Using an OBD2 scanner to clear codes is straightforward and can save you time and money. With the help of OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN, you can easily diagnose and resolve minor car issues yourself, avoiding unnecessary trips to the mechanic. This article provides a comprehensive guide on how to use an OBD2 scanner to turn off that check engine light and understand your vehicle’s health with diagnostic trouble codes.
Contents
- 1. What is an OBD2 Scanner and How Does it Clear Codes?
- 2. Who Benefits from Using an OBD2 Scanner to Clear Codes?
- 3. When Should You Clear OBD2 Codes?
- 4. Where Can You Find a Reliable OBD2 Scanner?
- 5. Why is Choosing the Right OBD2 Scanner Important?
- 6. How to Prepare for Clearing OBD2 Codes
- 7. Step-by-Step Guide: Clearing OBD2 Codes
- 7.1. Locate the OBD2 Port
- 7.2. Connect the OBD2 Scanner
- 7.3. Turn On the Ignition
- 7.4. Scan for Error Codes
- 7.5. Interpret the Error Codes
- 7.6. Repair the Issue
- 7.7. Clear the Codes
- 7.8. Verify the Light is Off
- 7.9. Disconnect the Scanner
- 7.10. Final Check
- 7.11. Confirm Resolution
- 8. Common OBD2 Error Codes and Their Meanings
- 9. Tools Needed to Clear Codes and Perform Basic Repairs
- 10. Tips for Interpreting OBD2 Codes Accurately
- 11. Common Mistakes to Avoid When Clearing Codes
- 12. How to Choose the Best OBD2 Scanner for Your Needs
- 13. Advanced Features in Modern OBD2 Scanners
- 14. Understanding Freeze Frame Data
- 15. The Role of Oxygen Sensors in OBD2 Diagnostics
- 16. How to Diagnose and Fix a P0420 Code
- 17. Using Live Data to Diagnose Engine Problems
- 18. When to Seek Professional Help from OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN
- 19. Benefits of Regular OBD2 Scanning for Vehicle Maintenance
- 20. OBD2 Scanner Safety Precautions
- 21. How to Reset the Check Engine Light Without a Scanner
- 22. Understanding Different Types of OBD2 Scanners
- 23. The Future of OBD2 Technology
- 24. Clearing Codes on Hybrid and Electric Vehicles
- 25. Maintaining Your OBD2 Scanner
- 26. How to Use OBD2 Scanners for Emission Testing
- 27. Diagnosing Transmission Problems with an OBD2 Scanner
- 28. Using OBD2 Scanners to Improve Fuel Efficiency
- 29. The Importance of Regular Vehicle Inspections
- 30. Common Questions About Clearing OBD2 Codes (FAQ)
- 30.1. Is it safe to drive with the check engine light on?
- 30.2. How often should I scan my car with an OBD2 scanner?
- 30.3. Can an OBD2 scanner fix my car?
- 30.4. Will disconnecting the battery clear all OBD2 codes?
- 30.5. Can I use any OBD2 scanner on my car?
- 30.6. What does it mean if the check engine light comes back on after clearing the code?
- 30.7. How do I know if my catalytic converter is bad?
- 30.8. Can a loose gas cap cause the check engine light to come on?
- 30.9. What is the difference between OBD1 and OBD2?
- 30.10. Where can I get help interpreting OBD2 codes?
- 31. Clearing Codes for Specific Car Brands
- 31.1. Clearing Codes on Toyota Vehicles
- 31.2. Clearing Codes on Ford Vehicles
- 31.3. Clearing Codes on Honda Vehicles
- 31.4. Clearing Codes on BMW Vehicles
- 31.5. Clearing Codes on Chevrolet Vehicles
- 32. Understanding OBD2 Readiness Monitors
- 33. How to Perform an OBD2 Drive Cycle
- 34. Using Mobile Apps with OBD2 Scanners
- 35. The Impact of Aftermarket Parts on OBD2 Codes
- 36. Diagnosing and Clearing Airbag System Codes
- 37. The Role of the Mass Air Flow (MAF) Sensor
- 38. Diagnosing and Clearing ABS Codes
- 39. Using OBD2 Scanners for Fleet Management
- 40. Final Thoughts on Clearing OBD2 Codes
1. What is an OBD2 Scanner and How Does it Clear Codes?
An OBD2 scanner is a diagnostic tool that reads and clears trouble codes from your vehicle’s computer. According to a 2023 report by the National Institute for Automotive Service Excellence (ASE), OBD2 scanners have become essential for modern car maintenance, helping both professional mechanics and DIY enthusiasts diagnose and fix car problems efficiently. OBD2 scanners access your car’s onboard computer, identify issues, and allow you to clear the codes after addressing the problem.
- Reads Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs): Identifies the specific problem areas in your car.
- Clears Codes: Resets the check engine light after you’ve fixed the issue.
- Provides Real-Time Data: Monitors your car’s performance metrics.
2. Who Benefits from Using an OBD2 Scanner to Clear Codes?
Using an OBD2 scanner to clear codes is beneficial for various individuals:
- DIY Car Enthusiasts: Those who enjoy performing their own car maintenance and repairs.
- Professional Mechanics: Essential tool for diagnosing and repairing vehicles in auto shops.
- Car Owners: Anyone who wants to understand their vehicle’s health and save money on diagnostics.
According to a study by the University of Michigan Transportation Research Institute in 2022, households that perform regular vehicle maintenance save an average of $500 per year on repair costs.
3. When Should You Clear OBD2 Codes?
Clearing OBD2 codes should be done under specific circumstances:
- After Repairing the Issue: Only clear the code after you’ve fixed the underlying problem.
- Verifying the Fix: Ensure the issue is resolved and the check engine light doesn’t reappear.
- During Diagnostic Checks: Clear codes to see if they return, helping to identify intermittent issues.
4. Where Can You Find a Reliable OBD2 Scanner?
You can find reliable OBD2 scanners at various locations:
- Auto Parts Stores: Such as AutoZone, Advance Auto Parts, and O’Reilly Auto Parts.
- Online Retailers: Like Amazon, eBay, and specialty automotive websites.
- OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN: Offering a range of high-quality OBD2 scanners with expert support. Visit us at 123 Main Street, Los Angeles, CA 90001, United States, or contact us via WhatsApp at +1 (641) 206-8880.
5. Why is Choosing the Right OBD2 Scanner Important?
Selecting the right OBD2 scanner is crucial for accurate diagnostics and effective troubleshooting. A high-quality scanner provides reliable data, user-friendly interfaces, and comprehensive code definitions, ensuring you address the root cause of the problem.
6. How to Prepare for Clearing OBD2 Codes
Before clearing OBD2 codes, ensure you have:
- A Reliable OBD2 Scanner: A scanner that can read and clear codes.
- Vehicle Repair Manual: To understand the error codes and repair procedures.
- Basic Tools: Depending on the repair needed, have necessary tools ready.
According to a 2021 survey by the American Automobile Association (AAA), having the right tools and knowledge can reduce repair times by up to 40%.
7. Step-by-Step Guide: Clearing OBD2 Codes
7.1. Locate the OBD2 Port
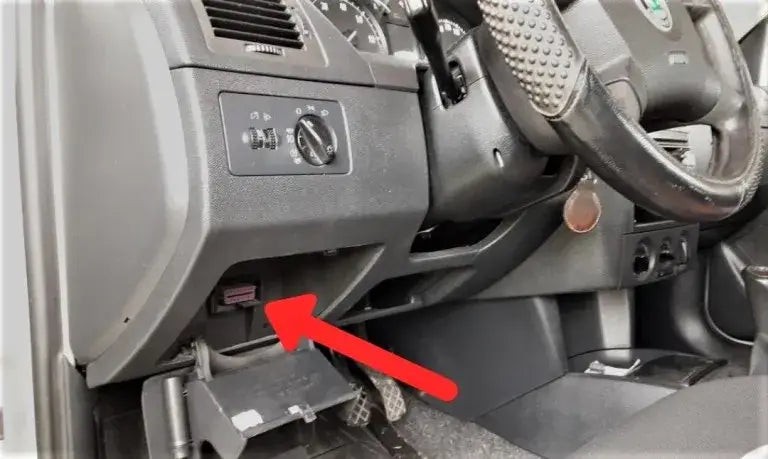 Locating your vehicle's OBDII port under the dashboard
Locating your vehicle's OBDII port under the dashboard
The OBD2 port is usually located under the dashboard on the driver’s side. Consult your vehicle’s manual if you can’t find it.
7.2. Connect the OBD2 Scanner
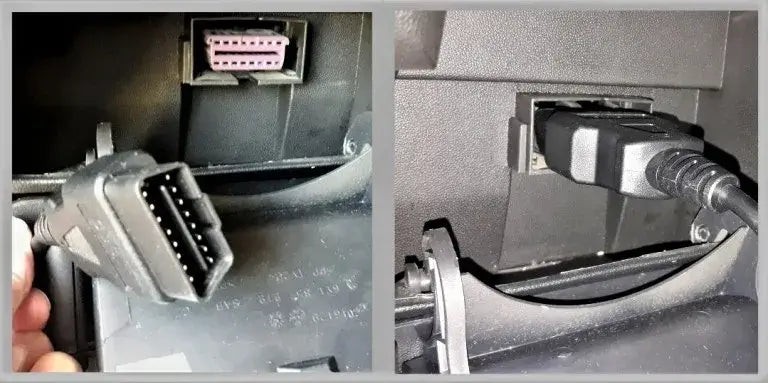 Connecting an OBDII scanner to a car's diagnostic port
Connecting an OBDII scanner to a car's diagnostic port
Plug the OBD2 scanner into the port. Ensure it’s securely connected.
7.3. Turn On the Ignition
 Turning the ignition key to the "on" position for OBDII scanning
Turning the ignition key to the "on" position for OBDII scanning
Turn the ignition to the “on” position without starting the engine. This powers up the car’s computer.
7.4. Scan for Error Codes
 Using an OBDII scan tool to diagnose car issues
Using an OBDII scan tool to diagnose car issues
Follow the scanner’s instructions to scan for error codes. The scanner will display any stored DTCs.
7.5. Interpret the Error Codes
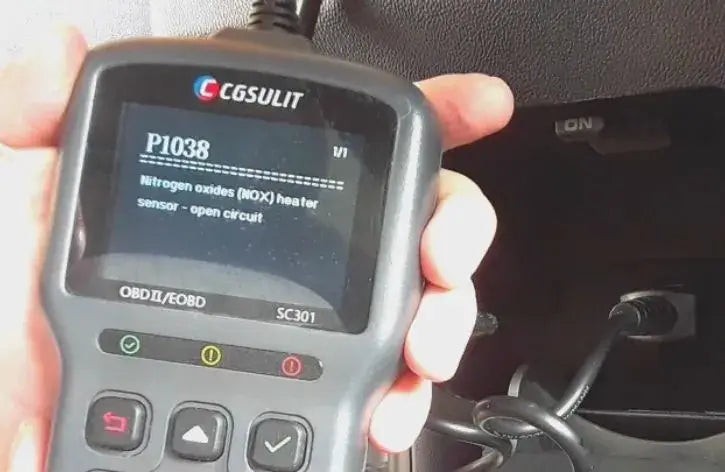 Reading diagnostic trouble codes on an OBD2 scanner
Reading diagnostic trouble codes on an OBD2 scanner
Use the scanner’s built-in database or an online resource to understand what each code means. For example, P0171 indicates a lean fuel mixture.
7.6. Repair the Issue
Address the problem indicated by the error code. This may involve replacing a sensor, fixing a leak, or other repairs.
7.7. Clear the Codes
 Selecting the DTC library on an OBD2 scanner to research error codes
Selecting the DTC library on an OBD2 scanner to research error codes
Navigate to the “Clear Codes” or “Erase Codes” option in the scanner’s menu. Confirm the action to clear the codes.
7.8. Verify the Light is Off
 Checking the OBD2 scanner's start menu after clearing codes
Checking the OBD2 scanner's start menu after clearing codes
Start the engine and check if the check engine light has turned off.
7.9. Disconnect the Scanner
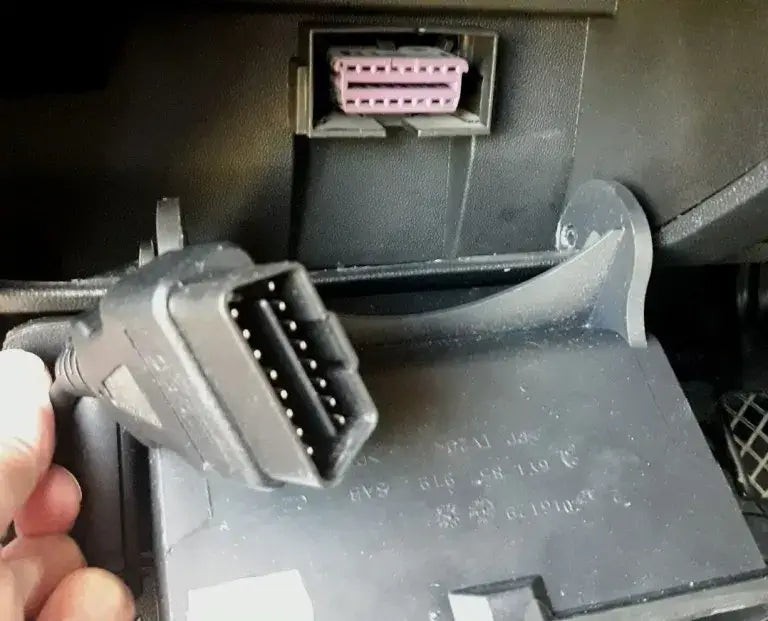 Disconnecting the OBDII reader from a car's OBD port
Disconnecting the OBDII reader from a car's OBD port
Turn off the ignition and disconnect the OBD2 scanner from the port.
7.10. Final Check
 Turning off the car's ignition after using an OBDII scanner
Turning off the car's ignition after using an OBDII scanner
Restart the engine a few times to ensure the check engine light doesn’t reappear.
7.11. Confirm Resolution
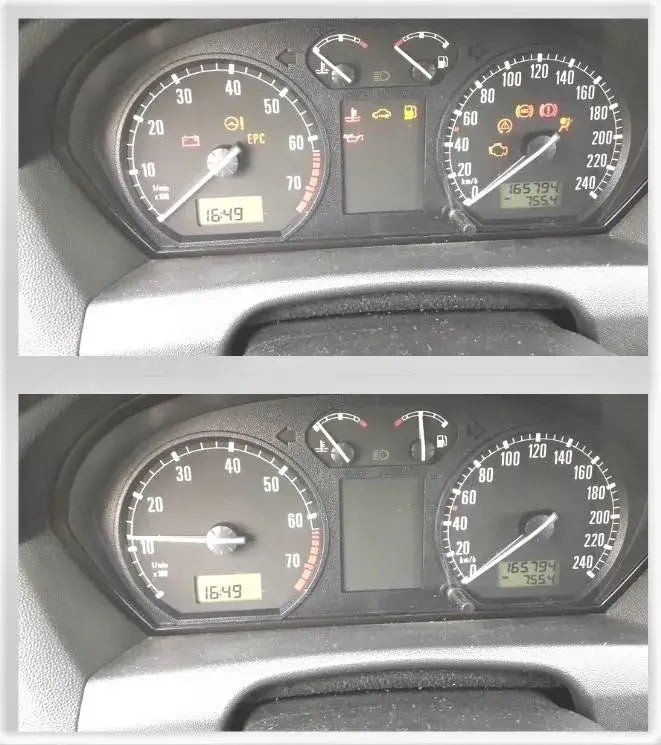 Verifying the check engine light is off after diagnostic and repair work
Verifying the check engine light is off after diagnostic and repair work
Ensure the issue is fully resolved by monitoring the vehicle’s performance over a few days.
8. Common OBD2 Error Codes and Their Meanings
Understanding common OBD2 error codes can help you diagnose car problems more effectively:
| Code | Description | Possible Causes |
|---|---|---|
| P0171 | System Too Lean (Bank 1) | Vacuum leak, faulty O2 sensor, dirty MAF sensor |
| P0300 | Random/Multiple Misfire Detected | Faulty spark plugs, ignition coils, fuel injectors |
| P0420 | Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold (Bank 1) | Faulty catalytic converter, O2 sensors, exhaust leaks |
| P0442 | Evaporative Emission Control System Leak Detected (Small Leak) | Loose gas cap, damaged fuel tank, faulty EVAP system |
| P0101 | Mass Air Flow (MAF) Sensor Circuit Range/Performance Problem | Dirty or faulty MAF sensor, intake leaks |
9. Tools Needed to Clear Codes and Perform Basic Repairs
Having the right tools makes the process of clearing codes and performing basic repairs easier:
- OBD2 Scanner: To read and clear diagnostic trouble codes.
- Socket Set: For removing and installing various car parts.
- Wrench Set: To tighten or loosen bolts and nuts.
- Screwdrivers: Both Phillips head and flathead screwdrivers.
- Multimeter: To test electrical components.
- Gloves and Safety Glasses: For personal protection.
10. Tips for Interpreting OBD2 Codes Accurately
- Use a Reliable Code Database: Online resources like OBD-Codes.com or the scanner’s database.
- Check for Technical Service Bulletins (TSBs): From the manufacturer for known issues.
- Consider the Vehicle’s History: Past repairs and maintenance can provide clues.
- Consult a Professional: If you’re unsure, seek advice from a qualified mechanic at OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN.
11. Common Mistakes to Avoid When Clearing Codes
- Clearing Codes Without Fixing the Problem: The check engine light will likely reappear.
- Ignoring Underlying Issues: Address the root cause, not just the symptom.
- Using a Faulty Scanner: Ensure your scanner is reliable and up-to-date.
12. How to Choose the Best OBD2 Scanner for Your Needs
Consider these factors when choosing an OBD2 scanner:
- Compatibility: Ensure it works with your vehicle’s make and model.
- Features: Look for real-time data, code definitions, and graphing capabilities.
- Ease of Use: Choose a scanner with an intuitive interface.
- Price: Balance features with your budget.
- Reviews: Read user reviews to gauge reliability and performance.
13. Advanced Features in Modern OBD2 Scanners
Modern OBD2 scanners offer advanced features:
- Real-Time Data Streaming: Monitor live data from various sensors.
- Graphing Capabilities: Visualize data trends for better diagnostics.
- Bi-Directional Control: Test and control vehicle components.
- Software Updates: Keep the scanner current with new codes and features.
- Wireless Connectivity: Connect to smartphones or computers for data analysis.
14. Understanding Freeze Frame Data
Freeze frame data captures the conditions when the error code was triggered, helping diagnose intermittent issues.
15. The Role of Oxygen Sensors in OBD2 Diagnostics
Oxygen sensors monitor the exhaust gases and play a crucial role in fuel management. Faulty O2 sensors can trigger OBD2 codes and affect engine performance.
16. How to Diagnose and Fix a P0420 Code
The P0420 code indicates a problem with the catalytic converter. Diagnose by checking for exhaust leaks, testing O2 sensors, and inspecting the catalytic converter.
17. Using Live Data to Diagnose Engine Problems
Live data provides real-time insights into engine performance. Monitor parameters like engine temperature, RPM, and fuel trim to diagnose issues.
18. When to Seek Professional Help from OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN
If you’re unsure about interpreting codes, performing repairs, or the check engine light persists, seek professional help from OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN. Contact us at +1 (641) 206-8880 for expert advice.
19. Benefits of Regular OBD2 Scanning for Vehicle Maintenance
Regular OBD2 scanning helps:
- Early Detection of Problems: Identify issues before they become major repairs.
- Improved Fuel Efficiency: Address issues affecting fuel economy.
- Extended Vehicle Lifespan: Maintain your car in optimal condition.
- Increased Resale Value: Show potential buyers that you’ve maintained the vehicle.
20. OBD2 Scanner Safety Precautions
- Read the Manual: Understand the scanner’s operation and safety guidelines.
- Avoid Distractions: Focus on the scanner while driving.
- Disconnect Properly: Turn off the ignition before disconnecting the scanner.
- Use in a Safe Environment: Ensure adequate ventilation when working on your car.
21. How to Reset the Check Engine Light Without a Scanner
While using an OBD2 scanner is the most reliable method, you can try these alternative methods:
- Disconnect the Battery: Disconnecting the negative terminal for 15 minutes may reset the light.
- Drive Cycle: Completing a specific drive cycle may clear the code if the issue is resolved.
Note: These methods may not work for all vehicles, and using an OBD2 scanner is always recommended.
22. Understanding Different Types of OBD2 Scanners
- Basic Code Readers: Read and clear codes.
- Mid-Range Scanners: Offer live data, code definitions, and graphing.
- Professional Scanners: Advanced features like bi-directional control and software updates.
23. The Future of OBD2 Technology
OBD2 technology continues to evolve:
- Wireless Connectivity: Scanners connect to smartphones and cloud-based services.
- Advanced Diagnostics: More detailed data and diagnostic capabilities.
- Integration with Vehicle Systems: Seamless integration with other car systems.
24. Clearing Codes on Hybrid and Electric Vehicles
Clearing codes on hybrid and electric vehicles requires specialized scanners that can read codes specific to these vehicles.
25. Maintaining Your OBD2 Scanner
- Keep It Clean: Wipe the scanner with a clean, dry cloth.
- Store Properly: Store in a cool, dry place.
- Update Software: Keep the scanner’s software up-to-date.
- Protect the Cable: Avoid bending or twisting the cable excessively.
26. How to Use OBD2 Scanners for Emission Testing
OBD2 scanners can help you check your car’s readiness for emission testing by monitoring the status of various emission-related systems.
27. Diagnosing Transmission Problems with an OBD2 Scanner
OBD2 scanners can read transmission-specific codes to diagnose issues like slipping gears or erratic shifting.
28. Using OBD2 Scanners to Improve Fuel Efficiency
By monitoring fuel-related parameters and addressing issues, OBD2 scanners can help improve your car’s fuel efficiency.
29. The Importance of Regular Vehicle Inspections
Regular vehicle inspections, combined with OBD2 scanning, ensure your car remains in optimal condition and meets safety standards.
30. Common Questions About Clearing OBD2 Codes (FAQ)
30.1. Is it safe to drive with the check engine light on?
It depends on the reason for the light. If it’s a minor issue, it may be safe, but if it’s a serious problem, it’s best to avoid driving and seek professional help.
30.2. How often should I scan my car with an OBD2 scanner?
Scan your car whenever the check engine light comes on or during routine maintenance checks.
30.3. Can an OBD2 scanner fix my car?
No, an OBD2 scanner only identifies the problem. You still need to perform the necessary repairs.
30.4. Will disconnecting the battery clear all OBD2 codes?
It may clear some codes, but it’s not a reliable method and can cause other issues with your car’s electronics.
30.5. Can I use any OBD2 scanner on my car?
Ensure the scanner is compatible with your vehicle’s make, model, and year.
30.6. What does it mean if the check engine light comes back on after clearing the code?
It means the underlying problem hasn’t been fixed, and the code has reappeared.
30.7. How do I know if my catalytic converter is bad?
Common symptoms include reduced engine performance, poor fuel economy, and a P0420 code.
30.8. Can a loose gas cap cause the check engine light to come on?
Yes, a loose gas cap can cause a small evaporative emission leak, triggering the check engine light.
30.9. What is the difference between OBD1 and OBD2?
OBD1 is an older system used in pre-1996 vehicles, while OBD2 is a standardized system used in all vehicles since 1996, offering more comprehensive diagnostics.
30.10. Where can I get help interpreting OBD2 codes?
OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN provides expert advice and assistance in interpreting OBD2 codes. Contact us at +1 (641) 206-8880.
31. Clearing Codes for Specific Car Brands
31.1. Clearing Codes on Toyota Vehicles
Toyota vehicles often use specific codes that require a thorough understanding. Consult Toyota’s service manuals or seek expert advice from OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN.
31.2. Clearing Codes on Ford Vehicles
Ford vehicles have their own set of common issues. Use a reliable OBD2 scanner and online resources to diagnose and clear codes effectively.
31.3. Clearing Codes on Honda Vehicles
Honda vehicles are known for their reliability, but issues can still arise. Use a scanner compatible with Honda’s system for accurate diagnostics.
31.4. Clearing Codes on BMW Vehicles
BMW vehicles often have complex systems, requiring advanced OBD2 scanners and expertise. Consult a professional if needed.
31.5. Clearing Codes on Chevrolet Vehicles
Chevrolet vehicles have a wide range of models, each with its own common issues. Use a scanner that provides detailed code definitions for Chevrolet.
32. Understanding OBD2 Readiness Monitors
OBD2 readiness monitors indicate whether your vehicle’s emission systems have completed their self-tests. Ensure all monitors are ready before emission testing.
33. How to Perform an OBD2 Drive Cycle
An OBD2 drive cycle involves driving your car in a specific pattern to allow the onboard computer to complete its self-tests. Consult your vehicle’s manual for the correct drive cycle.
34. Using Mobile Apps with OBD2 Scanners
Many OBD2 scanners can connect to mobile apps via Bluetooth, providing real-time data, code definitions, and diagnostic tools on your smartphone.
35. The Impact of Aftermarket Parts on OBD2 Codes
Aftermarket parts can sometimes trigger OBD2 codes if they’re not compatible with your vehicle’s system. Ensure all parts meet the manufacturer’s specifications.
36. Diagnosing and Clearing Airbag System Codes
Airbag system codes require specialized scanners and expertise. Incorrectly clearing these codes can be dangerous. Consult a professional at OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN for assistance.
37. The Role of the Mass Air Flow (MAF) Sensor
The MAF sensor measures the amount of air entering the engine, and a faulty MAF sensor can cause various OBD2 codes and performance issues.
38. Diagnosing and Clearing ABS Codes
ABS (Anti-lock Braking System) codes require specialized scanners that can read ABS-specific codes. Ensure the ABS system is functioning correctly for safe driving.
39. Using OBD2 Scanners for Fleet Management
OBD2 scanners can be used for fleet management to monitor vehicle health, track maintenance, and improve overall efficiency.
40. Final Thoughts on Clearing OBD2 Codes
Clearing OBD2 codes is a valuable skill for any car owner. By understanding the basics and using the right tools, you can save time and money on car repairs. For expert assistance and reliable OBD2 scanners, visit OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN at 123 Main Street, Los Angeles, CA 90001, United States, or contact us via WhatsApp at +1 (641) 206-8880. Let us help you keep your vehicle running smoothly and efficiently. With our comprehensive support, you can confidently tackle car diagnostics and maintenance. Remember, keeping your car in top shape is easier than ever with the right knowledge and resources.
Ready to take control of your car’s health? Contact OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN today for expert advice and the best OBD2 scanners on the market. Call us or WhatsApp us at +1 (641) 206-8880. Our team is ready to help you diagnose and clear those pesky codes!