Obd2 Programming Software Free options exist and can be valuable tools for automotive enthusiasts and professionals alike, offering capabilities from basic diagnostics to more advanced vehicle customization, so let’s dive into the world of OBD2 programming and find out what options are available at OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN to help you make informed decisions about vehicle maintenance and performance. These software programs can allow you to read diagnostic trouble codes, monitor real-time data, and even perform some basic programming tasks.
Contents
- 1. Understanding OBD2 Programming Software
- 1.1 What is OBD2?
- 1.2 Why Use OBD2 Programming Software?
- 1.3 Common OBD2 Functions
- 2. Identifying Your OBD2 Needs
- 2.1 Diagnostic vs. Programming
- 2.2 Skill Level and Intended Use
- 2.3 Vehicle Compatibility
- 2.4 Necessary Hardware
- 3. Top Free OBD2 Programming Software Options
- 3.1 ScanTool.net
- 3.2 Torque Lite (Android)
- 3.3 OBD Auto Doctor
- 3.4 Forscan (Ford, Lincoln, Mercury)
- 3.5 PyOBD
- 4. Essential Features to Look For
- 4.1 Compatibility
- 4.2 User Interface
- 4.3 Functionality
- 4.4 Reporting and Data Logging
- 5. Step-by-Step Guide to Using OBD2 Software
- 5.1 Connecting the OBD2 Adapter
- 5.2 Installing and Setting Up the Software
- 5.3 Reading and Clearing DTCs
- 5.4 Monitoring Live Data
- 6. Safety Precautions and Best Practices
- 6.1 Data Security
- 6.2 Vehicle Safety
- 6.3 Legal Considerations
- 7. Troubleshooting Common Issues
- 7.1 Connection Problems
- 7.2 Software Errors
- 7.3 Inaccurate Data
- 8. Advanced OBD2 Programming Techniques
- 8.1 ECU Flashing and Tuning
- 8.2 Module Reprogramming
- 8.3 Parameter Identification (PID) Tuning
- 9. Case Studies: Real-World Applications
- 9.1 Diagnosing a Misfire
- 9.2 Monitoring Fuel Efficiency
- 9.3 Performing a Forced Regeneration on a Diesel Vehicle
- 10. Future Trends in OBD2 Technology
- 10.1 Integration with AI and Machine Learning
- 10.2 Enhanced Security Measures
- 10.3 Cloud Connectivity
- 11. OBD2 Programming Software Free: Advantages & Disadvantages
- 11.1 Advantages
- 11.2 Disadvantages
- 12. OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN: Your Partner in Automotive Diagnostics
- 13. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. Understanding OBD2 Programming Software
OBD2 programming software enables users to interact with a vehicle’s On-Board Diagnostics (OBD) system. These tools, ranging from simple code readers to sophisticated programming suites, read diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs), monitor real-time data, and perform certain programming tasks. Free software options offer a cost-effective entry point into vehicle diagnostics and customization, though it’s important to know their capabilities and limitations.
1.1 What is OBD2?
OBD2, or On-Board Diagnostics II, is a standardized system used in vehicles to monitor and control various engine and emissions-related parameters. It provides a way for technicians and vehicle owners to access information about the vehicle’s performance and diagnose potential issues. According to the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), OBD2 was mandated in all cars and light trucks sold in the United States starting in 1996 to ensure compliance with emissions standards.
1.2 Why Use OBD2 Programming Software?
OBD2 programming software can be useful for:
- Diagnosing vehicle problems: Read and clear diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs).
- Monitoring performance: View real-time data such as engine speed, temperature, and fuel consumption.
- Customization: Adjust certain vehicle settings and parameters, such as idle speed and shift points.
- DIY Repair: Allows you to potentially fix some car issues yourself.
- Cost Savings: Reduces the need to visit a professional mechanic for simple diagnostics.
1.3 Common OBD2 Functions
OBD2 software typically supports the following functions:
- Reading Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs): Identifies the source of a problem.
- Clearing DTCs: Resets the check engine light after repairs.
- Live Data Monitoring: Displays real-time sensor data.
- Freeze Frame Data: Captures data when a DTC is set.
- I/M Readiness Tests: Checks if the vehicle is ready for emissions testing.
- Vehicle Information: Retrieves VIN, calibration IDs, and other vehicle-specific information.
2. Identifying Your OBD2 Needs
Before diving into specific software, assess your needs. Are you a DIY enthusiast, a professional mechanic, or someone needing basic diagnostics? This will determine the software features you require. Basic users might only need to read and clear codes, while professionals need advanced functions.
2.1 Diagnostic vs. Programming
Understand the difference between diagnostic and programming functions:
- Diagnostic: Reading and clearing DTCs, monitoring live data, and performing basic system tests.
- Programming: Modifying the vehicle’s software or firmware, such as remapping the ECU or changing vehicle settings.
2.2 Skill Level and Intended Use
Consider your skill level:
- Beginner: Basic code reading and clearing, simple data monitoring.
- Intermediate: More in-depth data analysis, advanced diagnostics.
- Advanced: ECU tuning, module programming, and complex troubleshooting.
2.3 Vehicle Compatibility
Ensure the software supports your vehicle’s make, model, and year. Not all software works with all vehicles. Check compatibility lists before downloading.
2.4 Necessary Hardware
The right OBD2 adapter can make or break your programming or diagnostic process. Here are some recommendations.
- Bluetooth OBD2 Adapters
- Pros: Wireless connectivity, portability, and compatibility with smartphones and tablets.
- Cons: Potential security risks, limited data transfer speeds, and compatibility issues with some vehicles or software.
- Wi-Fi OBD2 Adapters
- Pros: Wireless connectivity, faster data transfer speeds than Bluetooth, and compatibility with multiple devices.
- Cons: Potential security risks, more expensive than Bluetooth adapters, and may require a Wi-Fi network.
- USB OBD2 Adapters
- Pros: Reliable wired connection, faster data transfer speeds, and compatibility with most vehicles and software.
- Cons: Limited portability, requires a computer with a USB port, and can be cumbersome to use in tight spaces.
3. Top Free OBD2 Programming Software Options
3.1 ScanTool.net
- Overview: ScanTool.net offers a variety of OBD2 software solutions, including a free version with basic diagnostic capabilities.
- Features:
- Read and clear DTCs
- View freeze frame data
- Monitor live data parameters
- Vehicle information retrieval
- Pros: User-friendly interface, broad vehicle support, reliable performance.
- Cons: Limited advanced features in the free version.
- User Experience: Simple interface suitable for beginners.
3.2 Torque Lite (Android)
- Overview: A popular Android app for OBD2 diagnostics, Torque Lite provides a range of features for monitoring vehicle performance.
- Features:
- Real-time data display
- DTC reading and clearing
- Customizable dashboards
- GPS tracking
- Pros: Easy to use, customizable, supports many Bluetooth OBD2 adapters.
- Cons: Limited functionality in the free version, requires an Android device.
- User Experience: Intuitive, visually appealing interface for mobile use.
3.3 OBD Auto Doctor
- Overview: OBD Auto Doctor is a comprehensive OBD2 diagnostic tool available for Windows, Mac, and Linux.
- Features:
- Readiness monitors
- Diagnostic trouble codes
- Live sensor data
- Emissions readiness
- Pros: Multi-platform support, detailed diagnostic information, user-friendly.
- Cons: Advanced features require a paid upgrade.
- User Experience: Well-organized and easy to navigate on various operating systems.
3.4 Forscan (Ford, Lincoln, Mercury)
- Overview: While not universal, Forscan is a powerful, free option for Ford, Lincoln, and Mercury vehicles.
- Features:
- Module programming
- Advanced diagnostics
- Service functions
- Custom configurations
- Pros: Dealer-level diagnostics for Ford vehicles, extensive customization options.
- Cons: Limited to Ford, Lincoln, and Mercury vehicles, requires a compatible OBD2 adapter.
- User Experience: Advanced interface designed for experienced users.
3.5 PyOBD
- Overview: PyOBD is an open-source OBD2 diagnostic tool written in Python.
- Features:
- DTC reading and clearing
- Live data monitoring
- Customizable data logging
- Support for multiple protocols
- Pros: Open-source, customizable, supports various OBD2 adapters.
- Cons: Requires technical knowledge, less user-friendly interface.
- User Experience: Suited for users with programming knowledge.
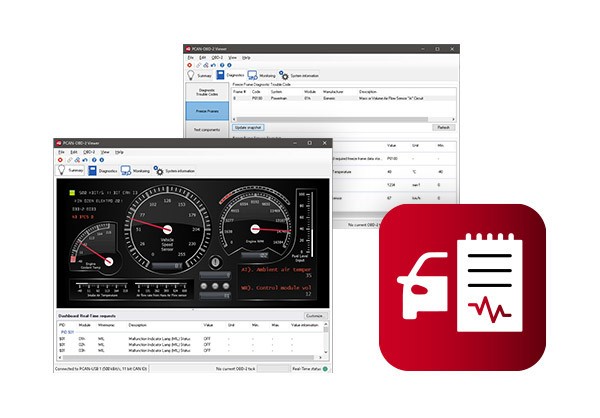 PyOBD Interface
PyOBD Interface
4. Essential Features to Look For
4.1 Compatibility
- Vehicle Makes and Models: Ensure the software supports your vehicle.
- Operating Systems: Check if it’s compatible with your computer or mobile device (Windows, macOS, Android, iOS).
- OBD2 Adapters: Verify compatibility with your OBD2 adapter (Bluetooth, Wi-Fi, USB).
4.2 User Interface
- Intuitive Design: Easy to navigate and understand.
- Customizable Dashboards: Ability to configure data displays.
- Clear Data Presentation: Graphs, charts, and numerical readouts.
4.3 Functionality
- DTC Reading and Clearing: Essential for diagnosing issues.
- Live Data Monitoring: Real-time sensor data for performance analysis.
- Freeze Frame Data: Snapshot of data when a DTC is set.
- Advanced Features: ECU programming, module configuration (if needed).
4.4 Reporting and Data Logging
- Data Logging: Ability to record and save data for analysis.
- Report Generation: Create detailed reports for diagnostics.
- Export Options: Export data in various formats (CSV, Excel).
5. Step-by-Step Guide to Using OBD2 Software
5.1 Connecting the OBD2 Adapter
- Locate the OBD2 Port: Typically under the dashboard on the driver’s side.
- Plug in the Adapter: Connect the OBD2 adapter to the port.
- Turn on the Ignition: Turn the key to the “on” position without starting the engine.
5.2 Installing and Setting Up the Software
- Download the Software: From the official website or app store.
- Install the Software: Follow the installation instructions.
- Configure the Software: Select the correct OBD2 adapter and communication protocol.
5.3 Reading and Clearing DTCs
- Connect to the Vehicle: Establish a connection between the software and the OBD2 adapter.
- Read DTCs: Select the “Read Codes” or similar option.
- Interpret the Codes: Look up the codes to understand the issue.
- Clear DTCs: Select the “Clear Codes” option to reset the check engine light.
5.4 Monitoring Live Data
- Select Live Data: Choose the parameters you want to monitor (e.g., engine speed, temperature).
- View Real-time Data: Observe the data displayed on the screen.
- Analyze the Data: Look for anomalies or out-of-range values.
6. Safety Precautions and Best Practices
6.1 Data Security
- Use Official Software: Download software from reputable sources.
- Secure Connections: Use secure Bluetooth or Wi-Fi connections.
- Update Software: Keep your software updated to patch security vulnerabilities.
6.2 Vehicle Safety
- Follow Instructions: Adhere to the software’s instructions and guidelines.
- Proper Tools: Use the correct OBD2 adapter and cables.
- Avoid Distractions: Do not operate the software while driving.
6.3 Legal Considerations
- Emissions Regulations: Be aware of local emissions regulations.
- Warranty Implications: Modifying vehicle settings may void the warranty.
- Data Privacy: Understand the software’s data collection policies.
7. Troubleshooting Common Issues
7.1 Connection Problems
- Check Adapter: Ensure the OBD2 adapter is properly connected.
- Verify Compatibility: Confirm the adapter is compatible with your vehicle and software.
- Restart Devices: Restart your computer or mobile device.
7.2 Software Errors
- Update Software: Ensure you have the latest version.
- Reinstall Software: Try reinstalling the software.
- Check Forums: Look for solutions in online forums or support communities.
7.3 Inaccurate Data
- Verify Sensor Data: Compare readings with other sources.
- Check Adapter: Ensure the OBD2 adapter is functioning correctly.
- Calibrate Sensors: Some software allows you to calibrate sensors.
8. Advanced OBD2 Programming Techniques
8.1 ECU Flashing and Tuning
- What It Is: ECU flashing involves overwriting the existing software on the vehicle’s Engine Control Unit (ECU) with a modified version. This is often done to improve performance, fuel efficiency, or customize specific parameters.
- Tools Required:
- ECU Flashing Software: Programs like WinOLS, EVC BDM100, or CMDFlash.
- OBD2 Interface: A reliable OBD2 adapter that supports ECU flashing.
- Battery Stabilizer: To ensure a stable voltage supply during the flashing process.
- Process:
- Backup Original ECU Data: Always create a backup of the original ECU software before making any changes.
- Modify the ECU File: Use ECU tuning software to adjust parameters such as fuel maps, ignition timing, and boost levels.
- Flash the ECU: Upload the modified file to the ECU using the flashing software.
- Risks and Precautions:
- Incorrect Flashing: Can lead to a bricked ECU, rendering the vehicle inoperable.
- Warranty Voidance: ECU modifications can void the vehicle’s warranty.
- Emissions Violations: Modifying emissions-related parameters can violate environmental regulations.
8.2 Module Reprogramming
- What It Is: Module reprogramming involves updating or replacing the software on other control modules in the vehicle, such as the Transmission Control Module (TCM), Anti-lock Braking System (ABS), or Body Control Module (BCM).
- Tools Required:
- Module Reprogramming Software: Typically OEM-specific software or advanced aftermarket tools like Autel MaxiSys or Bosch ESI[tronic].
- OBD2 Interface: A compatible OBD2 adapter that supports module reprogramming.
- Stable Power Supply: To maintain consistent voltage during the reprogramming process.
- Process:
- Identify the Module: Determine which module needs to be reprogrammed.
- Download the Latest Software: Obtain the latest software version from the vehicle manufacturer or a trusted source.
- Reprogram the Module: Follow the software’s instructions to reprogram the module.
- Risks and Precautions:
- Incorrect Software: Using the wrong software version can damage the module.
- Interrupted Reprogramming: Interruptions during the process can cause module failure.
- Compatibility Issues: Ensure the new software is compatible with the vehicle’s other systems.
8.3 Parameter Identification (PID) Tuning
- What It Is: PID tuning involves adjusting specific parameters within the ECU to optimize engine performance. This can include adjusting fuel trims, ignition timing, and other settings to achieve the desired results.
- Tools Required:
- OBD2 Data Logging Software: Programs like Datazap, or SCT Advantage.
- Wideband O2 Sensor: For accurate air/fuel ratio monitoring.
- Dynamometer: For measuring horsepower and torque gains.
- Process:
- Data Logging: Use the OBD2 software to log relevant engine parameters.
- Analyze the Data: Review the data to identify areas for improvement.
- Adjust Parameters: Make small adjustments to the ECU settings and re-log the data.
- Test and Refine: Repeat the process until the desired performance is achieved.
- Risks and Precautions:
- Over-Adjusting Parameters: Can lead to engine damage or reduced fuel efficiency.
- Inaccurate Data: Relying on faulty sensor data can result in incorrect tuning.
- Environmental Impact: Modifying emissions-related parameters can increase pollution.
9. Case Studies: Real-World Applications
9.1 Diagnosing a Misfire
Scenario: A vehicle experiences a misfire, causing rough idling and poor performance.
Tools Used: ScanTool.net (free version), OBD2 Bluetooth adapter.
Steps:
- Read DTCs: Connect the OBD2 adapter and use ScanTool.net to read the diagnostic trouble codes.
- Identify the Code: The software reports a P0301 code, indicating a misfire in cylinder 1.
- Inspect Cylinder 1: Check the spark plug, ignition coil, and fuel injector for cylinder 1.
- Replace Faulty Part: Replace the defective ignition coil.
- Clear DTCs: Clear the P0301 code and test drive the vehicle to confirm the misfire is resolved.
9.2 Monitoring Fuel Efficiency
Scenario: A driver wants to improve their vehicle’s fuel efficiency.
Tools Used: Torque Lite (Android), OBD2 Bluetooth adapter.
Steps:
- Connect OBD2 Adapter: Plug the Bluetooth adapter into the OBD2 port.
- Set Up Torque Lite: Pair the adapter with the Torque Lite app on an Android device.
- Monitor Fuel Consumption: Use the app to monitor real-time fuel consumption, engine load, and speed.
- Analyze Data: Identify driving habits that decrease fuel efficiency (e.g., aggressive acceleration, high speeds).
- Adjust Driving Habits: Modify driving behavior to improve fuel economy.
9.3 Performing a Forced Regeneration on a Diesel Vehicle
Scenario: A diesel vehicle’s Diesel Particulate Filter (DPF) is clogged, requiring a forced regeneration.
Tools Used: Forscan (Ford), OBD2 USB adapter.
Steps:
- Connect OBD2 Adapter: Plug the USB adapter into the OBD2 port.
- Set Up Forscan: Launch the Forscan software on a computer.
- Initiate Forced Regeneration: Use Forscan to initiate the forced DPF regeneration procedure.
- Monitor Process: Follow the software’s instructions and monitor the regeneration process.
- Verify Completion: Ensure the regeneration completes successfully and clear any related DTCs.
 Teensy 4.1 Triple CAN Bus Board
Teensy 4.1 Triple CAN Bus Board
10. Future Trends in OBD2 Technology
10.1 Integration with AI and Machine Learning
- Predictive Diagnostics: AI-powered software can predict potential issues before they occur.
- Personalized Recommendations: Tailored maintenance recommendations based on driving habits.
- Automated Troubleshooting: AI algorithms can guide users through complex diagnostic procedures.
10.2 Enhanced Security Measures
- Secure Boot: Ensures only authorized software runs on the vehicle’s ECU.
- Encryption: Protects sensitive data transmitted over the OBD2 port.
- Intrusion Detection: Monitors for unauthorized access attempts.
10.3 Cloud Connectivity
- Remote Diagnostics: Technicians can remotely diagnose and troubleshoot vehicle issues.
- Over-the-Air Updates: Software updates can be delivered wirelessly.
- Data Sharing: Vehicle data can be shared with manufacturers and service providers.
11. OBD2 Programming Software Free: Advantages & Disadvantages
11.1 Advantages
Affordability: The primary advantage of free OBD2 programming software is its cost-free availability, making it accessible to a wide range of users, including hobbyists, DIY enthusiasts, and small repair shops.
Basic Diagnostics: Free software options often provide essential diagnostic features such as reading and clearing diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs), viewing freeze frame data, and accessing basic sensor information.
Ease of Use: Many free OBD2 software programs are designed with user-friendly interfaces, making them easy to navigate and operate, especially for beginners and non-technical users.
Compatibility: Some free software options offer broad compatibility with various vehicle makes and models, as well as different operating systems (e.g., Windows, Android, iOS), providing flexibility and convenience for users.
*Community Support: Open-source and community-driven free software often have active online forums and communities where users can share tips, troubleshoot issues, and access resources.
11.2 Disadvantages
Limited Functionality: Free OBD2 programming software typically offers limited functionality compared to paid or professional-grade options. Advanced features such as ECU programming, module configuration, and bidirectional control may not be available.
Incomplete Vehicle Coverage: Some free software options may have limited vehicle coverage, meaning they may not support all makes, models, and years of vehicles. This can restrict their usefulness for users with diverse vehicle fleets.
Potential Risks: Downloading and installing software from unverified sources can pose security risks, including malware infections, data breaches, and system instability. It’s essential to download free software only from reputable websites or app stores.
Lack of Updates and Support: Free software may not receive regular updates or dedicated technical support, which can lead to compatibility issues, bugs, and security vulnerabilities over time.
*Accuracy and Reliability: The accuracy and reliability of free OBD2 programming software can vary, and some options may provide inaccurate or incomplete information. This can lead to misdiagnoses and incorrect repairs, potentially causing further damage to the vehicle.
12. OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN: Your Partner in Automotive Diagnostics
At OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN, we understand the challenges you face in diagnosing and repairing vehicles. That’s why we offer a range of solutions to help you stay ahead:
- Expert Guidance: Our team of experienced technicians provides expert advice and support.
- Comprehensive Resources: Access a library of articles, guides, and tutorials on OBD2 diagnostics and repair.
- Advanced Tools: Explore our selection of professional-grade OBD2 scanners and software.
- Custom Solutions: We tailor solutions to meet your specific needs and budget.
13. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- What is an OBD2 scanner?
An OBD2 scanner is a device used to access and interpret data from a vehicle’s On-Board Diagnostics system, helping diagnose issues and monitor performance. - Is OBD2 programming software free really free?
Some OBD2 programming software is available for free, but it often comes with limited features. Advanced functionalities usually require a paid version. - How do I read OBD2 codes?
Connect an OBD2 scanner to your vehicle’s OBD2 port, turn on the ignition, and use the scanner to read the diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) displayed. - Can I clear OBD2 codes myself?
Yes, you can clear OBD2 codes using an OBD2 scanner or software, but it’s important to address the underlying issue first to prevent the code from reappearing. - What are common OBD2 error codes and how do I fix them?
Common OBD2 error codes include P0300 (random misfire), P0171 (system too lean), and P0420 (catalyst system efficiency below threshold). Fixes vary depending on the specific code. - What is the difference between OBD2 and OBD1?
OBD1 is an older, less standardized system, while OBD2 is a standardized system used in vehicles since 1996, providing more comprehensive diagnostic information. - Do I need special training to use OBD2 software?
Basic OBD2 software is user-friendly, but advanced features and programming require technical knowledge and training. - What are the best OBD2 adapters to use with free software?
Popular OBD2 adapters include those from brands like Veepeak, OBDLink, and BAFX Products, ensuring compatibility with your chosen software. - Can OBD2 software improve my car’s performance?
OBD2 software can help you monitor and optimize your car’s performance by providing data and allowing you to adjust certain parameters, but significant improvements often require professional tuning. - How often should I scan my car with an OBD2 scanner?
You should scan your car whenever you notice a warning light or suspect an issue. Regular scans can also help identify potential problems early on. - Is it safe to modify my car’s ECU with OBD2 programming software?
Modifying your car’s ECU can be risky and may void your warranty. It’s best to consult with a professional tuner before making any changes. - Will using free OBD2 programming software void my car’s warranty?
Using free OBD2 programming software for diagnostics typically won’t void your warranty, but modifying your car’s ECU or other systems may do so. - What kind of customer support is available for free OBD2 programming software?
Customer support for free OBD2 programming software is often limited to online forums and community resources, with no guaranteed assistance from developers. - What should I do if my OBD2 scanner can’t connect to my car?
Ensure your OBD2 scanner is properly connected, compatible with your car, and powered on. Check your car’s OBD2 port for any damage or obstructions.
Navigating the world of OBD2 programming can be complex, but with the right tools and knowledge, you can effectively diagnose and maintain your vehicle. At OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN, we’re here to support you every step of the way.
Ready to take control of your vehicle’s diagnostics? Contact us today for expert guidance and solutions tailored to your needs!
Address: 123 Main Street, Los Angeles, CA 90001, United States
WhatsApp: +1 (641) 206-8880
Website: OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN