As your trusted automotive repair expert at OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN, we’re here to help you navigate the world of OBD2 diagnostics for your 2003 Silverado. Understanding the 2003 Silverado Iso Obd2 system empowers you to effectively diagnose vehicle issues, utilize car diagnostic tools, and maintain your truck’s optimal performance. This article will give you the necessary know-how for effective truck maintenance and repairs. Discover solutions now.
Contents
- 1. Understanding OBD2 and its Importance for Your 2003 Silverado
- 1.1. Key Benefits of Using OBD2 on a 2003 Silverado
- 1.2. How OBD2 Scanners Work
- 1.3. Understanding OBD2 Protocols
- 2. Identifying the Correct OBD2 Connector for Your 2003 Silverado
- 2.1. Location of the DLC in a 2003 Silverado
- 2.2. Understanding Type A and Type B Connectors
- 2.3. Pinout Configuration of the OBD2 Connector
- 3. Step-by-Step Guide to Using an OBD2 Scanner on Your 2003 Silverado
- 3.1. Connecting the OBD2 Scanner
- 3.2. Reading Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
- 3.3. Interpreting Common OBD2 Codes for a 2003 Silverado
- 3.4. Clearing OBD2 Codes
- 4. Advanced OBD2 Diagnostics for Your 2003 Silverado
- 4.1. Using Live Data Streaming
- 4.2. Utilizing Freeze Frame Data
- 4.3. Understanding Mode 6 Diagnostics
- 5. Common Issues and Solutions for a 2003 Silverado Based on OBD2 Codes
- 5.1. Addressing Misfire Issues (P0300)
- 5.2. Resolving Lean Fuel Mixture Problems (P0171)
- 5.3. Dealing with Catalytic Converter Efficiency Issues (P0420)
- 5.4. Fixing Evaporative Emission Control System Malfunctions (P0440)
- 5.5. Troubleshooting Mass Air Flow Sensor Issues (P0102)
- 6. Choosing the Right OBD2 Scanner for Your Needs
- 6.1. Basic OBD2 Scanners vs. Advanced Scanners
- 6.2. Features to Look for in an OBD2 Scanner
- 6.3. Top OBD2 Scanner Recommendations
- 7. Maintaining Your 2003 Silverado with OBD2
- 7.1. Regular Diagnostic Checks
- 7.2. Tracking Vehicle Performance with OBD2
- 7.3. Preventing Costly Repairs with Proactive Diagnostics
- 8. OBD2 Resources and Support
- 8.1. Online Forums and Communities
- 8.2. Technical Manuals and Databases
- 8.3. When to Seek Professional Help
- 9. Conclusion: Mastering OBD2 Diagnostics for Your 2003 Silverado
- 10. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About 2003 Silverado ISO OBD2
- 10.1. What is an OBD2 Scanner?
- 10.2. How Do I Locate the OBD2 Port in My 2003 Silverado?
- 10.3. Can I Use Any OBD2 Scanner on My 2003 Silverado?
- 10.4. What Do the OBD2 Codes Mean?
- 10.5. Can I Clear the OBD2 Codes Myself?
- 10.6. What is Live Data Streaming?
- 10.7. What is Freeze Frame Data?
- 10.8. What is Mode 6 Diagnostics?
- 10.9. How Often Should I Scan My 2003 Silverado for OBD2 Codes?
- 10.10. When Should I Seek Professional Help for OBD2 Diagnostics?
1. Understanding OBD2 and its Importance for Your 2003 Silverado
What is OBD2, and why is it so important for your 2003 Silverado? OBD2, or On-Board Diagnostics II, is a standardized system that provides access to the health information of your vehicle. OBD2 is crucial because it allows you to monitor engine performance, diagnose problems, and ensure your 2003 Silverado runs efficiently.
OBD2 is a standardized system implemented in all cars and light trucks sold in the United States after 1996, and it is also used in European Union countries. It serves as a crucial interface for accessing the health information of your vehicle, including the 2003 Silverado. According to the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), OBD2 helps reduce emissions by monitoring critical engine components and systems. The EPA mandated OBD2 to ensure vehicles meet stringent emission standards. By complying with OBD2 standards, manufacturers can effectively monitor and manage vehicle emissions, contributing to cleaner air quality.
1.1. Key Benefits of Using OBD2 on a 2003 Silverado
What are the key benefits of using OBD2 on your 2003 Silverado? Using OBD2 on your 2003 Silverado offers several key benefits, including early detection of potential issues, cost savings on repairs, improved fuel efficiency, and enhanced vehicle performance.
- Early Detection of Issues: OBD2 scanners can help identify minor problems before they escalate into major repairs.
- Cost Savings on Repairs: By diagnosing issues early, you can often prevent costly repairs down the line.
- Improved Fuel Efficiency: Monitoring engine performance helps ensure your Silverado is running efficiently, saving you money on fuel.
- Enhanced Vehicle Performance: Regular OBD2 checks can keep your Silverado running smoothly and reliably.
- Emission Compliance: OBD2 helps ensure your vehicle meets emission standards, avoiding potential fines and contributing to environmental protection.
1.2. How OBD2 Scanners Work
How do OBD2 scanners work? OBD2 scanners work by plugging into your vehicle’s diagnostic port (DLC), typically located under the dashboard. These scanners read diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) stored by the vehicle’s computer, providing insights into potential issues.
OBD2 scanners retrieve data from the vehicle’s computer, translating it into readable information for the user. These codes help you understand the nature and location of the problem, allowing you to take appropriate action. According to a study by AAA, using OBD2 scanners can reduce diagnostic time by up to 40%. AAA’s research highlights the effectiveness of OBD2 scanners in streamlining the diagnostic process, which saves both time and money for vehicle owners and mechanics.
1.3. Understanding OBD2 Protocols
What are the different OBD2 protocols you should know about? The OBD2 system uses various communication protocols to interact with your vehicle’s computer. Understanding these protocols is essential for ensuring compatibility between your scanner and your 2003 Silverado.
The primary protocols include:
- J1850 PWM (Pulse Width Modulation): Used mainly by Ford vehicles.
- J1850 VPW (Variable Pulse Width): Used primarily by General Motors vehicles.
- ISO9141-2: Commonly used by European and Asian vehicles.
- ISO14230-4 (Keyword Protocol 2000): Also used by European and Asian vehicles.
- ISO15765-4/SAE J2480 (CAN – Controller Area Network): The most modern protocol, used in all vehicles since 2008.
Prior to 2003, US car manufacturers were not allowed to use the CAN protocol. However, by model year 2008, all vehicles adopted the CAN protocol. Understanding these protocols helps ensure compatibility between your diagnostic tool and your vehicle.
2. Identifying the Correct OBD2 Connector for Your 2003 Silverado
Where can you find the OBD2 connector in your 2003 Silverado? Identifying the correct OBD2 connector, also known as the Diagnostic Link Connector (DLC), is the first step in using an OBD2 scanner. For the 2003 Silverado, the DLC is typically located under the dashboard on the driver’s side.
SAE J1962 defines two types of DLCs: Type A and Type B. According to J1962, the Type A DLC is “located in the passenger or driver’s compartment in the area bounded by the driver’s end of the instrument panel to 300 mm (~1 ft) beyond the vehicle centerline, attached to the instrument panel and easy to access from the driver’s seat. The preferred location is between the steering column and the vehicle centerline.” Knowing where to find this connector ensures you can quickly and easily plug in your OBD2 scanner.
2.1. Location of the DLC in a 2003 Silverado
Where exactly can you find the DLC in a 2003 Silverado? The DLC in a 2003 Silverado is typically located under the dashboard on the driver’s side, often near the steering column. This location is designed for easy access.
The connector is designed for easy access from the driver’s seat, making it convenient to plug in your OBD2 scanner. Ensure the area around the connector is clear of obstructions for easy access. Having unobstructed access to the DLC ensures you can quickly connect your scanner and begin the diagnostic process.
2.2. Understanding Type A and Type B Connectors
What are the differences between Type A and Type B OBD2 connectors? Type A and Type B connectors are defined by SAE J1962 and differ primarily in the shape of the alignment tab. This difference is essential to consider when connecting diagnostic tools.
- Type A: Typically found in most passenger vehicles and light trucks.
- Type B: Less common, often found in heavier-duty vehicles.
 J1962F, Type A
J1962F, Type A
Figure 1 – J1962 Vehicle Connector, Type A shows the connector type commonly found in the 2003 Silverado, which is Type A.
For a 2003 Silverado, you’ll most likely encounter a Type A connector. Knowing this ensures you have the correct adapter if needed.
2.3. Pinout Configuration of the OBD2 Connector
What is the pinout configuration of the OBD2 connector, and why is it important? The pinout configuration of the OBD2 connector refers to the arrangement and function of each pin within the connector. This arrangement is standardized to ensure compatibility across different vehicles and scanners.
The standard pins include:
- Pin 4: Chassis Ground
- Pin 5: Signal Ground
- Pin 6: CAN High (J-2284)
- Pin 7: ISO 9141-2 K Line
- Pin 10: J1850 PWM Bus (+)
- Pin 14: CAN Low (J-2284)
- Pin 15: ISO 9141-2 L Line (Optional)
- Pin 16: Battery Positive
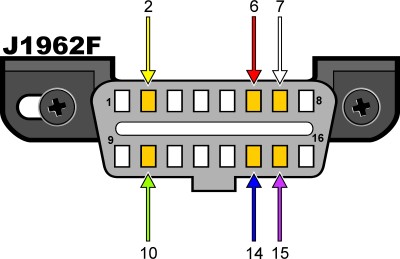 J1962F OBDII connector pinout
J1962F OBDII connector pinout
Figure 2 – J1962F OBDII connector pinout helps you identify the function of each pin in the OBD2 connector, crucial for diagnosing communication issues.
Understanding the pinout configuration can help diagnose communication problems between the scanner and the vehicle. For instance, missing pins or damaged connections can prevent the scanner from reading data. Knowledge of the pinout configuration can help you troubleshoot communication issues and ensure accurate readings.
3. Step-by-Step Guide to Using an OBD2 Scanner on Your 2003 Silverado
How do you use an OBD2 scanner on your 2003 Silverado? Using an OBD2 scanner on your 2003 Silverado is a straightforward process. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you:
- Locate the DLC: Find the Diagnostic Link Connector (DLC) under the dashboard on the driver’s side.
- Plug in the Scanner: Connect the OBD2 scanner to the DLC. Ensure it is securely plugged in.
- Turn on the Ignition: Turn the ignition key to the “ON” position without starting the engine.
- Power on the Scanner: Turn on the OBD2 scanner. It should power up and begin communicating with the vehicle’s computer.
- Read the Codes: Follow the scanner’s instructions to read diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs).
- Record the Codes: Write down any DTCs that appear. These codes will help you diagnose the issue.
- Interpret the Codes: Use a reference guide or online resource to interpret the meaning of the DTCs.
- Clear the Codes (Optional): If desired, you can clear the codes after recording them. However, be aware that the codes will reappear if the issue persists.
- Take Action: Based on the DTCs, take appropriate action to diagnose and repair the problem.
Following these steps ensures you can effectively use an OBD2 scanner to diagnose issues with your 2003 Silverado.
3.1. Connecting the OBD2 Scanner
How do you properly connect the OBD2 scanner to your 2003 Silverado? To properly connect the OBD2 scanner, first, locate the DLC under the dashboard. Then, firmly plug the scanner into the connector, ensuring a secure fit.
A secure connection is essential for accurate data retrieval. Ensure there are no loose connections or obstructions that could interfere with the scanner’s operation. A well-connected scanner provides reliable diagnostic information.
3.2. Reading Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
How do you read and understand Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)? Once the scanner is connected and powered on, navigate to the “Read Codes” or “Diagnostic Codes” option in the scanner’s menu. The scanner will then display any stored DTCs.
DTCs are typically five-character codes consisting of a letter followed by four numbers. The letter indicates the system related to the code:
- P: Powertrain (Engine, Transmission)
- B: Body (Airbags, Power Windows)
- C: Chassis (ABS, Suspension)
- U: Network (Communication)
The numbers provide more specific information about the fault. Understanding these codes is crucial for accurate diagnosis.
3.3. Interpreting Common OBD2 Codes for a 2003 Silverado
What are some common OBD2 codes you might encounter with a 2003 Silverado, and what do they mean? Several common OBD2 codes can appear on a 2003 Silverado, each indicating a specific issue. Here are a few examples:
- P0300: Random/Multiple Cylinder Misfire Detected: This code indicates that the engine is misfiring, which can be caused by faulty spark plugs, ignition coils, or fuel injectors.
- P0171: System Too Lean (Bank 1): This code suggests that the engine is running lean, meaning there is too much air and not enough fuel in the air-fuel mixture.
- P0420: Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold (Bank 1): This code indicates that the catalytic converter is not functioning efficiently, which can lead to increased emissions.
- P0440: Evaporative Emission Control System Malfunction: This code indicates a problem with the evaporative emission control system, which prevents fuel vapors from escaping into the atmosphere.
- P0102: Mass or Volume Air Flow Circuit Low Input: This code indicates that the mass air flow (MAF) sensor is reporting a lower-than-expected airflow, which can affect engine performance.
Understanding these common codes can help you quickly identify and address potential issues with your 2003 Silverado.
3.4. Clearing OBD2 Codes
When and how should you clear OBD2 codes on your 2003 Silverado? Clearing OBD2 codes should be done cautiously. After you have recorded and understood the DTCs, you can clear them using the scanner’s “Clear Codes” or “Erase Codes” function.
However, only clear the codes if you have addressed the underlying issue. Clearing codes without fixing the problem will only result in the codes reappearing. Clearing codes can be useful for:
- Verifying a repair: After fixing a problem, clear the code to see if it returns.
- Resetting the system: Some repairs require clearing the codes to reset the vehicle’s computer.
Be aware that clearing codes will also reset the vehicle’s emission monitors, which may take some time to reset.
4. Advanced OBD2 Diagnostics for Your 2003 Silverado
What advanced OBD2 diagnostic techniques can you use on your 2003 Silverado? For more in-depth diagnostics, consider using advanced features of your OBD2 scanner, such as live data streaming, freeze frame data, and advanced mode 6 diagnostics.
These features provide a more detailed view of your vehicle’s performance and can help pinpoint intermittent or complex issues.
4.1. Using Live Data Streaming
How can live data streaming help diagnose issues on your 2003 Silverado? Live data streaming allows you to view real-time data from your vehicle’s sensors and systems. This can be invaluable for diagnosing issues that don’t trigger a specific DTC.
For example, you can monitor:
- Engine RPM
- Coolant Temperature
- Fuel Trims
- O2 Sensor Readings
- MAF Sensor Readings
Monitoring these parameters in real-time can help identify anomalies that indicate a problem. If the MAF sensor reading is unusually low, it may indicate a faulty sensor or an air intake leak.
4.2. Utilizing Freeze Frame Data
What is freeze frame data, and how can you use it? Freeze frame data captures a snapshot of sensor data at the moment a DTC is triggered. This information can provide valuable clues about the conditions that led to the fault.
Freeze frame data typically includes:
- Engine Speed
- Engine Load
- Coolant Temperature
- Fuel Trim
- Vehicle Speed
By examining this data, you can often identify the specific conditions under which the problem occurred, making diagnosis easier. For instance, if a misfire code (P0300) is accompanied by high engine load and low coolant temperature, it may suggest an issue related to cold starts.
4.3. Understanding Mode 6 Diagnostics
What is Mode 6 diagnostics, and how can it help with complex issues? Mode 6 diagnostics provides access to non-standardized test results that can help diagnose complex or intermittent issues. This mode allows you to view detailed information about specific components and systems.
Mode 6 data can vary depending on the vehicle manufacturer but often includes:
- Catalyst Monitoring
- Evaporative System Monitoring
- Misfire Monitoring
Accessing Mode 6 data requires a more advanced OBD2 scanner but can provide invaluable insights into difficult-to-diagnose problems. If your catalytic converter is suspected of failing, Mode 6 data can provide detailed information about its performance.
5. Common Issues and Solutions for a 2003 Silverado Based on OBD2 Codes
What are some common issues and solutions for a 2003 Silverado based on OBD2 codes? Based on the OBD2 codes retrieved, you can identify and address common issues with your 2003 Silverado. Here are some examples:
- P0300 (Random/Multiple Cylinder Misfire Detected):
- Possible Causes: Faulty spark plugs, ignition coils, fuel injectors, vacuum leaks.
- Solutions: Replace spark plugs, test and replace ignition coils, clean or replace fuel injectors, check and repair vacuum leaks.
- P0171 (System Too Lean, Bank 1):
- Possible Causes: Vacuum leaks, faulty oxygen sensor, dirty fuel injectors, low fuel pressure.
- Solutions: Check and repair vacuum leaks, replace oxygen sensor, clean fuel injectors, check fuel pressure and replace fuel pump if necessary.
- P0420 (Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold, Bank 1):
- Possible Causes: Failing catalytic converter, exhaust leaks, faulty oxygen sensors.
- Solutions: Replace catalytic converter, repair exhaust leaks, replace oxygen sensors.
- P0440 (Evaporative Emission Control System Malfunction):
- Possible Causes: Loose or faulty gas cap, leaks in EVAP system hoses, faulty purge valve.
- Solutions: Tighten or replace gas cap, check and repair EVAP system hoses, replace purge valve.
- P0102 (Mass or Volume Air Flow Circuit Low Input):
- Possible Causes: Dirty or faulty MAF sensor, air intake leaks, wiring issues.
- Solutions: Clean or replace MAF sensor, check and repair air intake leaks, inspect and repair wiring.
Addressing these issues promptly can help maintain your 2003 Silverado’s performance and reliability.
5.1. Addressing Misfire Issues (P0300)
How do you address misfire issues indicated by code P0300? Addressing misfire issues indicated by code P0300 involves systematically checking and replacing components until the misfire is resolved.
Steps to take:
- Check Spark Plugs: Inspect and replace any worn or damaged spark plugs.
- Test Ignition Coils: Use a multimeter to test the resistance of each ignition coil and replace any that are faulty.
- Inspect Fuel Injectors: Check fuel injectors for proper function and clean or replace as needed.
- Check for Vacuum Leaks: Use a smoke machine to check for vacuum leaks and repair any leaks found.
By following these steps, you can effectively address misfire issues and restore your Silverado’s performance.
5.2. Resolving Lean Fuel Mixture Problems (P0171)
How do you resolve lean fuel mixture problems indicated by code P0171? Resolving lean fuel mixture problems involves identifying and correcting the causes of the lean condition.
Steps to take:
- Check for Vacuum Leaks: Inspect all vacuum lines and intake gaskets for leaks.
- Test Oxygen Sensor: Use an OBD2 scanner to monitor the oxygen sensor readings and replace the sensor if it’s not functioning correctly.
- Clean Fuel Injectors: Use a fuel injector cleaner or have the injectors professionally cleaned.
- Check Fuel Pressure: Use a fuel pressure gauge to check the fuel pressure and replace the fuel pump if necessary.
Addressing these issues will help restore the proper air-fuel mixture and improve engine performance.
5.3. Dealing with Catalytic Converter Efficiency Issues (P0420)
How do you deal with catalytic converter efficiency issues indicated by code P0420? Dealing with catalytic converter efficiency issues involves verifying the converter’s performance and addressing any underlying issues that may have caused the failure.
Steps to take:
- Inspect for Exhaust Leaks: Check the exhaust system for leaks before and after the catalytic converter.
- Test Oxygen Sensors: Ensure the oxygen sensors upstream and downstream of the converter are functioning correctly.
- Replace Catalytic Converter: If the converter is indeed failing, replace it with a new, high-quality unit.
Properly addressing these issues will help reduce emissions and ensure your Silverado meets environmental standards.
5.4. Fixing Evaporative Emission Control System Malfunctions (P0440)
How do you fix evaporative emission control system malfunctions indicated by code P0440? Fixing evaporative emission control system malfunctions involves identifying and repairing leaks or malfunctions in the EVAP system.
Steps to take:
- Check Gas Cap: Ensure the gas cap is properly tightened and in good condition.
- Inspect EVAP Hoses: Check all EVAP system hoses for cracks or leaks.
- Test Purge Valve: Use a multimeter to test the purge valve and replace it if it’s not functioning correctly.
Repairing these issues will help prevent fuel vapors from escaping into the atmosphere and ensure your Silverado meets emissions standards.
5.5. Troubleshooting Mass Air Flow Sensor Issues (P0102)
How do you troubleshoot mass air flow sensor issues indicated by code P0102? Troubleshooting mass air flow sensor issues involves verifying the sensor’s performance and addressing any related issues.
Steps to take:
- Clean MAF Sensor: Use a MAF sensor cleaner to clean the sensor element.
- Check for Air Intake Leaks: Inspect the air intake system for leaks between the MAF sensor and the throttle body.
- Inspect Wiring: Check the wiring and connectors to the MAF sensor for damage or corrosion.
Addressing these issues will help ensure the MAF sensor provides accurate airflow readings, improving engine performance.
6. Choosing the Right OBD2 Scanner for Your Needs
How do you choose the right OBD2 scanner for your needs? Choosing the right OBD2 scanner depends on your needs and budget. There are several types of scanners available, ranging from basic code readers to advanced diagnostic tools.
Consider these factors when choosing a scanner:
- Features: Basic scanners read and clear codes, while advanced scanners offer features like live data streaming, freeze frame data, and Mode 6 diagnostics.
- Compatibility: Ensure the scanner is compatible with your 2003 Silverado’s OBD2 protocol.
- Ease of Use: Choose a scanner with a user-friendly interface and clear instructions.
- Price: Scanners range in price from around $20 to several hundred dollars, depending on the features.
- Updates: Check if the scanner supports software updates to ensure it stays compatible with newer vehicles and diagnostic protocols.
Selecting the right scanner will make diagnosing and repairing your 2003 Silverado much easier.
6.1. Basic OBD2 Scanners vs. Advanced Scanners
What are the differences between basic and advanced OBD2 scanners? Basic OBD2 scanners primarily read and clear diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs), making them suitable for simple diagnostics. Advanced scanners, on the other hand, offer a wider range of features for more comprehensive analysis.
| Feature | Basic OBD2 Scanners | Advanced OBD2 Scanners |
|---|---|---|
| Code Reading | Reads and clears DTCs | Reads and clears DTCs, enhanced codes |
| Live Data | Limited or no live data | Extensive live data streaming |
| Freeze Frame Data | Limited or no freeze frame data | Captures freeze frame data |
| Mode 6 | Not supported | Supports Mode 6 diagnostics |
| Bi-Directional | Not supported | Supports bi-directional control |
| Price | Lower price range | Higher price range |
The choice between a basic and advanced scanner depends on your diagnostic needs and budget.
6.2. Features to Look for in an OBD2 Scanner
What key features should you look for when choosing an OBD2 scanner? When selecting an OBD2 scanner, consider these key features to ensure it meets your diagnostic needs:
- Code Reading and Clearing: Essential for basic diagnostics.
- Live Data Streaming: Allows you to monitor real-time sensor data.
- Freeze Frame Data: Captures data at the moment a DTC is triggered.
- Mode 6 Diagnostics: Provides access to non-standardized test results.
- Bi-Directional Control: Allows you to control vehicle components for testing purposes.
- Compatibility: Ensure the scanner is compatible with your vehicle’s OBD2 protocol.
- User-Friendly Interface: Choose a scanner with a clear display and intuitive menu.
- Software Updates: Ensures the scanner stays compatible with newer vehicles and diagnostic protocols.
These features will help you diagnose and repair your 2003 Silverado effectively.
6.3. Top OBD2 Scanner Recommendations
What are some top OBD2 scanner recommendations for a 2003 Silverado? Here are some top OBD2 scanner recommendations based on different needs and budgets:
- Basic:
- Autel AutoLink AL319: A reliable and affordable code reader with a user-friendly interface.
- Innova 3020RS: A simple and effective scanner for reading and clearing codes.
- Intermediate:
- BlueDriver Bluetooth Professional OBDII Scan Tool: A Bluetooth scanner that connects to your smartphone and offers live data and enhanced diagnostics.
- OBDLink MX+: A versatile scanner with excellent compatibility and advanced features like live data and Mode 6 support.
- Advanced:
- Autel MaxiCOM MK808: A professional-grade scanner with bi-directional control, advanced diagnostics, and extensive vehicle coverage.
- Snap-on Zeus: A high-end scanner with comprehensive features and capabilities for professional mechanics.
Choosing the right scanner from these recommendations will help you diagnose and repair your 2003 Silverado effectively.
7. Maintaining Your 2003 Silverado with OBD2
How can you maintain your 2003 Silverado using OBD2 diagnostics? Regular OBD2 diagnostics can help you maintain your 2003 Silverado by identifying potential issues early and ensuring optimal performance.
Here are some tips for maintaining your Silverado with OBD2:
- Regularly Scan for Codes: Scan your vehicle for DTCs every few months or whenever you notice unusual behavior.
- Address Issues Promptly: Don’t ignore DTCs. Address issues promptly to prevent them from escalating.
- Monitor Live Data: Use live data streaming to monitor engine performance and identify potential problems.
- Keep Records: Keep a record of DTCs and repairs to track your vehicle’s maintenance history.
- Stay Informed: Stay informed about common issues and solutions for your 2003 Silverado by consulting online resources and forums.
Following these tips will help you keep your Silverado running smoothly and reliably.
7.1. Regular Diagnostic Checks
How often should you perform regular diagnostic checks on your 2003 Silverado? Performing regular diagnostic checks on your 2003 Silverado is essential for maintaining its health and preventing major issues. It is recommended to perform a diagnostic check at least every three months.
- Quarterly Checks: Check for any stored diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) to catch potential problems early.
- Pre-Trip Checks: Before long trips, scan your vehicle for any issues that could affect your journey.
- Post-Repair Checks: After any repair work, use the OBD2 scanner to verify that the issue has been resolved and that no new codes have appeared.
These regular checks will help you stay on top of your vehicle’s maintenance needs.
7.2. Tracking Vehicle Performance with OBD2
How can you track vehicle performance using OBD2 data? Tracking vehicle performance with OBD2 data allows you to monitor various parameters and identify potential issues before they become major problems.
- Monitor Fuel Efficiency: Keep track of fuel trim values and fuel consumption to identify issues affecting fuel economy.
- Engine Health: Monitor engine temperature, RPM, and load to ensure the engine is running within optimal parameters.
- Emissions Readiness: Check the status of emissions monitors to ensure your vehicle will pass an emissions test.
By regularly monitoring these parameters, you can proactively address any issues and keep your vehicle running smoothly.
7.3. Preventing Costly Repairs with Proactive Diagnostics
How can proactive diagnostics with OBD2 help prevent costly repairs? Proactive diagnostics with OBD2 can help prevent costly repairs by identifying minor issues before they escalate into major problems.
- Early Detection: By regularly scanning for DTCs, you can identify potential problems early.
- Targeted Repairs: OBD2 data helps you pinpoint the exact cause of an issue, allowing for targeted repairs.
- Preventive Maintenance: Monitoring live data can help you identify components that are nearing the end of their lifespan, allowing you to replace them before they fail.
By taking a proactive approach to diagnostics, you can save money on repairs and keep your vehicle running reliably.
8. OBD2 Resources and Support
Where can you find OBD2 resources and support for your 2003 Silverado? There are numerous resources available to help you with OBD2 diagnostics and repairs for your 2003 Silverado.
- Online Forums: Join online forums dedicated to Silverado owners and OBD2 diagnostics.
- Technical Manuals: Consult technical manuals for your vehicle and OBD2 scanners.
- Online Databases: Use online databases to look up DTC definitions and troubleshooting tips.
- Professional Mechanics: Consult with professional mechanics for complex issues that require specialized knowledge.
Utilizing these resources will help you effectively diagnose and repair your 2003 Silverado.
8.1. Online Forums and Communities
What online forums and communities can you join for OBD2 support? Joining online forums and communities can provide valuable support and resources for OBD2 diagnostics. Here are some popular options:
- Silverado Forums: A dedicated forum for Silverado owners.
- OBD2 Diagnostic Forums: Forums focused on OBD2 diagnostics and troubleshooting.
- Automotive Repair Forums: General automotive repair forums with sections on diagnostics and repair.
These communities offer a wealth of knowledge and can help you troubleshoot issues with your 2003 Silverado.
8.2. Technical Manuals and Databases
What technical manuals and databases are helpful for OBD2 diagnostics? Technical manuals and databases provide detailed information about your vehicle’s systems and diagnostic codes.
- Haynes Repair Manuals: Comprehensive repair manuals for a wide range of vehicles.
- Chilton Repair Manuals: Another popular choice for repair manuals.
- OBD-Codes.com: An online database of OBD2 codes and troubleshooting tips.
- AutoCodes.com: A comprehensive resource for DTC definitions and repair information.
These resources can help you accurately diagnose and repair your 2003 Silverado.
8.3. When to Seek Professional Help
When should you seek professional help for OBD2 diagnostics and repairs? While OBD2 diagnostics can empower you to perform many repairs yourself, there are times when it’s best to seek professional help.
Consider seeking professional help if:
- You are unfamiliar with automotive repair.
- You lack the necessary tools or equipment.
- The issue is complex or difficult to diagnose.
- You are uncomfortable performing the repair yourself.
Consulting with a professional mechanic can ensure the job is done correctly and prevent further damage to your vehicle.
9. Conclusion: Mastering OBD2 Diagnostics for Your 2003 Silverado
How can you master OBD2 diagnostics for your 2003 Silverado? Mastering OBD2 diagnostics for your 2003 Silverado involves understanding the basics of the OBD2 system, using an OBD2 scanner effectively, and knowing how to interpret diagnostic codes.
By following the tips and guidelines in this article, you can:
- Diagnose common issues.
- Track vehicle performance.
- Prevent costly repairs.
- Maintain your Silverado’s reliability.
With the right knowledge and tools, you can confidently tackle OBD2 diagnostics and keep your 2003 Silverado running smoothly. Stay proactive with truck diagnostics and maintenance for long-lasting reliability. Consider regular truck maintenance for optimal performance.
Is your 2003 Silverado giving you trouble codes you can’t decipher? Do you want expert advice on how to use an OBD2 scanner or need help with a complex repair? Contact OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN today!
Our team of experienced mechanics is ready to assist you with all your diagnostic and repair needs. We offer comprehensive services, from basic code reading to advanced diagnostics, to ensure your Silverado is running at its best.
Call us now at +1 (641) 206-8880 or visit our website at OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN to schedule a consultation. You can also visit us at 123 Main Street, Los Angeles, CA 90001, United States. Let OBD2-SCANNER.EDU.VN be your trusted partner in maintaining your 2003 Silverado.
10. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About 2003 Silverado ISO OBD2
10.1. What is an OBD2 Scanner?
An OBD2 scanner is a diagnostic tool used to retrieve information from a vehicle’s computer system, including diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs), live data, and other parameters related to engine performance and emissions. It connects to the vehicle’s diagnostic port and allows users to identify and troubleshoot potential issues.
10.2. How Do I Locate the OBD2 Port in My 2003 Silverado?
The OBD2 port in a 2003 Silverado is typically located under the dashboard on the driver’s side. It is usually near the steering column and is easily accessible.
10.3. Can I Use Any OBD2 Scanner on My 2003 Silverado?
Yes, you can use any OBD2 scanner on your 2003 Silverado, as long as it is compatible with the OBD2 protocol. However, some scanners may offer more advanced features and capabilities than others.
10.4. What Do the OBD2 Codes Mean?
OBD2 codes are five-character alphanumeric codes that indicate specific issues or malfunctions in a vehicle’s systems. The first character indicates the system (e.g., P for Powertrain, B for Body), and the remaining characters provide more specific information about the fault.
10.5. Can I Clear the OBD2 Codes Myself?
Yes, you can clear the OBD2 codes yourself using an OBD2 scanner. However, it is essential to address the underlying issue before clearing the codes, as they will reappear if the problem persists.
10.6. What is Live Data Streaming?
Live data streaming is a feature of advanced OBD2 scanners that allows you to monitor real-time data from your vehicle’s sensors and systems. This can be helpful for diagnosing issues that don’t trigger a specific DTC.
10.7. What is Freeze Frame Data?
Freeze frame data captures a snapshot of sensor data at the moment a DTC is triggered. This information can provide valuable clues about the conditions that led to the fault.
10.8. What is Mode 6 Diagnostics?
Mode 6 diagnostics provides access to non-standardized test results that can help diagnose complex or intermittent issues. This mode allows you to view detailed information about specific components and systems.
10.9. How Often Should I Scan My 2003 Silverado for OBD2 Codes?
It is recommended to scan your 2003 Silverado for OBD2 codes every three months or whenever you notice unusual behavior. Regular checks can help you identify potential issues early and prevent them from escalating.
10.10. When Should I Seek Professional Help for OBD2 Diagnostics?
You should seek professional help for OBD2 diagnostics if you are unfamiliar with automotive repair, lack the necessary tools or equipment, the issue is complex or difficult to diagnose, or you are uncomfortable performing the repair yourself.
