The Smart Car Obd2 Port is essential for accessing vehicle diagnostics and performance data, offering valuable insights for maintenance and repairs, especially when utilizing tools and resources from OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN. By understanding its function and how to use it effectively, you can ensure your vehicle runs smoothly and efficiently. This knowledge empowers you with the capability to address issues promptly, reduce repair costs, and enhance the overall lifespan of your vehicle, coupled with expert support, detailed guides, and reliable OBD2 scanners for comprehensive diagnostics and maintenance solutions.
1. What is a Smart Car OBD2 Port?
A smart car OBD2 (On-Board Diagnostics II) port is a standardized interface in most modern vehicles, providing access to the car’s computer system for diagnostics and monitoring. This port allows mechanics and car owners to retrieve diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs), monitor real-time data, and perform various tests to ensure optimal vehicle performance, according to a study by the Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE).
1.1. The History and Evolution of OBD2 Ports
The journey of On-Board Diagnostics (OBD) started in the late 1960s due to increasing concerns about air pollution. Automakers began implementing basic diagnostic systems to monitor emission control components. However, these early systems were not standardized, leading to inconsistencies and difficulties for technicians.
- OBD-I (Early Systems): These were manufacturer-specific and lacked uniformity, making it challenging to diagnose issues across different car brands.
- OBD-II (Standardization): In the mid-1990s, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) mandated that all vehicles sold in the United States must comply with the OBD-II standard. This standardization ensured that all cars had a uniform diagnostic interface, facilitating easier and more accurate diagnostics. According to the EPA, this move significantly improved vehicle emission control and diagnostic capabilities.
Key improvements of OBD-II:
- Standardized Connector: A 16-pin connector located within easy reach inside the car’s cabin.
- Standardized Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs): Uniform codes that provide specific information about the detected problem.
- Access to Real-Time Data: Ability to monitor various parameters such as engine RPM, vehicle speed, and sensor readings.
1.2. Location of the OBD2 Port in Smart Cars
The OBD2 port is typically located inside the car’s cabin for easy access. Common locations include:
- Under the dashboard on the driver’s side
- Near the steering column
- Inside the center console
Because of the standardized location, technicians and car owners can quickly connect diagnostic tools without difficulty. However, different manufacturers may have slightly varied placements, so consulting the vehicle’s manual is always a good idea.
1.3. The Role of the OBD2 Port in Vehicle Diagnostics
The OBD2 port serves as the primary gateway to a vehicle’s computer system. It allows access to a wealth of information, including:
- Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs): These codes indicate specific problems detected by the car’s computer, such as engine misfires, faulty sensors, or emission control issues.
- Real-Time Data: Monitoring live data streams from various sensors and components, including engine speed (RPM), coolant temperature, oxygen sensor readings, and fuel trim values.
- Vehicle Information: Retrieving vital information such as the Vehicle Identification Number (VIN), calibration IDs, and other vehicle-specific data.
- System Tests: Performing on-demand tests of various systems, such as the evaporative emission control system (EVAP) and oxygen sensors.
By utilizing the OBD2 port, technicians can accurately diagnose issues, verify repairs, and ensure that the vehicle is operating within specified parameters. This capability not only saves time but also reduces the likelihood of misdiagnosis and unnecessary repairs, as highlighted in a study by the National Institute for Automotive Service Excellence (ASE).
2. What is a Smart Car OBD2 Scanner?
A smart car OBD2 scanner is a device used to read and interpret data from a vehicle’s OBD2 port. It helps diagnose problems, monitor performance, and ensure the car is running efficiently.
2.1. Types of OBD2 Scanners Available
OBD2 scanners come in various forms, each catering to different needs and levels of expertise:
- Basic Code Readers: These are simple, handheld devices that read and clear diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs). They are typically the most affordable option and suitable for basic diagnostics.
- Enhanced Scanners: These offer more advanced features such as live data streaming, graphing, and the ability to perform system tests. They are ideal for DIY enthusiasts and professional mechanics.
- Professional-Grade Scanners: These are comprehensive diagnostic tools used by professional mechanics. They offer advanced features such as bi-directional control, advanced coding, and access to manufacturer-specific data.
- Smartphone Adapters: These devices connect to the OBD2 port and transmit data to a smartphone or tablet via Bluetooth or Wi-Fi. They often work with a dedicated app that provides diagnostic information and additional features.
2.2. Key Features to Look for in an OBD2 Scanner
When choosing an OBD2 scanner, consider the following features to ensure it meets your needs:
- Compatibility: Ensure the scanner is compatible with your vehicle’s make and model.
- Ease of Use: Look for a scanner with an intuitive interface and clear instructions.
- Features: Determine which features are important to you, such as live data streaming, graphing, and bi-directional control.
- Updateability: Choose a scanner that can be updated with the latest vehicle information and diagnostic capabilities.
- Portability: Consider the size and portability of the scanner, especially if you plan to use it in multiple locations.
- Durability: Opt for a well-built scanner that can withstand regular use in a garage or shop environment.
- Customer Reviews: Research customer reviews to get an idea of the scanner’s reliability and performance.
2.3. How to Choose the Right Scanner for Your Smart Car
Selecting the right OBD2 scanner involves evaluating your specific needs and technical expertise. Here are some steps to guide you through the selection process:
-
Assess Your Needs:
- Basic Diagnostics: If you only need to read and clear codes, a basic code reader will suffice.
- Advanced Diagnostics: For more in-depth analysis and system testing, an enhanced or professional-grade scanner is necessary.
- DIY vs. Professional Use: Determine whether the scanner is for personal use or professional automotive repair.
-
Check Compatibility:
- Vehicle Make and Model: Ensure the scanner supports your vehicle’s make, model, and year.
- OBD2 Protocols: Verify that the scanner supports all OBD2 protocols, including CAN, ISO, and PWM.
-
Evaluate Features:
- Live Data: Essential for monitoring real-time sensor data.
- Graphing: Helps visualize data for better analysis.
- Bi-Directional Control: Allows you to command the vehicle’s systems for testing purposes.
- Special Functions: Look for features like ABS, SRS, and TPMS diagnostics, if needed.
-
Read Reviews and Recommendations:
- Online Reviews: Check customer reviews on websites like Amazon, automotive forums, and professional mechanic sites.
- Professional Recommendations: Consult with mechanics or automotive experts for their recommendations.
-
Consider Budget:
- Price Range: OBD2 scanners range from inexpensive code readers to high-end professional tools. Set a budget based on your needs and the features you require.
By following these steps, you can choose an OBD2 scanner that best fits your needs, technical expertise, and budget, ensuring effective vehicle diagnostics and maintenance.
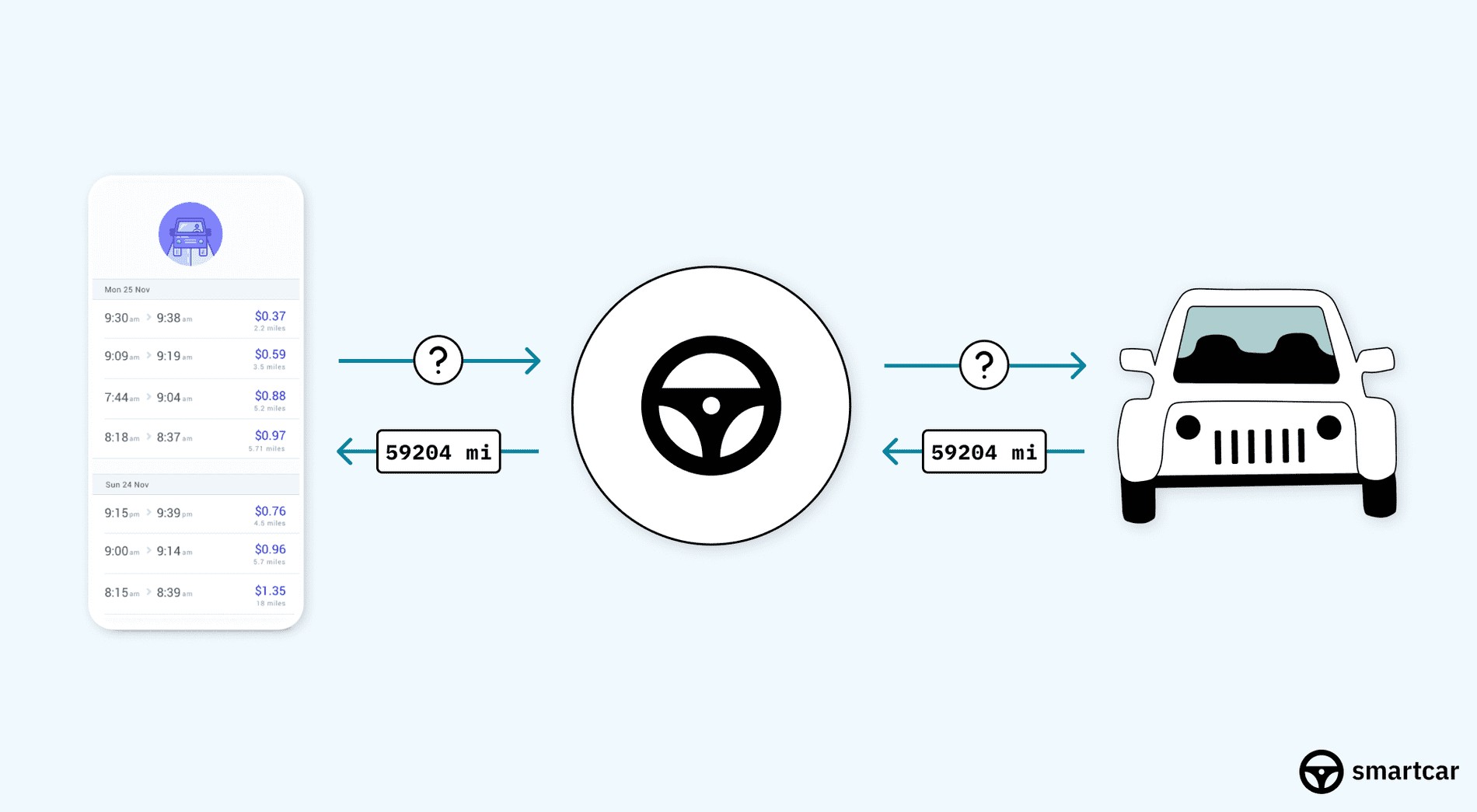 Smartcar API allows apps to retrieve telematics data from vehicles without a hardware device
Smartcar API allows apps to retrieve telematics data from vehicles without a hardware device
3. Using an OBD2 Scanner with Your Smart Car
Effectively using an OBD2 scanner with your smart car involves a few simple steps. Following these steps will allow you to accurately diagnose and address any issues your vehicle may be experiencing.
3.1. Step-by-Step Guide to Connecting and Using the Scanner
- Locate the OBD2 Port: Typically found under the dashboard on the driver’s side.
- Plug in the Scanner: Ensure the vehicle is turned off before connecting the scanner to the OBD2 port.
- Turn on the Ignition: Turn the key to the “on” position without starting the engine.
- Power on the Scanner: The scanner should power on automatically. If not, press the power button.
- Navigate the Menu: Use the scanner’s menu to select the appropriate function, such as reading diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs).
- Read the Codes: The scanner will display any stored DTCs. Record these codes for further investigation.
- Interpret the Codes: Use a code lookup resource to understand what each code means. Websites like OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN offer detailed explanations of various DTCs.
- Clear the Codes (Optional): After addressing the issue, you can clear the codes to reset the system. Be cautious when clearing codes, as it may erase important diagnostic data.
- Turn off the Ignition and Disconnect the Scanner: Once you have completed your diagnostics, turn off the ignition and disconnect the scanner.
3.2. Interpreting Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) are standardized codes used to identify specific issues within a vehicle’s systems. These codes consist of five characters:
- First Character: Indicates the system where the fault occurred:
- P: Powertrain (engine, transmission)
- B: Body (airbags, power windows)
- C: Chassis (ABS, suspension)
- U: Network (communication systems)
- Second Character: Indicates whether the code is generic or manufacturer-specific:
- 0: Generic (SAE) code
- 1: Manufacturer-specific code
- Third Character: Indicates the specific subsystem:
- 1: Fuel and air metering
- 2: Fuel and air metering (injector circuit)
- 3: Ignition system or misfire
- 4: Auxiliary emission controls
- 5: Vehicle speed control, idle control system
- 6: Computer output circuit
- 7, 8, 9: Transmission
- Fourth and Fifth Characters: Provide more specific information about the fault.
To interpret a DTC effectively:
- Record the Code: Write down the complete code (e.g., P0300).
- Consult a Code Lookup Resource: Use online databases, repair manuals, or scanner-provided information to find the code’s definition.
- Understand the Definition: The definition will describe the issue, such as “P0300 – Random/Multiple Cylinder Misfire Detected.”
- Further Diagnosis: Use the code as a starting point for further diagnosis, checking the affected components and systems.
3.3. Common Mistakes to Avoid When Using an OBD2 Scanner
- Ignoring Freeze Frame Data: Freeze frame data captures the vehicle’s operating conditions when the DTC was set. Ignoring this data can lead to misdiagnosis.
- Clearing Codes Without Addressing the Issue: Clearing codes without fixing the underlying problem will only result in the code returning.
- Misinterpreting Codes: Ensure you understand the definition of the code and its potential causes before taking action.
- Using Incompatible Scanners: Always verify that the scanner is compatible with your vehicle’s make, model, and year.
- Neglecting Scanner Updates: Keep your scanner updated with the latest software and vehicle information to ensure accurate diagnostics.
By avoiding these common mistakes, you can use your OBD2 scanner more effectively, leading to accurate diagnoses and successful vehicle repairs.
4. Benefits of Using an OBD2 Port in Smart Cars
Using an OBD2 port in smart cars offers numerous benefits, ranging from preventative maintenance to cost savings. By understanding and leveraging these advantages, car owners can ensure their vehicles remain in optimal condition while reducing potential expenses.
4.1. Real-Time Monitoring of Vehicle Performance
One of the primary benefits of using an OBD2 port is the ability to monitor vehicle performance in real-time. This feature allows you to observe various parameters as the car operates, providing insights into its overall health and efficiency.
- Engine Performance: Monitor engine RPM, coolant temperature, and throttle position to identify potential issues such as overheating or erratic behavior.
- Fuel Efficiency: Track fuel consumption, air-fuel ratio, and oxygen sensor readings to optimize fuel economy and reduce emissions.
- Transmission Health: Monitor transmission temperature and gear selection to ensure smooth operation and prevent transmission-related problems.
- Sensor Data: Observe live data from various sensors, including mass airflow (MAF), manifold absolute pressure (MAP), and oxygen sensors, to detect faulty readings.
By regularly monitoring these parameters, you can identify anomalies early on, address potential problems before they escalate, and maintain your vehicle’s peak performance.
4.2. Early Detection of Potential Problems
The OBD2 system is designed to detect potential problems before they lead to significant damage or breakdowns. By continuously monitoring various systems and components, the system can identify issues early and alert you through diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs).
- Emission Issues: Detect problems with the catalytic converter, oxygen sensors, and evaporative emission control system (EVAP) to ensure compliance with environmental regulations and prevent costly repairs.
- Engine Misfires: Identify misfires in specific cylinders to prevent damage to the engine and exhaust system.
- ABS and Brake Issues: Detect problems with the anti-lock braking system (ABS) and brake components to ensure safe braking performance.
- Transmission Problems: Identify transmission-related issues such as slipping gears or erratic shifting to prevent major transmission repairs.
Early detection allows you to address these issues promptly, often preventing them from escalating into more severe and expensive problems.
4.3. Cost Savings on Repairs and Maintenance
Using an OBD2 port for diagnostics and maintenance can lead to significant cost savings in the long run. By accurately identifying problems and addressing them early, you can avoid unnecessary repairs and reduce the overall cost of vehicle ownership.
- Accurate Diagnosis: The OBD2 system provides precise diagnostic information, reducing the likelihood of misdiagnosis and unnecessary repairs.
- Preventative Maintenance: Regular monitoring allows you to identify and address minor issues before they become major problems, reducing the need for costly repairs.
- Fuel Efficiency: Optimizing fuel efficiency through monitoring and adjustments can lower fuel costs and reduce emissions.
- DIY Repairs: With the information provided by the OBD2 system, you can perform some repairs yourself, saving on labor costs.
5. Advanced Features and Capabilities of Smart Car OBD2 Ports
Smart car OBD2 ports offer advanced features and capabilities that extend beyond basic diagnostics. These include enhanced data access, customization options, and integration with other vehicle systems, providing a more comprehensive understanding of vehicle performance and potential for improvement.
5.1. Accessing Advanced Data Parameters
Beyond standard diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) and real-time data, smart car OBD2 ports allow access to advanced data parameters that provide deeper insights into vehicle operation.
- Manufacturer-Specific Data: Many OBD2 scanners can access manufacturer-specific data parameters, which are not standardized across all vehicles. These parameters can provide detailed information about specific systems and components unique to the vehicle’s make and model.
- Enhanced PID Support: Enhanced Parameter IDs (PIDs) provide access to more detailed sensor data and diagnostic information. These PIDs can include parameters such as individual cylinder fuel trim, misfire counts, and detailed transmission data.
- OBD Mode 6 Data: OBD Mode 6 data provides access to on-board diagnostic test results for various systems, including the catalytic converter, oxygen sensors, and evaporative emission control system (EVAP). This data can help identify potential issues before they trigger a DTC.
Accessing these advanced data parameters requires a capable OBD2 scanner and a thorough understanding of the vehicle’s systems. However, the insights gained can be invaluable for diagnosing complex issues and optimizing vehicle performance.
5.2. Customization and Programming Options
Some smart car OBD2 ports support customization and programming options that allow you to modify certain vehicle settings and parameters.
- ECU Tuning: With the appropriate software and hardware, you can reprogram the engine control unit (ECU) to optimize performance, fuel efficiency, or both. This can involve adjusting parameters such as fuel injection timing, ignition timing, and boost pressure (for turbocharged engines).
- Parameter Adjustments: Some vehicles allow you to adjust certain parameters, such as idle speed, throttle response, and shift points (for automatic transmissions), through the OBD2 port.
- Feature Activation/Deactivation: Depending on the vehicle, you may be able to activate or deactivate certain features, such as daytime running lights, automatic door locks, and traction control, through the OBD2 port.
It is important to note that customization and programming can void your vehicle’s warranty and may not be legal in all areas. Proceed with caution and consult with a qualified technician before making any modifications.
5.3. Integration with Vehicle Telematics Systems
Smart car OBD2 ports can be integrated with vehicle telematics systems, providing a wide range of connected services and features.
- Remote Diagnostics: Telematics systems can remotely access and monitor vehicle data, allowing for proactive diagnostics and maintenance.
- Location Tracking: Telematics systems can track the vehicle’s location, providing valuable information for fleet management, theft recovery, and emergency services.
- Driver Behavior Monitoring: Telematics systems can monitor driver behavior, such as speeding, hard braking, and rapid acceleration, providing insights for improving driving habits and reducing accidents.
- Over-the-Air Updates: Some telematics systems support over-the-air (OTA) updates, allowing you to update the vehicle’s software and firmware without visiting a dealership.
6. Maintaining and Troubleshooting Your Smart Car OBD2 Port
Proper maintenance and troubleshooting of your smart car OBD2 port are essential to ensure its functionality and accuracy. Regular checks and prompt attention to any issues can prevent diagnostic disruptions and maintain the integrity of your vehicle’s data.
6.1. Regular Checks and Maintenance
- Visual Inspection: Regularly inspect the OBD2 port for any physical damage, such as bent pins, cracks, or corrosion. Ensure the port is clean and free from debris.
- Connector Cleanliness: Use a contact cleaner to clean the pins and connector of the OBD2 port. This helps ensure a reliable connection with the diagnostic tool.
- Check for Loose Connections: Ensure the OBD2 port is securely mounted and that there are no loose connections. A loose port can cause intermittent connectivity issues.
- Protective Measures: Consider using a protective cover for the OBD2 port to prevent dust and moisture from entering, especially in harsh environments.
6.2. Common Problems and Solutions
- No Power to the OBD2 Port:
- Problem: The diagnostic tool does not power on when connected to the OBD2 port.
- Solution: Check the vehicle’s fuses related to the OBD2 port. Replace any blown fuses. If the issue persists, there may be a wiring problem requiring professional attention.
- Inability to Connect:
- Problem: The diagnostic tool cannot establish a connection with the vehicle’s computer.
- Solution: Ensure the diagnostic tool is compatible with your vehicle’s make, model, and year. Check the tool’s software for updates. Verify that the ignition is turned on but the engine is not running.
- Intermittent Connection:
- Problem: The connection between the diagnostic tool and the OBD2 port is unstable, causing frequent disconnections.
- Solution: Check the OBD2 port for loose connections or damaged pins. Clean the connector with contact cleaner. Secure the OBD2 port to prevent movement.
- Error Messages:
- Problem: The diagnostic tool displays error messages during use.
- Solution: Consult the diagnostic tool’s manual for troubleshooting steps related to the specific error message. Update the tool’s software. If the problem persists, the tool may need repair or replacement.
6.3. When to Seek Professional Help
While many OBD2 port issues can be resolved with basic troubleshooting, certain situations require professional assistance.
- Complex Wiring Issues: If you suspect a wiring problem affecting the OBD2 port, it is best to consult a qualified mechanic. Wiring issues can be difficult to diagnose and repair without specialized tools and knowledge.
- ECU-Related Problems: If the OBD2 port issues are related to the engine control unit (ECU), professional diagnostic and repair services are necessary.
- Persistent Connectivity Problems: If you have tried all the basic troubleshooting steps and the OBD2 port still does not function correctly, seek professional help to avoid further damage to the vehicle’s systems.
- Unfamiliar Error Codes: If you encounter error codes that you do not understand or cannot resolve, consult a professional mechanic for assistance.
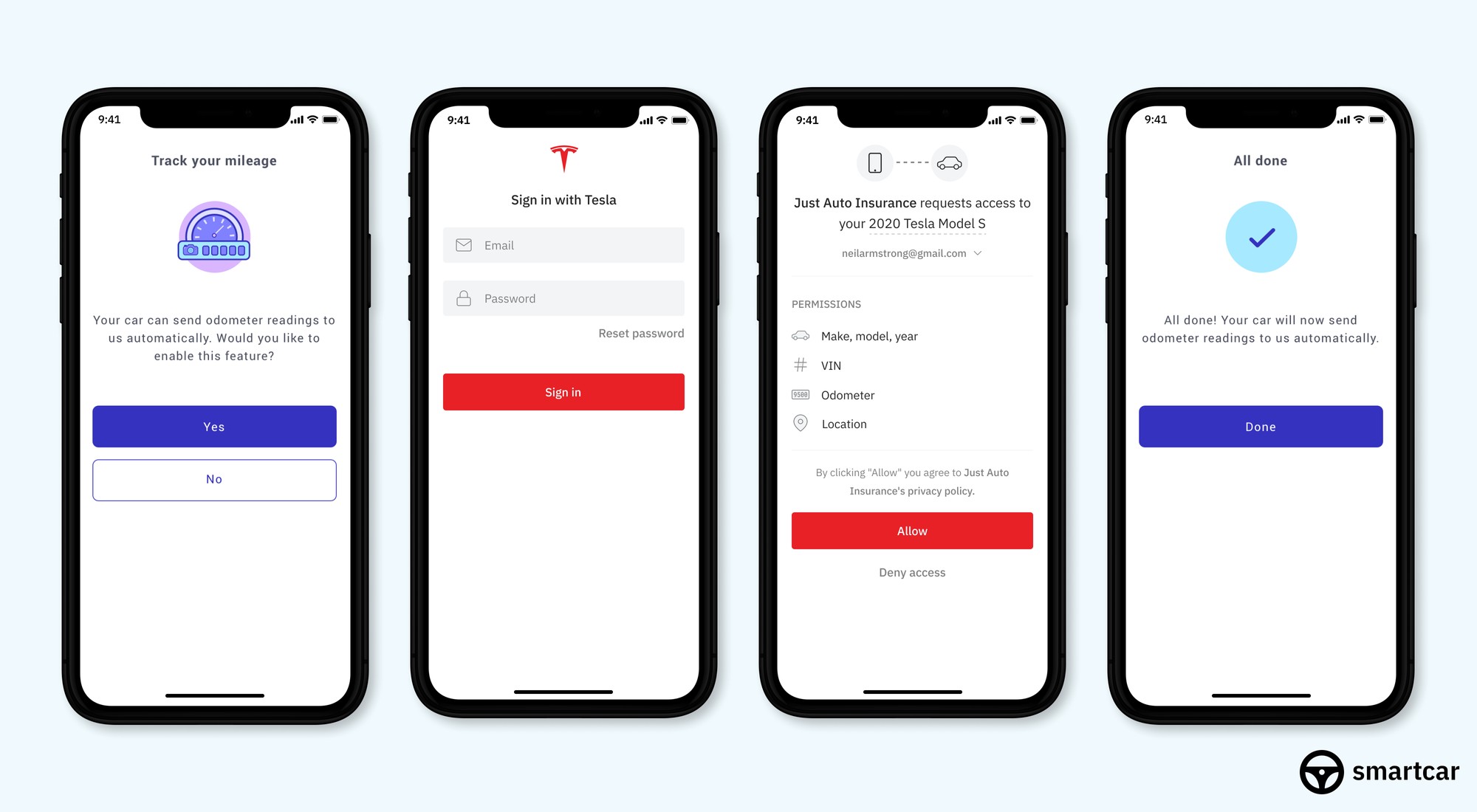 Phone screens showing a vehicle being connected to the Just Auto Insurance mobile app
Phone screens showing a vehicle being connected to the Just Auto Insurance mobile app
7. The Future of OBD2 Ports in Smart Cars
The future of OBD2 ports in smart cars is evolving with advancements in vehicle technology and connectivity. While the traditional OBD2 port has been a staple for accessing vehicle diagnostics, emerging trends suggest potential changes and enhancements in its role and capabilities.
7.1. Emerging Technologies and Innovations
- Wireless OBD2 Adapters: Wireless OBD2 adapters are becoming increasingly popular, offering convenience and flexibility in accessing vehicle data. These adapters connect to the OBD2 port and transmit data to smartphones, tablets, or other devices via Bluetooth or Wi-Fi.
- Cloud-Based Diagnostics: Cloud-based diagnostic platforms are emerging, allowing vehicle data to be stored and analyzed in the cloud. This enables remote diagnostics, predictive maintenance, and over-the-air (OTA) updates.
- Enhanced Security Measures: With the increasing connectivity of vehicles, security is a growing concern. Future OBD2 ports may incorporate enhanced security measures to prevent unauthorized access and protect vehicle data.
- Integration with ADAS: Advanced Driver Assistance Systems (ADAS) are becoming more prevalent in modern vehicles. Future OBD2 ports may integrate with ADAS to provide access to sensor data and diagnostic information related to these systems.
7.2. Potential Changes in Diagnostic Standards
- OBD-III: While not yet widely adopted, OBD-III is a proposed standard that would expand the capabilities of OBD systems. OBD-III would include more comprehensive monitoring of vehicle systems, as well as the ability to report emissions-related issues to regulatory agencies in real-time.
- Ethernet-Based Diagnostics: Ethernet-based diagnostic systems are emerging as a faster and more reliable alternative to traditional CAN-based systems. These systems offer higher bandwidth and improved data transfer rates, enabling more advanced diagnostic capabilities.
- Standardization of Security Protocols: As vehicle connectivity increases, standardization of security protocols for OBD systems is becoming more important. Future standards may include mandatory security measures to prevent unauthorized access and protect vehicle data.
7.3. How These Changes Will Impact Car Owners and Mechanics
- Increased Convenience: Wireless OBD2 adapters and cloud-based diagnostics will make it easier for car owners to access vehicle data and perform basic diagnostics.
- Improved Accuracy: Enhanced diagnostic capabilities and access to more detailed data will improve the accuracy of vehicle diagnostics, reducing the likelihood of misdiagnosis and unnecessary repairs.
- Remote Diagnostics: Remote diagnostics will enable mechanics to diagnose vehicle problems remotely, saving time and reducing the need for in-person visits.
- Predictive Maintenance: Predictive maintenance systems will use vehicle data to identify potential problems before they occur, allowing for proactive maintenance and preventing costly breakdowns.
- Increased Complexity: As vehicle technology becomes more complex, diagnosing and repairing vehicles will require more specialized knowledge and skills. Mechanics will need to stay up-to-date with the latest diagnostic tools and techniques.
- Enhanced Security: Enhanced security measures will protect vehicle data and prevent unauthorized access, but may also make it more difficult for car owners and mechanics to access certain vehicle functions.
FAQ: Smart Car OBD2 Port
What is an OBD2 scanner?
An OBD2 scanner is a diagnostic tool used to read and interpret data from a vehicle’s On-Board Diagnostics II (OBD2) port, helping diagnose issues and monitor performance.
Where is the OBD2 port located in my car?
The OBD2 port is typically located under the dashboard on the driver’s side, near the steering column or in the center console.
How do I connect an OBD2 scanner to my car?
To connect an OBD2 scanner, locate the OBD2 port, plug the scanner into the port, turn on the ignition without starting the engine, and follow the scanner’s instructions to read the data.
What do the diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) mean?
Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) are standardized codes that indicate specific issues detected by the vehicle’s computer system. These codes help identify problems such as engine misfires, faulty sensors, or emission control issues.
Can I clear the diagnostic trouble codes myself?
Yes, you can clear the diagnostic trouble codes using an OBD2 scanner. However, it is essential to address the underlying issue before clearing the codes to prevent the problem from recurring.
What are the benefits of using an OBD2 port in my car?
The benefits of using an OBD2 port include real-time monitoring of vehicle performance, early detection of potential problems, cost savings on repairs and maintenance, and access to advanced data parameters.
Are there any risks associated with using an OBD2 scanner?
While generally safe, using an OBD2 scanner can pose risks such as misinterpreting codes, using incompatible scanners, and neglecting scanner updates. Always follow the manufacturer’s instructions and consult with a professional if needed.
How often should I check my car’s OBD2 port?
You should check your car’s OBD2 port whenever you notice unusual symptoms, such as the check engine light illuminating, decreased fuel efficiency, or performance issues. Regular checks can help identify potential problems early.
Can I use a smartphone app with an OBD2 scanner?
Yes, many OBD2 scanners are compatible with smartphone apps via Bluetooth or Wi-Fi. These apps provide diagnostic information, real-time data, and additional features, enhancing the user experience.
Where can I find reliable OBD2 scanners and information?
You can find reliable OBD2 scanners and information at automotive parts stores, online retailers, and specialized websites like OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN, which offer expert support, detailed guides, and reliable scanners for comprehensive diagnostics and maintenance solutions.
By understanding and utilizing the smart car OBD2 port, car owners and mechanics can ensure optimal vehicle performance, prevent costly repairs, and stay informed about their vehicle’s health. Whether you are a seasoned technician or a novice car owner, leveraging the capabilities of the OBD2 port can significantly enhance your vehicle maintenance practices. Remember, for expert support, detailed guides, and reliable OBD2 scanners, visit OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN.
Ready to take control of your vehicle’s diagnostics? Contact OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN today for expert advice and premium OBD2 scanner solutions. Whether you’re a seasoned mechanic or a first-time user, we’re here to help you understand and address your car’s needs with confidence.
Call us at +1 (641) 206-8880 or visit our website OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN for more information. You can also visit our location at 123 Main Street, Los Angeles, CA 90001, United States. Let us help you keep your car running smoothly and efficiently. Your journey to optimal vehicle performance starts here.
