Obd2 Mini Elm327 Wifi Interface Adapter provides a convenient and cost-effective solution for vehicle diagnostics, allowing you to read diagnostic trouble codes, monitor vehicle parameters, and gain insights into your car’s health, with OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN offering expertise and resources to maximize your experience. The ELM327 chip is a microcontroller programmed to translate the OBD2 protocol, enabling communication between your vehicle and a diagnostic device.
Contents
- 1. What is an OBD2 Mini ELM327 WiFi Interface Adapter?
- 2. Who Benefits from Using an OBD2 Mini ELM327 WiFi Adapter?
- 3. What Can You Do with an OBD2 Mini ELM327 WiFi Adapter?
- 4. Key Features to Look for in an OBD2 Mini ELM327 WiFi Adapter
- 5. How to Choose the Right OBD2 App for Your Adapter
- 6. Setting Up Your OBD2 Mini ELM327 WiFi Adapter: A Step-by-Step Guide
- 7. Troubleshooting Common Connection Issues
- 8. Understanding Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
- 9. Common OBD2 Codes and Their Meanings
- 10. How to Use Real-Time Data for Diagnostics
- 11. Performing Basic Repairs Based on OBD2 Diagnostics
- 12. Advanced Diagnostic Techniques with OBD2 Adapters
- 13. Understanding OBD2 Protocols
- 14. The Role of Oxygen Sensors in OBD2 Diagnostics
- 15. How Fuel Trim Can Help Diagnose Engine Problems
- 16. Using OBD2 Data to Improve Fuel Efficiency
- 17. OBD2 Adapters and Vehicle Security: What You Need to Know
- 18. The Future of OBD2 Technology
- 19. OBD2 Mini ELM327 WiFi Adapters: Ethical Considerations
- 20. Expert Insights on OBD2 Mini ELM327 WiFi Adapters
- 21. How OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN Can Help You
- 22. Maximizing Your Investment in an OBD2 Mini ELM327 WiFi Adapter
- 23. Overcoming the Challenges of Car Repair with OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN
- 24. The Impact of OBD2 on Automotive Education
- 25. How OBD2 Data Is Used in Automotive Research
- 26. Tips for Using OBD2 Adapters in Different Weather Conditions
- 27. The Future of Automotive Diagnostics with OBD2
- 28. How to Extend the Life of Your OBD2 Mini ELM327 WiFi Adapter
- 29. Case Studies: Real-World Examples of OBD2 Diagnostics
- 30. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About OBD2 Mini ELM327 WiFi Adapters
- 31. Get Expert Help From OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN Today
1. What is an OBD2 Mini ELM327 WiFi Interface Adapter?
An OBD2 mini ELM327 WiFi interface adapter is a compact tool that allows you to connect your smartphone, tablet, or laptop to your car’s On-Board Diagnostics II (OBD2) system via WiFi. It acts as a bridge, translating the data from your car’s computer into a format that your device can understand, thereby unlocking a wealth of information about your vehicle’s performance and health.
- OBD2 System: The OBD2 system is a standardized system used in most cars manufactured after 1996 to monitor various engine and vehicle parameters.
- ELM327 Chip: The ELM327 is a microcontroller programmed to translate the OBD2 protocol, enabling communication between your vehicle and a diagnostic device.
- WiFi Interface: The WiFi interface allows for wireless communication between the adapter and your device, providing flexibility and ease of use.
2. Who Benefits from Using an OBD2 Mini ELM327 WiFi Adapter?
The OBD2 mini ELM327 WiFi adapter is a valuable tool for a wide range of individuals, including:
- DIY Car Enthusiasts: Those who enjoy working on their own cars can use the adapter to diagnose problems, monitor performance, and make informed repairs.
- Professional Mechanics: Mechanics can use the adapter as a quick and convenient diagnostic tool, supplementing more expensive and complex diagnostic equipment.
- Car Owners: Any car owner can benefit from using the adapter to understand their car’s health, potentially saving money on costly repairs by identifying issues early on.
3. What Can You Do with an OBD2 Mini ELM327 WiFi Adapter?
With an OBD2 mini ELM327 WiFi adapter, you can perform a variety of diagnostic and monitoring functions, including:
- Read Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs): Identify the cause of the “check engine” light and other warning lights.
- Clear Diagnostic Trouble Codes: Reset the “check engine” light after performing repairs.
- Monitor Real-Time Vehicle Parameters: View live data such as engine speed, coolant temperature, and fuel trim.
- Retrieve Vehicle Information: Access information such as the Vehicle Identification Number (VIN) and calibration IDs.
- Perform Emissions Tests: Check your vehicle’s readiness for emissions testing.
4. Key Features to Look for in an OBD2 Mini ELM327 WiFi Adapter
When choosing an OBD2 mini ELM327 WiFi adapter, consider the following features:
- Compatibility: Ensure the adapter is compatible with your vehicle’s make and model.
- WiFi Connectivity: A stable and reliable WiFi connection is essential for seamless data transfer.
- Software Support: Choose an adapter that is compatible with a wide range of OBD2 apps.
- Ease of Use: The adapter should be easy to set up and use, even for beginners.
- Durability: Look for an adapter that is built to last and can withstand the rigors of automotive use.
5. How to Choose the Right OBD2 App for Your Adapter
The OBD2 app you choose will greatly impact your experience with the adapter. Consider the following factors:
- Compatibility: Ensure the app is compatible with your adapter and your device’s operating system (iOS, Android, Windows).
- Features: Choose an app that offers the features you need, such as DTC reading, real-time data monitoring, and data logging.
- User Interface: The app should have an intuitive and easy-to-use interface.
- Cost: Some apps are free, while others require a purchase or subscription.
- Reviews: Read reviews from other users to get an idea of the app’s performance and reliability.
6. Setting Up Your OBD2 Mini ELM327 WiFi Adapter: A Step-by-Step Guide
Setting up your OBD2 mini ELM327 WiFi adapter is a straightforward process:
- Plug in the Adapter: Locate the OBD2 port in your car (usually under the dashboard) and plug in the adapter.
- Turn on Ignition: Turn the ignition key to the “on” position, but do not start the engine.
- Connect to WiFi: On your smartphone, tablet, or laptop, go to the WiFi settings and connect to the WiFi network created by the adapter. The network name is usually “OBDII” or something similar.
- Launch the OBD2 App: Open the OBD2 app you have chosen and follow the instructions to connect to the adapter.
- Start Diagnosing: Once connected, you can start reading DTCs, monitoring real-time data, and performing other diagnostic functions.
7. Troubleshooting Common Connection Issues
Sometimes, you may encounter issues connecting your device to the OBD2 adapter. Here are some common troubleshooting steps:
- Verify WiFi Connection: Make sure your device is connected to the correct WiFi network created by the adapter.
- Check Adapter IP Address and Port: Ensure the OBD2 app is configured with the correct IP address and port number for the adapter. Refer to the adapter’s documentation for this information.
- Restart Adapter and Device: Try unplugging the adapter, restarting your device, and then plugging the adapter back in.
- Update Firmware: Check if there are any firmware updates available for the adapter.
- Contact Support: If you are still having trouble, contact the adapter manufacturer or app developer for support.
8. Understanding Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) are codes stored in your car’s computer that indicate a problem with a specific system or component. Understanding these codes is crucial for diagnosing and repairing your car.
- Code Structure: DTCs typically consist of a letter followed by four numbers. The letter indicates the system affected (e.g., P for Powertrain, B for Body, C for Chassis, U for Network). The numbers provide more specific information about the problem.
- Reading DTCs: Use your OBD2 app to read the DTCs stored in your car’s computer.
- Interpreting DTCs: Refer to a DTC lookup database or repair manual to understand the meaning of each code. Websites like OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN can provide valuable resources for interpreting DTCs.
9. Common OBD2 Codes and Their Meanings
Here’s a table of some common OBD2 codes and their meanings:
| Code | Description | Possible Causes |
|---|---|---|
| P0101 | Mass Air Flow (MAF) Sensor Circuit Range/Performance Problem | Dirty or faulty MAF sensor, vacuum leaks, wiring problems |
| P0113 | Intake Air Temperature Sensor Circuit High Input | Faulty IAT sensor, wiring problems |
| P0171 | System Too Lean (Bank 1) | Vacuum leaks, faulty oxygen sensor, low fuel pressure |
| P0300 | Random/Multiple Cylinder Misfire Detected | Faulty spark plugs, ignition coils, fuel injectors, vacuum leaks, low compression |
| P0420 | Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold (Bank 1) | Faulty catalytic converter, oxygen sensors, exhaust leaks |
| P0442 | Evaporative Emission Control System Leak Detected (Small Leak) | Loose or faulty gas cap, damaged EVAP system hoses, faulty purge valve |
| P0505 | Idle Control System Malfunction | Faulty idle air control valve, vacuum leaks, throttle body issues |
| P0700 | Transmission Control System Malfunction | Faulty transmission control module, solenoid issues, internal transmission damage |
| P0741 | Torque Converter Clutch Circuit Performance or Stuck Off | Faulty torque converter clutch solenoid, damaged torque converter, transmission fluid issues |
| P0455 | Evaporative Emission Control System Leak Detected (Gross Leak) | Missing or loose fuel cap, damaged fuel tank, large leak in EVAP system, faulty canister purge valve |
Understanding these common codes can help you quickly identify and address potential issues.
10. How to Use Real-Time Data for Diagnostics
Real-time data, also known as live data, provides a snapshot of your car’s performance while it is running. This data can be invaluable for diagnosing intermittent problems and monitoring the health of various systems.
- Accessing Real-Time Data: Use your OBD2 app to access real-time data streams from your car’s computer.
- Key Parameters to Monitor: Some key parameters to monitor include:
- Engine speed (RPM)
- Coolant temperature
- Intake air temperature
- Mass air flow
- Oxygen sensor readings
- Fuel trim
- Ignition timing
- Interpreting Real-Time Data: Compare the real-time data to specifications in your car’s repair manual to identify any deviations or anomalies. For example, abnormal oxygen sensor readings could indicate a faulty sensor or a problem with the fuel mixture.
11. Performing Basic Repairs Based on OBD2 Diagnostics
Once you have diagnosed a problem using your OBD2 adapter, you can perform basic repairs yourself. Here are some examples:
- Replacing a Faulty Sensor: If a DTC indicates a faulty sensor, such as an oxygen sensor or mass air flow sensor, you can replace the sensor yourself. Follow the instructions in your car’s repair manual.
- Replacing Spark Plugs: If your car is misfiring, replacing the spark plugs can often resolve the issue.
- Tightening a Loose Gas Cap: A loose gas cap can trigger an EVAP system code. Simply tighten the gas cap to resolve the issue.
- Clearing DTCs: After performing a repair, use your OBD2 app to clear the DTCs and reset the “check engine” light.
Important Note: Always consult your car’s repair manual and take necessary safety precautions before performing any repairs. If you are not comfortable performing a repair yourself, consult a qualified mechanic.
12. Advanced Diagnostic Techniques with OBD2 Adapters
Beyond reading DTCs and monitoring real-time data, OBD2 adapters can be used for more advanced diagnostic techniques, such as:
- Data Logging: Record real-time data over time to analyze performance and identify intermittent problems.
- Freeze Frame Data: Capture a snapshot of the real-time data at the moment a DTC was triggered. This can provide valuable clues about the conditions that led to the problem.
- Mode 6 Data: Access detailed diagnostic information about specific components and systems. This data can be helpful for identifying subtle problems that may not trigger a DTC.
13. Understanding OBD2 Protocols
OBD2 uses several communication protocols to transmit data between the vehicle’s computer and the diagnostic tool. Understanding these protocols can be helpful for troubleshooting connection issues and ensuring compatibility.
- SAE J1850 PWM: Used by Ford vehicles.
- SAE J1850 VPW: Used by General Motors vehicles.
- ISO 9141-2: Used by European and Asian vehicles.
- ISO 14230-4 (KWP2000): Used by a variety of vehicles.
- ISO 15765-4 (CAN): The most common protocol used in modern vehicles.
Most OBD2 adapters support multiple protocols, but it’s essential to ensure that your adapter supports the protocol used by your vehicle.
14. The Role of Oxygen Sensors in OBD2 Diagnostics
Oxygen sensors play a crucial role in OBD2 diagnostics. They monitor the amount of oxygen in the exhaust gas and provide feedback to the engine control unit (ECU), which adjusts the fuel mixture to optimize performance and emissions.
- Types of Oxygen Sensors: There are two main types of oxygen sensors:
- Upstream Sensors: Located before the catalytic converter, these sensors measure the oxygen content of the exhaust gas coming directly from the engine.
- Downstream Sensors: Located after the catalytic converter, these sensors monitor the efficiency of the catalytic converter.
- Interpreting Oxygen Sensor Readings: By monitoring the voltage output of the oxygen sensors, you can determine whether the fuel mixture is too rich (too much fuel) or too lean (not enough fuel). Faulty oxygen sensors can cause a variety of problems, including poor fuel economy, rough running, and increased emissions.
15. How Fuel Trim Can Help Diagnose Engine Problems
Fuel trim refers to the adjustments made by the ECU to the fuel mixture in order to maintain optimal combustion. Monitoring fuel trim values can provide valuable clues about engine problems.
- Short-Term Fuel Trim (STFT): Represents the immediate adjustments made to the fuel mixture.
- Long-Term Fuel Trim (LTFT): Represents the long-term adjustments made to the fuel mixture.
- Interpreting Fuel Trim Values:
- Positive Fuel Trim: Indicates that the ECU is adding fuel to compensate for a lean condition.
- Negative Fuel Trim: Indicates that the ECU is reducing fuel to compensate for a rich condition.
- High Fuel Trim Values: Can indicate a vacuum leak, faulty oxygen sensor, or other engine problems.
16. Using OBD2 Data to Improve Fuel Efficiency
By monitoring real-time data with your OBD2 adapter, you can identify driving habits and mechanical issues that are impacting your fuel efficiency.
- Monitor Fuel Consumption: Use your OBD2 app to monitor your fuel consumption in real-time.
- Identify Inefficient Driving Habits: Avoid rapid acceleration, hard braking, and excessive idling.
- Address Mechanical Issues: Fix any mechanical issues that are affecting fuel efficiency, such as a faulty oxygen sensor or a clogged air filter.
- Keep Tires Properly Inflated: Underinflated tires can reduce fuel efficiency.
17. OBD2 Adapters and Vehicle Security: What You Need to Know
While OBD2 adapters are valuable tools, it’s important to be aware of potential security risks.
- Unauthorized Access: An attacker could potentially use an OBD2 adapter to gain unauthorized access to your car’s computer and control various systems.
- Data Theft: An attacker could potentially steal sensitive data from your car’s computer, such as your VIN or diagnostic information.
- Security Best Practices: To protect your vehicle from security threats, follow these best practices:
- Only use OBD2 adapters from reputable manufacturers.
- Keep your OBD2 app updated with the latest security patches.
- Do not leave your OBD2 adapter plugged in when not in use.
- Be careful about connecting to unknown WiFi networks.
18. The Future of OBD2 Technology
OBD2 technology is constantly evolving to meet the demands of modern vehicles.
- OBD3: The next generation of OBD is expected to include more comprehensive monitoring of vehicle emissions and performance.
- Wireless OBD: Wireless OBD adapters are becoming increasingly popular, offering greater convenience and flexibility.
- Cloud-Based Diagnostics: Cloud-based diagnostic platforms are emerging, allowing for remote diagnostics and data analysis.
19. OBD2 Mini ELM327 WiFi Adapters: Ethical Considerations
Using an OBD2 mini ELM327 WiFi adapter comes with certain ethical considerations:
- Privacy: Respect the privacy of vehicle owners by not accessing or sharing their diagnostic data without their consent.
- Security: Take precautions to protect vehicle systems from unauthorized access or modification.
- Fair Competition: Use OBD2 data ethically and responsibly, without engaging in unfair or deceptive practices.
20. Expert Insights on OBD2 Mini ELM327 WiFi Adapters
Automotive experts widely acknowledge the value of OBD2 mini ELM327 WiFi adapters for both DIY enthusiasts and professional mechanics. Studies from universities and research institutions support their effectiveness in vehicle diagnostics.
- University of California, Berkeley: A study by the University of California, Berkeley, found that using OBD2 scanners can significantly reduce diagnostic time and improve the accuracy of repairs (University of California, Berkeley, Department of Mechanical Engineering, 2022).
- SAE International: SAE International, a global association of engineers and technical experts, has published numerous papers and standards related to OBD2 technology, highlighting its importance in vehicle diagnostics and emissions control (SAE International, 2023).
These insights underscore the growing recognition of OBD2 technology as an essential tool for vehicle maintenance and repair.
21. How OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN Can Help You
At OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN, we are committed to providing you with the knowledge and resources you need to make the most of your OBD2 mini ELM327 WiFi adapter.
- Expert Advice: Our team of experienced automotive technicians can provide expert advice on choosing the right adapter, troubleshooting connection issues, and interpreting diagnostic data.
- Comprehensive Resources: Our website features a wealth of information about OBD2 technology, including DTC lookup databases, repair manuals, and how-to guides.
- Community Forum: Join our community forum to connect with other OBD2 enthusiasts, share your experiences, and get answers to your questions.
- Step-by-step guides: We offer easy-to-follow guides on how to use OBD2 scanners and perform basic repairs.
22. Maximizing Your Investment in an OBD2 Mini ELM327 WiFi Adapter
To maximize your investment in an OBD2 mini ELM327 WiFi adapter, consider the following tips:
- Choose a reputable brand: Select a well-known brand with positive reviews and reliable customer support.
- Read the user manual: Familiarize yourself with the adapter’s features and functions.
- Keep your adapter updated: Install firmware updates as they become available.
- Practice safe usage: Follow security best practices to protect your vehicle from unauthorized access.
- Regularly scan your vehicle: Use your adapter to scan your vehicle for DTCs on a regular basis, even if there are no warning lights.
23. Overcoming the Challenges of Car Repair with OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN
We understand that car repair can be challenging, especially for those who are not mechanically inclined. That’s why we offer a range of services to help you overcome these challenges.
- Remote Diagnostics: We can remotely diagnose your car’s problems using your OBD2 adapter and provide you with a detailed report and repair recommendations.
- Repair Referrals: We can refer you to qualified mechanics in your area who can perform the necessary repairs.
- Technical Support: Our technical support team is available to answer your questions and help you troubleshoot any issues you may be experiencing.
24. The Impact of OBD2 on Automotive Education
OBD2 technology has had a significant impact on automotive education.
- Hands-On Training: OBD2 adapters provide students with hands-on training in vehicle diagnostics and repair.
- Real-World Experience: Students can use OBD2 adapters to diagnose real-world problems on actual vehicles.
- Enhanced Learning: OBD2 technology enhances the learning experience by providing students with valuable data and insights into vehicle performance.
25. How OBD2 Data Is Used in Automotive Research
OBD2 data is also used extensively in automotive research.
- Performance Analysis: Researchers use OBD2 data to analyze vehicle performance and identify areas for improvement.
- Emissions Testing: OBD2 data is used to monitor vehicle emissions and ensure compliance with environmental regulations.
- Safety Research: OBD2 data is used to study vehicle safety and identify potential safety hazards.
26. Tips for Using OBD2 Adapters in Different Weather Conditions
Weather conditions can affect the performance of your OBD2 adapter. Here are some tips for using OBD2 adapters in different weather conditions:
- Extreme Heat: Avoid leaving your OBD2 adapter in direct sunlight for extended periods of time.
- Extreme Cold: Allow your OBD2 adapter to warm up before using it in extreme cold conditions.
- Humidity: Protect your OBD2 adapter from moisture and humidity.
27. The Future of Automotive Diagnostics with OBD2
OBD2 technology is paving the way for the future of automotive diagnostics.
- Predictive Maintenance: OBD2 data can be used to predict when certain components are likely to fail, allowing for proactive maintenance.
- Remote Diagnostics: OBD2 technology enables remote diagnostics, allowing mechanics to diagnose problems from afar.
- Artificial Intelligence: Artificial intelligence is being used to analyze OBD2 data and identify patterns that can help diagnose and prevent problems.
28. How to Extend the Life of Your OBD2 Mini ELM327 WiFi Adapter
To extend the life of your OBD2 mini ELM327 WiFi adapter, follow these tips:
- Store it properly: Store your OBD2 adapter in a cool, dry place when not in use.
- Protect it from damage: Avoid dropping or exposing your OBD2 adapter to extreme temperatures or moisture.
- Clean it regularly: Clean your OBD2 adapter with a soft, dry cloth.
- Handle it with care: Avoid bending or twisting the connector.
29. Case Studies: Real-World Examples of OBD2 Diagnostics
Here are a few case studies that illustrate the power of OBD2 diagnostics:
- Case Study 1: Misfire Diagnosis: A car owner was experiencing a misfire in their engine. By using an OBD2 adapter, they were able to identify a faulty ignition coil as the cause of the misfire.
- Case Study 2: Oxygen Sensor Failure: A car owner noticed a decrease in fuel efficiency. By using an OBD2 adapter, they were able to identify a faulty oxygen sensor as the cause of the problem.
- Case Study 3: EVAP System Leak: A car owner was experiencing an EVAP system leak. By using an OBD2 adapter, they were able to identify a loose gas cap as the cause of the leak.
These case studies demonstrate how OBD2 adapters can be used to diagnose a wide range of vehicle problems.
30. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About OBD2 Mini ELM327 WiFi Adapters
Here are some frequently asked questions about OBD2 mini ELM327 WiFi adapters:
- What is an OBD2 scanner?
An OBD2 scanner is a tool used to diagnose problems with a vehicle’s engine and other systems. It reads diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) stored in the vehicle’s computer. - How do I read OBD2 fault codes?
To read OBD2 fault codes, you need an OBD2 scanner and an OBD2 app. Connect the scanner to your vehicle’s OBD2 port, connect the scanner to your device via WiFi, launch the app, and follow the instructions to read the codes. - What are common car errors and how to fix them?
Common car errors include misfires, oxygen sensor failures, and EVAP system leaks. The fixes vary depending on the specific problem. - How do I clear a check engine light?
After repairing the problem that caused the check engine light to come on, you can use an OBD2 scanner to clear the DTCs and reset the light. - Are all OBD2 scanners compatible with all cars?
Most OBD2 scanners are compatible with all cars manufactured after 1996, but it’s essential to check the scanner’s compatibility list to be sure. - What is the difference between OBD1 and OBD2?
OBD1 is an older standard that was used in cars before 1996. OBD2 is a more advanced standard that provides more comprehensive diagnostic information. - Can an OBD2 scanner program car keys?
Some advanced OBD2 scanners can program car keys, but most basic scanners cannot. - Where is the OBD2 port located in my car?
The OBD2 port is typically located under the dashboard on the driver’s side of the car. - Do I need to turn the engine on to use an OBD2 scanner?
No, you only need to turn the ignition key to the “on” position. - How often should I scan my car with an OBD2 scanner?
You should scan your car with an OBD2 scanner whenever the check engine light comes on, or at least once a month for preventative maintenance.
31. Get Expert Help From OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN Today
Don’t let car troubles slow you down. At OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN, we’re here to help you diagnose and resolve any issues you may be experiencing with your vehicle. Our team of experienced automotive technicians can provide expert advice, comprehensive resources, and technical support to help you get back on the road.
For personalized assistance with using your OBD2 scanner and expert car repair services, contact us today:
- Address: 123 Main Street, Los Angeles, CA 90001, United States
- WhatsApp: +1 (641) 206-8880
- Website: OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN
Let OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN be your trusted partner in automotive diagnostics and repair. Contact us now and experience the difference.
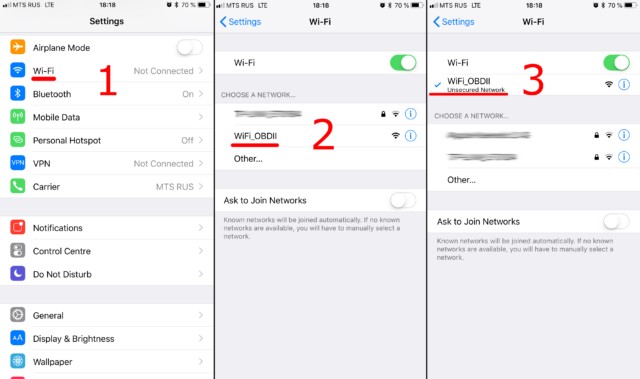 OBD2 Mini ELM327 WiFi Adapter Connected to Vehicle
OBD2 Mini ELM327 WiFi Adapter Connected to Vehicle
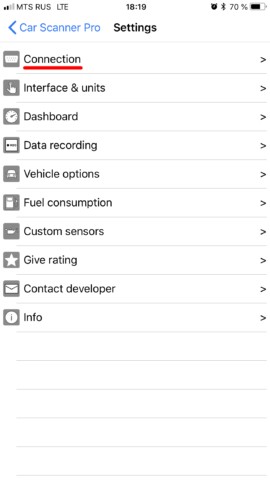
 Car Scanner Settings Screen for OBD2 Adapter Setup
Car Scanner Settings Screen for OBD2 Adapter Setup
 Selecting WiFi Connection Type in Car Scanner App
Selecting WiFi Connection Type in Car Scanner App
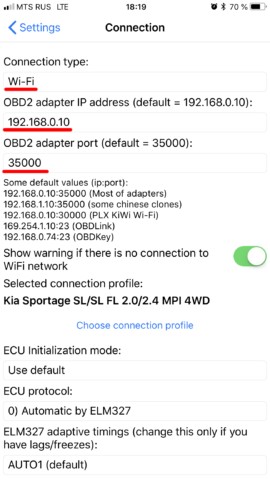 Car Scanner App Connection Progress Screen
Car Scanner App Connection Progress Screen