Is Obd2 Backwards Compatible with older OBD systems? Yes, OBD2 is designed to be somewhat backwards compatible, but with limitations, and at OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN, we will guide you through the intricacies of OBD2 compatibility, ensuring you can effectively diagnose and maintain your vehicle. While OBD2 offers a standardized approach to vehicle diagnostics, full compatibility depends on several factors, including the age and make of the vehicle. This article explores these factors and provides insights into achieving successful OBD2 integration, ensuring you understand onboard diagnostics, diagnostic trouble codes, and real-time data effectively.
Contents
- 1. What is OBD2 and Why Does Backwards Compatibility Matter?
- 1.1 Understanding OBD2: A Quick Overview
- 1.2 Why Backwards Compatibility is Crucial
- 2. The History of OBD Systems: From OBD1 to OBD2
- 2.1 OBD1: The Predecessor to OBD2
- 2.2 The Transition to OBD2
- 2.3 Key Milestones in OBD2 Development
- 3. Understanding OBD2 Compatibility: Key Factors
- 3.1 Vehicle Year and Make
- 3.2 Connector Type
- 3.3 Communication Protocols
- 3.4 Software and Firmware
- 4. How to Determine OBD2 Compatibility
- 4.1 Checking the Vehicle’s Manual
- 4.2 Visual Inspection of the Connector
- 4.3 Using an OBD2 Compatibility Checker
- 4.4 Testing with an OBD2 Scanner
- 5. Common OBD2 Compatibility Issues and Solutions
- 5.1 Protocol Mismatches
- 5.2 Incompatible Software/Firmware
- 5.3 Faulty Connector or Wiring
- 5.4 CAN Bus Issues
- 6. Advanced OBD2 Features and Compatibility
- 6.1 Reading and Clearing DTCs
- 6.2 Live Data Streaming
- 6.3 Freeze Frame Data
- 6.4 On-Board Monitoring Tests
- 7. The Future of OBD: OBD3 and Beyond
- 7.1 OBD3: The Next Generation
- 7.2 Impact on Compatibility
- 7.3 Other Emerging Technologies
- 8. Practical Tips for Ensuring OBD2 Compatibility
- 8.1 Keep Your Scanner Updated
- 8.2 Use a Reliable OBD2 Scanner
- 8.3 Understand Your Vehicle’s Specifications
- 8.4 Seek Professional Help When Needed
- 9. Case Studies: OBD2 Compatibility in Real-World Scenarios
- 9.1 Diagnosing an Older Vehicle
- 9.2 Live Data Streaming on a Modern Car
- 9.3 Clearing DTCs on a Hybrid Vehicle
- 10. Why Choose OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN for Your OBD2 Needs?
- 10.1 Expert Advice and Support
- 10.2 Wide Range of OBD2 Scanners
- 10.3 Comprehensive Resources
- 10.4 Customer Satisfaction
- FAQ: Addressing Common Questions About OBD2 Compatibility
- 1. What is an OBD2 scanner?
- 2. How do I read OBD2 codes?
- 3. What are common car problems and how can OBD2 scanners help?
- 4. Can I use an OBD2 scanner on any car?
- 5. How do I know if my car is OBD2 compliant?
- 6. What does OBD2 compatibility mean?
- 7. Are all OBD2 scanners the same?
- 8. Can I update my OBD2 scanner?
- 9. What are the benefits of using an OBD2 scanner?
- 10. Where can I get help with OBD2 compatibility issues?
1. What is OBD2 and Why Does Backwards Compatibility Matter?
OBD2 (On-Board Diagnostics II) is a standardized system used in vehicles to monitor and report on various engine and vehicle parameters. Understanding its backwards compatibility is essential for diagnosing and maintaining a wide range of vehicles.
The Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE) set the OBD2 standard, standardizing diagnostic trouble codes and the OBD connector. This allowed for easier diagnosis and repair across different manufacturers.
1.1 Understanding OBD2: A Quick Overview
OBD2 is a sophisticated system that monitors a vehicle’s engine and other systems, providing valuable data for diagnosing issues. This system is crucial for maintaining vehicle health and performance.
- Standardized Diagnostics: OBD2 offers a uniform way to access vehicle data.
- Real-Time Data: It provides live information about vehicle performance.
- Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs): OBD2 generates codes that pinpoint specific problems.
1.2 Why Backwards Compatibility is Crucial
Backwards compatibility ensures that newer OBD2 tools can be used on older vehicles, facilitating easier diagnostics and repairs. It also matters in keeping with the California Air Resources Board (CARB) emission control purposes for all new cars from 1991+.
- Wider Range of Vehicle Support: A single tool can service various vehicle models and years.
- Cost Efficiency: Reduces the need for multiple diagnostic tools.
- Ease of Use: Simplifies the diagnostic process for technicians.
2. The History of OBD Systems: From OBD1 to OBD2
To appreciate the compatibility aspects of OBD2, it’s helpful to know a bit about its evolution from earlier OBD systems.
2.1 OBD1: The Predecessor to OBD2
OBD1 was the initial attempt at on-board diagnostics, but it lacked standardization, making it difficult to use across different vehicle makes.
- Limited Standardization: Each manufacturer had their own unique system.
- Basic Diagnostic Capabilities: Provided only fundamental diagnostic information.
- Difficult to Use: Required specialized tools and knowledge for each vehicle.
2.2 The Transition to OBD2
The transition to OBD2 brought about much-needed standardization, enhancing diagnostic capabilities and ease of use. The OBD2 standard was recommended by the Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE) and standardized DTCs and the OBD connector across manufacturers
- Mandatory Implementation: OBD2 became mandatory in the USA in 1996 for cars and light trucks.
- Enhanced Diagnostic Capabilities: It offers more detailed and comprehensive data.
- Standardized Connector and Codes: OBD2 uses a universal connector and a standardized set of diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs).
2.3 Key Milestones in OBD2 Development
The development of OBD2 was a gradual process, with key milestones marking its evolution and widespread adoption.
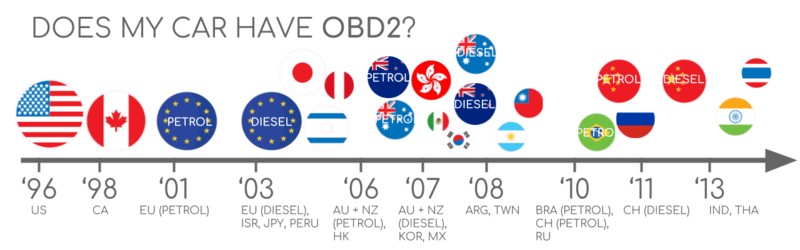
- 1996: OBD2 made mandatory in USA for cars/light trucks
- 2001: Required in EU for gasoline cars
- 2003: Required in EU also for diesel cars (EOBD)
- 2005: OBD2 was required in US for medium duty vehicles
- 2008: US cars must use ISO 15765-4 (CAN) as OBD2 basis
- 2010: Finally, OBD2 was required in US heavy duty vehicles
3. Understanding OBD2 Compatibility: Key Factors
OBD2 compatibility isn’t always straightforward. Several factors influence whether an OBD2 scanner will work with a particular vehicle.
3.1 Vehicle Year and Make
The year and make of the vehicle are primary determinants of OBD2 compatibility. Generally, vehicles manufactured after 1996 are OBD2 compliant in the US.
- US Compliance: Most vehicles from 1996 onwards are OBD2 compliant.
- European Compliance: Gasoline cars from 2001 and diesel cars from 2003 are typically OBD2 compliant in the EU.
- Variations: Some manufacturers adopted OBD2 before it became mandatory, while others may have specific implementations.
3.2 Connector Type
The presence of a 16-pin Data Link Connector (DLC) is a good indicator of OBD2 compatibility, but not a guarantee.
- Standard Connector: OBD2 uses a 16-pin DLC.
- Non-Standard Use: Some older vehicles may have the 16-pin connector but not fully support OBD2.
- Connector Location: The connector is usually located under the dashboard, near the steering wheel.
3.3 Communication Protocols
OBD2 uses various communication protocols. Compatibility depends on whether the vehicle supports the protocol used by the scanner.
- ISO 9141-2: Used in some European and Asian vehicles.
- SAE J1850 VPW and PWM: Common in older GM and Ford vehicles.
- CAN (Controller Area Network): Mandatory in US vehicles since 2008 and is today used in the vast majority of cars
- KWP2000 (Keyword Protocol 2000): The Keyword Protocol 2000 was a common protocol for 2003+ cars in e.g. Asia
3.4 Software and Firmware
The software and firmware of the OBD2 scanner must be compatible with the vehicle’s diagnostic system.
- Scanner Updates: Regularly update your scanner’s software to support newer vehicles and protocols.
- Protocol Support: Ensure the scanner supports the specific protocols used by the vehicle.
- Firmware Compatibility: Check that the scanner’s firmware is compatible with the vehicle’s diagnostic system.
4. How to Determine OBD2 Compatibility
Determining OBD2 compatibility involves several checks and verifications.
4.1 Checking the Vehicle’s Manual
The vehicle’s owner’s manual is a reliable source of information on OBD2 compatibility.
- Compliance Information: The manual should state whether the vehicle is OBD2 compliant.
- Connector Details: It may provide information about the location and type of the OBD2 connector.
4.2 Visual Inspection of the Connector
Inspect the OBD2 connector to verify its presence and type.
- 16-Pin Connector: Look for a 16-pin Data Link Connector (DLC) usually located under the dashboard.
- Pin Configuration: Check the pin configuration to match the OBD2 standard.
4.3 Using an OBD2 Compatibility Checker
Online OBD2 compatibility checkers can help determine if a vehicle is OBD2 compliant.
- VIN Lookup: Enter the vehicle’s VIN to check compatibility.
- Make and Model Selection: Select the vehicle’s make, model, and year to verify compatibility.
- Database Information: These tools use databases of vehicle information to provide compatibility details.
4.4 Testing with an OBD2 Scanner
The most direct way to determine compatibility is to connect an OBD2 scanner to the vehicle.
- Scanner Connection: Plug the scanner into the OBD2 port.
- Reading Data: Attempt to read data from the vehicle’s computer.
- Error Messages: Note any error messages or communication failures, which may indicate incompatibility.
5. Common OBD2 Compatibility Issues and Solutions
Even with OBD2 compliance, you may encounter compatibility issues. Here are some common problems and solutions.
5.1 Protocol Mismatches
A mismatch between the scanner’s supported protocols and the vehicle’s protocol can prevent communication.
- Solution: Use a scanner that supports multiple protocols or a protocol converter.
- Protocol Identification: Identify the vehicle’s protocol using a compatibility checker or vehicle manual.
- Scanner Selection: Choose a scanner that supports the identified protocol.
5.2 Incompatible Software/Firmware
Outdated or incompatible software can cause communication problems.
- Solution: Update the scanner’s software and firmware regularly.
- Update Availability: Check the manufacturer’s website for updates.
- Installation: Follow the manufacturer’s instructions to install updates correctly.
5.3 Faulty Connector or Wiring
A damaged OBD2 connector or faulty wiring can prevent the scanner from communicating with the vehicle.
- Solution: Inspect and repair or replace the connector and wiring.
- Visual Inspection: Look for damaged pins, corrosion, or loose wires.
- Wiring Diagram: Use a wiring diagram to ensure proper connections.
5.4 CAN Bus Issues
Problems with the vehicle’s CAN bus can interfere with OBD2 communication.
- Solution: Diagnose and repair the CAN bus system.
- CAN Bus Testing: Use a CAN bus tester to identify issues.
- Professional Diagnosis: Consult a professional technician for complex CAN bus problems.
6. Advanced OBD2 Features and Compatibility
OBD2 offers advanced features that require specific compatibility considerations.
6.1 Reading and Clearing DTCs
Reading and clearing Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) is a basic OBD2 function, but compatibility issues can arise.
- Standard DTCs: Most scanners can read standard DTCs.
- Manufacturer-Specific DTCs: Some scanners may not support manufacturer-specific DTCs.
- Clearing Codes: Ensure the scanner can clear codes without causing unintended consequences.
6.2 Live Data Streaming
Live data streaming provides real-time information about vehicle parameters.
- Parameter Support: Ensure the scanner supports the specific parameters you want to monitor.
- Data Accuracy: Verify that the data is accurate and reliable.
- Update Rate: Check the update rate to ensure real-time monitoring.
6.3 Freeze Frame Data
Freeze frame data captures vehicle conditions when a DTC was set.
- Data Availability: Ensure the scanner can access and display freeze frame data.
- Relevance: Verify that the freeze frame data is relevant to the DTC.
- Interpretation: Understand how to interpret the freeze frame data for accurate diagnosis.
6.4 On-Board Monitoring Tests
On-board monitoring tests evaluate the performance of various vehicle systems.
- Test Support: Ensure the scanner supports the specific tests you want to perform.
- Test Procedures: Follow the correct test procedures for accurate results.
- Result Interpretation: Understand how to interpret the test results for effective troubleshooting.
7. The Future of OBD: OBD3 and Beyond
The future of OBD systems includes enhancements and new technologies to improve vehicle diagnostics and monitoring.
7.1 OBD3: The Next Generation
OBD3 aims to improve emissions monitoring and vehicle diagnostics through remote data transmission.
- Remote Monitoring: OBD3 will allow for remote monitoring of vehicle emissions and performance.
- Real-Time Data Transmission: Vehicles will transmit data to a central server for analysis.
- Early Problem Detection: OBD3 will enable early detection of potential issues, improving maintenance and reducing emissions.
7.2 Impact on Compatibility
OBD3 will likely require new scanners and diagnostic tools to support its advanced features.
- New Hardware: Scanners will need to support wireless communication and data transmission.
- Software Updates: Existing scanners may require significant software updates.
- Transition Period: A transition period will be necessary to allow for the adoption of OBD3 technology.
7.3 Other Emerging Technologies
Emerging technologies like WWH-OBD (World Wide Harmonized OBD) and OBDonUDS (OBD on UDS) are set to enhance OBD communication.
- WWH-OBD: Streamlines and enhances OBD communication by leveraging the UDS protocol as basis.
- OBDonUDS: Streamlines and enhances OBD communication by leveraging the UDS protocol as basis.
8. Practical Tips for Ensuring OBD2 Compatibility
Here are some practical tips to ensure OBD2 compatibility and effective vehicle diagnostics.
8.1 Keep Your Scanner Updated
Regularly update your OBD2 scanner’s software and firmware to support the latest vehicles and protocols.
- Automatic Updates: Enable automatic updates if your scanner supports them.
- Manual Updates: Check the manufacturer’s website for updates and install them manually.
- Update Notifications: Subscribe to update notifications to stay informed about new releases.
8.2 Use a Reliable OBD2 Scanner
Invest in a high-quality OBD2 scanner from a reputable manufacturer.
- Brand Research: Research different brands and models to find a scanner that meets your needs.
- User Reviews: Read user reviews to get insights into the scanner’s performance and reliability.
- Feature Comparison: Compare features and specifications to choose the best scanner for your budget and requirements.
8.3 Understand Your Vehicle’s Specifications
Familiarize yourself with your vehicle’s OBD2 specifications and requirements.
- Vehicle Manual: Consult the vehicle’s owner’s manual for OBD2 information.
- Online Resources: Use online resources and databases to find OBD2 specifications for your vehicle.
- Technical Forums: Join online forums and communities to discuss OBD2 issues with other vehicle owners.
8.4 Seek Professional Help When Needed
Don’t hesitate to seek professional help from a qualified technician if you encounter compatibility issues or complex diagnostic problems.
- Experienced Technicians: Consult technicians with experience in OBD2 diagnostics.
- Diagnostic Services: Utilize professional diagnostic services for accurate and reliable results.
- Technical Support: Contact the scanner manufacturer’s technical support for assistance.
9. Case Studies: OBD2 Compatibility in Real-World Scenarios
Examining real-world scenarios can provide valuable insights into OBD2 compatibility.
9.1 Diagnosing an Older Vehicle
A technician attempts to use a modern OBD2 scanner on a 1995 vehicle and encounters communication issues.
- Problem: The vehicle uses an older, non-standard OBD protocol.
- Solution: The technician uses a legacy scanner with support for older protocols or an adapter cable.
- Result: The technician successfully diagnoses and repairs the vehicle.
9.2 Live Data Streaming on a Modern Car
A user tries to stream live data from a 2020 vehicle but finds that some parameters are missing.
- Problem: The scanner does not support all the parameters available in the vehicle.
- Solution: The user updates the scanner’s software and firmware or uses a more advanced scanner.
- Result: The user successfully streams all the desired live data parameters.
9.3 Clearing DTCs on a Hybrid Vehicle
A mechanic attempts to clear DTCs on a hybrid vehicle but faces difficulties.
- Problem: The scanner is not fully compatible with the hybrid vehicle’s diagnostic system.
- Solution: The mechanic uses a scanner specifically designed for hybrid vehicles.
- Result: The mechanic successfully clears the DTCs without causing any issues.
10. Why Choose OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN for Your OBD2 Needs?
At OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN, we offer comprehensive guidance and support for all your OBD2 needs.
10.1 Expert Advice and Support
Our team of experienced technicians provides expert advice and support to help you navigate the complexities of OBD2 compatibility.
- Personalized Assistance: Get personalized assistance to choose the right scanner for your vehicle.
- Troubleshooting: Receive troubleshooting support for any OBD2 issues you encounter.
- Technical Guidance: Benefit from technical guidance on using OBD2 scanners and interpreting diagnostic data.
10.2 Wide Range of OBD2 Scanners
We offer a wide range of high-quality OBD2 scanners from leading manufacturers.
- Scanner Selection: Choose from a variety of scanners to meet your specific needs and budget.
- Product Reviews: Read detailed product reviews to make informed purchasing decisions.
- Competitive Prices: Get competitive prices on all our OBD2 scanners.
10.3 Comprehensive Resources
Our website provides comprehensive resources to help you understand OBD2 technology and diagnostics.
- Educational Articles: Access informative articles and tutorials on OBD2 topics.
- How-To Guides: Follow step-by-step how-to guides for performing various diagnostic tasks.
- Troubleshooting Tips: Find troubleshooting tips and solutions for common OBD2 problems.
10.4 Customer Satisfaction
We are committed to providing excellent customer satisfaction.
- Reliable Support: Count on us for reliable support and assistance.
- Quality Products: Purchase high-quality products that meet your expectations.
- Trusted Partner: Partner with a trusted resource for all your OBD2 needs.
FAQ: Addressing Common Questions About OBD2 Compatibility
Here are some frequently asked questions about OBD2 compatibility.
1. What is an OBD2 scanner?
An OBD2 scanner is a diagnostic tool used to read and interpret data from a vehicle’s on-board computer. It helps diagnose issues and monitor vehicle performance.
2. How do I read OBD2 codes?
Connect the scanner to the OBD2 port, turn on the ignition, and follow the scanner’s instructions to read diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs).
3. What are common car problems and how can OBD2 scanners help?
Common car problems include engine issues, transmission problems, and sensor failures. OBD2 scanners help identify these problems by providing DTCs and live data.
4. Can I use an OBD2 scanner on any car?
Most cars manufactured after 1996 are OBD2 compliant. However, compatibility can vary based on the vehicle’s make, model, and year.
5. How do I know if my car is OBD2 compliant?
Check your vehicle’s owner’s manual or look for a 16-pin OBD2 port under the dashboard. You can also use an online OBD2 compatibility checker.
6. What does OBD2 compatibility mean?
OBD2 compatibility means that an OBD2 scanner can successfully communicate with and retrieve data from a vehicle’s diagnostic system.
7. Are all OBD2 scanners the same?
No, OBD2 scanners vary in features, compatibility, and price. Some scanners support advanced functions like live data streaming and on-board monitoring tests.
8. Can I update my OBD2 scanner?
Yes, most OBD2 scanners can be updated with new software and firmware to support the latest vehicles and protocols.
9. What are the benefits of using an OBD2 scanner?
Using an OBD2 scanner can help you diagnose and repair vehicle problems quickly, save money on repairs, and monitor your vehicle’s performance.
10. Where can I get help with OBD2 compatibility issues?
You can get help with OBD2 compatibility issues from OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN, experienced technicians, online forums, and the scanner manufacturer’s technical support.
Ensuring OBD2 compatibility is essential for effective vehicle diagnostics and maintenance. At OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN, we are committed to providing you with the knowledge, tools, and support you need to keep your vehicle running smoothly.
Do you need assistance with using an OBD2 scanner or require auto repair services? Contact us today for expert advice and solutions. Visit our website at OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN or reach us via WhatsApp at +1 (641) 206-8880. You can also visit our location at 123 Main Street, Los Angeles, CA 90001, United States. Let us help you ensure your vehicle is in top condition!
 OBD2 connector
OBD2 connector