Using an Obd2 Scanner Elm327 Wifi is a straightforward way to diagnose car problems. This guide from OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN simplifies the process, empowering you to troubleshoot your vehicle efficiently. Learn how to connect your device and interpret data for informed maintenance decisions.
Contents
- 1. What is an OBD2 Scanner ELM327 WiFi and How Does it Work?
- 1.1 Why Use an ELM327 WiFi Scanner?
- 1.2 Basic Functionality of an OBD2 Scanner
- 2. What are the Key Benefits of Using an OBD2 Scanner?
- 2.1 Early Detection of Problems
- 2.2 Cost Savings
- 2.3 Improved Fuel Efficiency
- 2.4 Informed Decision Making
- 2.5 Emission Compliance
- 3. How to Choose the Right OBD2 Scanner ELM327 WiFi?
- 3.1 Compatibility
- 3.2 Features
- 3.3 Software and App Support
- 3.4 Ease of Use
- 3.5 Reviews and Ratings
- 4. Step-by-Step Guide: How to Connect and Use an OBD2 Scanner ELM327 WiFi
- 4.1 Step 1: Prepare Your Device
- 4.2 Step 2: Locate the OBD2 Port
- 4.3 Step 3: Plug in the OBD2 Scanner
- 4.4 Step 4: Turn on the Ignition
- 4.5 Step 5: Connect to the Scanner’s WiFi Network
- 4.6 Step 6: Open the OBD2 App
- 4.7 Step 7: Configure the App
- 4.8 Step 8: Connect to the Vehicle
- 4.9 Step 9: Read and Interpret Data
- 5. What Are Common OBD2 Codes and Their Meanings?
- 5.1 P0171 – System Too Lean (Bank 1)
- 5.2 P0300 – Random/Multiple Cylinder Misfire Detected
- 5.3 P0420 – Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold (Bank 1)
- 5.4 P0113 – Intake Air Temperature Sensor Circuit High Input
- 5.5 P0011 – “A” Camshaft Position – Timing Over-Advanced or System Performance (Bank 1)
- 5.6 Table of Common OBD2 Codes
- 6. How to Interpret Live Data from an OBD2 Scanner?
- 6.1 Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT)
- 6.2 Oxygen Sensor Voltage
- 6.3 Mass Air Flow (MAF)
- 6.4 Fuel Trim
- 6.5 Engine RPM
- 7. What Are the Best Apps for OBD2 Scanner ELM327 WiFi?
- 7.1 Torque Pro
- 7.2 OBD Fusion
- 7.3 Car Scanner ELM OBD2
- 7.4 BimmerCode
- 7.5 Dr. Prius/Dr. Hybrid
- 8. What Are Common Issues and Troubleshooting Tips?
- 8.1 Cannot Connect to the Scanner
- 8.2 Cannot Read Diagnostic Codes
- 8.3 Inaccurate Data
- 8.4 App Crashes or Freezes
- 9. What Are the Limitations of Using an OBD2 Scanner?
- 9.1 Limited to Powertrain Issues
- 9.2 Basic Diagnostic Information
- 9.3 Requires Technical Knowledge
- 9.4 Not a Substitute for Professional Diagnosis
- 10. How Can OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN Help You With Your Car Diagnostics and Repairs?
- 10.1 Expert Guidance and Support
- 10.2 Comprehensive OBD2 Resources
- 10.3 High-Quality Diagnostic Tools
- 10.4 Repair Services
- 10.5 Training Programs
- FAQ: Common Questions About OBD2 Scanners
- What is an OBD2 scanner?
- How do I read OBD2 fault codes?
- Can an OBD2 scanner clear fault codes?
- What cars are compatible with OBD2 scanners?
- Do OBD2 scanners read ABS codes?
- Can an OBD2 scanner test car batteries?
- Is it safe to drive with an OBD2 scanner plugged in?
- What do I do if my OBD2 scanner won’t connect?
- Can OBD2 scanners provide real-time data?
- How often should I use an OBD2 scanner?
1. What is an OBD2 Scanner ELM327 WiFi and How Does it Work?
An OBD2 scanner ELM327 WiFi is a diagnostic tool that retrieves data from your vehicle’s On-Board Diagnostics (OBD) system via a wireless connection. This device plugs into your car’s OBD2 port, usually located under the dashboard, and transmits data to your smartphone, tablet, or laptop through a WiFi connection. According to a study by the Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE), the OBD2 system was standardized in 1996 in the United States to monitor engine performance and emissions. The ELM327 is a microcontroller that interprets the OBD2 protocols, allowing you to read diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs), view live sensor data, and perform other diagnostic functions.
1.1 Why Use an ELM327 WiFi Scanner?
Using an ELM327 WiFi scanner offers several advantages:
- Wireless Convenience: Connects to your device without needing cables.
- Cost-Effective: Affordable compared to professional diagnostic tools.
- User-Friendly: Many compatible apps simplify data interpretation.
- Real-Time Data: Provides live sensor readings for accurate diagnostics.
- Portability: Small and easy to carry, allowing for on-the-go diagnostics.
1.2 Basic Functionality of an OBD2 Scanner
The primary function of an OBD2 scanner is to access and interpret data from your vehicle’s computer. This data includes:
- Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs): These codes indicate specific problems in the engine, transmission, and other systems.
- Live Sensor Data: Real-time readings from various sensors, such as engine temperature, oxygen sensor voltage, and mass airflow.
- Freeze Frame Data: A snapshot of sensor values when a DTC was triggered, aiding in problem diagnosis.
- Vehicle Information: Retrieves the vehicle identification number (VIN) and calibration information.
- Emission Readiness Tests: Checks if the vehicle has completed the necessary tests for emissions compliance.
2. What are the Key Benefits of Using an OBD2 Scanner?
Using an OBD2 scanner can significantly improve your car maintenance routine, offering numerous advantages. According to a 2022 report by the National Institute for Automotive Service Excellence (ASE), regular diagnostics can prevent costly repairs and extend vehicle lifespan.
2.1 Early Detection of Problems
Identifying issues early can prevent minor problems from turning into major, expensive repairs. By regularly scanning your vehicle, you can catch issues like a faulty oxygen sensor or a misfiring engine before they cause significant damage.
2.2 Cost Savings
Diagnosing issues yourself can save money on diagnostic fees at a mechanic. Knowing the problem beforehand allows you to discuss repairs more knowledgeably and avoid unnecessary services.
2.3 Improved Fuel Efficiency
Many engine problems can reduce fuel efficiency. By identifying and fixing these issues, you can improve your car’s MPG and save money on gas.
2.4 Informed Decision Making
Having diagnostic information empowers you to make informed decisions about repairs. You can research the issue, get multiple quotes, and decide whether to fix it yourself or take it to a professional.
2.5 Emission Compliance
Regularly checking your vehicle’s emission readiness can help you avoid failing an emissions test. Addressing any issues beforehand ensures your car meets environmental standards.
3. How to Choose the Right OBD2 Scanner ELM327 WiFi?
Selecting the right OBD2 scanner ELM327 WiFi involves considering several factors to ensure it meets your needs. Here are some key points to consider:
3.1 Compatibility
Ensure the scanner is compatible with your vehicle’s make, model, and year. Most OBD2 scanners work with vehicles manufactured after 1996, but it’s always best to verify compatibility.
3.2 Features
Consider the features you need. Basic scanners read and clear DTCs, while advanced models offer live data, freeze frame data, and advanced diagnostic functions.
3.3 Software and App Support
The scanner’s compatibility with various apps can significantly enhance its functionality. Look for scanners that work with popular apps like Torque Pro, OBD Fusion, and Car Scanner ELM OBD2.
3.4 Ease of Use
Choose a scanner that is easy to set up and use. The interface should be intuitive, and the app should provide clear and understandable data.
3.5 Reviews and Ratings
Check online reviews and ratings to get an idea of the scanner’s performance and reliability. Look for scanners with positive reviews and high ratings from other users.
4. Step-by-Step Guide: How to Connect and Use an OBD2 Scanner ELM327 WiFi
Here’s a detailed guide on how to connect and use an OBD2 scanner ELM327 WiFi:
4.1 Step 1: Prepare Your Device
Before you begin, make sure you have the following:
- An OBD2 scanner ELM327 WiFi
- A smartphone, tablet, or laptop with WiFi capability
- A compatible OBD2 app installed on your device
- Your vehicle parked in a safe location
4.2 Step 2: Locate the OBD2 Port
The OBD2 port is usually located under the dashboard on the driver’s side. Common locations include:
- Under the steering wheel column
- Near the center console
- Inside the glove box (less common)
Refer to your vehicle’s manual if you cannot find the port.
4.3 Step 3: Plug in the OBD2 Scanner
Insert the OBD2 scanner into the OBD2 port. Ensure it is securely connected. Some scanners have a power button that needs to be turned on.
4.4 Step 4: Turn on the Ignition
Turn the ignition to the “ON” position without starting the engine. This provides power to the OBD2 system.
4.5 Step 5: Connect to the Scanner’s WiFi Network
On your smartphone or tablet, go to the WiFi settings and search for available networks. The OBD2 scanner will broadcast a WiFi network, usually named “OBDII,” “OBD2,” or something similar. Connect to this network. Most scanners do not require a password, but if prompted, refer to the scanner’s documentation.
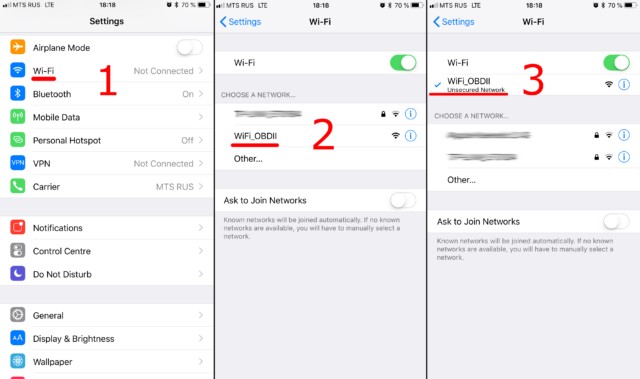 Connect to WiFi network created by ELM327 OBDII adapter
Connect to WiFi network created by ELM327 OBDII adapter
4.6 Step 6: Open the OBD2 App
Launch the OBD2 app on your device.
4.7 Step 7: Configure the App
In the app settings, select “WiFi” as the connection type. You may need to enter the IP address and port number for the scanner. The default IP address is usually 192.168.0.10, and the port number is 35000. Refer to your scanner’s documentation for the correct settings.
4.8 Step 8: Connect to the Vehicle
Tap the “Connect” button in the app. The app will establish a connection with the OBD2 scanner and begin retrieving data from your vehicle’s computer.
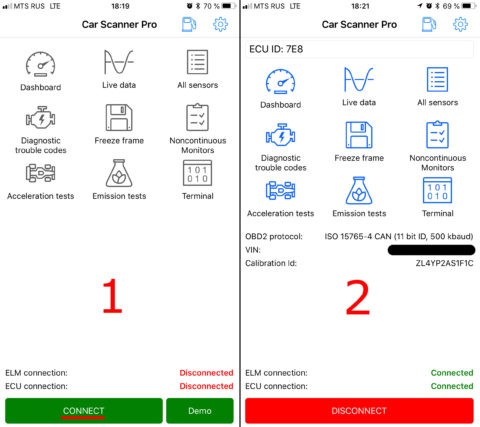 Connect to OBD2 scanner with Car Scanner app
Connect to OBD2 scanner with Car Scanner app
4.9 Step 9: Read and Interpret Data
Once connected, you can read diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs), view live sensor data, and perform other diagnostic functions. The app will display the DTCs with descriptions, helping you understand the problem.
5. What Are Common OBD2 Codes and Their Meanings?
Understanding common OBD2 codes can help you diagnose and address vehicle issues more effectively. Here’s a list of some frequent codes and their typical meanings:
5.1 P0171 – System Too Lean (Bank 1)
This code indicates that the engine is running with too much air and not enough fuel in bank 1. Common causes include:
- Vacuum leaks
- Faulty oxygen sensor
- Dirty mass airflow sensor
- Fuel injector problems
5.2 P0300 – Random/Multiple Cylinder Misfire Detected
This code indicates that the engine is experiencing misfires in multiple cylinders. Possible causes include:
- Faulty spark plugs
- Bad ignition coils
- Vacuum leaks
- Low fuel pressure
5.3 P0420 – Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold (Bank 1)
This code indicates that the catalytic converter is not functioning efficiently. Common causes include:
- Faulty catalytic converter
- Oxygen sensor problems
- Exhaust leaks
5.4 P0113 – Intake Air Temperature Sensor Circuit High Input
This code indicates a problem with the intake air temperature (IAT) sensor circuit. Possible causes include:
- Faulty IAT sensor
- Wiring problems
- Loose connections
5.5 P0011 – “A” Camshaft Position – Timing Over-Advanced or System Performance (Bank 1)
This code indicates a problem with the camshaft timing. Common causes include:
- Faulty camshaft position sensor
- Oil flow issues
- Timing chain problems
5.6 Table of Common OBD2 Codes
| Code | Description | Possible Causes |
|---|---|---|
| P0171 | System Too Lean (Bank 1) | Vacuum leaks, faulty oxygen sensor, dirty mass airflow sensor, fuel injector problems |
| P0300 | Random/Multiple Cylinder Misfire Detected | Faulty spark plugs, bad ignition coils, vacuum leaks, low fuel pressure |
| P0420 | Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold (Bank 1) | Faulty catalytic converter, oxygen sensor problems, exhaust leaks |
| P0113 | Intake Air Temperature Sensor Circuit High Input | Faulty IAT sensor, wiring problems, loose connections |
| P0011 | “A” Camshaft Position – Timing Over-Advanced or System Performance (Bank 1) | Faulty camshaft position sensor, oil flow issues, timing chain problems |
| P0301 | Cylinder 1 Misfire Detected | Faulty spark plug, bad ignition coil, fuel injector problem, low compression |
| P0401 | Exhaust Gas Recirculation Flow Insufficient Detected | Clogged EGR valve, faulty EGR solenoid, vacuum leaks |
| P0102 | Mass or Volume Air Flow Circuit Low Input | Dirty or faulty MAF sensor, wiring problems, vacuum leaks |
| P0505 | Idle Air Control System Malfunction | Faulty IAC valve, vacuum leaks, throttle body issues |
| P0135 | O2 Sensor Heater Circuit Malfunction (Bank 1, Sensor 1) | Faulty oxygen sensor, wiring problems, blown fuse |
6. How to Interpret Live Data from an OBD2 Scanner?
Interpreting live data from an OBD2 scanner can provide valuable insights into your vehicle’s performance. Here’s how to understand some key parameters:
6.1 Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT)
The ECT sensor measures the temperature of the engine coolant. Normal operating temperature is typically between 195°F and 220°F (90°C and 104°C). High or low readings can indicate problems with the cooling system.
6.2 Oxygen Sensor Voltage
Oxygen sensors measure the amount of oxygen in the exhaust gas. The voltage should fluctuate between 0.1V and 0.9V. A steady voltage can indicate a faulty sensor.
6.3 Mass Air Flow (MAF)
The MAF sensor measures the amount of air entering the engine. Readings vary depending on engine size and load. Unusual readings can indicate a dirty or faulty MAF sensor.
6.4 Fuel Trim
Fuel trim values indicate how much the engine control unit (ECU) is adjusting the fuel mixture. Positive values mean the ECU is adding fuel, while negative values mean it is reducing fuel. High values can indicate vacuum leaks or fuel delivery problems.
6.5 Engine RPM
Engine RPM (revolutions per minute) measures how fast the engine is turning. Normal idle RPM is typically between 600 and 1000 RPM. Unstable or high idle RPM can indicate various issues.
7. What Are the Best Apps for OBD2 Scanner ELM327 WiFi?
Choosing the right app can greatly enhance the functionality of your OBD2 scanner. Here are some of the best apps available:
7.1 Torque Pro
Torque Pro is a popular app for Android devices. It offers a wide range of features, including:
- Real-time data monitoring
- DTC reading and clearing
- Customizable dashboards
- Performance testing
7.2 OBD Fusion
OBD Fusion is available for both iOS and Android devices. It provides:
- Comprehensive diagnostic information
- Live data graphing
- Emission readiness tests
- Support for multiple vehicles
7.3 Car Scanner ELM OBD2
Car Scanner ELM OBD2 is a user-friendly app with:
- Customizable profiles for different vehicles
- Advanced diagnostic features
- Support for a wide range of OBD2 adapters
- Easy-to-read data displays
7.4 BimmerCode
BimmerCode is specifically designed for BMW and Mini vehicles. It allows you to:
- Customize vehicle settings
- Read and clear diagnostic codes
- Access advanced diagnostic functions
7.5 Dr. Prius/Dr. Hybrid
Dr. Prius and Dr. Hybrid are designed for Toyota and Lexus hybrid vehicles. They offer:
- Hybrid battery health checks
- Live data monitoring
- Diagnostic code reading and clearing
8. What Are Common Issues and Troubleshooting Tips?
While OBD2 scanners are user-friendly, you may encounter some issues. Here are common problems and how to troubleshoot them:
8.1 Cannot Connect to the Scanner
- Problem: The app cannot connect to the OBD2 scanner.
- Solution:
- Ensure the scanner is securely plugged into the OBD2 port.
- Verify the scanner has power (if it has a power button).
- Make sure your device is connected to the scanner’s WiFi network.
- Check the IP address and port number in the app settings.
- Restart your device and try again.
8.2 Cannot Read Diagnostic Codes
- Problem: The app cannot read diagnostic codes from the vehicle.
- Solution:
- Ensure the ignition is turned to the “ON” position.
- Verify the scanner is compatible with your vehicle.
- Try a different OBD2 app.
- Check for any physical damage to the OBD2 port or scanner.
8.3 Inaccurate Data
- Problem: The data displayed by the app seems inaccurate.
- Solution:
- Ensure the app is using the correct vehicle profile.
- Check for any updates to the app or scanner firmware.
- Try a different OBD2 app to see if the issue persists.
- Verify the accuracy of the sensor readings with a professional mechanic.
8.4 App Crashes or Freezes
- Problem: The OBD2 app crashes or freezes frequently.
- Solution:
- Close other apps running in the background.
- Clear the app’s cache and data.
- Reinstall the app.
- Ensure your device meets the app’s minimum system requirements.
9. What Are the Limitations of Using an OBD2 Scanner?
While OBD2 scanners are valuable tools, they have limitations:
9.1 Limited to Powertrain Issues
OBD2 systems primarily monitor the engine, transmission, and emissions-related components. They may not provide information about other systems, such as the brakes, suspension, or airbags.
9.2 Basic Diagnostic Information
OBD2 scanners provide basic diagnostic information, such as DTCs and live data. They may not offer advanced diagnostic capabilities, such as bidirectional control or component testing.
9.3 Requires Technical Knowledge
Interpreting the data from an OBD2 scanner requires some technical knowledge. Understanding DTCs, sensor readings, and other parameters can be challenging for novice users.
9.4 Not a Substitute for Professional Diagnosis
While an OBD2 scanner can help you identify problems, it is not a substitute for a professional diagnosis. Complex issues may require specialized tools and expertise to diagnose accurately.
10. How Can OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN Help You With Your Car Diagnostics and Repairs?
At OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN, we understand the challenges of diagnosing and repairing modern vehicles. Our mission is to provide you with the knowledge, tools, and support you need to keep your car running smoothly.
10.1 Expert Guidance and Support
Our team of experienced automotive technicians is available to provide expert guidance and support. Whether you’re a seasoned mechanic or a DIY enthusiast, we can help you interpret diagnostic data, troubleshoot problems, and find the right solutions.
10.2 Comprehensive OBD2 Resources
We offer a comprehensive library of OBD2 resources, including:
- Detailed explanations of DTCs
- Troubleshooting guides
- Tips for using OBD2 scanners
- Information on vehicle-specific diagnostic procedures
10.3 High-Quality Diagnostic Tools
We offer a wide selection of high-quality OBD2 scanners and diagnostic tools from leading brands. Our products are tested and verified to ensure accuracy and reliability.
10.4 Repair Services
If you need help with repairs, our network of certified mechanics can provide professional services. We can connect you with trusted repair shops in your area that offer competitive pricing and quality workmanship.
10.5 Training Programs
We offer training programs for automotive technicians and DIY enthusiasts. Our courses cover a wide range of topics, including:
- OBD2 diagnostics
- Engine repair
- Electrical systems
- Advanced troubleshooting techniques
Navigating car diagnostics and repairs can be challenging, but with the right tools and guidance, you can keep your vehicle running smoothly and avoid costly repairs. Don’t hesitate to reach out for personalized support. Contact us today at +1 (641) 206-8880 or visit our website at OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN for expert assistance. Our address is 123 Main Street, Los Angeles, CA 90001, United States.
FAQ: Common Questions About OBD2 Scanners
What is an OBD2 scanner?
An OBD2 scanner is a tool used to read diagnostic information from a vehicle’s onboard computer system. It helps identify issues by reading diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) and providing live sensor data.
How do I read OBD2 fault codes?
To read OBD2 fault codes, plug the scanner into the OBD2 port, turn on the ignition, and use the scanner’s interface or a connected app to retrieve and interpret the codes.
Can an OBD2 scanner clear fault codes?
Yes, most OBD2 scanners can clear fault codes after you’ve addressed the underlying issue. However, clearing codes without fixing the problem will only result in the codes reappearing.
What cars are compatible with OBD2 scanners?
Most cars manufactured after 1996 are OBD2-compatible. However, it’s always a good idea to check your vehicle’s manual or the scanner’s compatibility list to be sure.
Do OBD2 scanners read ABS codes?
Some advanced OBD2 scanners can read ABS (Anti-lock Braking System) codes, but basic models may only read engine and transmission codes.
Can an OBD2 scanner test car batteries?
While OBD2 scanners can provide information about the charging system voltage, they typically don’t offer comprehensive battery testing capabilities. Dedicated battery testers are more suitable for this purpose.
Is it safe to drive with an OBD2 scanner plugged in?
Generally, it’s safe to drive with an OBD2 scanner plugged in, but it’s best to use it primarily for diagnostics and remove it when not needed.
What do I do if my OBD2 scanner won’t connect?
Ensure the scanner is properly plugged in, the ignition is on, and your device is connected to the scanner’s network. Also, verify compatibility and update the scanner’s software if necessary.
Can OBD2 scanners provide real-time data?
Yes, many OBD2 scanners can provide real-time data, such as engine temperature, RPM, and sensor readings, helping you monitor your vehicle’s performance.
How often should I use an OBD2 scanner?
You should use an OBD2 scanner whenever you suspect an issue with your vehicle or when the check engine light comes on. Regular scans can also help catch minor problems before they become major repairs.
With the right knowledge and tools, you can confidently diagnose and address many common car problems. Remember, OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN is here to support you every step of the way. Contact us for expert advice and assistance!
