expert guidance to navigate this process seamlessly. This guide provides a step-by-step approach to connecting and utilizing your OBD2 scanner with your laptop, empowering you with the knowledge to troubleshoot vehicle issues effectively.
Contents
- 1. Understanding OBD2 Scanners and Their Benefits
- What is an OBD2 Scanner?
- Why Use an OBD2 Scanner with a Laptop?
- Benefits of Diagnosing Your Car Yourself
- 2. Essential Equipment and Software
- Choosing the Right OBD2 Scanner
- Recommended OBD2 Scanners
- Software Options for Your Laptop
- Installing the Necessary Software
- 3. Connecting Your OBD2 Scanner to Your Laptop
- Step-by-Step Guide for Bluetooth Connection
- Step-by-Step Guide for USB Connection
- Troubleshooting Connection Issues
- 4. Reading and Interpreting OBD2 Codes
- How to Read Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
- Understanding Common OBD2 Codes
- Using Online Resources to Decode Codes
- Clearing Codes and Understanding the Implications
- 5. Live Data Monitoring and Advanced Diagnostics
- Accessing and Interpreting Live Data
- Using Freeze Frame Data
- Performing Advanced Diagnostic Tests
- Data Logging and Analysis
- 6. Common Issues and Solutions
- Addressing Misfire Codes (P0300 Series)
- Resolving Lean/Rich Codes (P0171, P0174, P0172, P0175)
- Dealing with Oxygen Sensor Codes (P0130 Series)
- Fixing Catalytic Converter Codes (P0420, P0430)
- 7. Tips for Effective OBD2 Scanning
- Regularly Scan Your Vehicle
- Keep Your Software Updated
- Document Your Findings
- Consult Repair Manuals and Online Forums
- Seek Professional Help When Needed
- 8. Legal and Ethical Considerations
- Understanding Emissions Regulations
- Respecting Privacy and Security
- Disclaimer of Liability
- 9. The Future of OBD2 Technology
- OBD3 and Beyond
- Integration with Mobile Apps and Cloud Services
- Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
- 10. OBD2 Scanner FAQs
- What is an OBD2 scanner?
- How do I choose the right OBD2 scanner for my needs?
- Can I use an OBD2 scanner on any car?
- Is it safe to clear OBD2 codes?
- What does “freeze frame data” mean?
- How often should I scan my vehicle with an OBD2 scanner?
- Can an OBD2 scanner improve my car’s fuel efficiency?
- Are there any legal restrictions on using OBD2 scanners?
- Where can I find more information and support for using OBD2 scanners?
- What should I do if I’m unsure about a diagnosis or repair?
1. Understanding OBD2 Scanners and Their Benefits
What is an OBD2 Scanner?
An On-Board Diagnostics II (OBD2) scanner is a device used to access a vehicle’s computer system, retrieve diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs), and monitor various parameters related to its performance. According to the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), OBD2 systems have been mandatory on all cars and light trucks manufactured for sale in the United States since 1996. These scanners connect to your car’s OBD2 port, typically located under the dashboard, and communicate with the vehicle’s engine control unit (ECU).
Why Use an OBD2 Scanner with a Laptop?
Using an OBD2 scanner with a laptop offers several advantages over standalone handheld devices:
- Larger Display: Laptops provide a much larger screen, making it easier to view and analyze data.
- Advanced Software: Laptop-based software often includes more advanced diagnostic features, such as data logging, graphing, and custom reporting.
- Software Updates: Updating software on a laptop is generally easier and faster than updating firmware on a handheld device.
- Cost-Effectiveness: In many cases, purchasing an OBD2 adapter and using free or low-cost software on your laptop can be more economical than buying a high-end standalone scanner.
- Comprehensive Data Analysis: Laptops can store and process large amounts of data, enabling more comprehensive analysis of vehicle performance over time.
Benefits of Diagnosing Your Car Yourself
Diagnosing your car’s problems yourself using an OBD2 scanner can lead to several benefits:
- Cost Savings: Identifying issues early can prevent costly repairs down the line.
- Informed Decisions: Knowing the exact problem allows you to discuss repairs intelligently with mechanics.
- DIY Repairs: For simple issues, you may be able to perform the repairs yourself, saving on labor costs.
- Preventative Maintenance: Monitoring your car’s performance can help you identify potential problems before they become major issues.
- Peace of Mind: Understanding your car’s health can give you peace of mind and confidence on the road.
2. Essential Equipment and Software
Choosing the Right OBD2 Scanner
Selecting the right OBD2 scanner is crucial for a successful diagnostic experience. Here are some factors to consider:
- Compatibility: Ensure the scanner is compatible with your vehicle’s make and model. Most scanners support standard OBD2 protocols, but some may have limited support for specific manufacturers.
- Connectivity: Decide whether you prefer a Bluetooth, Wi-Fi, or USB connection. Bluetooth scanners offer wireless convenience, while USB scanners provide a direct and reliable connection.
- Features: Consider the features you need, such as reading and clearing DTCs, live data monitoring, freeze frame data, and advanced diagnostics.
- Price: Set a budget and compare different scanners within your price range. Keep in mind that higher-priced scanners often offer more features and better performance.
- Reviews: Read online reviews to get feedback from other users about the scanner’s reliability and ease of use.
Recommended OBD2 Scanners
Here are a few recommended OBD2 scanners for use with a laptop:
| Scanner | Connectivity | Features | Price |
|---|---|---|---|
| OBDLink MX+ | Bluetooth | Advanced diagnostics, OEM-specific data, mobile app | $139.95 |
| Veepeak Mini Bluetooth OBD2 Scanner | Bluetooth | Basic diagnostics, compact size, affordable | $22.99 |
| BAFX Products OBD2 Reader | Bluetooth | Android compatibility, user-friendly interface, reliable performance | $25.99 |
| ScanTool 427201 OBDLink LX | Bluetooth | Fast data transfer, battery monitoring, wide vehicle compatibility | $79.95 |
| Autel MaxiSys MS906BT | Bluetooth | Comprehensive diagnostics, advanced functions, professional-grade | $1,299.00 |
Software Options for Your Laptop
Various software options are available for use with OBD2 scanners on laptops, ranging from free to professional-grade:
- Free Software:
- OBDWiz: A free software that comes with OBDLink scanners, offering basic diagnostic functions.
- ScanTool.net: Provides a range of free and paid software options for OBD2 diagnostics.
- Easy OBDII: A user-friendly software with basic OBD2 functions.
- Paid Software:
- Torque Pro: A popular Android app that can be used with Bluetooth OBD2 scanners via an emulator on your laptop.
- FORScan: Specifically designed for Ford, Lincoln, and Mercury vehicles, offering advanced diagnostic capabilities.
- OBD Auto Doctor: A comprehensive software with advanced features like data logging and custom dashboards.
Installing the Necessary Software
To install the software, follow these general steps:
- Download the Software: Visit the software provider’s website and download the installation file.
- Run the Installer: Double-click the downloaded file and follow the on-screen instructions to install the software.
- Install Drivers: If prompted, install the necessary drivers for your OBD2 scanner.
- Restart Your Computer: Restart your computer to ensure the software is properly installed.
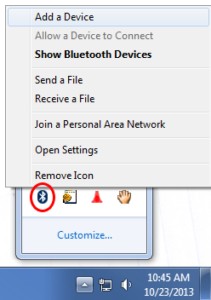 Windows Bluetooth settings to add device.
Windows Bluetooth settings to add device.
Alternative text: A screenshot illustrating how to access Bluetooth settings in Windows to add a new device.
3. Connecting Your OBD2 Scanner to Your Laptop
Step-by-Step Guide for Bluetooth Connection
Connecting your OBD2 scanner to your laptop via Bluetooth involves several steps:
- Enable Bluetooth on Your Laptop:
- Go to Settings > Devices > Bluetooth & other devices.
- Turn on the Bluetooth toggle switch.
- Plug the OBD2 Scanner into Your Car:
- Locate the OBD2 port, typically under the dashboard on the driver’s side.
- Plug the OBD2 scanner into the port.
- Turn On Your Car’s Ignition:
- Turn the ignition key to the “ON” position without starting the engine.
- Make OBDLink discoverable:
- Press the ‘Connect’ button.
- Pair the OBD2 Scanner with Your Laptop:
- Click Add Bluetooth or other device.
- Select Bluetooth.
- Your laptop will scan for available devices. Select your OBD2 scanner from the list.
- If prompted for a PIN, enter 1234 or 0000.
- Follow any additional on-screen instructions to complete the pairing process.
- Configure the Software:
- Open the OBD2 software on your laptop.
- Go to Settings or Preferences.
- Select the correct COM port for your Bluetooth adapter. This may be listed as “Bluetooth Serial Port” or similar.
- Test the connection to ensure the software can communicate with the OBD2 scanner.
Step-by-Step Guide for USB Connection
Connecting your OBD2 scanner to your laptop via USB is generally straightforward:
- Install the Drivers:
- Connect the OBD2 scanner to your laptop using the USB cable.
- Windows should automatically detect the device and attempt to install the drivers.
- If the drivers are not automatically installed, you may need to download them from the scanner manufacturer’s website and install them manually.
- Plug the OBD2 Scanner into Your Car:
- Locate the OBD2 port in your car.
- Plug the OBD2 scanner into the port.
- Turn On Your Car’s Ignition:
- Turn the ignition key to the “ON” position without starting the engine.
- Configure the Software:
- Open the OBD2 software on your laptop.
- Go to Settings or Preferences.
- Select the correct COM port for your USB adapter. This is often listed as “USB Serial Port” or similar.
- Test the connection to ensure the software can communicate with the OBD2 scanner.
Troubleshooting Connection Issues
If you encounter connection issues, try these troubleshooting steps:
- Verify Bluetooth is Enabled: Ensure Bluetooth is turned on in your laptop settings.
- Check the COM Port: Make sure the correct COM port is selected in the software settings.
- Reinstall Drivers: Reinstall the drivers for your OBD2 scanner.
- Restart Devices: Restart your laptop and your car.
- Check Compatibility: Verify that the OBD2 scanner is compatible with your car’s make and model.
- Update Software: Ensure you are using the latest version of the OBD2 software.
- Contact Support: Contact the scanner manufacturer’s support team for assistance.
4. Reading and Interpreting OBD2 Codes
How to Read Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
Once your OBD2 scanner is connected to your laptop and your car, you can start reading diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs):
- Open the OBD2 Software: Launch the OBD2 software on your laptop.
- Connect to the Vehicle: Establish a connection to your car through the software.
- Select “Read Codes”: Look for an option like “Read Codes,” “Trouble Codes,” or “DTCs.”
- View the Codes: The software will display a list of DTCs, each with a code and a brief description.
Understanding Common OBD2 Codes
OBD2 codes consist of five characters: a letter followed by four numbers. The letter indicates the system the code refers to:
- P: Powertrain (engine, transmission)
- B: Body (interior, exterior)
- C: Chassis (brakes, suspension)
- U: Network (communication)
The first number indicates whether the code is generic (0) or manufacturer-specific (1). The remaining three numbers specify the exact fault.
Here are some common OBD2 codes and their meanings:
| Code | Description | Possible Causes |
|---|---|---|
| P0300 | Random/Multiple Cylinder Misfire Detected | Faulty spark plugs, ignition coils, fuel injectors, vacuum leaks |
| P0171 | System Too Lean (Bank 1) | Vacuum leaks, faulty oxygen sensor, low fuel pressure, dirty mass airflow sensor |
| P0420 | Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold (Bank 1) | Faulty catalytic converter, oxygen sensors, exhaust leaks |
| P0301 | Cylinder 1 Misfire Detected | Faulty spark plug, ignition coil, fuel injector, low compression in cylinder 1 |
| P0113 | Intake Air Temperature Sensor Circuit High Input | Faulty intake air temperature sensor, wiring issues |
Using Online Resources to Decode Codes
Several online resources can help you decode OBD2 codes:
- OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN: Our website offers a comprehensive database of OBD2 codes and their meanings.
- OBD-Codes.com: A popular website with a detailed OBD2 code database and troubleshooting tips.
- AutoCodes.com: Provides code definitions, possible causes, and repair information.
Clearing Codes and Understanding the Implications
After addressing the issue causing the DTC, you can clear the code using the OBD2 software:
- Select “Clear Codes”: Look for an option like “Clear Codes,” “Erase DTCs,” or similar.
- Confirm the Action: The software may ask you to confirm that you want to clear the codes.
- Verify the Code is Cleared: After clearing the codes, rescan to ensure the code does not reappear.
Keep in mind that clearing codes does not fix the underlying problem. The code will likely return if the issue is not resolved. Additionally, clearing codes will reset the car’s emissions monitors, which may take some time to reset after driving.
 OBD2 adapter connected to a car's OBD2 port.
OBD2 adapter connected to a car's OBD2 port.
Alternative text: A close-up view of an OBD2 adapter plugged into the OBD2 port of a vehicle.
5. Live Data Monitoring and Advanced Diagnostics
Accessing and Interpreting Live Data
Live data monitoring allows you to view real-time information about your car’s performance:
- Select “Live Data”: Look for an option like “Live Data,” “Real-Time Data,” or “Data Stream.”
- Choose Parameters: Select the parameters you want to monitor, such as engine RPM, coolant temperature, oxygen sensor readings, and fuel trim.
- View the Data: The software will display the data in real-time, often in the form of graphs or charts.
Interpreting live data requires some knowledge of how your car’s systems operate. For example:
- Engine RPM: Indicates the speed at which the engine is running.
- Coolant Temperature: Shows the temperature of the engine coolant.
- Oxygen Sensor Readings: Reflects the air-fuel mixture in the exhaust.
- Fuel Trim: Indicates how much the ECU is adjusting the fuel mixture.
Using Freeze Frame Data
Freeze frame data captures a snapshot of the car’s operating conditions when a DTC was triggered. This information can be valuable for diagnosing intermittent problems. To access freeze frame data:
- Read Trouble Codes: First, read the DTCs.
- Select “Freeze Frame”: Look for an option like “Freeze Frame Data” or “View Freeze Frame.”
- Analyze the Data: The software will display the data captured when the DTC was triggered.
Performing Advanced Diagnostic Tests
Some OBD2 software offers advanced diagnostic tests, such as:
- Oxygen Sensor Tests: Checks the performance of the oxygen sensors.
- EGR System Tests: Evaluates the functionality of the exhaust gas recirculation system.
- EVAP System Tests: Tests the evaporative emissions control system for leaks.
These tests can provide valuable insights into the health of your car’s systems.
Data Logging and Analysis
Data logging allows you to record live data over time, which can be useful for diagnosing intermittent problems or tracking performance. To use data logging:
- Select “Data Logging”: Look for an option like “Data Logging” or “Record Data.”
- Choose Parameters: Select the parameters you want to log.
- Start Recording: Begin recording data while driving or running the engine.
- Stop Recording: Stop recording data when you have captured the desired information.
- Analyze the Data: Use the software to analyze the logged data, looking for patterns or anomalies.
6. Common Issues and Solutions
Addressing Misfire Codes (P0300 Series)
Misfire codes, such as P0300 (Random/Multiple Cylinder Misfire Detected) and P0301 (Cylinder 1 Misfire Detected), indicate that one or more cylinders are not firing properly. Possible causes include:
- Faulty Spark Plugs: Replace worn or damaged spark plugs.
- Faulty Ignition Coils: Test and replace faulty ignition coils.
- Faulty Fuel Injectors: Clean or replace faulty fuel injectors.
- Vacuum Leaks: Inspect and repair vacuum leaks.
- Low Compression: Perform a compression test to check for low compression in the affected cylinder.
Resolving Lean/Rich Codes (P0171, P0174, P0172, P0175)
Lean codes (P0171, P0174) indicate that the air-fuel mixture is too lean (too much air, not enough fuel), while rich codes (P0172, P0175) indicate the opposite. Possible causes include:
- Vacuum Leaks: Inspect and repair vacuum leaks.
- Faulty Oxygen Sensors: Test and replace faulty oxygen sensors.
- Low Fuel Pressure: Check fuel pressure and replace the fuel pump if necessary.
- Dirty Mass Airflow Sensor: Clean or replace the mass airflow sensor.
- Faulty Fuel Injectors: Clean or replace faulty fuel injectors.
Dealing with Oxygen Sensor Codes (P0130 Series)
Oxygen sensor codes, such as P0130 (Oxygen Sensor Circuit Malfunction (Bank 1, Sensor 1)), indicate a problem with one of the oxygen sensors. Possible causes include:
- Faulty Oxygen Sensor: Replace the faulty oxygen sensor.
- Wiring Issues: Inspect and repair wiring issues to the oxygen sensor.
- Exhaust Leaks: Repair exhaust leaks near the oxygen sensor.
Fixing Catalytic Converter Codes (P0420, P0430)
Catalytic converter codes, such as P0420 (Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold (Bank 1)), indicate that the catalytic converter is not functioning properly. Possible causes include:
- Faulty Catalytic Converter: Replace the faulty catalytic converter.
- Faulty Oxygen Sensors: Replace faulty oxygen sensors.
- Exhaust Leaks: Repair exhaust leaks.
7. Tips for Effective OBD2 Scanning
Regularly Scan Your Vehicle
Scanning your vehicle regularly, even if there are no apparent problems, can help you identify potential issues early.
Keep Your Software Updated
Ensure that your OBD2 software is always up to date to take advantage of the latest features and bug fixes.
Document Your Findings
Keep a record of the DTCs and live data you collect, along with any repairs you perform. This can help you track your car’s performance over time.
Consult Repair Manuals and Online Forums
Refer to your car’s repair manual and online forums for specific troubleshooting tips and repair procedures.
Seek Professional Help When Needed
If you are unsure about a diagnosis or repair, seek professional help from a qualified mechanic.
8. Legal and Ethical Considerations
Understanding Emissions Regulations
Many states have emissions regulations that require vehicles to pass an emissions test. Clearing DTCs shortly before an emissions test may result in a failed test, as the car’s emissions monitors may not be ready.
Respecting Privacy and Security
Be mindful of the data you are accessing and sharing when using an OBD2 scanner. Avoid sharing sensitive information and take steps to protect your car’s computer system from unauthorized access.
Disclaimer of Liability
Using an OBD2 scanner involves some risk. Be aware that you are responsible for any repairs or modifications you make to your car. OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN is not liable for any damages or injuries that may result from using the information provided in this guide.
9. The Future of OBD2 Technology
OBD3 and Beyond
The future of OBD2 technology includes advancements like OBD3, which aims to provide real-time emissions monitoring and reporting. This could lead to more efficient emissions control and better air quality.
Integration with Mobile Apps and Cloud Services
OBD2 technology is increasingly integrated with mobile apps and cloud services, allowing for remote diagnostics, vehicle tracking, and predictive maintenance.
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
Artificial intelligence and machine learning are being used to analyze OBD2 data, identify patterns, and predict potential problems before they occur.
10. OBD2 Scanner FAQs
What is an OBD2 scanner?
An OBD2 scanner is a diagnostic tool used to read and interpret data from a vehicle’s On-Board Diagnostics system, helping identify issues and potential problems. The University of Michigan’s Transportation Research Institute highlights the importance of OBD2 systems in modern vehicle maintenance and diagnostics.
How do I choose the right OBD2 scanner for my needs?
Consider factors like vehicle compatibility, features, connectivity (Bluetooth, USB), and budget to select an OBD2 scanner that meets your requirements. A study by Consumer Reports suggests that reading reviews and comparing features can significantly improve satisfaction with diagnostic tools.
Can I use an OBD2 scanner on any car?
OBD2 scanners are generally compatible with all cars and light trucks manufactured for sale in the United States since 1996, as mandated by the EPA.
Is it safe to clear OBD2 codes?
It is generally safe to clear OBD2 codes after addressing the underlying issue, but be aware that this will reset the car’s emissions monitors, which may take some time to reset after driving. A paper from the Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE) discusses the implications of clearing diagnostic codes on vehicle performance and emissions testing.
What does “freeze frame data” mean?
Freeze frame data is a snapshot of the car’s operating conditions when a DTC was triggered, providing valuable information for diagnosing intermittent problems. Research at Carnegie Mellon University’s Robotics Institute emphasizes the value of freeze frame data in diagnosing and predicting vehicle failures.
How often should I scan my vehicle with an OBD2 scanner?
Regularly scanning your vehicle, even if there are no apparent problems, can help you identify potential issues early and prevent costly repairs.
Can an OBD2 scanner improve my car’s fuel efficiency?
By identifying and addressing issues that affect engine performance, an OBD2 scanner can help improve your car’s fuel efficiency.
Are there any legal restrictions on using OBD2 scanners?
There are generally no legal restrictions on using OBD2 scanners for personal use, but be mindful of emissions regulations and privacy concerns. The National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) provides guidelines on vehicle safety and diagnostic practices.
Where can I find more information and support for using OBD2 scanners?
OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN is a great resource for information and support. You can also consult your car’s repair manual, online forums, and qualified mechanics.
What should I do if I’m unsure about a diagnosis or repair?
If you are unsure about a diagnosis or repair, seek professional help from a qualified mechanic to avoid potential damage or injury.
Using an OBD2 scanner with your laptop can empower you to diagnose and repair your car’s problems effectively. By following the steps outlined in this guide and utilizing the resources available at OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN, you can save time and money while keeping your car running smoothly.
Do you want personalized guidance on using OBD2 scanners or need expert diagnostics? Contact us today at 123 Main Street, Los Angeles, CA 90001, United States, via WhatsApp at +1 (641) 206-8880, or visit our website at OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN for immediate assistance. Our team is ready to help you navigate any car diagnostic challenges.