The 2001 Ford F-150 OBD2 fuse location is crucial for diagnosing and resolving issues with your vehicle’s onboard diagnostics system, and OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN provides a comprehensive guide to help you locate it efficiently. Understanding the OBD2 system and the fuses that support it allows you to maintain your truck’s performance. For expert assistance, contact us at +1 (641) 206-8880.
Contents
- 1. Understanding the Importance of Fuses in Your 2001 Ford F-150’s OBD2 System
- 1.1 What is the Role of Fuses?
- 1.2 Why is the OBD2 System Important?
- 1.3 Common Issues Related to Blown Fuses
- 1.4 How to Identify a Blown Fuse
- 1.5 Tools You’ll Need
- 2. Locating the Fuse Boxes in Your 2001 Ford F-150
- 2.1 Passenger Compartment Fuse Panel
- 2.1.1 Location Details
- 2.1.2 Diagram and Fuse Layout
- 2.1.3 Step-by-Step Instructions to Access
- 2.2 Power Distribution Box
- 2.2.1 Location Details
- 2.2.2 Diagram and Fuse Layout
- 2.2.3 Step-by-Step Instructions to Access
- 3. Specific Fuses Related to the OBD2 System in the 2001 Ford F-150
- 3.1 Fuses in the Passenger Compartment
- 3.2 Fuses in the Power Distribution Box
- 4. Step-by-Step Guide to Replacing a Blown Fuse
- 4.1 Turn Off the Vehicle
- 4.2 Locate the Fuse Box
- 4.3 Open the Fuse Box
- 4.4 Identify the Blown Fuse
- 4.5 Remove the Blown Fuse
- 4.6 Install a New Fuse
- 4.7 Test the System
- 4.8 Replace the Cover
- 5. Common Problems and Solutions
- 5.1 OBD2 Scanner Still Not Working After Fuse Replacement
- 5.2 Fuse Blows Again Immediately After Replacement
- 5.3 Check Engine Light Stays On
- 6. Advanced Troubleshooting Tips
- 6.1 Using a Wiring Diagram
- 6.2 Testing for Voltage Drops
- 6.3 Checking Ground Connections
- 6.4 PCM Diagnostics
- 7. Maintaining Your 2001 Ford F-150’s Electrical System
- 7.1 Regular Inspections
- 7.2 Battery Maintenance
- 7.3 Proper Fuse Replacement
- 7.4 Professional Service
- 8. The Benefits of Using OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN
- 8.1 Expert Advice
- 8.2 Comprehensive Guides
- 8.3 Reliable Information
- 8.4 Support and Assistance
- 9. Call to Action
- 10. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- 10.1 What is an OBD2 Scanner?
- 10.2 How Do I Read OBD2 Codes?
- 10.3 What Are Common OBD2 Error Codes and How to Fix Them?
- 10.4 Where Can I Find the OBD2 Port in My 2001 Ford F-150?
- 10.5 Can a Blown Fuse Affect the OBD2 System?
- 10.6 How Do I Know Which Fuse is for the OBD2 Port?
- 10.7 What Should I Do If My Check Engine Light is On?
- 10.8 Is It Safe to Drive With the Check Engine Light On?
- 10.9 How Can OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN Help Me?
- 10.10 What Are the Benefits of Regularly Scanning My Vehicle?
1. Understanding the Importance of Fuses in Your 2001 Ford F-150’s OBD2 System
Fuses are critical components in your 2001 Ford F-150’s electrical system, acting as safeguards to protect various circuits from overcurrent and potential damage. The OBD2 (On-Board Diagnostics II) system, which is essential for monitoring and diagnosing your vehicle’s performance, relies on these fuses to function correctly. According to a study by the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA), a properly functioning OBD2 system can significantly reduce emissions and improve fuel efficiency. Knowing the 2001 Ford F-150 OBD2 fuse location is important for maintaining your truck.
1.1 What is the Role of Fuses?
Fuses are designed to break an electrical circuit when the current exceeds a specified level. This prevents damage to sensitive electronic components and reduces the risk of electrical fires. In your 2001 Ford F-150, multiple fuses protect different parts of the OBD2 system, including the diagnostic port itself, the PCM (Powertrain Control Module), and related sensors.
1.2 Why is the OBD2 System Important?
The OBD2 system monitors various aspects of your vehicle’s performance, including engine operation, emissions, and fuel efficiency. When it detects a problem, it stores a diagnostic trouble code (DTC) that can be accessed using an OBD2 scanner. According to the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), OBD2 systems have been mandatory on all cars and light trucks sold in the United States since 1996 to ensure compliance with emissions standards.
1.3 Common Issues Related to Blown Fuses
Several issues can arise if the fuses related to the OBD2 system are blown:
- OBD2 Scanner Not Working: If the fuse protecting the OBD2 port is blown, the scanner may not power on or be able to communicate with the vehicle’s computer.
- Check Engine Light Issues: A blown fuse can sometimes cause the check engine light to illuminate or prevent it from turning on when there’s a problem.
- Performance Problems: Fuses related to the PCM and sensors can affect engine performance, fuel efficiency, and overall drivability.
1.4 How to Identify a Blown Fuse
Identifying a blown fuse is usually straightforward. Here are a few methods:
- Visual Inspection: Most fuses have a transparent window that allows you to see the internal filament. If the filament is broken or the fuse appears burnt, it’s likely blown.
- Multimeter Testing: A multimeter can be used to check the continuity of the fuse. If there’s no continuity, the fuse is blown.
- Fuse Tester: A dedicated fuse tester can quickly determine if a fuse is good or bad.
1.5 Tools You’ll Need
Before you start looking for the 2001 Ford F-150 OBD2 fuse location, gather these essential tools:
- Fuse Puller: This tool makes it easier to remove fuses without damaging them.
- Multimeter: For testing fuse continuity.
- Flashlight: To help you see clearly in the fuse box.
- OBD2 Scanner: To check if the system is functioning after replacing the fuse.
2. Locating the Fuse Boxes in Your 2001 Ford F-150
The 2001 Ford F-150 has two primary fuse box locations:
- Passenger Compartment Fuse Panel: Located inside the cabin, usually under the dashboard on the driver’s side or passenger’s side.
- Power Distribution Box: Situated in the engine compartment, near the battery.
2.1 Passenger Compartment Fuse Panel
The passenger compartment fuse panel is typically the first place to check for OBD2-related fuse issues.
2.1.1 Location Details
In the 2001 Ford F-150, the passenger compartment fuse panel is usually found beneath the dashboard on the driver’s side. You may need to kneel down and look up to locate it. It’s often behind a small access panel that can be easily removed.
2.1.2 Diagram and Fuse Layout
Once you’ve located the fuse panel, you’ll need a diagram to identify the correct fuse. The diagram is usually printed on the inside of the access panel or in the owner’s manual. Here’s a general idea of what you might find:
| Fuse Number | Amp Rating | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 3 | 20A | Cigar Lighter, OBD-II Scan Tool Connector |
| 20 | 5A | Audio, GEM (or CTM) Module, Powertrain Control Module (PCM) |
| 21 | 15A | Starter Relay, Fuse 20 |
| 30 | 30A | Passive Anti Theft Transceiver, Cluster, Ignition Coils, Powertrain Control Module Relay |
 2001 Ford F-150 passenger compartment fuse panel
2001 Ford F-150 passenger compartment fuse panel
2.1.3 Step-by-Step Instructions to Access
- Locate the Panel: Kneel down on the driver’s side and look under the dashboard.
- Remove the Access Panel: Gently pull the access panel to remove it. It might be held in place by clips or screws.
- Consult the Diagram: Use the fuse box diagram to identify the fuse related to the OBD2 system.
- Inspect the Fuse: Visually inspect the fuse to see if the filament is broken.
- Test the Fuse: Use a multimeter to check continuity if you’re unsure.
- Replace the Fuse: If the fuse is blown, replace it with a new fuse of the same amp rating.
2.2 Power Distribution Box
The power distribution box, located in the engine compartment, contains fuses and relays that protect higher-current circuits.
2.2.1 Location Details
The power distribution box is typically located under the hood, near the battery. It’s usually a black plastic box with a lid that can be easily opened.
2.2.2 Diagram and Fuse Layout
The fuse layout for the power distribution box is usually printed on the underside of the lid. Here’s a general idea of what you might find:
| Fuse Number | Amp Rating | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 2 | 30A | Powertrain Control Module |
| 18 | 15A | Powertrain Control Module, Fuel Injectors, Fuel Pump Relay, Idle Air Control, Mass Air Flow Sensor |
| 102 | 50A | Four Wheel Antilock Brake Module |
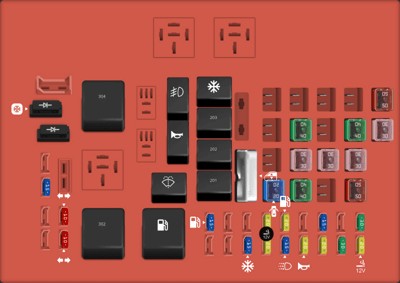 2001 Ford F-150 power distribution box diagram
2001 Ford F-150 power distribution box diagram
2.2.3 Step-by-Step Instructions to Access
- Open the Hood: Locate the hood release lever inside the cabin and pull it to open the hood.
- Locate the Box: Find the power distribution box near the battery.
- Open the Lid: Press the release clips or unscrew the fasteners to open the lid.
- Consult the Diagram: Use the fuse box diagram to identify the fuse related to the OBD2 system.
- Inspect the Fuse: Visually inspect the fuse to see if the filament is broken.
- Test the Fuse: Use a multimeter to check continuity if you’re unsure.
- Replace the Fuse: If the fuse is blown, replace it with a new fuse of the same amp rating.
3. Specific Fuses Related to the OBD2 System in the 2001 Ford F-150
Identifying the specific fuses related to the OBD2 system can save you time and effort. Here are some key fuses to check:
3.1 Fuses in the Passenger Compartment
- Fuse 3 (20A): This fuse is often associated with the cigar lighter and the OBD-II scan tool connector. If your OBD2 scanner isn’t powering on, this is a good place to start.
- Fuse 20 (5A): This fuse protects the audio system, GEM (Generic Electronic Module), and the Powertrain Control Module (PCM). A problem here can affect the OBD2 system’s ability to communicate.
- Fuse 30 (30A): This fuse protects the Passive Anti-Theft Transceiver, Cluster, Ignition Coils, and Powertrain Control Module Relay. If this fuse is blown, it can cause significant issues with the OBD2 system and overall vehicle performance.
3.2 Fuses in the Power Distribution Box
- Fuse 2 (30A): This fuse directly protects the Powertrain Control Module (PCM). If the PCM isn’t receiving power, the OBD2 system won’t function.
- Fuse 18 (15A): This fuse protects the Powertrain Control Module, Fuel Injectors, Fuel Pump Relay, Idle Air Control, and Mass Air Flow Sensor. Issues with this fuse can lead to a variety of performance problems and affect the OBD2 system.
- Fuse 102 (50A): While primarily for the Four-Wheel Antilock Brake Module, this fuse can indirectly affect the OBD2 system, as the ABS is often monitored by the OBD2 system.
4. Step-by-Step Guide to Replacing a Blown Fuse
Replacing a blown fuse is a simple process. Follow these steps to ensure you do it correctly:
4.1 Turn Off the Vehicle
Before you start working on the electrical system, turn off the ignition and remove the key. This prevents any accidental electrical shorts.
4.2 Locate the Fuse Box
Determine whether the fuse you need to replace is in the passenger compartment fuse panel or the power distribution box.
4.3 Open the Fuse Box
Remove the access panel or open the lid of the fuse box.
4.4 Identify the Blown Fuse
Use the fuse box diagram to locate the fuse related to the OBD2 system. Visually inspect the fuse to see if the filament is broken. If you’re unsure, use a multimeter to check for continuity.
4.5 Remove the Blown Fuse
Use a fuse puller to gently remove the blown fuse. If you don’t have a fuse puller, you can use a pair of small pliers, but be careful not to damage the surrounding fuses.
4.6 Install a New Fuse
Insert a new fuse of the same amp rating into the empty slot. Make sure the fuse is fully seated.
4.7 Test the System
Turn on the ignition and use an OBD2 scanner to check if the system is functioning correctly. If the scanner powers on and can communicate with the vehicle’s computer, the fuse replacement was successful.
4.8 Replace the Cover
Replace the access panel or close the lid of the fuse box.
5. Common Problems and Solutions
Even with a good understanding of fuse locations and replacement procedures, you might encounter some common problems. Here are a few scenarios and their solutions:
5.1 OBD2 Scanner Still Not Working After Fuse Replacement
If the OBD2 scanner still isn’t working after replacing the fuse, consider these possibilities:
- Incorrect Fuse: Double-check that you replaced the correct fuse and that it has the correct amp rating.
- Wiring Issues: There might be a problem with the wiring leading to the OBD2 port. Check for any visible damage or corrosion.
- Scanner Malfunction: The OBD2 scanner itself might be faulty. Try using a different scanner to see if it works.
According to a study by the American Automobile Association (AAA), electrical system issues are a common cause of vehicle breakdowns, so it’s important to address these problems promptly.
5.2 Fuse Blows Again Immediately After Replacement
If the fuse blows again immediately after replacement, there’s likely a short circuit in the system. Here’s how to troubleshoot:
- Inspect Wiring: Check the wiring connected to the components protected by the fuse. Look for any signs of damage, such as frayed wires or melted insulation.
- Disconnect Components: Disconnect the components one by one to see if you can isolate the short circuit. For example, disconnect the OBD2 port, PCM, and related sensors.
- Professional Help: If you can’t find the short circuit, it’s best to take your vehicle to a qualified mechanic.
5.3 Check Engine Light Stays On
If the check engine light remains illuminated after replacing the fuse, it means the underlying problem that triggered the light is still present. Use an OBD2 scanner to read the diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) and diagnose the issue.
6. Advanced Troubleshooting Tips
For those who want to delve deeper into troubleshooting OBD2 system issues, here are some advanced tips:
6.1 Using a Wiring Diagram
A wiring diagram can be invaluable for tracing circuits and identifying potential problems. You can find wiring diagrams for the 2001 Ford F-150 in the service manual or online.
6.2 Testing for Voltage Drops
Voltage drops can indicate resistance in a circuit, which can cause fuses to blow. Use a multimeter to test for voltage drops across the circuit.
6.3 Checking Ground Connections
Poor ground connections can also cause electrical problems. Make sure all ground connections are clean and tight.
6.4 PCM Diagnostics
If you suspect a problem with the PCM, you can perform a series of diagnostic tests using an OBD2 scanner. These tests can help you identify internal PCM failures.
7. Maintaining Your 2001 Ford F-150’s Electrical System
Proper maintenance of your vehicle’s electrical system can prevent many common problems. Here are some tips:
7.1 Regular Inspections
Inspect the fuses, wiring, and connections regularly. Look for any signs of damage or corrosion.
7.2 Battery Maintenance
A weak or failing battery can put a strain on the electrical system. Have the battery tested regularly and replace it if necessary. According to a study by J.D. Power, battery problems are a common cause of vehicle starting issues.
7.3 Proper Fuse Replacement
Always replace blown fuses with fuses of the same amp rating. Using a fuse with a higher amp rating can damage the electrical system.
7.4 Professional Service
If you’re not comfortable working on the electrical system yourself, take your vehicle to a qualified mechanic for regular service.
8. The Benefits of Using OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN
At OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN, we are committed to providing you with the most accurate and up-to-date information on OBD2 systems and vehicle diagnostics. Here are some of the benefits of using our services:
8.1 Expert Advice
Our team of experienced mechanics and technicians can provide you with expert advice on diagnosing and repairing OBD2 system issues.
8.2 Comprehensive Guides
We offer comprehensive guides on various OBD2-related topics, including fuse locations, diagnostic trouble codes, and repair procedures.
8.3 Reliable Information
Our information is based on the latest research and industry standards, ensuring you receive reliable and accurate guidance.
8.4 Support and Assistance
We are here to support you every step of the way. If you have any questions or need assistance, don’t hesitate to contact us at +1 (641) 206-8880.
9. Call to Action
Are you experiencing OBD2 system issues with your 2001 Ford F-150? Don’t let electrical problems keep you off the road. Contact OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN today for expert advice and assistance. Whether you need help locating a fuse or diagnosing a complex issue, our team is here to help. Reach out to us via WhatsApp at +1 (641) 206-8880 or visit our website at OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN. Our address is 123 Main Street, Los Angeles, CA 90001, United States. Let us help you keep your 2001 Ford F-150 running smoothly and efficiently.
10. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
10.1 What is an OBD2 Scanner?
An OBD2 scanner is a diagnostic tool used to retrieve diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) from a vehicle’s onboard computer system. These codes can help identify issues with the engine, transmission, emissions system, and other components.
10.2 How Do I Read OBD2 Codes?
To read OBD2 codes, you’ll need an OBD2 scanner. Plug the scanner into the OBD2 port, turn on the ignition, and follow the scanner’s instructions to retrieve the codes.
10.3 What Are Common OBD2 Error Codes and How to Fix Them?
Common OBD2 error codes include P0300 (random misfire), P0171 (system too lean), and P0420 (catalyst system efficiency below threshold). Each code has specific troubleshooting steps, which may involve replacing sensors, repairing vacuum leaks, or replacing the catalytic converter.
10.4 Where Can I Find the OBD2 Port in My 2001 Ford F-150?
The OBD2 port in the 2001 Ford F-150 is typically located under the dashboard on the driver’s side. It’s usually near the steering column or in the center console area.
10.5 Can a Blown Fuse Affect the OBD2 System?
Yes, a blown fuse can definitely affect the OBD2 system. If the fuse protecting the OBD2 port or the PCM is blown, the OBD2 scanner may not be able to communicate with the vehicle’s computer.
10.6 How Do I Know Which Fuse is for the OBD2 Port?
Consult the fuse box diagram for your 2001 Ford F-150. The diagram will identify the fuse that protects the OBD2 port. It’s often labeled as “OBD-II Scan Tool Connector” or something similar.
10.7 What Should I Do If My Check Engine Light is On?
If your check engine light is on, use an OBD2 scanner to retrieve the diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs). Research the codes to understand the underlying problem and take appropriate action to repair the issue.
10.8 Is It Safe to Drive With the Check Engine Light On?
It depends on the nature of the problem. If the check engine light is flashing, it indicates a serious issue that could damage the engine. In this case, it’s best to stop driving and have the vehicle towed to a mechanic. If the light is on but not flashing, it’s generally safe to drive, but you should still have the problem diagnosed and repaired as soon as possible.
10.9 How Can OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN Help Me?
OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN provides expert advice, comprehensive guides, and reliable information on OBD2 systems and vehicle diagnostics. We can help you diagnose and repair OBD2 system issues, saving you time and money.
10.10 What Are the Benefits of Regularly Scanning My Vehicle?
Regularly scanning your vehicle with an OBD2 scanner can help you identify potential problems early, before they become serious and costly. It can also help you monitor your vehicle’s performance and ensure it’s running efficiently.