The OBD2 port is primarily used for accessing a vehicle’s diagnostic data, allowing mechanics and car owners to identify and address potential issues. OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN is your trusted resource for understanding the capabilities of your OBD2 port and how to effectively use it for vehicle maintenance and repair. By using an OBD2 scanner, you can read diagnostic trouble codes, monitor real-time vehicle parameters, and gain valuable insights into your car’s health, leading to proactive maintenance and cost savings.
Contents
- 1. Understanding the OBD2 Port and Its Evolution
- 1.1 The Genesis of On-Board Diagnostics
- 1.2 From OBD-I to OBD-II: A Leap in Standardization
- 1.3 OBD-II Protocols: Ensuring Compatibility
- 2. Decoding the Functionality of the OBD2 Port
- 2.1 Accessing Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
- 2.2 Monitoring Real-Time Data
- 2.3 Clearing Diagnostic Trouble Codes
- 2.4 Performing Vehicle Inspections
- 2.5 Customizing Vehicle Settings
- 3. Who Benefits From Using an OBD2 Port?
- 3.1 Professional Mechanics
- 3.2 Car Enthusiasts
- 3.3 Everyday Drivers
- 3.4 Fleet Managers
- 4. Types of Devices That Connect to the OBD2 Port
- 4.1 Basic OBD2 Scanners
- 4.2 Advanced OBD2 Scanners
- 4.3 Wireless OBD2 Adapters
- 4.4 GPS Trackers
- 4.5 Telematics Devices
- 5. Benefits of Using the OBD2 Port
- 5.1 Early Detection of Problems
- 5.2 Cost Savings on Repairs
- 5.3 Improved Fuel Efficiency
- 5.4 Enhanced Vehicle Performance
- 5.5 Informed Decision-Making
- 6. How to Use an OBD2 Scanner: A Step-by-Step Guide
- 6.1 Locating the OBD2 Port
- 6.2 Connecting the OBD2 Scanner
- 6.3 Turning on the Ignition
- 6.4 Navigating the Scanner Menu
- 6.5 Reading Diagnostic Trouble Codes
- 6.6 Clearing Diagnostic Trouble Codes
- 6.7 Monitoring Live Data
- 7. Common OBD2 Codes and Their Meanings
- 8. Advanced Uses of the OBD2 Port
- 8.1 Performance Tuning
- 8.2 Vehicle Tracking
- 8.3 Usage-Based Insurance
- 8.4 Remote Diagnostics
- 9. FAQ About the OBD2 Port
- 10. Contact OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN for Expert Assistance
1. Understanding the OBD2 Port and Its Evolution
The On-Board Diagnostics II (OBD2) port is a standardized interface in modern vehicles, mandated in all cars and trucks manufactured since 1996 in the United States. This port provides access to a wealth of information about your vehicle’s performance and health. To fully appreciate its capabilities, let’s delve into its origins and how it evolved.
1.1 The Genesis of On-Board Diagnostics
Before OBD systems, diagnosing vehicle issues was a complex, manufacturer-specific task. Each car manufacturer had its own diagnostic tools and protocols, making it difficult for mechanics to service a wide range of vehicles. This led to the development of OBD systems, aiming to standardize the diagnostic process.
1.2 From OBD-I to OBD-II: A Leap in Standardization
OBD-I, introduced in the late 1980s, represented the initial attempt to standardize on-board diagnostics. However, OBD-I systems were limited in their capabilities and lacked uniformity across different manufacturers.
The Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE) played a crucial role in developing the standards for OBD-II. According to a study by the SAE, the transition to OBD-II resulted in a significant improvement in emission control and diagnostic accuracy.
 OBD-II port under the dashboard for car diagnostics
OBD-II port under the dashboard for car diagnostics
Image Credit: Alain Van den Hende/Wikimedia Commons – OBD-II port location for vehicle diagnostics and maintenance.
In 1996, OBD-II was introduced as a more advanced and standardized system. Unlike its predecessor, OBD-II offered:
- Standardized Connector: A 16-pin Data Link Connector (DLC) that is universally located within reach of the driver.
- Comprehensive Diagnostics: Enhanced monitoring of engine, transmission, and emission control systems.
- Standardized Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs): A consistent set of codes to identify specific issues, regardless of the vehicle manufacturer.
1.3 OBD-II Protocols: Ensuring Compatibility
While OBD-II brought standardization, different manufacturers still used various communication protocols. These protocols define how data is transmitted between the vehicle’s computer and the diagnostic tool. The five primary OBD-II protocols include:
- SAE J1850 PWM (Pulse Width Modulation): Used primarily in Ford vehicles.
- SAE J1850 VPW (Variable Pulse Width): Used mainly in General Motors vehicles.
- ISO 9141-2: Common in Chrysler and many European and Asian vehicles.
- ISO 14230-4 (KWP2000): Employed by various American, European, and Japanese brands such as Honda, Jeep, Land Rover, Subaru, Mazda, Nissan, and more.
- ISO 15765 CAN (Controller Area Network): Mandatory for all vehicles manufactured after 2008, this protocol has become the standard for modern vehicles.
Pins 4 and 5 are designated for ground connections, while pin 16 provides power from the car’s battery. Understanding these protocols helps ensure compatibility between your vehicle and the OBD2 scanner you use.
2. Decoding the Functionality of the OBD2 Port
The OBD2 port serves as a gateway to your vehicle’s internal systems, offering a wide range of diagnostic and monitoring capabilities. By connecting an OBD2 scanner to this port, you can access valuable data that can help you maintain your vehicle and address potential issues. Let’s explore what the OBD2 port allows you to do.
2.1 Accessing Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
One of the primary functions of the OBD2 port is to provide access to Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs). When your vehicle’s computer detects a problem, it stores a specific DTC that corresponds to the issue. These codes can range from minor problems like a loose fuel cap to more severe issues like engine misfires or transmission malfunctions.
OBD2 scanners read these DTCs, giving you a starting point for diagnosing the problem. For instance, a P0171 code indicates that the system is running lean, while a P0300 code suggests random or multiple cylinder misfires. Knowing these codes allows you to research the potential causes and plan the necessary repairs.
2.2 Monitoring Real-Time Data
Beyond reading DTCs, the OBD2 port also allows you to monitor real-time data from various sensors throughout your vehicle. This data can provide valuable insights into your car’s performance and help you identify potential problems before they trigger a DTC.
Real-time data parameters include:
- Engine RPM: Revolutions per minute, indicating engine speed.
- Vehicle Speed: Current speed of the vehicle.
- Engine Temperature: Temperature of the engine coolant.
- Fuel Trim: Adjustments made to the fuel mixture by the engine control unit (ECU).
- Oxygen Sensor Readings: Data from the oxygen sensors, indicating the efficiency of the combustion process.
- Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP): Pressure in the intake manifold.
- Mass Air Flow (MAF): Rate of air entering the engine.
Monitoring these parameters can help you detect anomalies. For example, consistently high engine temperatures could indicate a cooling system problem, while unusual fuel trim values might suggest a vacuum leak or a faulty sensor.
According to a study by the National Institute for Automotive Service Excellence (ASE), monitoring real-time data can significantly improve diagnostic accuracy and reduce repair times.
2.3 Clearing Diagnostic Trouble Codes
Once you have addressed the issue causing a DTC, the OBD2 port allows you to clear the code, turning off the check engine light. However, it’s crucial to ensure that the problem has been genuinely resolved before clearing the code. If the underlying issue persists, the code will likely reappear.
Clearing DTCs is a useful feature for verifying that your repairs have been effective. If the check engine light stays off after clearing the code, it’s a good indication that the problem has been resolved.
2.4 Performing Vehicle Inspections
In many states and countries, vehicles are required to pass emissions tests to ensure they meet environmental standards. The OBD2 port plays a crucial role in these inspections by providing access to emissions-related data.
During an emissions test, the inspector connects to the OBD2 port to check for DTCs and verify the status of various emissions control systems. If the vehicle fails any of these tests, it will not pass the inspection.
2.5 Customizing Vehicle Settings
Some advanced OBD2 scanners and software allow you to customize certain vehicle settings. These customizations can include adjusting parameters such as:
- Idle Speed: Adjusting the engine’s idle speed.
- Timing Advance: Modifying the ignition timing for improved performance.
- Speed Limiter: Adjusting or removing the vehicle’s speed limiter.
However, it’s important to exercise caution when customizing vehicle settings, as incorrect adjustments can negatively impact performance or even damage the engine. Always consult with a qualified mechanic before making any significant changes.
3. Who Benefits From Using an OBD2 Port?
The OBD2 port is not just for professional mechanics; it offers benefits to a wide range of users, from car enthusiasts to everyday drivers. Understanding how different individuals can leverage this technology can highlight its versatility and value.
3.1 Professional Mechanics
For professional mechanics, the OBD2 port is an indispensable tool. It allows them to quickly and accurately diagnose vehicle problems, saving time and improving the efficiency of their work.
- Efficient Diagnostics: OBD2 scanners provide mechanics with instant access to DTCs, helping them pinpoint the source of the problem.
- Real-Time Data Analysis: Mechanics can monitor real-time data to assess the performance of various components and identify subtle issues that might not trigger a DTC.
- Comprehensive System Checks: OBD2 scanners enable mechanics to perform thorough system checks, ensuring that all components are functioning correctly.
According to a survey by the Automotive Service Association (ASA), mechanics who use OBD2 scanners report a significant increase in diagnostic accuracy and a reduction in diagnostic time.
3.2 Car Enthusiasts
Car enthusiasts often enjoy tinkering with their vehicles and monitoring their performance. The OBD2 port offers a wealth of data that can be used to track performance metrics, identify areas for improvement, and customize vehicle settings.
- Performance Monitoring: Enthusiasts can use OBD2 scanners to monitor parameters like engine RPM, vehicle speed, and fuel consumption, gaining insights into their car’s performance.
- Customization: Some advanced OBD2 scanners allow enthusiasts to customize vehicle settings, such as idle speed and timing advance, to optimize performance.
- DIY Repairs: With access to DTCs and real-time data, enthusiasts can perform their own repairs, saving money and gaining a deeper understanding of their vehicles.
3.3 Everyday Drivers
Even if you’re not a mechanic or a car enthusiast, the OBD2 port can still be a valuable tool. It can help you stay informed about your vehicle’s health, identify potential problems early, and make informed decisions about maintenance and repairs.
- Early Problem Detection: By regularly scanning your vehicle for DTCs, you can identify potential problems before they escalate into costly repairs.
- Informed Maintenance Decisions: The OBD2 port provides access to data that can help you make informed decisions about maintenance, such as when to change your oil or replace your spark plugs.
- Cost Savings: By identifying and addressing problems early, you can avoid costly repairs and extend the life of your vehicle.
For instance, if you notice a recurring DTC related to your oxygen sensor, you can address the issue before it leads to decreased fuel efficiency or damage to your catalytic converter.
3.4 Fleet Managers
Fleet managers are responsible for maintaining a large number of vehicles. The OBD2 port can be a valuable tool for monitoring the health and performance of their fleet, improving efficiency, and reducing costs.
- Remote Monitoring: Some OBD2 scanners offer remote monitoring capabilities, allowing fleet managers to track the location, performance, and health of their vehicles in real-time.
- Preventative Maintenance: By monitoring vehicle data, fleet managers can identify potential problems early and schedule preventative maintenance to avoid costly breakdowns.
- Improved Efficiency: OBD2 data can be used to optimize driving behavior, reduce fuel consumption, and improve the overall efficiency of the fleet.
According to a study by the National Transportation Safety Board (NTSB), the use of OBD2 data in fleet management can lead to significant cost savings and improved safety.
4. Types of Devices That Connect to the OBD2 Port
The OBD2 port has become a versatile interface, accommodating a variety of devices designed for different purposes. From basic code readers to advanced telematics systems, understanding the available options can help you choose the right tool for your needs.
4.1 Basic OBD2 Scanners
Basic OBD2 scanners are designed primarily for reading and clearing Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs). These scanners are typically inexpensive and easy to use, making them a popular choice for everyday drivers who want to monitor their vehicle’s health.
- Functionality: Read and clear DTCs, display basic vehicle information.
- Pros: Affordable, easy to use.
- Cons: Limited functionality, may not provide detailed information.
4.2 Advanced OBD2 Scanners
Advanced OBD2 scanners offer a wider range of features, including the ability to monitor real-time data, perform system tests, and customize vehicle settings. These scanners are often used by professional mechanics and car enthusiasts who need more comprehensive diagnostic capabilities.
- Functionality: Read and clear DTCs, monitor real-time data, perform system tests, customize vehicle settings.
- Pros: Comprehensive functionality, detailed information.
- Cons: More expensive, may require some technical knowledge.
4.3 Wireless OBD2 Adapters
Wireless OBD2 adapters connect to the OBD2 port and transmit data to a smartphone, tablet, or laptop via Bluetooth or Wi-Fi. These adapters offer a convenient way to monitor your vehicle’s health and performance using a mobile device.
- Functionality: Read and clear DTCs, monitor real-time data, transmit data wirelessly to a mobile device.
- Pros: Convenient, mobile, often used with smartphone apps.
- Cons: May require a compatible mobile device, some features may require a subscription.
4.3.1 Veepeak Mini WiFi OBD II Scanner
 Veepeak Mini WiFi OBD II Scanner for Android devices
Veepeak Mini WiFi OBD II Scanner for Android devices
Image Credit: Amazon – Veepeak OBD-II scanner for Android diagnostic apps.
The Veepeak Mini WiFi OBD II Scanner is an affordable option for Android users. It works with apps like Torque Pro, Torque Lite, and OBD Car Doctor, allowing you to view sensor data and diagnose error codes. It also lets you clear error codes for minor issues.
4.3.2 BAFX Products OBDII Code Reader and Scan Tool
 BAFX Products OBDII Code Reader and Scan Tool for iOS devices
BAFX Products OBDII Code Reader and Scan Tool for iOS devices
Image Credit: Amazon – BAFX OBD-II wireless reader for iOS advanced diagnostics.
The BAFX Products OBDII Code Reader transforms your iOS device into an advanced OBD tool. You can monitor real-time parameters like engine temperature, fuel rate, O2 sensor voltages, and battery voltage.
4.3.3 Veepeak OBDCheck BLE Bluetooth OBD II Scanner
 Veepeak OBDCheck BLE Bluetooth OBD II Scanner for Android and iOS
Veepeak OBDCheck BLE Bluetooth OBD II Scanner for Android and iOS
Image Credit: Amazon – Veepeak OBDCheck BLE for comprehensive vehicle diagnostics.
The Veepeak OBDCheck BLE with Bluetooth 4.0 is compatible with both Android and iOS devices. It supports all OBD-II protocols and works with software like Torque, BimmerCode, BimmerLink, DashCommand, and ScanMaster.
4.3.4 BlueDriver Pro OBD2 Bluetooth Scan Tool
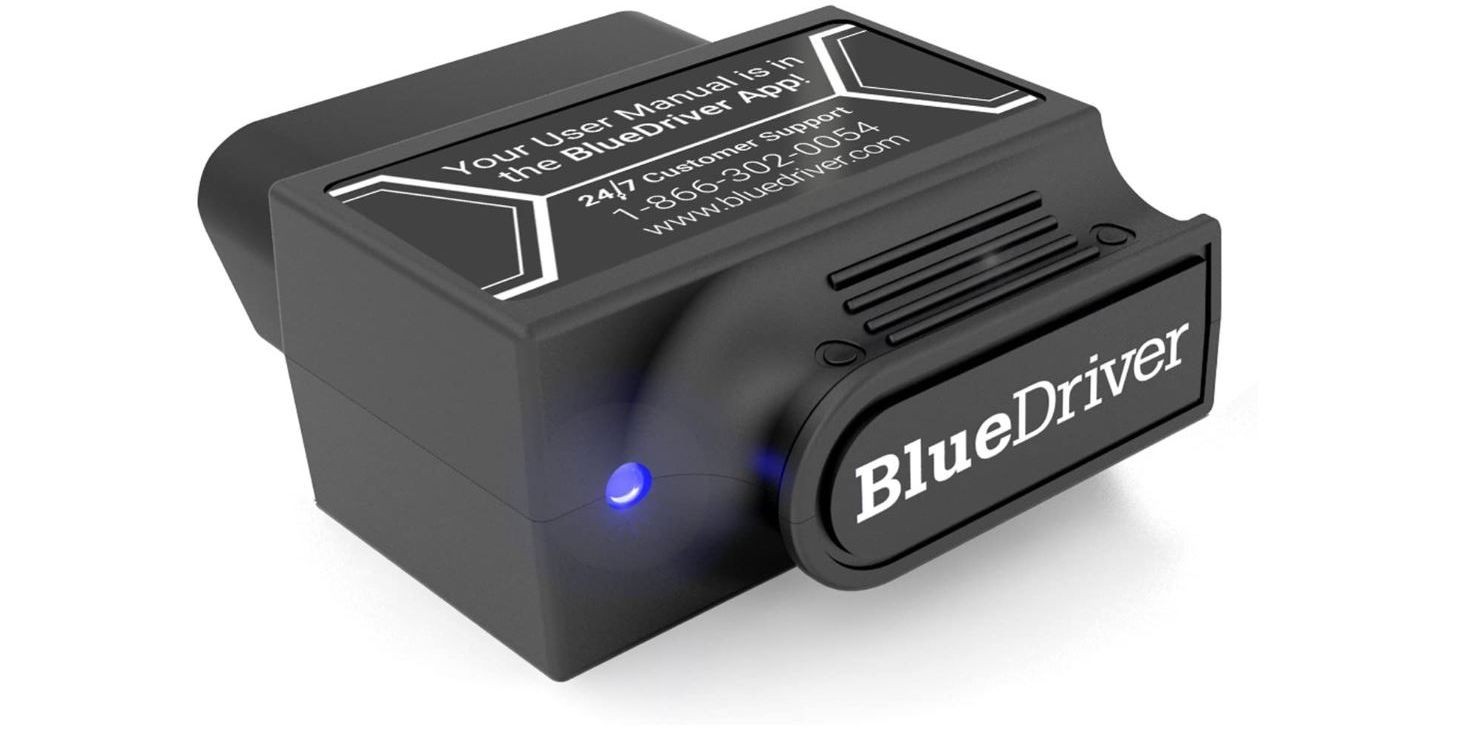 BlueDriver Pro OBD2 Bluetooth Scan Tool for professional diagnostics
BlueDriver Pro OBD2 Bluetooth Scan Tool for professional diagnostics
Image Credit: Amazon – BlueDriver Bluetooth Professional OBDII Scan Tool for advanced diagnostics.
The BlueDriver Bluetooth Professional OBDII Scan Tool is a more functional option that works with both Android and iOS devices. It includes advanced tests with live data, graphs, and repair reports from an online database.
4.3.5 OBDLink MX+ OBD2 Bluetooth Scanner
Image Credit: Amazon – OBDLink MX+ for real-time vehicle data and enhanced support.
The OBDLink MX+ OBD2 Bluetooth Scanner provides real-time vehicle data, enhanced support for various manufacturers, and the ability to display, graph, and log hundreds of parameters. It even allows you to lock or unlock doors on select vehicles.
4.4 GPS Trackers
GPS trackers can be plugged into the OBD2 port to provide location tracking and other telematics data. These devices are often used for fleet management, vehicle security, and monitoring young drivers.
- Functionality: Track vehicle location, monitor driving behavior, provide telematics data.
- Pros: Real-time location tracking, improved vehicle security.
- Cons: Limited diagnostic capabilities, may require a subscription.
4.5 Telematics Devices
Telematics devices combine the functionality of OBD2 scanners and GPS trackers, providing a comprehensive solution for vehicle monitoring and management. These devices can track location, monitor performance, and provide diagnostic data, making them ideal for fleet management and usage-based insurance programs.
- Functionality: Track vehicle location, monitor driving behavior, provide diagnostic data, offer telematics services.
- Pros: Comprehensive vehicle monitoring, improved efficiency, reduced costs.
- Cons: More expensive, may require a subscription.
Choosing the right device depends on your specific needs and budget. Basic OBD2 scanners are suitable for simple tasks like reading and clearing DTCs, while advanced scanners and telematics devices offer more comprehensive capabilities.
5. Benefits of Using the OBD2 Port
The OBD2 port provides numerous benefits, ranging from cost savings to improved vehicle performance. By understanding these advantages, you can make the most of this valuable resource.
5.1 Early Detection of Problems
One of the most significant benefits of using the OBD2 port is the ability to detect potential problems early. By regularly scanning your vehicle for DTCs, you can identify issues before they escalate into costly repairs.
For example, if you notice a recurring DTC related to your oxygen sensor, you can address the issue before it leads to decreased fuel efficiency or damage to your catalytic converter. Early detection can save you money and extend the life of your vehicle.
5.2 Cost Savings on Repairs
By identifying and addressing problems early, you can avoid costly repairs and reduce your overall vehicle maintenance expenses. The OBD2 port empowers you to take a proactive approach to vehicle maintenance, rather than waiting for problems to arise.
Additionally, with access to DTCs and real-time data, you can perform some repairs yourself, saving on labor costs. Many common issues, such as replacing a faulty sensor or tightening a loose fuel cap, can be easily addressed with the help of an OBD2 scanner and some basic tools.
5.3 Improved Fuel Efficiency
The OBD2 port can help you improve your vehicle’s fuel efficiency by identifying issues that may be affecting its performance. For example, a faulty oxygen sensor can cause your engine to run rich, leading to decreased fuel economy.
By monitoring real-time data and addressing any issues that may be affecting your fuel efficiency, you can save money at the pump and reduce your carbon footprint.
5.4 Enhanced Vehicle Performance
In addition to improving fuel efficiency, the OBD2 port can also help you enhance your vehicle’s overall performance. By monitoring real-time data and customizing vehicle settings, you can optimize your car’s performance for your specific driving needs.
For example, you can adjust the timing advance to improve acceleration or modify the idle speed to reduce engine noise. However, it’s important to exercise caution when customizing vehicle settings, as incorrect adjustments can negatively impact performance or even damage the engine.
5.5 Informed Decision-Making
The OBD2 port provides you with valuable information that can help you make informed decisions about vehicle maintenance and repairs. With access to DTCs and real-time data, you can assess the severity of a problem and determine the best course of action.
For example, if you receive a DTC related to your transmission, you can use an OBD2 scanner to gather more information about the problem before taking your vehicle to a mechanic. This can help you avoid unnecessary repairs and ensure that you receive the best possible service.
6. How to Use an OBD2 Scanner: A Step-by-Step Guide
Using an OBD2 scanner is a straightforward process that can be completed in a few simple steps. Whether you’re a professional mechanic or an everyday driver, this guide will help you get the most out of your OBD2 scanner.
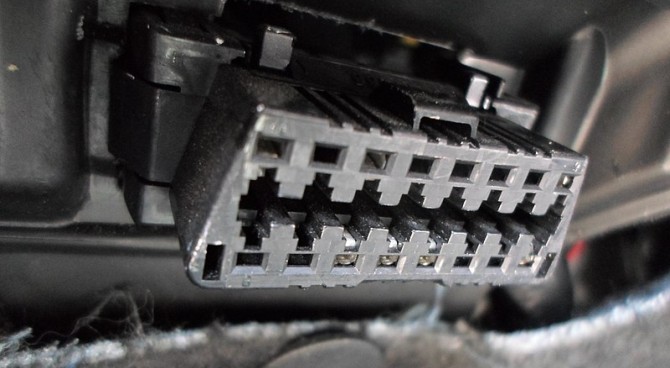
6.1 Locating the OBD2 Port
The first step in using an OBD2 scanner is to locate the OBD2 port in your vehicle. In most cars and trucks, the OBD2 port is located under the driver’s side dashboard, within easy reach. However, the exact location may vary depending on the make and model of your vehicle.
If you’re having trouble finding the OBD2 port, consult your vehicle’s owner’s manual. The manual should provide a diagram or description of the port’s location.
6.2 Connecting the OBD2 Scanner
Once you have located the OBD2 port, connect the OBD2 scanner to the port. The scanner should plug in easily, but don’t force it if you encounter resistance. Make sure that the scanner is properly aligned with the port before inserting it.
6.3 Turning on the Ignition
After connecting the OBD2 scanner, turn on your vehicle’s ignition. You don’t need to start the engine, but the ignition must be in the “on” position for the scanner to communicate with the vehicle’s computer.
6.4 Navigating the Scanner Menu
Once the ignition is on, the OBD2 scanner should power on and display a menu. The menu options may vary depending on the scanner, but typically include options such as “Read Codes,” “Clear Codes,” and “Live Data.”
Use the scanner’s buttons or touchscreen to navigate the menu and select the option you want to use.
6.5 Reading Diagnostic Trouble Codes
To read Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs), select the “Read Codes” option from the scanner menu. The scanner will then communicate with the vehicle’s computer and display any stored DTCs.
Each DTC is typically accompanied by a brief description of the problem. For more detailed information about a specific DTC, consult your vehicle’s service manual or an online database.
6.6 Clearing Diagnostic Trouble Codes
After addressing the issue causing a DTC, you can clear the code by selecting the “Clear Codes” option from the scanner menu. The scanner will then send a command to the vehicle’s computer to clear the stored DTCs.
However, it’s important to ensure that the problem has been genuinely resolved before clearing the code. If the underlying issue persists, the code will likely reappear.
6.7 Monitoring Live Data
To monitor real-time data, select the “Live Data” option from the scanner menu. The scanner will then display a list of available data parameters, such as engine RPM, vehicle speed, and engine temperature.
Select the parameters you want to monitor and the scanner will display their current values. You can use this data to assess your vehicle’s performance and identify potential problems.
7. Common OBD2 Codes and Their Meanings
Understanding common OBD2 codes can help you quickly diagnose and address vehicle problems. Here’s a table of some of the most frequently encountered codes and their meanings:
| Code | Description | Possible Causes |
|---|---|---|
| P0171 | System Too Lean (Bank 1) | Vacuum leak, faulty oxygen sensor, fuel pump issue |
| P0300 | Random/Multiple Cylinder Misfire Detected | Faulty spark plugs, ignition coil issue, fuel injector problem |
| P0420 | Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold (Bank 1) | Faulty catalytic converter, exhaust leak, oxygen sensor issue |
| P0442 | Evaporative Emission Control System Leak Detected (Small Leak) | Loose fuel cap, damaged fuel tank, faulty vent valve |
| P0505 | Idle Air Control System Malfunction | Faulty IAC valve, vacuum leak, throttle body issue |
| P0102 | Mass or Volume Air Flow Circuit Low Input | Dirty or faulty MAF sensor, wiring issue, vacuum leak |
| P0113 | Intake Air Temperature Circuit High Input | Faulty IAT sensor, wiring issue |
| P0301 | Cylinder 1 Misfire Detected | Faulty spark plug, ignition coil issue, fuel injector problem in cylinder 1 |
| P0302 | Cylinder 2 Misfire Detected | Faulty spark plug, ignition coil issue, fuel injector problem in cylinder 2 |
| B1000 | ECU Failure | Faulty ECU |
This table provides a starting point for diagnosing common vehicle problems. However, it’s important to consult your vehicle’s service manual or an online database for more detailed information about specific codes.
8. Advanced Uses of the OBD2 Port
Beyond basic diagnostics, the OBD2 port can be used for a variety of advanced applications, ranging from performance tuning to vehicle tracking. Exploring these advanced uses can help you unlock the full potential of this versatile interface.
8.1 Performance Tuning
The OBD2 port can be used to reprogram your vehicle’s engine control unit (ECU) to optimize performance. This process, known as performance tuning, can improve horsepower, torque, and fuel efficiency.
However, it’s important to note that performance tuning can void your vehicle’s warranty and may not be legal in all areas. Always consult with a qualified mechanic before attempting to tune your vehicle.
8.2 Vehicle Tracking
GPS trackers can be plugged into the OBD2 port to provide real-time location tracking. This can be useful for fleet management, vehicle security, and monitoring young drivers.
Some GPS trackers also offer additional features, such as geofencing, which allows you to set up virtual boundaries and receive alerts when your vehicle enters or exits a specific area.
8.3 Usage-Based Insurance
Some insurance companies offer usage-based insurance programs that use data from the OBD2 port to track your driving behavior. This data is used to calculate your insurance premiums, with safer drivers receiving lower rates.
Usage-based insurance can be a good option for drivers who are confident in their driving skills and want to save money on their insurance premiums.
8.4 Remote Diagnostics
Some advanced telematics systems offer remote diagnostics capabilities, allowing you to monitor your vehicle’s health and performance from a remote location. This can be useful for fleet management and for drivers who want to stay informed about their vehicle’s condition.
Remote diagnostics systems typically provide access to DTCs, real-time data, and other diagnostic information, allowing you to identify potential problems and schedule maintenance as needed.
9. FAQ About the OBD2 Port
Here are some frequently asked questions about the OBD2 port:
9.1 What is an OBD2 scanner?
An OBD2 scanner is a device used to read diagnostic information from a vehicle’s On-Board Diagnostics II (OBD2) system, helping to identify and troubleshoot potential issues.
9.2 How do I read OBD2 error codes?
Connect an OBD2 scanner to your vehicle’s OBD2 port, turn on the ignition, and select the “Read Codes” option on the scanner’s menu to view any stored Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs).
9.3 Can I use an OBD2 scanner on any car?
OBD2 scanners are compatible with all cars and trucks manufactured since 1996 in the United States, as OBD2 is a standardized system.
9.4 What are common car errors and how can I fix them?
Common car errors include engine misfires, oxygen sensor faults, and evaporative emission system leaks. These can often be diagnosed and addressed using an OBD2 scanner to identify the specific issue.
9.5 Is it safe to clear OBD2 codes myself?
Yes, it is generally safe to clear OBD2 codes yourself, but only after you have addressed the underlying issue causing the code. Clearing codes without fixing the problem will only result in the code reappearing.
9.6 Will clearing OBD2 codes affect my car’s performance?
Clearing OBD2 codes will not directly affect your car’s performance, but addressing the underlying issues that triggered the codes can lead to improved performance and fuel efficiency.
9.7 Where is the OBD2 port located in my car?
The OBD2 port is typically located under the driver’s side dashboard, within easy reach. Consult your vehicle’s owner’s manual for the exact location.
9.8 Can an OBD2 scanner improve fuel efficiency?
Yes, by identifying issues that may be affecting your fuel efficiency, such as a faulty oxygen sensor, an OBD2 scanner can help you improve your car’s fuel economy.
9.9 What does the check engine light indicate?
The check engine light indicates that your vehicle’s computer has detected a problem. An OBD2 scanner can be used to read the Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) associated with the check engine light, providing insight into the nature of the problem.
9.10 Are there any risks associated with using an OBD2 port?
There are minimal risks associated with using an OBD2 port. However, it’s important to use a reputable scanner and avoid making unauthorized modifications to your vehicle’s computer.
10. Contact OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN for Expert Assistance
Navigating the complexities of vehicle diagnostics can be challenging, but you don’t have to do it alone. OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN is here to provide expert assistance and guidance on all your OBD2-related needs.
Whether you’re a seasoned mechanic or a first-time car owner, our team of experienced professionals can help you understand the capabilities of your OBD2 port and how to effectively use it for vehicle maintenance and repair. We offer a range of services, including:
- OBD2 Scanner Recommendations: We can help you choose the right OBD2 scanner for your specific needs and budget.
- Diagnostic Assistance: Our team can help you interpret DTCs and diagnose vehicle problems.
- Repair Guidance: We can provide guidance on how to perform common repairs and maintenance tasks.
Don’t let vehicle problems keep you off the road. Contact OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN today and let us help you get back on track.
Contact Information:
- Address: 123 Main Street, Los Angeles, CA 90001, United States
- WhatsApp: +1 (641) 206-8880
- Website: OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN
Take control of your vehicle’s health and performance with OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN. Contact us today to learn more about how we can help you save money, improve fuel efficiency, and extend the life of your vehicle. We are dedicated to providing the knowledge and tools you need to confidently manage your car’s diagnostics and repairs.