The Obd2 Diagnostic Port is your gateway to understanding your vehicle’s health and performance. At OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN, we provide expert insights and services to help you effectively use this port for vehicle diagnostics and repairs, offering solutions that ensure you stay informed and in control. Unlock the full potential of your car with our detailed guidance and support, enhanced by cutting-edge tools and advanced techniques.
Contents
- 1. What is the OBD2 Diagnostic Port?
- 1.1. Key Functions of the OBD2 Port
- 1.2. Location of the OBD2 Port
- 1.3. Evolution of On-Board Diagnostics
- 2. Why is the OBD2 Diagnostic Port Important?
- 2.1. Vehicle Health Monitoring
- 2.2. Regulatory Compliance
- 2.3. Fleet Management
- 3. Understanding OBD2 Protocols and Standards
- 3.1. Key OBD2 Protocols
- 3.2. Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
- 3.3. OBD2 Modes
- 4. How to Use an OBD2 Scanner
- 4.1. Step-by-Step Guide to Using an OBD2 Scanner
- 4.2. Choosing the Right OBD2 Scanner
- 4.3. Common Mistakes to Avoid
- 5. Interpreting OBD2 Codes and Troubleshooting
- 5.1. Common OBD2 Codes and Their Meanings
- 5.2. Troubleshooting Steps for Common Codes
- 5.3. When to Seek Professional Help
- 6. Advanced OBD2 Diagnostics and Customization
- 6.1. Accessing Manufacturer-Specific Data
- 6.2. Customizing Vehicle Settings
- 6.3. Risks and Precautions
- 7. The Future of OBD and Vehicle Diagnostics
- 7.1. Integration of AI and Machine Learning
- 7.2. Cloud Connectivity and Remote Diagnostics
- 7.3. Enhanced Security Measures
- 8. OBD2 and Electric Vehicles (EVs)
- 8.1. Unique Diagnostic Parameters for EVs
- 8.2. Common EV Trouble Codes
- 8.3. Specialized EV Diagnostic Tools
- 9. WWH-OBD: The Next Generation of Diagnostics
- 9.1. Advantages of WWH-OBD
- 9.2. Key Features of WWH-OBD
- 9.3. Implementation of WWH-OBD
- 10. Choosing the Right OBD2 Diagnostic Service at OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN
- 10.1. Services Offered at OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN
- 10.2. Benefits of Choosing OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN
- 10.3. Contact Us Today
- FAQ: Understanding the OBD2 Diagnostic Port
1. What is the OBD2 Diagnostic Port?
The OBD2 diagnostic port, also known as the OBDII port, is a standardized interface in vehicles that allows access to the vehicle’s onboard computer systems for diagnostics and monitoring. According to the EPA, this port is essential for monitoring vehicle emissions and ensuring compliance with environmental standards.
The OBD2 diagnostic port serves as a crucial access point for technicians and vehicle owners to retrieve data related to engine performance, emissions, and overall system health. This data is invaluable for diagnosing issues, performing maintenance, and ensuring the vehicle operates efficiently. By connecting a diagnostic tool to this port, you can read diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs), monitor real-time data, and even perform certain system tests.
1.1. Key Functions of the OBD2 Port
- Accessing Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs): The primary function is to retrieve DTCs, which indicate specific problems within the vehicle’s systems. According to the SAE, these codes are standardized across all OBD2-compliant vehicles, making diagnostics more straightforward.
- Monitoring Real-Time Data: The port allows you to monitor various parameters in real-time, such as engine RPM, vehicle speed, and sensor readings. This data is crucial for identifying intermittent issues and assessing overall performance.
- Performing System Tests: Some diagnostic tools can use the OBD2 port to perform system tests, such as activating components or running diagnostic routines, helping to pinpoint problems more accurately.
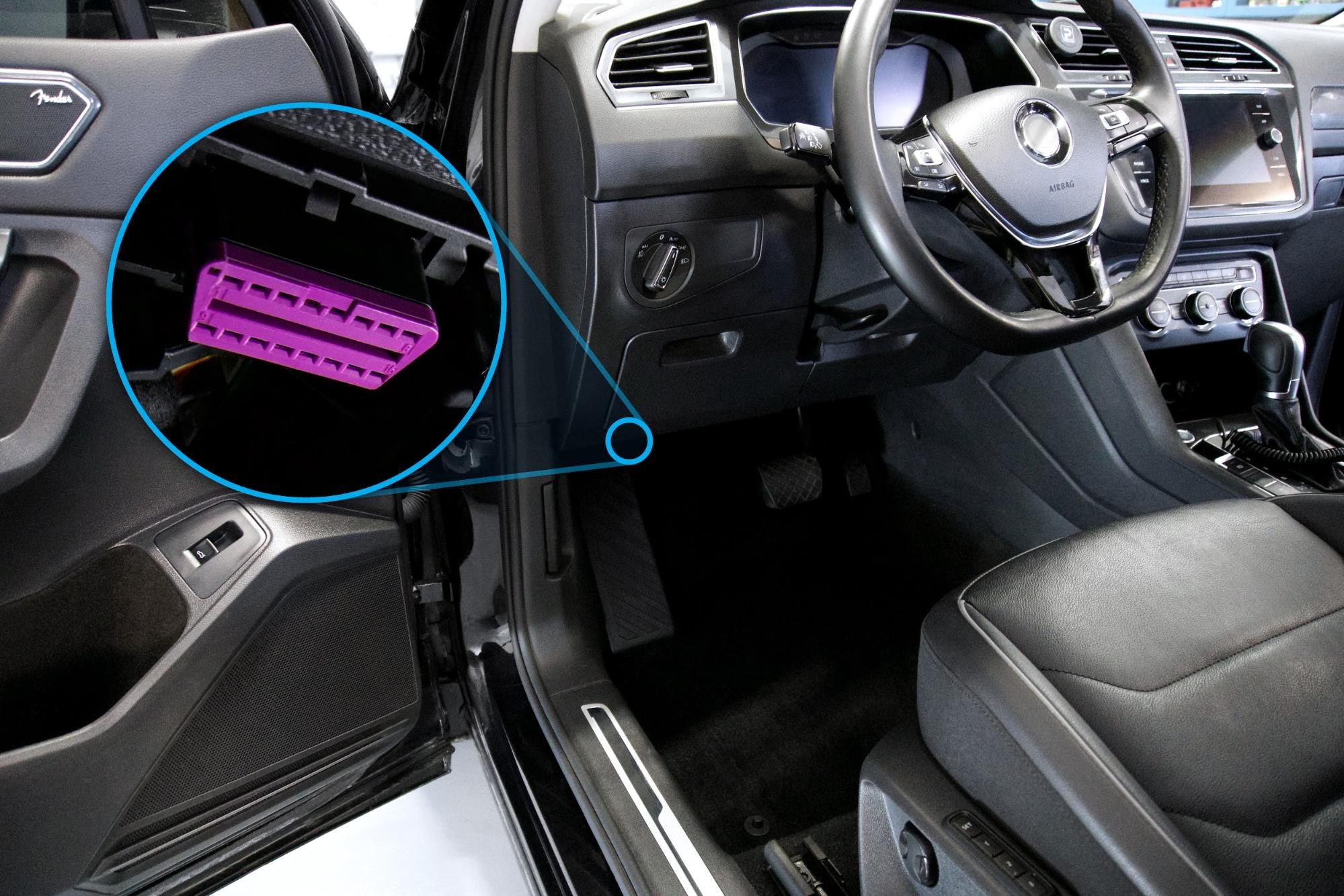
1.2. Location of the OBD2 Port
In most passenger vehicles, the OBD2 port is located under the dashboard on the driver’s side. However, the exact location can vary depending on the vehicle make and model. It’s typically within easy reach and clearly visible once you know where to look.
- Standard Location: Typically found under the dashboard on the driver’s side.
- Alternative Locations: In some vehicles, it may be located in the center console or behind an access panel.
- Consult the Manual: Always refer to your vehicle’s owner’s manual for the precise location.
1.3. Evolution of On-Board Diagnostics
The journey of on-board diagnostics started with basic systems in the 1960s and evolved into the standardized OBD2 system we use today. This evolution was driven by the need for better emissions control and improved diagnostics.
- Early Systems (OBD-I): These were manufacturer-specific and lacked standardization, making diagnostics challenging.
- OBD2 Standardization: Mandated in the USA in 1996, OBD2 provided a standardized port, diagnostic codes, and data parameters.
- Global Adoption: EOBD in Europe and other global standards followed, ensuring consistent diagnostic capabilities worldwide.
 OBD2 Port Location
OBD2 Port Location
2. Why is the OBD2 Diagnostic Port Important?
The OBD2 diagnostic port is vital for several reasons, including its ability to provide valuable insights into vehicle health, facilitate proactive maintenance, and ensure regulatory compliance. This port enables vehicle owners and technicians to diagnose problems quickly and efficiently, saving time and money.
The OBD2 port plays a crucial role in modern vehicle maintenance and management. It provides a standardized way to access a wealth of data about your vehicle’s performance and health. By understanding and utilizing the information available through this port, you can make informed decisions about maintenance and repairs, ultimately extending the life of your vehicle and ensuring its optimal performance.
2.1. Vehicle Health Monitoring
The OBD2 port allows for continuous monitoring of various vehicle systems, providing early warnings of potential problems. This proactive approach can prevent minor issues from escalating into major repairs.
- Early Detection: Identifies issues before they cause significant damage.
- Performance Insights: Provides data on engine performance, fuel efficiency, and more.
- Preventative Maintenance: Enables timely maintenance to keep your vehicle running smoothly.
2.2. Regulatory Compliance
The OBD2 system ensures that vehicles meet emissions standards, helping to protect the environment. Regular monitoring and diagnostics through the OBD2 port are essential for maintaining compliance.
- Emissions Testing: Facilitates accurate and reliable emissions testing.
- Environmental Protection: Helps reduce vehicle emissions and environmental impact.
- Compliance Standards: Ensures vehicles adhere to environmental regulations.
2.3. Fleet Management
For businesses with vehicle fleets, the OBD2 port is invaluable for tracking vehicle health, optimizing performance, and reducing downtime. Telematics devices connected to the OBD2 port can provide real-time data and insights that improve fleet efficiency.
- Real-Time Tracking: Monitors vehicle location, speed, and other parameters.
- Performance Optimization: Identifies areas for improvement in driving habits and vehicle maintenance.
- Cost Reduction: Reduces fuel consumption, maintenance costs, and downtime.
3. Understanding OBD2 Protocols and Standards
OBD2 protocols and standards ensure compatibility and consistency across different vehicle makes and models. These standards define how diagnostic information is communicated and accessed, making it easier for technicians to diagnose and repair vehicles.
The OBD2 system operates on a set of standardized protocols that govern how data is transmitted and interpreted. Understanding these protocols is essential for anyone working with OBD2 diagnostic tools. The SAE and ISO have played key roles in defining these standards.
3.1. Key OBD2 Protocols
- SAE J1850 PWM and VPW: Used primarily by Ford and GM vehicles, these protocols define the communication standards for data transmission.
- ISO 9141-2: Used by European and Asian vehicles, this protocol specifies the serial communication interface for diagnostics.
- ISO 14230 (KWP2000): An evolution of ISO 9141-2, this protocol provides faster data transfer rates and improved diagnostic capabilities.
- ISO 15765 (CAN): The Controller Area Network protocol is the most modern and widely used standard, offering high-speed communication and advanced diagnostic features.
3.2. Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
DTCs are standardized codes used to identify specific issues within the vehicle’s systems. These codes are crucial for diagnosing problems and performing effective repairs. According to RepairPal, DTCs are categorized into four main groups:
- P-Codes (Powertrain): Related to the engine, transmission, and associated components.
- C-Codes (Chassis): Related to the braking system, suspension, and steering.
- B-Codes (Body): Related to the vehicle’s body, including airbags, power windows, and locks.
- U-Codes (Network): Related to the vehicle’s communication network.
3.3. OBD2 Modes
OBD2 defines several modes of operation, each providing different types of diagnostic information. Understanding these modes is essential for using diagnostic tools effectively.
- Mode 01: Shows current data parameters.
- Mode 02: Displays freeze frame data.
- Mode 03: Reveals stored diagnostic trouble codes.
- Mode 04: Clears diagnostic trouble codes and resets monitors.
- Mode 05: Tests oxygen sensors.
- Mode 06: Shows results of on-board diagnostic monitoring for specific systems.
- Mode 07: Displays pending diagnostic trouble codes.
- Mode 08: Allows for bi-directional control of on-board systems.
- Mode 09: Shows vehicle information.
- Mode 0A: Displays permanent diagnostic trouble codes.
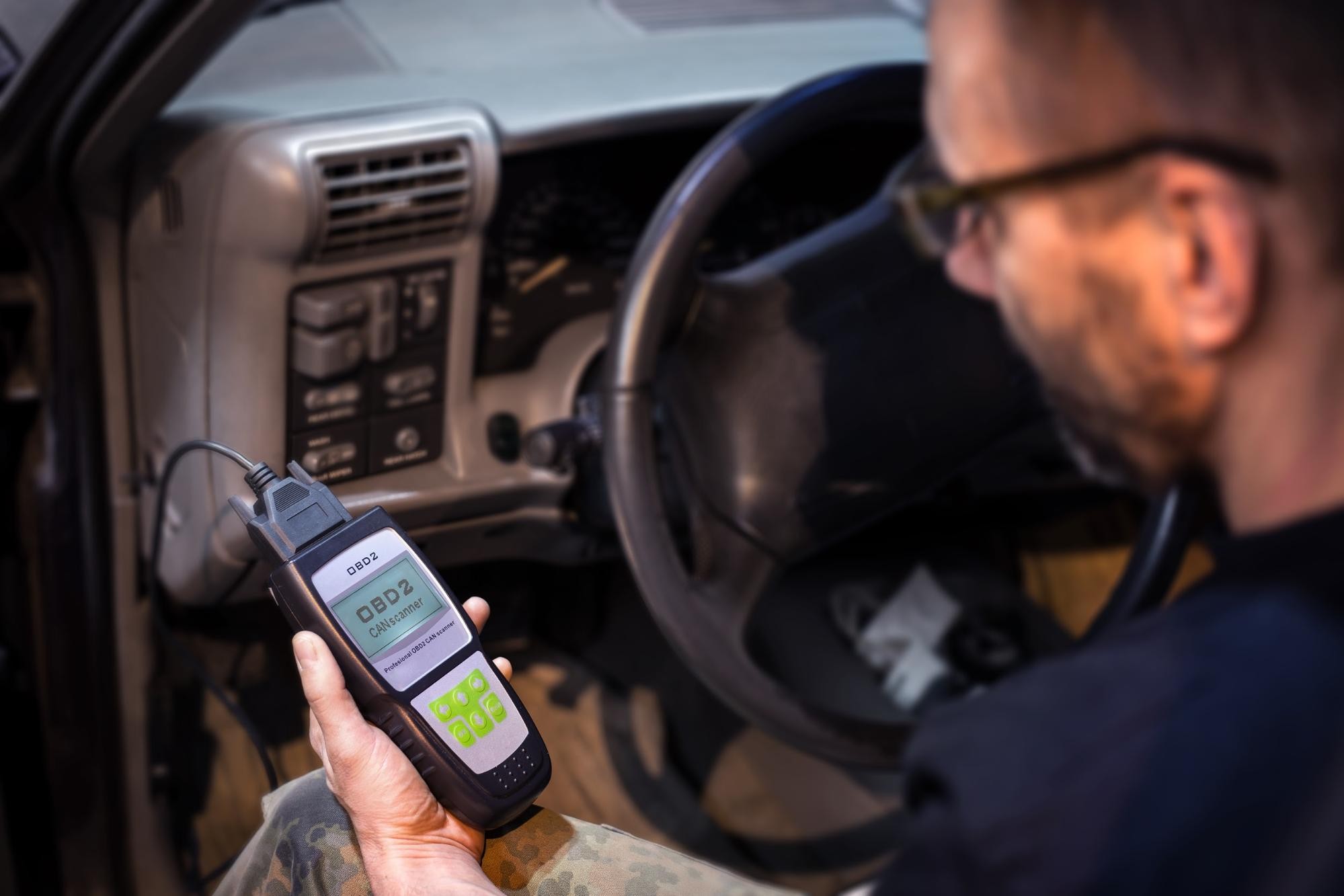
4. How to Use an OBD2 Scanner
Using an OBD2 scanner is straightforward, but it’s essential to follow the correct steps to ensure accurate diagnostics. This process involves connecting the scanner to the OBD2 port, reading diagnostic trouble codes, interpreting the codes, and taking appropriate action.
An OBD2 scanner is a valuable tool for any vehicle owner or technician. It allows you to access the wealth of diagnostic information available through the OBD2 port, helping you to identify and resolve issues quickly and efficiently. At OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN, we provide comprehensive guides and support to help you make the most of your OBD2 scanner.
4.1. Step-by-Step Guide to Using an OBD2 Scanner
- Locate the OBD2 Port: Find the OBD2 port in your vehicle, typically located under the dashboard on the driver’s side.
- Connect the Scanner: Plug the OBD2 scanner into the port, ensuring it is securely connected.
- Turn on the Ignition: Turn the vehicle’s ignition to the “on” position without starting the engine.
- Power on the Scanner: Turn on the OBD2 scanner and wait for it to establish a connection with the vehicle’s computer.
- Read Diagnostic Trouble Codes: Use the scanner’s interface to read and display any stored diagnostic trouble codes.
- Interpret the Codes: Refer to a DTC code chart or database to understand the meaning of each code.
- Clear the Codes (Optional): After addressing the issue, you can use the scanner to clear the codes and reset the check engine light.
- Test and Verify: After clearing the codes, start the engine and monitor the vehicle to ensure the issue is resolved.
4.2. Choosing the Right OBD2 Scanner
Selecting the right OBD2 scanner depends on your needs and budget. There are several types of scanners available, ranging from basic code readers to advanced diagnostic tools.
- Basic Code Readers: These are inexpensive and easy to use, suitable for reading and clearing DTCs.
- Mid-Range Scanners: These offer additional features such as live data streaming and enhanced diagnostic capabilities.
- Professional-Grade Scanners: These provide advanced functions such as bi-directional control, system testing, and programming capabilities, suitable for professional technicians.
4.3. Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Ignoring the Codes: Never ignore diagnostic trouble codes, as they indicate potential problems that need attention.
- Clearing Codes Without Fixing the Issue: Clearing codes without addressing the underlying problem will only result in the codes reappearing.
- Using Incompatible Scanners: Ensure the OBD2 scanner is compatible with your vehicle’s make and model.
- Misinterpreting the Codes: Always refer to a reliable DTC code chart or database to accurately interpret the codes.
 OBD2 Scanner in Use
OBD2 Scanner in Use
5. Interpreting OBD2 Codes and Troubleshooting
Interpreting OBD2 codes correctly is crucial for effective troubleshooting. Understanding the meaning of these codes allows you to diagnose the problem accurately and take the appropriate steps for repair.
OBD2 codes provide valuable information about the health and performance of your vehicle. However, interpreting these codes can be challenging without the right knowledge and resources. At OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN, we offer expert guidance and tools to help you accurately interpret OBD2 codes and troubleshoot vehicle issues effectively.
5.1. Common OBD2 Codes and Their Meanings
- P0171 (System Too Lean, Bank 1): Indicates that the engine is not receiving enough fuel or there is too much air in the air-fuel mixture.
- P0300 (Random/Multiple Cylinder Misfire Detected): Indicates that there is a misfire occurring in one or more cylinders.
- P0420 (Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold, Bank 1): Indicates that the catalytic converter is not functioning efficiently.
- P0401 (Exhaust Gas Recirculation Flow Insufficient Detected): Indicates that the EGR system is not flowing enough exhaust gas back into the engine.
- P0101 (Mass Air Flow Circuit Range/Performance Problem): Indicates that there is an issue with the mass air flow sensor.
5.2. Troubleshooting Steps for Common Codes
- Verify the Code: Use an OBD2 scanner to confirm the code and ensure it is accurate.
- Gather Information: Research the code and its potential causes using reliable resources.
- Inspect the Components: Visually inspect the components related to the code for any signs of damage or wear.
- Test the Components: Use diagnostic tools to test the components and verify their functionality.
- Repair or Replace: Repair or replace any faulty components as needed.
- Clear the Code: After addressing the issue, clear the code and monitor the vehicle to ensure the problem is resolved.
5.3. When to Seek Professional Help
While some OBD2 code issues can be resolved with DIY repairs, others require professional assistance. It’s important to know when to seek help from a qualified technician.
- Complex Issues: If the code indicates a complex issue that requires specialized knowledge or tools, seek professional help.
- Unfamiliar Repairs: If you are not comfortable performing the necessary repairs, it’s best to consult a technician.
- Persistent Codes: If the code reappears after attempting DIY repairs, it may indicate a more serious underlying problem that requires professional diagnosis.
6. Advanced OBD2 Diagnostics and Customization
Advanced OBD2 diagnostics involve using sophisticated tools and techniques to access deeper levels of vehicle data and customize vehicle settings. This level of diagnostics is typically performed by experienced technicians with specialized equipment.
For those looking to go beyond basic code reading, advanced OBD2 diagnostics offer a range of possibilities. From accessing manufacturer-specific data to customizing vehicle settings, these advanced techniques can provide valuable insights and improvements. At OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN, we offer training and resources to help you explore the world of advanced OBD2 diagnostics.
6.1. Accessing Manufacturer-Specific Data
In addition to standardized OBD2 data, many vehicles offer manufacturer-specific data that can provide more detailed insights into vehicle performance and health. Accessing this data requires specialized diagnostic tools and knowledge.
- Enhanced Diagnostics: Access data beyond the standardized OBD2 parameters.
- Custom Parameters: Monitor specific parameters unique to the vehicle make and model.
- Detailed Insights: Gain deeper insights into vehicle performance and potential issues.
6.2. Customizing Vehicle Settings
Some advanced OBD2 tools allow you to customize vehicle settings, such as adjusting engine parameters, disabling certain features, or programming new keys. However, it’s important to proceed with caution and understand the potential risks.
- Performance Tuning: Adjust engine parameters to improve performance and fuel efficiency.
- Feature Customization: Disable or enable certain vehicle features.
- Key Programming: Program new keys or remotes for the vehicle.
6.3. Risks and Precautions
- Potential Damage: Incorrectly modifying vehicle settings can cause damage to the engine or other systems.
- Warranty Voiding: Customizing vehicle settings may void the manufacturer’s warranty.
- Legal Compliance: Ensure any modifications comply with local laws and regulations.
- Professional Guidance: Seek guidance from experienced technicians before attempting advanced customization.
7. The Future of OBD and Vehicle Diagnostics
The future of OBD and vehicle diagnostics is evolving rapidly, driven by advancements in technology and the increasing complexity of modern vehicles. These advancements promise to provide more comprehensive and accurate diagnostic capabilities.
As vehicles become more sophisticated, the role of OBD and vehicle diagnostics will continue to grow. The integration of new technologies, such as AI and cloud connectivity, is transforming the way we diagnose and maintain vehicles. At OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN, we are committed to staying at the forefront of these advancements and providing our customers with the latest diagnostic solutions.
7.1. Integration of AI and Machine Learning
AI and machine learning are being integrated into OBD diagnostic tools to improve accuracy, efficiency, and predictive capabilities.
- Predictive Diagnostics: AI algorithms can analyze vehicle data to predict potential issues before they occur.
- Improved Accuracy: Machine learning can enhance the accuracy of diagnostic trouble code interpretation.
- Automated Troubleshooting: AI-powered tools can provide step-by-step troubleshooting guidance.
7.2. Cloud Connectivity and Remote Diagnostics
Cloud connectivity enables remote diagnostics, allowing technicians to access vehicle data and perform diagnostics from anywhere in the world.
- Remote Monitoring: Monitor vehicle health and performance remotely.
- Real-Time Diagnostics: Perform diagnostics in real-time, regardless of location.
- Data Analysis: Analyze vehicle data in the cloud to identify trends and patterns.
7.3. Enhanced Security Measures
As vehicles become more connected, security is a growing concern. Enhanced security measures are being implemented to protect vehicle data and prevent unauthorized access. According to a study by the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA), cybersecurity is a critical aspect of modern vehicle diagnostics.
- Data Encryption: Encrypt vehicle data to protect it from unauthorized access.
- Secure Communication: Implement secure communication protocols to prevent hacking.
- Access Controls: Restrict access to sensitive vehicle data and functions.
8. OBD2 and Electric Vehicles (EVs)
OBD2 is also relevant for electric vehicles (EVs), although the diagnostic parameters and trouble codes may differ from those in gasoline-powered vehicles. EVs have unique systems and components that require specialized diagnostics.
While EVs don’t have internal combustion engines, they still rely on OBD2 for monitoring and diagnostics. The OBD2 port in EVs provides access to data related to battery health, motor performance, and other critical systems. At OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN, we offer specialized diagnostic tools and resources for EVs.
8.1. Unique Diagnostic Parameters for EVs
- Battery Health: Monitor battery voltage, temperature, and state of charge.
- Motor Performance: Track motor RPM, torque, and efficiency.
- Charging System: Monitor charging voltage, current, and charging time.
8.2. Common EV Trouble Codes
- P0A0F (Drive Motor Performance): Indicates an issue with the drive motor’s performance.
- P0A80 (Replace Battery Pack): Indicates that the battery pack needs to be replaced.
- P0AA6 (Battery Voltage System Isolation Fault): Indicates an isolation fault in the battery voltage system.
8.3. Specialized EV Diagnostic Tools
- Battery Analyzers: Test the health and performance of the battery pack.
- Motor Testers: Evaluate the performance and efficiency of the electric motor.
- Charging System Analyzers: Diagnose issues with the charging system.
9. WWH-OBD: The Next Generation of Diagnostics
WWH-OBD (World Wide Harmonized On-Board Diagnostics) is an international standard aimed at harmonizing vehicle diagnostics across different regions and manufacturers. This standard expands on the capabilities of OBD2 and provides more detailed and comprehensive diagnostic information.
WWH-OBD represents the next step in the evolution of vehicle diagnostics. By standardizing diagnostic protocols and data parameters, WWH-OBD aims to improve the accuracy and efficiency of vehicle diagnostics worldwide. At OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN, we are committed to supporting WWH-OBD and providing our customers with the tools and resources they need to stay ahead of the curve.
9.1. Advantages of WWH-OBD
- More Data Types: Expands the number of available data parameters for more comprehensive diagnostics.
- Detailed Fault Data: Provides more detailed information about fault conditions, including severity and status.
- Improved Standardization: Harmonizes diagnostic protocols across different regions and manufacturers.
9.2. Key Features of WWH-OBD
- Unified Diagnostic Services (UDS): Incorporates UDS protocols to provide more detailed diagnostic information.
- 3-Byte DTCs: Expands the Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) from 2 bytes to 3 bytes, providing more specific fault information.
- Fault Severity Indicators: Indicates the severity of the fault, helping to prioritize repairs.
9.3. Implementation of WWH-OBD
- Global Adoption: WWH-OBD is being adopted by vehicle manufacturers worldwide.
- Firmware Updates: Diagnostic tool manufacturers are updating their firmware to support WWH-OBD.
- Training and Resources: Technicians are receiving training and resources to effectively use WWH-OBD.
10. Choosing the Right OBD2 Diagnostic Service at OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN
Choosing the right OBD2 diagnostic service is essential for accurate and effective vehicle maintenance. At OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN, we offer a range of services to meet your diagnostic needs, from basic code reading to advanced troubleshooting.
Selecting the right diagnostic service can save you time, money, and frustration. Our team of experienced technicians and state-of-the-art equipment ensures that you receive the highest quality diagnostic services. Contact us today to learn more about how we can help you keep your vehicle running smoothly.
10.1. Services Offered at OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN
- Basic Code Reading: Quick and accurate reading of diagnostic trouble codes.
- Advanced Diagnostics: In-depth analysis of vehicle systems using advanced diagnostic tools.
- Troubleshooting: Expert troubleshooting to identify the root cause of vehicle issues.
- Repair Services: Professional repair services to address any identified problems.
- Maintenance Services: Preventative maintenance services to keep your vehicle running smoothly.
10.2. Benefits of Choosing OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN
- Experienced Technicians: Our team of experienced technicians has the knowledge and skills to accurately diagnose and repair any vehicle issue.
- State-of-the-Art Equipment: We use the latest diagnostic tools and equipment to ensure the highest quality service.
- Comprehensive Services: We offer a full range of diagnostic and repair services to meet all of your vehicle needs.
- Customer Satisfaction: We are committed to providing excellent customer service and ensuring your satisfaction.
10.3. Contact Us Today
- Address: 123 Main Street, Los Angeles, CA 90001, United States.
- WhatsApp: +1 (641) 206-8880.
- Website: OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN
Don’t let vehicle issues slow you down. Contact OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN today and let our experts help you keep your vehicle running at its best.
Are you facing difficulties in understanding OBD2 scanner outputs or need assistance with vehicle diagnostics? Contact us via WhatsApp at +1 (641) 206-8880 or visit our website at OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN for immediate support and expert advice. Our team at 123 Main Street, Los Angeles, CA 90001, United States is ready to help you resolve any automotive issues quickly and efficiently.
FAQ: Understanding the OBD2 Diagnostic Port
Q1: What exactly is an OBD2 scanner?
An OBD2 scanner is a diagnostic tool used to read and interpret data from a vehicle’s On-Board Diagnostics system, helping identify potential issues. It connects to the OBD2 port in your car.
Q2: How do I locate the OBD2 port in my vehicle?
The OBD2 port is typically located under the dashboard on the driver’s side. However, the exact location can vary depending on the vehicle make and model, consult your vehicle’s owner’s manual for the precise location.
Q3: What types of issues can an OBD2 scanner detect?
An OBD2 scanner can detect a wide range of issues related to the engine, transmission, emissions systems, and more. Common issues include engine misfires, faulty oxygen sensors, and catalytic converter problems.
Q4: Can I use any OBD2 scanner with my vehicle?
Most OBD2 scanners are compatible with all vehicles manufactured after 1996 in the United States. However, it’s important to ensure that the scanner supports the specific protocols used by your vehicle.
Q5: What do the diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) mean?
Diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) are standardized codes used to identify specific issues within the vehicle’s systems. These codes are crucial for diagnosing problems and performing effective repairs, refer to a DTC code chart or database to understand the meaning of each code.
Q6: Is it possible to fix vehicle problems using just an OBD2 scanner?
While an OBD2 scanner can help you identify the problem, it cannot fix it. You will need to perform the necessary repairs or seek professional assistance to resolve the issue.
Q7: How often should I use an OBD2 scanner to check my vehicle?
You should use an OBD2 scanner whenever you notice any symptoms or warning lights in your vehicle. Regular checks can help identify potential issues early and prevent major repairs.
Q8: What are the benefits of using OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN for my diagnostic needs?
OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN offers experienced technicians, state-of-the-art equipment, comprehensive services, and a commitment to customer satisfaction, ensuring that you receive the highest quality diagnostic and repair services.
Q9: Can I clear the diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) myself after fixing the issue?
Yes, you can use an OBD2 scanner to clear the diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) after fixing the issue. However, it’s important to ensure that the problem is resolved before clearing the codes, as they may reappear if the issue persists.
Q10: Are there any risks associated with using an OBD2 scanner?
When used correctly, there are minimal risks associated with using an OBD2 scanner. However, it’s important to follow the instructions carefully and avoid making any unauthorized changes to the vehicle’s settings.