Obd2 Scanner Uses are multifaceted, empowering you to diagnose car problems, understand their causes, and potentially save on repair costs. OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN offers insights and solutions to help you effectively utilize these tools for optimal vehicle maintenance. Understanding how to use an OBD2 scanner is crucial for both DIY enthusiasts and professional mechanics.
Contents
- 1. What Is an OBD2 Scanner and What Are Its Core Uses?
- 1.1 Understanding Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
- 1.2 Accessing Live Data for Real-Time Monitoring
- 1.3 Verifying Emissions Readiness
- 1.4 Contact OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN for Expert Guidance
- 2. How to Connect and Set Up Your OBD2 Scanner
- 2.1 Locating the OBD2 Port
- 2.2 Connecting the Scanner
- 2.3 Powering Up the Scanner
- 2.4 Initial Setup
- 2.5 OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN Can Help You Connect Your Scanner
- 3. Understanding the OBD2 Scanner Interface and Its Functions
- 3.1 Navigating the Menu
- 3.2 Reading Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
- 3.3 Erasing Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
- 3.4 Accessing Live Data
- 3.5 Utilizing Freeze Frame Data
- 3.6 OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN Explains Scanner Functions
- 4. Deciphering Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
- 4.1 Understanding the DTC Structure
- 4.2 Common DTC Examples and Their Meanings
- 4.3 Using Online Resources for DTC Lookup
- 4.4 Seeking Professional Assistance
- 4.5 OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN Decodes Your DTCs
- 5. Performing Common Diagnostic Tests with an OBD2 Scanner
- 5.1 Oxygen Sensor Testing
- 5.2 Misfire Detection
- 5.3 Fuel Trim Analysis
- 5.4 Evaporative Emissions (EVAP) System Testing
- 5.5 Battery and Charging System Analysis
- 5.6 OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN Guides You Through Diagnostic Tests
- 6. Saving Money on Auto Repairs with an OBD2 Scanner
- 6.1 Identifying Problems Early
- 6.2 Avoiding Unnecessary Repairs
- 6.3 Performing DIY Repairs
- 6.4 Negotiating with Mechanics
- 6.5 Checking Smog Test Readiness
- 6.6 OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN Helps You Save on Repairs
- 7. Choosing the Right OBD2 Scanner for Your Needs
- 7.1 Types of Scanners
- 7.2 Features to Consider
- 7.3 Compatibility
- 7.4 Price Range
- 7.5 Wireless vs. Wired
- 7.6 OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN Helps You Choose the Right Scanner
- 8. Advanced OBD2 Scanner Uses: Beyond Basic Code Reading
- 8.1 Bi-Directional Control
- 8.2 Key Programming
- 8.3 Module Programming
- 8.4 Data Logging
- 8.5 Custom Parameter Identification (PID)
- 8.6 OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN Provides Advanced Diagnostic Solutions
- 9. Common Mistakes to Avoid When Using an OBD2 Scanner
- 9.1 Not Connecting the Scanner Properly
- 9.2 Misinterpreting DTCs
- 9.3 Erasing Codes Without Fixing the Problem
- 9.4 Relying Solely on the Scanner
- 9.5 Neglecting Software Updates
- 9.6 OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN Helps You Avoid Common Mistakes
- 10. Maintaining and Storing Your OBD2 Scanner
- 10.1 Cleaning the Scanner
- 10.2 Protecting the Cable
- 10.3 Storing the Scanner in a Safe Place
- 10.4 Replacing Batteries
- 10.5 Calibrating the Scanner
- 10.6 OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN Offers Maintenance Tips
- FAQ: Frequently Asked Questions About OBD2 Scanner Uses
- What is an OBD2 scanner used for?
- Does the car have to be running to use an OBD2 scanner?
- How do I read my OBD scanner?
- Can you plug in an OBD scanner while the car is running?
- What do the different letters in an OBD2 code mean?
- What is live data on an OBD2 scanner?
- How do I clear a check engine light with an OBD2 scanner?
- Can an OBD2 scanner tell me what’s wrong with my car?
- What’s the difference between a basic OBD2 scanner and an advanced scan tool?
- Where can I get help using my OBD2 scanner?
1. What Is an OBD2 Scanner and What Are Its Core Uses?
An OBD2 (On-Board Diagnostics II) scanner is a tool that accesses a vehicle’s computer system to diagnose problems and monitor performance. OBD2 scanner uses include reading diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs), accessing live data, and checking emissions readiness, making it a valuable asset for vehicle maintenance and repair.
The OBD2 system became mandatory in all cars sold in the US after 1996 to standardize emissions monitoring, as noted by the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). This standardization means that any OBD2 scanner can communicate with any compatible vehicle, simplifying diagnostics across different makes and models. These scanners connect to a 16-pin port, typically located under the dashboard on the driver’s side. By plugging into this port, users can access a wealth of information about their vehicle’s operation.
1.1 Understanding Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
DTCs are alphanumeric codes that pinpoint specific issues within the vehicle. When a problem occurs, the vehicle’s computer stores a relevant DTC. Reading these codes is one of the most common OBD2 scanner uses.
- Generic vs. Manufacturer-Specific Codes: DTCs beginning with “P0” are generic and apply to all vehicles. Codes starting with “P1” or other numbers are manufacturer-specific, providing more detailed information.
- Example: A P0301 code indicates a misfire in cylinder 1. Knowing this allows you to focus your diagnostic efforts on that specific area.
- Impact: According to a study by the National Institute for Automotive Service Excellence (ASE), accurate DTC interpretation can reduce diagnostic time by up to 40%.
1.2 Accessing Live Data for Real-Time Monitoring
Many OBD2 scanners can display live data, showing real-time readings from various sensors throughout the vehicle. This is invaluable for diagnosing intermittent problems or monitoring system performance.
- Examples of Live Data: Engine RPM, coolant temperature, oxygen sensor readings, and fuel trim values are all accessible via live data.
- Benefits: Live data allows you to see how systems are behaving under different conditions, helping identify issues that wouldn’t trigger a DTC.
- Research Support: Research from SAE International indicates that monitoring live data can help identify performance issues before they lead to more significant problems.
1.3 Verifying Emissions Readiness
OBD2 scanner uses also include checking a vehicle’s readiness for emissions testing. The scanner can determine if all required emissions systems have been tested and are functioning correctly.
- I/M Readiness Monitors: These monitors check systems like the oxygen sensors, catalytic converter, and evaporative emissions control system.
- Importance: Failing an emissions test can lead to fines and prevent vehicle registration. Using an OBD2 scanner to check readiness beforehand can save time and money.
- Regulatory Compliance: The EPA mandates that vehicles pass emissions tests to ensure compliance with air quality standards.
1.4 Contact OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN for Expert Guidance
Navigating the intricacies of OBD2 scanners can be challenging. At OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN, we offer expert guidance and support to help you maximize the benefits of these tools. Whether you’re a seasoned mechanic or a DIY enthusiast, our team can provide the knowledge and resources you need. Contact us via WhatsApp at +1 (641) 206-8880 or visit our location at 123 Main Street, Los Angeles, CA 90001, United States.
2. How to Connect and Set Up Your OBD2 Scanner
Connecting an OBD2 scanner is a straightforward process, but proper setup is crucial for accurate readings. Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to connect and set up your OBD2 scanner:
2.1 Locating the OBD2 Port
The OBD2 port is typically located under the dashboard on the driver’s side. It is a 16-pin, trapezoid-shaped connector. In some vehicles, it may be hidden behind a small panel or in the center console.
- Common Locations: The most common location is under the dashboard, near the steering column.
- Less Common Locations: Some vehicles may have the port in the glove box, center console, or behind an ashtray.
- Importance: Knowing the location of the OBD2 port is the first step in using the scanner effectively.
2.2 Connecting the Scanner
With the ignition off, plug the OBD2 scanner into the port. The connector is keyed, meaning it will only fit in one direction. Gently push the connector in until it clicks into place.
- Keyed Connector: Ensure the connector is properly aligned before pushing it in.
- Secure Connection: A loose connection can lead to inaccurate readings or communication errors.
- Compatibility: As confirmed by Consumer Reports, all OBD2 scanners are designed to be universally compatible with OBD2-compliant vehicles.
2.3 Powering Up the Scanner
Once the scanner is connected, turn the ignition to the “ON” position without starting the engine. The scanner should power up automatically. Some scanners may require you to manually turn them on.
- Ignition Position: The “ON” position provides power to the vehicle’s electrical system without starting the engine.
- Scanner Power Source: The OBD2 port provides power to the scanner.
- Troubleshooting: If the scanner does not power up, check the connection and ensure the vehicle’s battery is charged.
2.4 Initial Setup
Some scanners require initial setup, such as selecting the vehicle’s make and model. Follow the on-screen prompts to complete the setup process.
- Vehicle Information: Providing accurate vehicle information ensures the scanner can properly interpret the data.
- Software Updates: Many scanners can be updated with the latest software to improve performance and compatibility.
- User Manual: Consult the scanner’s user manual for specific setup instructions.
2.5 OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN Can Help You Connect Your Scanner
If you encounter any difficulties connecting or setting up your OBD2 scanner, OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN is here to assist you. Our expert technicians can guide you through the process, ensuring you get the most out of your diagnostic tool. Reach out to us via WhatsApp at +1 (641) 206-8880 or visit us at 123 Main Street, Los Angeles, CA 90001, United States.
3. Understanding the OBD2 Scanner Interface and Its Functions
Navigating the OBD2 scanner interface is essential for effective diagnostics. Different scanners may have varying interfaces, but the core functions remain consistent.
3.1 Navigating the Menu
Most OBD2 scanners feature a menu-driven interface. Use the arrow keys to navigate through the options and the “Enter” key to select a function.
- Common Menu Options: “Read Codes,” “Erase Codes,” “Live Data,” “Freeze Frame,” and “Vehicle Information” are common menu options.
- User-Friendly Design: Many modern scanners have intuitive interfaces with clear icons and text.
- Customization: Some scanners allow you to customize the menu layout for easier access to frequently used functions.
3.2 Reading Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
Selecting the “Read Codes” option will display any stored DTCs. The scanner may also provide a brief description of the fault.
- Code Display: DTCs are displayed in a standard format (e.g., P0301).
- Code Descriptions: The scanner may provide a short description of the code, such as “Cylinder 1 Misfire Detected.”
- Multiple Codes: If multiple codes are stored, the scanner will scroll through them.
3.3 Erasing Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
The “Erase Codes” function clears the stored DTCs. Use this function with caution, as it will also erase any freeze frame data.
- Confirmation Prompt: The scanner will typically ask for confirmation before erasing codes.
- Potential Issues: Erasing codes without addressing the underlying problem will only temporarily clear the check engine light.
- Use Cases: Erasing codes is appropriate after repairing the issue that triggered the code.
3.4 Accessing Live Data
The “Live Data” option displays real-time sensor readings. You can scroll through the available data and monitor how the sensors are behaving.
- Sensor Parameters: Common parameters include engine RPM, coolant temperature, oxygen sensor voltage, and fuel trim.
- Graphing Capabilities: Some scanners can graph the live data for easier analysis.
- Identifying Faults: Monitoring live data can help identify intermittent faults or sensors that are out of range.
3.5 Utilizing Freeze Frame Data
Freeze frame data captures sensor readings at the moment a DTC was triggered. This information can help you understand the conditions that led to the fault.
- Snapshot of Data: Freeze frame data provides a snapshot of the vehicle’s operating conditions when the DTC was set.
- Diagnostic Aid: This information can help you narrow down the possible causes of the fault.
- Example: Freeze frame data might show that the engine was running lean at the time the misfire occurred.
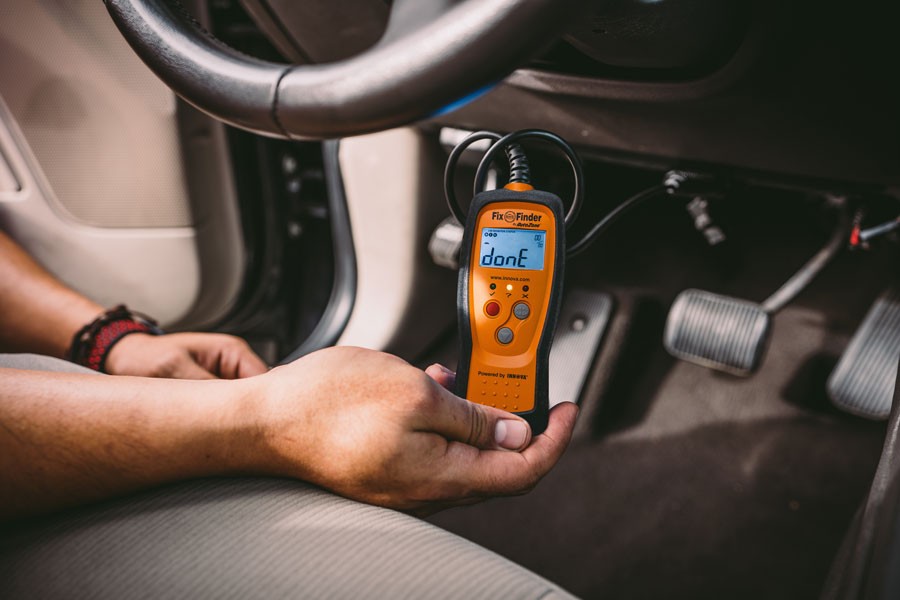 OBD-II scanner interface displaying diagnostic trouble codes
OBD-II scanner interface displaying diagnostic trouble codes
An OBD-II scanner interface displays diagnostic trouble codes, helping mechanics and car owners identify and address vehicle issues effectively.
3.6 OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN Explains Scanner Functions
Understanding the functions of your OBD2 scanner is crucial for accurate diagnostics. OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN provides detailed explanations and tutorials to help you master your scanner’s interface. Contact us via WhatsApp at +1 (641) 206-8880 or visit us at 123 Main Street, Los Angeles, CA 90001, United States, for expert assistance.
4. Deciphering Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
Understanding what DTCs mean is critical for effective car repair. DTCs are standardized codes that provide clues about the nature and location of a problem.
4.1 Understanding the DTC Structure
DTCs consist of five characters: one letter followed by four numbers. The letter indicates the system affected:
- P (Powertrain): Engine, transmission, and related systems.
- B (Body): Interior components like airbags, power windows, and seats.
- C (Chassis): Brakes, steering, and suspension.
- U (Network): Communication issues between electronic control units (ECUs).
The first number after the letter indicates whether the code is generic (0) or manufacturer-specific (1). The remaining three numbers provide more specific information about the fault.
4.2 Common DTC Examples and Their Meanings
Here are some common DTCs and their meanings:
- P0171 (System Too Lean, Bank 1): Indicates that the engine is not getting enough fuel.
- P0300 (Random/Multiple Cylinder Misfire Detected): Indicates that there is a misfire occurring in one or more cylinders.
- P0420 (Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold, Bank 1): Indicates that the catalytic converter is not functioning efficiently.
- P0505 (Idle Air Control System Malfunction): Indicates that there is a problem with the idle air control system.
4.3 Using Online Resources for DTC Lookup
Many online resources can help you decipher DTCs. Websites like OBD-Codes.com and the AutoZone website provide detailed information about DTCs, including possible causes and troubleshooting steps.
- Reliable Resources: Use reputable websites and databases for accurate information.
- Cross-Referencing: Cross-reference information from multiple sources to ensure accuracy.
- Manufacturer-Specific Information: Consult your vehicle’s service manual for manufacturer-specific DTC information.
4.4 Seeking Professional Assistance
If you’re unsure about a DTC’s meaning or how to proceed with repairs, seek professional assistance. A qualified mechanic can diagnose the problem and recommend the appropriate repairs.
- Benefits of Professional Help: Mechanics have the expertise and tools to accurately diagnose and repair complex issues.
- Cost-Effectiveness: In some cases, professional help can be more cost-effective than attempting DIY repairs.
- Avoiding Further Damage: Incorrect repairs can cause further damage to your vehicle.
4.5 OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN Decodes Your DTCs
Decoding DTCs can be daunting. OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN offers a comprehensive DTC lookup service and expert guidance to help you understand your vehicle’s diagnostic codes. Contact us via WhatsApp at +1 (641) 206-8880 or visit us at 123 Main Street, Los Angeles, CA 90001, United States, for reliable DTC interpretation.
5. Performing Common Diagnostic Tests with an OBD2 Scanner
OBD2 scanners are not just for reading codes; they can also perform various diagnostic tests to help pinpoint problems. Here are some common diagnostic tests you can perform with an OBD2 scanner:
5.1 Oxygen Sensor Testing
Oxygen sensors measure the amount of oxygen in the exhaust gas. Testing these sensors can help identify problems with the fuel mixture or catalytic converter.
- How to Test: Use the live data function to monitor the oxygen sensor voltage. The voltage should fluctuate rapidly between 0.1 and 0.9 volts.
- Interpreting Results: A slow or constant voltage reading indicates a faulty sensor.
- Impact: Faulty oxygen sensors can cause poor fuel economy and emissions problems.
5.2 Misfire Detection
Misfires occur when one or more cylinders do not fire properly. OBD2 scanners can detect misfires and identify which cylinder is affected.
- How to Detect: Look for DTCs such as P0300 (Random Misfire) or P0301 (Cylinder 1 Misfire).
- Troubleshooting: Check the spark plugs, ignition coils, and fuel injectors for the affected cylinder.
- Consequences: Misfires can cause rough running, poor performance, and engine damage.
5.3 Fuel Trim Analysis
Fuel trim values indicate how much the engine control unit (ECU) is adjusting the fuel mixture to compensate for lean or rich conditions.
- Types of Fuel Trim: Short-term fuel trim (STFT) and long-term fuel trim (LTFT).
- Interpreting Results: High positive fuel trim values indicate a lean condition, while high negative values indicate a rich condition.
- Causes: Fuel trim problems can be caused by vacuum leaks, faulty sensors, or fuel system issues.
5.4 Evaporative Emissions (EVAP) System Testing
The EVAP system prevents fuel vapors from escaping into the atmosphere. OBD2 scanners can perform tests to check the integrity of the EVAP system.
- EVAP System Components: Fuel tank, charcoal canister, purge valve, and vent valve.
- Testing Procedure: The scanner can command the purge valve to open and close, allowing you to check for leaks.
- Common Problems: Leaks in the fuel cap, hoses, or canister can cause EVAP system problems.
5.5 Battery and Charging System Analysis
Some advanced OBD2 scanners can perform tests on the battery and charging system. These tests can help identify problems with the battery, alternator, or starter.
- Testing Procedure: The scanner measures the battery voltage, charging voltage, and starter current.
- Interpreting Results: Low battery voltage, high or low charging voltage, or excessive starter current indicates a problem.
- Importance: A healthy battery and charging system are essential for reliable vehicle operation.
5.6 OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN Guides You Through Diagnostic Tests
Performing diagnostic tests with an OBD2 scanner can seem complex, but OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN simplifies the process with step-by-step guides and expert advice. Contact us via WhatsApp at +1 (641) 206-8880 or visit us at 123 Main Street, Los Angeles, CA 90001, United States, for personalized support.
6. Saving Money on Auto Repairs with an OBD2 Scanner
One of the key OBD2 scanner uses is the potential to save money on auto repairs. By diagnosing problems yourself, you can avoid unnecessary trips to the mechanic and potentially fix the issue yourself.
6.1 Identifying Problems Early
Using an OBD2 scanner regularly can help you identify problems early before they become more serious and expensive to repair.
- Preventive Maintenance: Regular scanning can help you catch minor issues before they escalate.
- Cost Savings: Addressing problems early can prevent costly repairs down the road.
- Increased Lifespan: Regular maintenance can extend the lifespan of your vehicle.
6.2 Avoiding Unnecessary Repairs
Some mechanics may recommend unnecessary repairs. An OBD2 scanner can help you verify the mechanic’s diagnosis and avoid being overcharged.
- Second Opinion: Use the scanner to get a second opinion on the diagnosis.
- Verifying Repairs: After a repair, use the scanner to verify that the problem has been resolved.
- Empowerment: Knowing the problem yourself empowers you to make informed decisions about repairs.
6.3 Performing DIY Repairs
Many common car problems can be easily repaired at home with basic tools. An OBD2 scanner can help you identify these problems and guide you through the repair process.
- Simple Repairs: Replacing spark plugs, air filters, and oxygen sensors are examples of DIY repairs.
- Online Resources: YouTube and online forums provide tutorials and guidance for DIY repairs.
- Cost Savings: DIY repairs can save you a significant amount of money on labor costs.
6.4 Negotiating with Mechanics
Knowing the DTC and possible causes allows you to negotiate with mechanics and ensure you’re getting a fair price for repairs.
- Informed Negotiation: Being informed about the problem gives you leverage in negotiations.
- Fair Pricing: Knowing the typical cost of repairs helps you ensure you’re not being overcharged.
- Building Trust: Demonstrating knowledge can help build trust with the mechanic.
6.5 Checking Smog Test Readiness
Before taking your car for a smog test, use an OBD2 scanner to check if it’s ready. This can help you avoid failing the test and paying for a retest.
- I/M Readiness: The scanner will indicate whether all the necessary systems have been tested.
- Addressing Issues: If the scanner indicates that the car is not ready, address the underlying issues before the smog test.
- Cost Savings: Avoiding a failed smog test can save you time and money.
6.6 OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN Helps You Save on Repairs
OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN is committed to helping you save money on auto repairs. Our expert advice and resources empower you to diagnose problems yourself and make informed decisions about repairs. Contact us via WhatsApp at +1 (641) 206-8880 or visit us at 123 Main Street, Los Angeles, CA 90001, United States, for cost-saving strategies.
7. Choosing the Right OBD2 Scanner for Your Needs
With so many OBD2 scanners on the market, choosing the right one can be overwhelming. Here are some factors to consider when selecting an OBD2 scanner:
7.1 Types of Scanners
There are two main types of OBD2 scanners: basic code readers and advanced scan tools.
- Basic Code Readers: These scanners can read and erase DTCs. They are typically less expensive but have limited features.
- Advanced Scan Tools: These scanners offer more features, such as live data, freeze frame data, and bidirectional control. They are more expensive but provide more comprehensive diagnostic capabilities.
7.2 Features to Consider
When choosing an OBD2 scanner, consider the following features:
- Live Data: Ability to monitor real-time sensor readings.
- Freeze Frame Data: Ability to view sensor readings at the time a DTC was triggered.
- Bidirectional Control: Ability to command certain components to activate or deactivate.
- Software Updates: Ability to update the scanner with the latest software and DTC definitions.
- Ease of Use: An intuitive interface and clear instructions make the scanner easier to use.
7.3 Compatibility
Ensure the scanner is compatible with your vehicle’s make and model. Most OBD2 scanners are universally compatible with OBD2-compliant vehicles, but some may have limited functionality with certain makes or models.
- OBD2 Compliance: All cars sold in the US after 1996 are OBD2-compliant.
- Manufacturer-Specific Features: Some scanners offer enhanced features for specific makes or models.
- Checking Compatibility: Check the scanner’s product description or consult with the manufacturer to ensure compatibility.
7.4 Price Range
OBD2 scanners range in price from around $20 for basic code readers to several hundred dollars for advanced scan tools.
- Budget: Determine your budget before you start shopping.
- Value: Consider the features and capabilities of the scanner relative to its price.
- Long-Term Investment: A good OBD2 scanner can be a valuable long-term investment.
7.5 Wireless vs. Wired
OBD2 scanners can be either wireless or wired.
- Wireless Scanners: These scanners connect to your smartphone or tablet via Bluetooth or Wi-Fi. They offer more flexibility and convenience.
- Wired Scanners: These scanners connect directly to the OBD2 port with a cable. They are typically more reliable and less prone to connectivity issues.
7.6 OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN Helps You Choose the Right Scanner
Choosing the right OBD2 scanner can be challenging, but OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN is here to help. Our experts can assess your needs and recommend the best scanner for your vehicle and budget. Contact us via WhatsApp at +1 (641) 206-8880 or visit us at 123 Main Street, Los Angeles, CA 90001, United States, for personalized recommendations.
8. Advanced OBD2 Scanner Uses: Beyond Basic Code Reading
While reading and clearing codes is a fundamental function, advanced OBD2 scanner uses offer deeper insights into vehicle diagnostics and performance.
8.1 Bi-Directional Control
Bi-directional control allows you to send commands to the vehicle’s computer to activate or deactivate certain components. This can be useful for testing and troubleshooting.
- Component Testing: Activate fuel injectors, cooling fans, or other components to check their operation.
- System Calibration: Perform calibrations for throttle position sensors or idle air control valves.
- Enhanced Diagnostics: Isolate and diagnose problems more efficiently.
8.2 Key Programming
Some advanced scanners can program new keys for your vehicle. This can be useful if you lose your keys or need to add an extra key.
- Security Measures: Key programming requires access to the vehicle’s security system.
- Professional Use: Typically used by locksmiths or automotive technicians.
- Cost Savings: Programming your own keys can save money compared to going to the dealership.
8.3 Module Programming
Module programming allows you to update or reprogram the vehicle’s electronic control units (ECUs). This can be necessary after replacing a module or to install updated software.
- Software Updates: Install the latest software updates to improve performance or fix bugs.
- Module Replacement: Program a new module to match the vehicle’s configuration.
- Complexity: Module programming is a complex procedure that should be performed by a trained technician.
8.4 Data Logging
Data logging allows you to record live data over a period of time. This can be useful for diagnosing intermittent problems or analyzing vehicle performance under different conditions.
- Record Parameters: Select the parameters you want to record, such as engine RPM, speed, and sensor readings.
- Analyze Data: Review the data to identify patterns or anomalies.
- Troubleshooting: Diagnose intermittent problems that are difficult to capture in real-time.
8.5 Custom Parameter Identification (PID)
Custom PID allows you to access and monitor specific data parameters that are not typically available on standard OBD2 scanners.
- Access Hidden Data: Monitor data that is specific to your vehicle’s make and model.
- Advanced Diagnostics: Gain deeper insights into vehicle performance and operation.
- Technical Knowledge: Requires a good understanding of vehicle systems and data parameters.
8.6 OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN Provides Advanced Diagnostic Solutions
Unlock the full potential of your OBD2 scanner with advanced diagnostic solutions from OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN. Our expert technicians can guide you through advanced features and techniques. Contact us via WhatsApp at +1 (641) 206-8880 or visit us at 123 Main Street, Los Angeles, CA 90001, United States, for advanced support.
9. Common Mistakes to Avoid When Using an OBD2 Scanner
Using an OBD2 scanner effectively requires avoiding common mistakes that can lead to inaccurate diagnoses or further problems.
9.1 Not Connecting the Scanner Properly
A loose or incomplete connection can result in inaccurate readings or communication errors. Ensure the scanner is securely connected to the OBD2 port.
- Secure Connection: Listen for a click to ensure the scanner is fully seated in the port.
- Check Connections: If you’re not getting any readings, check the connection and try again.
- Port Damage: Be careful not to damage the OBD2 port when connecting the scanner.
9.2 Misinterpreting DTCs
DTCs provide clues about the problem, but they don’t always tell the whole story. It’s important to understand the DTC and perform further diagnostics to confirm the cause.
- DTC Definitions: Use reliable resources to understand the DTC definition.
- Further Testing: Perform additional tests to confirm the DTC’s accuracy.
- Multiple Causes: Be aware that a DTC can have multiple potential causes.
9.3 Erasing Codes Without Fixing the Problem
Erasing codes without fixing the underlying problem will only temporarily clear the check engine light. The light will eventually come back on, and the problem will persist.
- Address the Issue: Always fix the problem that triggered the DTC before erasing the code.
- Temporary Fix: Erasing codes without fixing the problem is only a temporary fix.
- Diagnostic Data: Erasing codes also clears valuable freeze frame data that can help with diagnosis.
9.4 Relying Solely on the Scanner
An OBD2 scanner is a valuable tool, but it’s not a substitute for good diagnostic skills and experience. Use the scanner as a starting point and perform further diagnostics as needed.
- Experienced Technician: Consult with a qualified mechanic if you’re unsure about the diagnosis.
- Comprehensive Approach: Use the scanner in conjunction with other diagnostic tools and techniques.
- Vehicle Knowledge: A good understanding of vehicle systems is essential for accurate diagnostics.
9.5 Neglecting Software Updates
OBD2 scanners require regular software updates to maintain accuracy and compatibility. Neglecting software updates can lead to inaccurate readings or communication errors.
- Update Frequency: Check for updates regularly, especially if you’re working on newer vehicles.
- Improved Performance: Software updates can improve the scanner’s performance and add new features.
- Compatibility: Updates ensure the scanner is compatible with the latest vehicles and DTC definitions.
9.6 OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN Helps You Avoid Common Mistakes
Avoid common pitfalls and maximize the effectiveness of your OBD2 scanner with guidance from OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN. Our experts provide valuable tips and advice to help you avoid mistakes and get accurate diagnoses. Contact us via WhatsApp at +1 (641) 206-8880 or visit us at 123 Main Street, Los Angeles, CA 90001, United States, for reliable support.
10. Maintaining and Storing Your OBD2 Scanner
Proper maintenance and storage are essential for ensuring the longevity and reliability of your OBD2 scanner.
10.1 Cleaning the Scanner
Keep the scanner clean by wiping it down with a soft, dry cloth. Avoid using harsh chemicals or solvents that could damage the scanner.
- Gentle Cleaning: Use a mild cleaner if necessary.
- Avoid Liquids: Prevent liquids from entering the scanner.
- Regular Cleaning: Clean the scanner regularly to remove dirt and grime.
10.2 Protecting the Cable
The cable is a vulnerable part of the scanner. Avoid bending or twisting the cable excessively, and store it properly when not in use.
- Cable Storage: Coil the cable loosely and secure it with a Velcro strap or rubber band.
- Avoid Pinching: Be careful not to pinch the cable when storing the scanner.
- Cable Inspection: Inspect the cable regularly for damage.
10.3 Storing the Scanner in a Safe Place
Store the scanner in a clean, dry place away from extreme temperatures and humidity. A protective case can help prevent damage.
- Protective Case: Use a hard case to protect the scanner from impact and scratches.
- Temperature Control: Avoid storing the scanner in direct sunlight or in a hot car.
- Humidity Control: Store the scanner in a dry environment to prevent corrosion.
10.4 Replacing Batteries
If your scanner uses batteries, replace them regularly to ensure proper operation. Use the correct type of batteries, and dispose of them properly.
- Battery Type: Refer to the scanner’s user manual for the correct battery type.
- Battery Disposal: Dispose of used batteries according to local regulations.
- Battery Leakage: Remove the batteries if you’re not going to use the scanner for an extended period.
10.5 Calibrating the Scanner
Some advanced scanners require periodic calibration to maintain accuracy. Follow the manufacturer’s instructions for calibration.
- Calibration Frequency: Calibrate the scanner according to the manufacturer’s recommendations.
- Calibration Tools: Use the appropriate calibration tools and procedures.
- Professional Calibration: Consider having the scanner professionally calibrated for optimal accuracy.
10.6 OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN Offers Maintenance Tips
Ensure your OBD2 scanner remains in top condition with maintenance tips from OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN. Our experts provide valuable advice on cleaning, storing, and maintaining your scanner. Contact us via WhatsApp at +1 (641) 206-8880 or visit us at 123 Main Street, Los Angeles, CA 90001, United States, for expert maintenance support.
By understanding and utilizing the diverse OBD2 scanner uses, you can effectively diagnose and maintain your vehicle, saving time and money while ensuring optimal performance. Let OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN be your trusted partner in mastering these essential tools.
FAQ: Frequently Asked Questions About OBD2 Scanner Uses
What is an OBD2 scanner used for?
OBD2 scanners are used to read diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs), access live data, check emissions readiness, and perform various diagnostic tests on a vehicle’s computer system.
Does the car have to be running to use an OBD2 scanner?
No, in most instances, you can read trouble codes with the ignition in the ON position, without the engine running.
How do I read my OBD scanner?
Select “Read Codes” on your scanner’s screen and note any active and pending diagnostic codes. The letter indicates the system involved, and the numbers identify the specifics of the issue.
Can you plug in an OBD scanner while the car is running?
While it’s technically possible to plug in an OBD scanner while the engine is running, it’s generally not advised. It may be necessary to turn the ignition off and back on to initiate the test.
What do the different letters in an OBD2 code mean?
The letters in an OBD2 code indicate the system affected: P for powertrain, B for body, C for chassis, and U for network.
What is live data on an OBD2 scanner?
Live data refers to real-time sensor readings that you can monitor using an OBD2 scanner. This includes parameters like engine RPM, coolant temperature, and oxygen sensor voltage.
How do I clear a check engine light with an OBD2 scanner?
After addressing the underlying issue that caused the check engine light to illuminate, select the “Erase Codes” option on your OBD2 scanner.
Can an OBD2 scanner tell me what’s wrong with my car?
An OBD2 scanner provides diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) that point to potential issues, but further diagnostics may be required to pinpoint the exact problem.
What’s the difference between a basic OBD2 scanner and an advanced scan tool?
Basic OBD2 scanners read and erase codes, while advanced scan tools offer features like live data, bi-directional control, and more comprehensive diagnostic capabilities.
Where can I get help using my OBD2 scanner?
OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN offers expert guidance and support to help you effectively use your OBD2 scanner for vehicle maintenance and repair. Contact us via WhatsApp at +1 (641) 206-8880 or visit us at 123 Main Street, Los Angeles, CA 90001, United States.