Is My Car Obd2 Compliant Uk? Yes, most petrol cars sold in the UK from 2001 and diesel cars from 2004 are OBD2 compliant. To ensure you have the correct information for your vehicle, let’s explore how to check your car’s compliance, understand the benefits of OBD2, and how to use an OBD2 scanner effectively with guidance from OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN to diagnose and maintain your vehicle.
Contents
- 1. Understanding OBD2 Compliance in the UK
- 1.1. What is OBD2?
- 1.2. History of OBD2
- 1.3. UK Regulations and OBD2
- 2. How to Check if Your Car is OBD2 Compliant in the UK
- 2.1. Check Your Vehicle’s Manual
- 2.2. Visual Inspection of the DLC
- 2.3. Check the Vehicle Emission Control Information (VECI) Label
- 2.4. Online Database Lookup
- 2.5. Consult with a Mechanic
- 3. Benefits of OBD2 Compliance
- 3.1. Enhanced Diagnostics
- 3.2. Improved Emission Control
- 3.3. Cost Savings
- 3.4. Standardized Interface
- 3.5. Access to Real-Time Data
- 4. Understanding OBD2 Protocols
- 4.1. What are OBD2 Protocols?
- 4.2. Common OBD2 Protocols
- 4.3. How to Determine Your Vehicle’s Protocol
- 5. Essential OBD2 Scanner Features
- 5.1. Code Reading and Clearing
- 5.2. Live Data Streaming
- 5.3. Freeze Frame Data
- 5.4. I/M Readiness Monitors
- 5.5. Vehicle Information Retrieval
- 6. Choosing the Right OBD2 Scanner for Your Needs
- 6.1. Basic OBD2 Scanners
- 6.2. Mid-Range OBD2 Scanners
- 6.3. Professional OBD2 Scanners
- 6.4. OBD2 Scanner Brands
- 6.5. Considerations for UK Users
- 7. Step-by-Step Guide to Using an OBD2 Scanner
- 7.1. Preparing for the Scan
- 7.2. Connecting the Scanner
- 7.3. Reading Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
- 7.4. Interpreting the Codes
- 7.5. Clearing Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
- 8. Common OBD2 Trouble Codes and Their Meanings
- 8.1. P0100-P0199: Fuel and Air Metering
- 8.2. P0200-P0299: Injector Circuit
- 8.3. P0300-P0399: Ignition System or Misfire
- 8.4. P0400-P0499: Auxiliary Emission Controls
- 8.5. P0500-P0599: Vehicle Speed Controls and Idle Control System
- 9. Advanced OBD2 Diagnostics and Techniques
- 9.1. Using Live Data for Diagnostics
- 9.2. Performing Component Tests
- 9.3. Using Bi-Directional Control
- 9.4. Diagnosing Intermittent Issues
- 10. OBD2 and MOT Tests in the UK
- 10.1. What is an MOT Test?
- 10.2. OBD2 and Emissions Testing
- 10.3. Preparing for an MOT Test
- 11. Common Misconceptions About OBD2
- 11.1. OBD2 Fixes the Problem
- 11.2. All OBD2 Scanners are the Same
- 11.3. OBD2 is Only for Professionals
- 11.4. Clearing Codes Solves the Problem
- 12. Maintaining Your OBD2 System
- 12.1. Keep the DLC Clean
- 12.2. Ensure Proper Connections
- 12.3. Keep Your Scanner Updated
- 13. The Future of OBD and Vehicle Diagnostics
- 13.1. OBD3 and Beyond
- 13.2. Integration with Telematics
- 13.3. Smartphone-Based Diagnostics
- 14. Case Studies: OBD2 in Action
- 14.1. Case Study 1: Diagnosing a Misfire
- 14.2. Case Study 2: Identifying an Emissions Issue
- 14.3. Case Study 3: Resolving a Fuel Efficiency Problem
- 15. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- 15.1. What is an OBD2 Scanner?
- 15.2. How Do I Know if My Car is OBD2 Compliant?
- 15.3. Where is the OBD2 Port Located in My Car?
- 15.4. Can I Use Any OBD2 Scanner on My Car?
- 15.5. What Do I Do After I Get an OBD2 Code?
- 15.6. Can I Clear the OBD2 Codes Myself?
- 15.7. Will Clearing OBD2 Codes Affect My Car’s Performance?
- 15.8. Is it Safe to Drive with an OBD2 Code?
- 15.9. How Often Should I Scan My Car with an OBD2 Scanner?
- 15.10. What is the Difference Between OBD1 and OBD2?
1. Understanding OBD2 Compliance in the UK
OBD2, or On-Board Diagnostics version 2, is a standardized system that allows you to access the health information of your vehicle.
1.1. What is OBD2?
OBD2 is a system that monitors and reports on a vehicle’s performance. According to a study by the University of California, Berkeley’s Institute of Transportation Studies, the introduction of OBD2 has significantly reduced vehicle emissions by enabling quicker identification and resolution of engine-related issues.
1.2. History of OBD2
- Early OBD Systems: Before OBD2, manufacturers used various proprietary diagnostic systems.
- OBD2 Standardization: In the mid-1990s, OBD2 was mandated in the US, leading to its adoption worldwide.
- European Adoption: The European Union adopted EOBD (European On-Board Diagnostics), which is largely compatible with OBD2.
1.3. UK Regulations and OBD2
- Petrol Cars: Petrol cars sold in the UK from 2001 are generally OBD2 compliant.
- Diesel Cars: Diesel cars sold in the UK from 2004 are generally OBD2 compliant.
- Legislation: European Directive 98/69/EC mandated EOBD for petrol cars from 2001 and diesel cars from 2004.
2. How to Check if Your Car is OBD2 Compliant in the UK
Determining whether your vehicle adheres to OBD2 standards involves multiple verification methods.
2.1. Check Your Vehicle’s Manual
The vehicle’s owner’s manual often contains information about OBD2 compliance.
- Locate the Manual: Find the manual in your car’s glove compartment or online.
- Search for OBD2: Use keywords like “OBD2,” “EOBD,” or “on-board diagnostics.”
- Compliance Statement: Look for a statement confirming OBD2 or EOBD compliance.
2.2. Visual Inspection of the DLC
The Diagnostic Link Connector (DLC) is a standard 16-pin connector used for OBD2 diagnostics.
- Locate the DLC: Typically found under the dashboard, near the steering column.
- Check the Connector: Ensure it is a 16-pin connector.
- Shape and Pins: The DLC should be trapezoidal with two rows of pins.
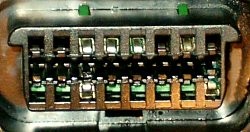 Ford Escort DLC
Ford Escort DLC
2.3. Check the Vehicle Emission Control Information (VECI) Label
The VECI label, usually found under the hood, can indicate OBD2 compliance.
- Locate the Label: Look for a sticker under the hood, often near the engine.
- Read the Label: Check for mentions of “OBD2,” “EOBD,” or compliance with environmental regulations.
- Example Phrases: Look for phrases like “OBD2 compliant” or “Meets EPA OBD2 requirements.”
2.4. Online Database Lookup
Several online databases can provide OBD2 compliance information based on your car’s make, model, and year.
- Use Online Resources: Websites like OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN often have compatibility checkers.
- Enter Vehicle Details: Input the make, model, and year of your car.
- Check Results: View the information to confirm OBD2 compliance.
2.5. Consult with a Mechanic
A professional mechanic can quickly determine OBD2 compliance.
- Visit a Garage: Take your car to a trusted mechanic.
- Diagnostic Check: Ask them to perform a quick OBD2 check.
- Expert Advice: Get professional confirmation and advice.
3. Benefits of OBD2 Compliance
OBD2 compliance offers numerous advantages for vehicle owners.
3.1. Enhanced Diagnostics
OBD2 provides standardized diagnostic information, making it easier to identify and fix issues.
- Standardized Codes: Uses standard Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs).
- Comprehensive Data: Provides data on engine performance, emissions, and more.
- Quick Issue Identification: Allows for quick identification of problems.
3.2. Improved Emission Control
OBD2 monitors emission-related components, helping to reduce pollution.
- Emission Monitoring: Tracks the performance of emission control systems.
- Early Problem Detection: Detects issues early, preventing excessive emissions.
- Environmental Benefits: Contributes to cleaner air and reduced environmental impact.
3.3. Cost Savings
By identifying issues early, OBD2 can help prevent costly repairs.
- Preventive Maintenance: Allows for timely maintenance and repairs.
- Reduced Repair Costs: Prevents minor issues from becoming major problems.
- Fuel Efficiency: Helps maintain optimal fuel efficiency.
3.4. Standardized Interface
The standardized DLC allows any compatible scanner to read vehicle data.
- Universal Compatibility: Works with any OBD2 scanner.
- Easy Access: Provides easy access to vehicle diagnostics.
- Wider Choice of Tools: Allows you to choose from a wide range of scanning tools.
3.5. Access to Real-Time Data
OBD2 provides real-time data on various vehicle parameters.
- Live Data Streaming: Provides real-time data on engine performance.
- Parameter Monitoring: Allows monitoring of various parameters like RPM, speed, and temperature.
- Performance Analysis: Helps in analyzing vehicle performance.
4. Understanding OBD2 Protocols
OBD2 utilizes various communication protocols.
4.1. What are OBD2 Protocols?
OBD2 protocols are the communication languages used between the vehicle’s computer and the diagnostic tool. A study by the Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE) highlighted the importance of understanding these protocols for effective vehicle diagnostics and repair.
4.2. Common OBD2 Protocols
- SAE J1850 PWM and VPW: Used mainly by Ford and GM vehicles.
- ISO 9141-2: Used by European and Asian vehicles.
- ISO 14230-4 (KWP2000): Also used by European and Asian vehicles.
- ISO 15765-4 (CAN): The modern standard, used by most vehicles from 2008 onwards.
4.3. How to Determine Your Vehicle’s Protocol
- Check the Vehicle Manual: The manual may specify the OBD2 protocol used.
- Use a Scanner: Some scanners can automatically detect the protocol.
- Consult a Mechanic: A mechanic can identify the protocol using diagnostic tools.
5. Essential OBD2 Scanner Features
Selecting the right OBD2 scanner involves considering several key features.
5.1. Code Reading and Clearing
The primary function of an OBD2 scanner is to read and clear Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs).
- Reading Codes: Scanners read codes indicating problems in the vehicle.
- Clearing Codes: Scanners can clear codes after the issue is resolved.
- Confirmation: Always confirm the issue is fixed before clearing codes.
5.2. Live Data Streaming
Live data streaming allows you to monitor real-time vehicle parameters.
- Real-Time Monitoring: View data such as RPM, speed, and sensor readings.
- Performance Analysis: Analyze vehicle performance under different conditions.
- Troubleshooting: Helps in diagnosing intermittent issues.
5.3. Freeze Frame Data
Freeze frame data captures vehicle data at the moment a DTC is triggered.
- Snapshot of Data: Provides a snapshot of vehicle parameters when a fault occurs.
- Diagnostic Aid: Helps in understanding the conditions that led to the fault.
- Issue Recreation: Can assist in recreating the issue for diagnosis.
5.4. I/M Readiness Monitors
I/M readiness monitors check if the vehicle’s emission systems are ready for testing.
- Emission Readiness: Checks if emission systems have completed their self-tests.
- Pre-Test Check: Ensures the vehicle will pass an emissions test.
- Monitor Status: Displays the status of various emission monitors.
5.5. Vehicle Information Retrieval
Retrieving vehicle information such as VIN, calibration ID, and CVN is a useful feature.
- VIN Retrieval: Retrieves the Vehicle Identification Number.
- Calibration ID: Identifies the vehicle’s software calibration.
- CVN: Checks the Calibration Verification Number.
6. Choosing the Right OBD2 Scanner for Your Needs
Selecting the appropriate OBD2 scanner involves evaluating different types and brands.
6.1. Basic OBD2 Scanners
Basic scanners are affordable and suitable for simple tasks.
- Functionality: Read and clear DTCs.
- Ease of Use: Simple and user-friendly interface.
- Cost-Effective: Budget-friendly option.
6.2. Mid-Range OBD2 Scanners
Mid-range scanners offer additional features like live data streaming and freeze frame data.
- Additional Features: Includes live data, freeze frame, and I/M readiness.
- Enhanced Diagnostics: Provides more comprehensive diagnostic capabilities.
- Price Range: Moderately priced, offering good value for money.
6.3. Professional OBD2 Scanners
Professional scanners offer advanced features and are designed for automotive technicians.
- Advanced Features: Includes bi-directional control, advanced diagnostics, and vehicle-specific functions.
- Comprehensive Analysis: Provides in-depth analysis of vehicle systems.
- Higher Cost: More expensive but offers extensive capabilities.
6.4. OBD2 Scanner Brands
Several reputable brands offer high-quality OBD2 scanners.
- Autel: Known for reliable and feature-rich scanners.
- Launch: Offers a wide range of scanners for different needs.
- BlueDriver: Popular for its smartphone-based scanners.
- OBDLink: Renowned for its high-performance and accurate devices.
6.5. Considerations for UK Users
- EOBD Compatibility: Ensure the scanner supports EOBD protocols.
- Language Support: Check if the scanner supports English.
- UK Vehicle Coverage: Confirm the scanner is compatible with UK vehicle models.
7. Step-by-Step Guide to Using an OBD2 Scanner
Using an OBD2 scanner is straightforward.
7.1. Preparing for the Scan
- Turn Off the Engine: Ensure the engine is off before connecting the scanner.
- Locate the DLC: Find the 16-pin Diagnostic Link Connector.
- Check the Scanner: Make sure the scanner is powered on or has fresh batteries.
7.2. Connecting the Scanner
- Plug in the Scanner: Connect the scanner to the DLC.
- Ensure a Secure Connection: Make sure the connection is secure.
- Turn on the Ignition: Turn the ignition to the “ON” position without starting the engine.
7.3. Reading Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
- Select “Read Codes”: Navigate to the “Read Codes” or “Diagnostic Codes” option on the scanner.
- Wait for the Scan: Allow the scanner to retrieve the codes.
- Record the Codes: Write down the codes and their descriptions.
7.4. Interpreting the Codes
- Consult the Manual: Refer to the vehicle’s manual or an online database for code definitions.
- Identify the Issue: Determine the potential problem based on the code.
- Prioritize Codes: Address the most critical codes first.
7.5. Clearing Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
- Select “Clear Codes”: Navigate to the “Clear Codes” or “Erase Codes” option on the scanner.
- Confirm the Action: Follow the prompts to confirm the action.
- Verify the Clearing: Ensure the codes are cleared by rescanning.
8. Common OBD2 Trouble Codes and Their Meanings
Understanding common OBD2 codes is essential for effective diagnostics.
8.1. P0100-P0199: Fuel and Air Metering
These codes relate to issues with the fuel and air mixture.
- P0100: Mass Air Flow (MAF) Sensor Circuit Malfunction.
- P0113: Intake Air Temperature (IAT) Sensor Circuit High Input.
- P0171: System Too Lean (Bank 1).
8.2. P0200-P0299: Injector Circuit
These codes indicate problems with the fuel injectors.
- P0201: Injector Circuit Malfunction – Cylinder 1.
- P0230: Fuel Pump Primary Circuit Malfunction.
8.3. P0300-P0399: Ignition System or Misfire
These codes relate to ignition system issues and engine misfires.
- P0300: Random/Multiple Cylinder Misfire Detected.
- P0301: Cylinder 1 Misfire Detected.
- P0325: Knock Sensor 1 Circuit Malfunction (Bank 1 or Single Sensor).
8.4. P0400-P0499: Auxiliary Emission Controls
These codes indicate problems with emission control systems.
- P0401: Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) Flow Insufficient Detected.
- P0420: Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold (Bank 1).
- P0442: Evaporative Emission Control System Leak Detected (Small Leak).
8.5. P0500-P0599: Vehicle Speed Controls and Idle Control System
These codes relate to vehicle speed and idle control.
- P0500: Vehicle Speed Sensor (VSS) Malfunction.
- P0505: Idle Control System Malfunction.
9. Advanced OBD2 Diagnostics and Techniques
Advanced diagnostics involve using specialized techniques and tools.
9.1. Using Live Data for Diagnostics
Live data can provide insights into real-time vehicle performance.
- Monitor Key Parameters: Monitor parameters like RPM, MAF, and O2 sensor readings.
- Identify Anomalies: Look for unusual or out-of-range values.
- Correlate Data: Correlate data with symptoms to diagnose issues.
9.2. Performing Component Tests
Component tests involve activating and monitoring individual components.
- Actuator Tests: Use the scanner to activate components like fuel injectors and EGR valves.
- Monitor Response: Check if the component responds correctly.
- Verify Functionality: Ensure the component is functioning as expected.
9.3. Using Bi-Directional Control
Bi-directional control allows you to send commands to the vehicle’s computer.
- Command Execution: Send commands to activate or deactivate certain functions.
- System Testing: Test various systems and components.
- Advanced Diagnostics: Perform advanced diagnostic procedures.
9.4. Diagnosing Intermittent Issues
Intermittent issues can be challenging to diagnose.
- Record Data: Use the scanner to record data during the issue.
- Analyze Freeze Frame Data: Review freeze frame data for clues.
- Monitor Conditions: Monitor conditions that trigger the issue.
10. OBD2 and MOT Tests in the UK
OBD2 plays a role in the UK’s MOT (Ministry of Transport) tests.
10.1. What is an MOT Test?
The MOT test is an annual inspection to ensure vehicles meet minimum safety and environmental standards.
10.2. OBD2 and Emissions Testing
- Emissions Check: Part of the MOT test involves checking vehicle emissions.
- OBD2 Scan: Testers may use an OBD2 scanner to check for emission-related DTCs.
- Pass/Fail Criteria: Failing the emissions test can result in MOT failure.
10.3. Preparing for an MOT Test
- Check for DTCs: Use an OBD2 scanner to check for DTCs before the test.
- Address Issues: Resolve any issues indicated by the codes.
- Ensure Readiness: Make sure the vehicle is ready for the emissions test.
11. Common Misconceptions About OBD2
Several misconceptions exist regarding OBD2.
11.1. OBD2 Fixes the Problem
- Misconception: OBD2 automatically fixes vehicle problems.
- Reality: OBD2 only identifies the problem; it does not fix it.
- Action Required: You need to diagnose and repair the issue manually.
11.2. All OBD2 Scanners are the Same
- Misconception: All OBD2 scanners offer the same features and capabilities.
- Reality: Scanners vary in features, functionality, and price.
- Choose Wisely: Select a scanner that meets your specific needs.
11.3. OBD2 is Only for Professionals
- Misconception: OBD2 is too complex for the average car owner.
- Reality: Basic OBD2 scanning is simple and can be done by anyone.
- User-Friendly Tools: Many user-friendly scanners are available for beginners.
11.4. Clearing Codes Solves the Problem
- Misconception: Clearing DTCs permanently solves the underlying issue.
- Reality: Clearing codes only hides the symptom; the problem still exists.
- Underlying Fix: You must address the root cause of the issue.
12. Maintaining Your OBD2 System
Proper maintenance of the OBD2 system ensures accurate and reliable diagnostics.
12.1. Keep the DLC Clean
- Dirt and Debris: Prevent dirt and debris from entering the DLC.
- Protective Cap: Use a protective cap when the DLC is not in use.
- Cleaning: Clean the DLC with a soft cloth if necessary.
12.2. Ensure Proper Connections
- Secure Connection: Ensure the scanner is securely connected to the DLC.
- Check Pins: Inspect the DLC pins for damage or corrosion.
- Replace if Necessary: Replace the DLC if it is damaged.
12.3. Keep Your Scanner Updated
- Software Updates: Regularly update the scanner’s software.
- New Features: Updates often include new features and vehicle coverage.
- Improved Performance: Updates can improve the scanner’s performance and accuracy.
13. The Future of OBD and Vehicle Diagnostics
OBD technology continues to evolve, with new features and capabilities being introduced.
13.1. OBD3 and Beyond
- Enhanced Monitoring: Future OBD systems may include more comprehensive monitoring.
- Remote Diagnostics: Potential for remote diagnostics and vehicle health monitoring.
- Improved Integration: Better integration with vehicle systems.
13.2. Integration with Telematics
- Telematics Systems: OBD2 data can be integrated with telematics systems.
- Data Analysis: Allows for real-time data analysis and vehicle tracking.
- Preventive Maintenance: Enables proactive maintenance and alerts.
13.3. Smartphone-Based Diagnostics
- Mobile Apps: Increasing use of smartphone apps for OBD2 diagnostics.
- Wireless Connectivity: Bluetooth and Wi-Fi connectivity for easy data transfer.
- User-Friendly Interface: Simple and intuitive interfaces for easy use.
14. Case Studies: OBD2 in Action
Real-world examples demonstrate the effectiveness of OBD2 diagnostics.
14.1. Case Study 1: Diagnosing a Misfire
- Symptom: Vehicle experiencing a misfire.
- OBD2 Scan: Code P0301 (Cylinder 1 Misfire Detected).
- Diagnosis: Faulty ignition coil on cylinder 1.
- Solution: Replaced the ignition coil, resolving the misfire.
14.2. Case Study 2: Identifying an Emissions Issue
- Symptom: Vehicle failing an emissions test.
- OBD2 Scan: Code P0420 (Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold).
- Diagnosis: Failing catalytic converter.
- Solution: Replaced the catalytic converter, allowing the vehicle to pass the emissions test.
14.3. Case Study 3: Resolving a Fuel Efficiency Problem
- Symptom: Reduced fuel efficiency.
- OBD2 Scan: Code P0171 (System Too Lean).
- Diagnosis: Faulty mass airflow (MAF) sensor.
- Solution: Replaced the MAF sensor, restoring fuel efficiency.
15. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
15.1. What is an OBD2 Scanner?
An OBD2 scanner is a diagnostic tool that reads data from a vehicle’s computer to identify issues. It retrieves Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) and provides real-time data for analysis.
15.2. How Do I Know if My Car is OBD2 Compliant?
Check your vehicle’s manual, look for the DLC connector, check the VECI label, or use an online database. Most petrol cars sold in the UK from 2001 and diesel cars from 2004 are OBD2 compliant.
15.3. Where is the OBD2 Port Located in My Car?
The OBD2 port is typically located under the dashboard, near the steering column. It is a 16-pin connector.
15.4. Can I Use Any OBD2 Scanner on My Car?
Yes, OBD2 scanners are designed to be universally compatible with all OBD2-compliant vehicles. However, ensure the scanner supports the correct protocols for your car.
15.5. What Do I Do After I Get an OBD2 Code?
Research the code to understand the potential issue. Consult your vehicle’s manual or an online database for code definitions. Diagnose the problem and perform the necessary repairs.
15.6. Can I Clear the OBD2 Codes Myself?
Yes, you can clear OBD2 codes using an OBD2 scanner. However, ensure the underlying issue is resolved before clearing the codes.
15.7. Will Clearing OBD2 Codes Affect My Car’s Performance?
Clearing OBD2 codes will not directly affect your car’s performance. However, if the underlying issue is not resolved, the code will likely reappear.
15.8. Is it Safe to Drive with an OBD2 Code?
It depends on the nature of the code. Some codes indicate minor issues, while others may indicate serious problems that could damage your vehicle. Consult a mechanic if you are unsure.
15.9. How Often Should I Scan My Car with an OBD2 Scanner?
You should scan your car whenever you notice any performance issues or warning lights. Regular scanning can help identify potential problems early.
15.10. What is the Difference Between OBD1 and OBD2?
OBD1 was a proprietary system used before the mid-1990s, while OBD2 is a standardized system used in modern vehicles. OBD2 provides more comprehensive diagnostic information and is universally compatible.
Is your car OBD2 compliant UK? Understanding OBD2 compliance, its benefits, and how to use an OBD2 scanner can empower you to maintain your vehicle effectively. Whether you’re a seasoned mechanic or a car owner, OBD2 diagnostics can save you time and money.
For expert guidance and services, contact OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN at 123 Main Street, Los Angeles, CA 90001, United States. Call us on Whatsapp: +1 (641) 206-8880 or visit our website at OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN for more information. Let us help you keep your vehicle running smoothly and efficiently.
